25+ Report Examples to Download
When it comes to gathering and presenting information in a structured format, reports play a crucial role in both professional and academic settings. A report effectively compiles data and insights into a coherent document, aiming to inform, analyze, or recommend. Whether you’re a business professional analyzing quarterly sales, a student detailing experimental results, or a policymaker evaluating the impacts of a program, mastering the art of report writing can significantly enhance your ability to communicate complex ideas clearly and persuasively. This introduction to report writing offers essential tips and guidelines to help you create well-structured, clear, and impactful reports that can stand out and serve their intended purpose effectively
What is Report?


Report Format
Title Page
Includes the title of the report, author’s name, date, and the organization for which the report is prepared.
Abstract or Executive Summary
A brief summary of the report’s contents, highlighting the main points and conclusions.
Table of Contents
Lists the headings and subheadings with their corresponding page numbers.
Introduction
Introduces the topic of the report, its objectives, and the methods used for gathering information.
Body
The main section that contains the detailed information, analysis, and findings of the report, divided into subsections.
Conclusion
Summarizes the findings, presents conclusions based on the body, and may include recommendations.
References or Bibliography
Lists the sources used in the report in a detailed and formatted manner.
Appendices
Includes additional materials related to the content of the report, such as charts, graphs, and tables.
Report Example
Report Examples
Report for Work

Report for Students

Report for Business

More Examples on Report
- Report for Class 12
- Lab Report
- News Report
- Book Report
- Police Report
- Research Report
- Report for University
Technical Report Template

Free Report Technical Specification Template

Restaurant Feasibility Report

Project Feasibility Report

Business Annual Report Template

Field Report Template

Academic Research Report Template

Progress Report Template

Case Report Template

Incident Information Report
Final Internship Report

Performance Management Report

Final Narrative Report

Psychological Assessment Report

Final Recommendation Report

Audit Report Example

Sample Report Example

Types of Report
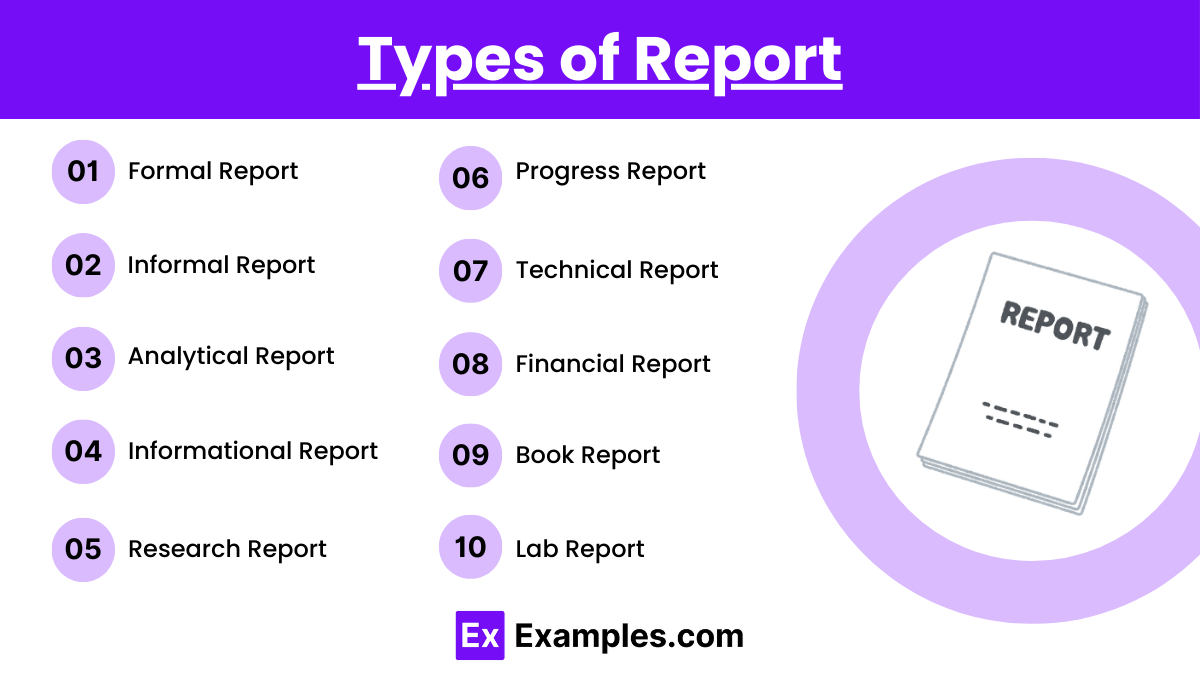
1. Formal Report
A formal report is a highly structured document with specific sections like title page, abstract, table of contents, introduction, body, conclusion, and appendices. It is used in business, academic, and professional settings to convey complex information, research findings, or project results.
2. Informal Report
Informal reports are usually shorter and less structured than formal reports. They might be used internally within organizations to update staff on business operations or project statuses and typically do not include sections like a table of contents or abstract.
3. Analytical Report
Analytical reports focus on examining a specific problem or set of data, analyzing the information, and recommending a course of action. These reports are crucial for decision-making processes in business, science, and technology fields.
4. Informational Report
Informational reports are used to present data or factual information without analysis or recommendations. Examples include financial reports, compliance reports, and annual reports that summarize an entity’s status or performance.
5. Research Report
Research reports are detailed documents that present the methodology, data, analysis, and findings from research activities. These are common in scientific, academic, and business contexts where thorough investigation is required.
6. Progress Report
Progress reports are periodic updates on the progress of a project or task. They are crucial in project management for communicating what has been accomplished, what remains to be done, and any issues that have arisen.
7. Technical Report
Technical reports convey technical information in a clear and accessible format. They cover various topics from engineering, IT, and other technical disciplines, detailing experiments, designs, or project developments.
8. Financial Report
Financial reports include documents like balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements. These reports are essential for businesses to track financial health and for stakeholders to make informed financial decisions.
9. Book Report
Book reports are educational tools that summarize and critique a book’s content, characters, themes, and author’s intent. They are commonly assigned in educational settings to develop students’ analytical and communication skills.
10. Lab Report
Lab reports document the process, results, and conclusions of laboratory experiments. They follow a clear structure to detail the experiment’s purpose, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn, critical for scientific studies
Report Functions
- Informing: Reports provide detailed information on specific topics, helping stakeholders stay informed about current conditions or developments.
- Analyzing: Many reports are used to analyze data or situations to understand what is happening, why it is happening, and what the implications are.
- Recommending: Reports often include recommendations based on analysis, suggesting courses of action to address issues or capitalize on opportunities.
- Documenting: They serve as a formal record of events, experiments, or statuses, ensuring there is a historical account that can be referenced later.
- Monitoring: Reports help in tracking the progress of ongoing projects or activities, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments as needed.
- Evaluating: Through reports, organizations can evaluate the outcomes of various initiatives or projects, measuring success and identifying areas for improvement.
- Communicating: They facilitate communication between different parts of an organization or between businesses and external stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned.
- Complying: In many cases, reports are required for compliance with laws, regulations, or standards, providing necessary documentation to authorities or regulators.
- Decision Making: The insights provided by reports are often critical in helping leaders make informed decisions that affect the future of organizations or projects.
- Educating: Reports can be educational tools, especially in academic and professional training settings, teaching readers about specific topics or skills.
How to Write a Report

- Define the Purpose: Begin by clearly defining the objective of the report. Understand what information needs to be conveyed, to whom, and why it is important.
- Gather Information: Collect all necessary data from relevant sources. This could involve conducting research, interviews, surveys, or gathering data from existing databases.
- Organize Your Findings: Sort the information logically. This typically involves creating an outline that includes an introduction, body (where the main information is divided into sections), and a conclusion.
- Write the Report: Start with an introduction that outlines the purpose and objectives of the report, followed by the body that details your findings, analysis, and any conclusions. Use clear, concise language and visualize data with charts or graphs if applicable.
- Review and Revise: After drafting the report, review it to ensure clarity and coherence. Check for grammatical errors, ensure all facts are accurate, and that the content flows logically.
- Add References and Appendices: Include a references section if you have cited any sources, and appendices for any supplementary information that is too detailed to include in the body of the report.
Tips for Writing a Report
- Clarity and Conciseness: Use simple and direct language to ensure your report is easy to understand. Avoid unnecessary jargon and overly complex sentences, focusing instead on being concise and clear.
- Structured Format: Organize your report in a logical structure with clearly labeled sections, such as introduction, body, conclusion, and appendices. This helps readers follow your arguments and findings more easily.
- Objective Analysis: Maintain objectivity by presenting the information factually and without bias. Analyze the data critically and present both sides of any arguments to give a balanced view.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to visually represent data. Visual aids can help clarify complex information and make the report more engaging.
- Proofread and Edit: Always thoroughly proofread your report to correct any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Editing for style and consistency is also crucial to enhance readability and professionalism.
Report Guidelines for Research
- Title and Abstract: Begin with a concise and informative title that reflects the content of the report. The abstract should provide a brief summary of the research, including the main objectives, methodology, results, and conclusions. Keep the abstract around 150-250 words.
- Introduction: The introduction should lay the foundation for the report. It should clearly state the research problem, objectives, and the significance of the research. Provide background information and a review of relevant literature to situate your study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Methodology: Detail the methods and procedures used in your research. Describe the research design, data collection techniques, instruments used, and the approach to data analysis. Ensure that the methodology is detailed enough to allow replication of the study.
- Results: Present the findings of your research without any interpretation. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate your data clearly. Make sure to describe the results in a logical sequence and refer to your visual aids appropriately within the text.
- Discussion: Interpret and discuss the implications of your findings in relation to the research questions or hypotheses. Compare your results with those from other studies and discuss any similarities or differences. Address the limitations of your study and suggest areas for future research.
- Conclusion: Summarize the key findings and their implications. Highlight how the research contributes to the field and any practical applications. Keep the conclusion focused and avoid introducing new information.
- References: List all the sources cited in your report in a reference section, formatted according to a recognized academic style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). This demonstrates scholarly rigor and allows readers to locate the sources for further reading.
- Appendices: Include any supplementary material in the appendices. This could be raw data, additional analyses, or detailed information that supports the report but is too voluminous to include in the main body.
FAQs
How do I start a report?
Begin by clearly defining the purpose, conducting thorough research, and organizing your findings into a clear outline.
What should be included in a report conclusion?
A conclusion should summarize key findings, restate the report’s purpose, and may suggest future actions or research.
How can I make my report more effective?
Enhance your report by maintaining clarity, using visual aids like charts, and ensuring the content is logically organized.
What is the difference between a report and an essay?
A report typically presents data and analysis intended for practical use, while an essay argues a point of view or discusses a topic.
How long should a report be?
The length of a report depends on its purpose and audience. Short reports may be 1-2 pages, while detailed reports can be several pages long.
25+ Report Examples to Download

When it comes to gathering and presenting information in a structured format, reports play a crucial role in both professional and academic settings. A report effectively compiles data and insights into a coherent document, aiming to inform, analyze, or recommend. Whether you’re a business professional analyzing quarterly sales, a student detailing experimental results, or a policymaker evaluating the impacts of a program, mastering the art of report writing can significantly enhance your ability to communicate complex ideas clearly and persuasively. This introduction to report writing offers essential tips and guidelines to help you create well-structured, clear, and impactful reports that can stand out and serve their intended purpose effectively
What is Report?
A report is a document that presents information in an organized format for a specific audience and purpose. Typically, it outlines observations, findings, or research, and often includes recommendations based on that information.
Report Format
Title Page
Includes the title of the report, author’s name, date, and the organization for which the report is prepared.
Abstract or Executive Summary
A brief summary of the report’s contents, highlighting the main points and conclusions.
Table of Contents
Lists the headings and subheadings with their corresponding page numbers.
Introduction
Introduces the topic of the report, its objectives, and the methods used for gathering information.
Body
The main section that contains the detailed information, analysis, and findings of the report, divided into subsections.
Conclusion
Summarizes the findings, presents conclusions based on the body, and may include recommendations.
References or Bibliography
Lists the sources used in the report in a detailed and formatted manner.
Appendices
Includes additional materials related to the content of the report, such as charts, graphs, and tables.
Report Example
Title: Annual Sales Report
Author: John Doe
Date: February 7, 2025
Organization: XYZ Corporation
This report provides an analysis of the annual sales performance of XYZ Corporation for the year 2024. It highlights key growth areas and identifies challenges faced during the period.
Introduction
Sales Performance Analysis
Market Trends
Competitive Analysis
Conclusions and Recommendations
References
Appendices
The report examines the sales trends, market dynamics, and competitive environment of XYZ Corporation over the past year. The objective is to assess the company’s performance and strategize for future growth.
Sales Performance Analysis
Details monthly and quarterly sales volumes, discusses revenue achievements, and compares these figures with the previous year’s data.
Market Trends
Analyzes current trends in the market, customer preferences, and buying patterns that influenced sales outcomes.
Competitive Analysis
Reviews competitor activities, market share comparisons, and strategic moves made by competitors during the year.
Summarizes key findings from the analysis, outlines successes, and addresses areas of concern. Recommendations for future strategies and areas for improvement are also presented.
Lists all the scholarly and commercial sources of data used to compile the report.
Includes detailed charts, graphs, and tables that provide a comprehensive view of the data analyzed in the report.
Report Examples
Report for Work
Report for Students
Report for Business
More Examples on Report
Technical Report Template

Free Report Technical Specification Template

Restaurant Feasibility Report

Project Feasibility Report

Business Annual Report Template

Field Report Template

Academic Research Report Template

Progress Report Template

Case Report Template

Incident Information Report

ncacbsa.org
Final Internship Report

Performance Management Report

Final Narrative Report

Psychological Assessment Report

Final Recommendation Report

Audit Report Example

Sample Report Example

Types of Report
1. Formal Report
A formal report is a highly structured document with specific sections like title page, abstract, table of contents, introduction, body, conclusion, and appendices. It is used in business, academic, and professional settings to convey complex information, research findings, or project results.
2. Informal Report
Informal reports are usually shorter and less structured than formal reports. They might be used internally within organizations to update staff on business operations or project statuses and typically do not include sections like a table of contents or abstract.
3. Analytical Report
Analytical reports focus on examining a specific problem or set of data, analyzing the information, and recommending a course of action. These reports are crucial for decision-making processes in business, science, and technology fields.
4. Informational Report
Informational reports are used to present data or factual information without analysis or recommendations. Examples include financial reports, compliance reports, and annual reports that summarize an entity’s status or performance.
5. Research Report
Research reports are detailed documents that present the methodology, data, analysis, and findings from research activities. These are common in scientific, academic, and business contexts where thorough investigation is required.
6. Progress Report
Progress reports are periodic updates on the progress of a project or task. They are crucial in project management for communicating what has been accomplished, what remains to be done, and any issues that have arisen.
7. Technical Report
Technical reports convey technical information in a clear and accessible format. They cover various topics from engineering, IT, and other technical disciplines, detailing experiments, designs, or project developments.
8. Financial Report
Financial reports include documents like balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements. These reports are essential for businesses to track financial health and for stakeholders to make informed financial decisions.
9. Book Report
Book reports are educational tools that summarize and critique a book’s content, characters, themes, and author’s intent. They are commonly assigned in educational settings to develop students’ analytical and communication skills.
10. Lab Report
Lab reports document the process, results, and conclusions of laboratory experiments. They follow a clear structure to detail the experiment’s purpose, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn, critical for scientific studies
Report Functions
Informing: Reports provide detailed information on specific topics, helping stakeholders stay informed about current conditions or developments.
Analyzing: Many reports are used to analyze data or situations to understand what is happening, why it is happening, and what the implications are.
Recommending: Reports often include recommendations based on analysis, suggesting courses of action to address issues or capitalize on opportunities.
Documenting: They serve as a formal record of events, experiments, or statuses, ensuring there is a historical account that can be referenced later.
Monitoring: Reports help in tracking the progress of ongoing projects or activities, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments as needed.
Evaluating: Through reports, organizations can evaluate the outcomes of various initiatives or projects, measuring success and identifying areas for improvement.
Communicating: They facilitate communication between different parts of an organization or between businesses and external stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned.
Complying: In many cases, reports are required for compliance with laws, regulations, or standards, providing necessary documentation to authorities or regulators.
Decision Making: The insights provided by reports are often critical in helping leaders make informed decisions that affect the future of organizations or projects.
Educating: Reports can be educational tools, especially in academic and professional training settings, teaching readers about specific topics or skills.
How to Write a Report
Define the Purpose: Begin by clearly defining the objective of the report. Understand what information needs to be conveyed, to whom, and why it is important.
Gather Information: Collect all necessary data from relevant sources. This could involve conducting research, interviews, surveys, or gathering data from existing databases.
Organize Your Findings: Sort the information logically. This typically involves creating an outline that includes an introduction, body (where the main information is divided into sections), and a conclusion.
Write the Report: Start with an introduction that outlines the purpose and objectives of the report, followed by the body that details your findings, analysis, and any conclusions. Use clear, concise language and visualize data with charts or graphs if applicable.
Review and Revise: After drafting the report, review it to ensure clarity and coherence. Check for grammatical errors, ensure all facts are accurate, and that the content flows logically.
Add References and Appendices: Include a references section if you have cited any sources, and appendices for any supplementary information that is too detailed to include in the body of the report.
Tips for Writing a Report
Clarity and Conciseness: Use simple and direct language to ensure your report is easy to understand. Avoid unnecessary jargon and overly complex sentences, focusing instead on being concise and clear.
Structured Format: Organize your report in a logical structure with clearly labeled sections, such as introduction, body, conclusion, and appendices. This helps readers follow your arguments and findings more easily.
Objective Analysis: Maintain objectivity by presenting the information factually and without bias. Analyze the data critically and present both sides of any arguments to give a balanced view.
Visual Aids: Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to visually represent data. Visual aids can help clarify complex information and make the report more engaging.
Proofread and Edit: Always thoroughly proofread your report to correct any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Editing for style and consistency is also crucial to enhance readability and professionalism.
Report Guidelines for Research
Title and Abstract: Begin with a concise and informative title that reflects the content of the report. The abstract should provide a brief summary of the research, including the main objectives, methodology, results, and conclusions. Keep the abstract around 150-250 words.
Introduction: The introduction should lay the foundation for the report. It should clearly state the research problem, objectives, and the significance of the research. Provide background information and a review of relevant literature to situate your study within the existing body of knowledge.
Methodology: Detail the methods and procedures used in your research. Describe the research design, data collection techniques, instruments used, and the approach to data analysis. Ensure that the methodology is detailed enough to allow replication of the study.
Results: Present the findings of your research without any interpretation. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate your data clearly. Make sure to describe the results in a logical sequence and refer to your visual aids appropriately within the text.
Discussion: Interpret and discuss the implications of your findings in relation to the research questions or hypotheses. Compare your results with those from other studies and discuss any similarities or differences. Address the limitations of your study and suggest areas for future research.
Conclusion: Summarize the key findings and their implications. Highlight how the research contributes to the field and any practical applications. Keep the conclusion focused and avoid introducing new information.
References: List all the sources cited in your report in a reference section, formatted according to a recognized academic style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). This demonstrates scholarly rigor and allows readers to locate the sources for further reading.
Appendices: Include any supplementary material in the appendices. This could be raw data, additional analyses, or detailed information that supports the report but is too voluminous to include in the main body.
FAQs
How do I start a report?
Begin by clearly defining the purpose, conducting thorough research, and organizing your findings into a clear outline.
What should be included in a report conclusion?
A conclusion should summarize key findings, restate the report’s purpose, and may suggest future actions or research.
How can I make my report more effective?
Enhance your report by maintaining clarity, using visual aids like charts, and ensuring the content is logically organized.
What is the difference between a report and an essay?
A report typically presents data and analysis intended for practical use, while an essay argues a point of view or discusses a topic.
How long should a report be?
The length of a report depends on its purpose and audience. Short reports may be 1-2 pages, while detailed reports can be several pages long.

