10 Risk Assessment Examples
Risk assessment is a fundamental aspect of risk management, essential for identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential hazards and their impacts. It involves a systematic process that integrates needs assessment and specific domains like food safety risk assessment, needs assessment determines the scope and objectives of risk assessment activities, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. In the context of food safety, risk assessment evaluates potential risks associated with food production, handling, and consumption, aiming to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure consumer safety. Effective risk assessment facilitates informed decision-making and the implementation of proactive measures to mitigate identified risks.
What is Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks to understand their likelihood and potential impact. It involves systematically assessing hazards, vulnerabilities, and exposures, considering various factors such as severity, frequency, and consequences. By quantifying risks, organizations can prioritize mitigation strategies and allocate resources effectively. Risk assessment enables informed decision-making, proactive risk management, and the implementation of preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of adverse events and their associated consequences.
Risk assessment examples
- Financial Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential financial losses due to market fluctuations, credit defaults, or investment risks.
- Operational Risk Assessment: Identifying risks associated with internal processes, systems, and procedures that may impact business operations.
- Health and Safety Risk Assessment: Assessing workplace hazards to prevent accidents, injuries, and occupational health issues.
- Cybersecurity Risk Assessment: Analyzing vulnerabilities in digital systems and networks to protect against cyber threats such as data breaches and malware attacks.
- Environmental Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential environmental impacts of activities, projects, or developments to mitigate harm to ecosystems and human health.
- Project Risk Assessment: Identifying and managing risks that may affect the successful completion of a project, including budget overruns, delays, and resource constraints.
- Supply Chain Risk Assessment: Assessing risks within the supply chain, such as disruptions in the flow of materials, transportation delays, and supplier dependencies.
- Legal and Regulatory Risk Assessment: Identifying compliance risks related to laws, regulations, and industry standards to ensure adherence and avoid legal liabilities.
- Reputational Risk Assessment: Evaluating risks that may damage an organization’s reputation, such as negative publicity, ethical lapses, or customer dissatisfaction.
- Natural Disaster Risk Assessment: Assessing the likelihood and potential impacts of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires to implement appropriate mitigation measures.
Why is it Important?
Risk assessment is crucial for various aspects of life, including home safety and health, as it helps identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate risks. Conducting a home risk assessment enables homeowners to identify safety hazards such as tripping hazards, fire risks, or faulty electrical wiring, thereby reducing the likelihood of accidents or injuries within the household. Similarly, health risk assessments evaluate individual health status, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures to identify potential health risks and prevent or manage chronic diseases. By systematically assessing risks, individuals can take preventive actions, such as installing safety devices at home or making lifestyle changes to improve health outcomes. Overall, risk assessment empowers individuals to make informed decisions, prioritize resources effectively, and promote safety and well-being in both home and health environments.
When Do You Perform a Risk Assessment?
A risk assessment is typically performed at various stages depending on the context and purpose. In general, risk assessments are conducted:
- Before Initiating a Project: To identify potential risks and plan risk management strategies before starting a new project or endeavor.
- During Project Planning: To assess risks associated with project objectives, timelines, resources, and stakeholders, ensuring effective risk mitigation and contingency planning.
- Regularly and Periodically: To review and update risk assessments as circumstances change, such as changes in project scope, external factors, or regulatory requirements.
- Before Implementing Changes: To evaluate the potential risks and impacts of any significant changes to processes, systems, or operations before implementation.
- After Incidents or Near-Misses: To analyze the root causes of incidents, accidents, or near-misses and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- As Part of Compliance Requirements: To comply with regulatory standards or industry best practices that mandate regular risk assessments in specific domains such as health and safety, cybersecurity, or environmental management.
Types of Risk Assessments
| Type of Risk Assessment | Description |
|---|---|
| Health Risk Assessment | Evaluates individual health status, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures for preventive healthcare. |
| Safety Risk Assessment | Identifies workplace hazards and evaluates risks to prevent accidents, injuries, and ensure occupational safety. |
| Financial Risk Assessment | Analyzes potential financial losses from market fluctuations, credit defaults, or mismanagement for effective planning. |
| Environmental Risk Assessment | Assesses impacts of activities on ecosystems, resources, and human health to ensure compliance and minimize harm. |
| Cybersecurity Risk Assessment | Evaluates vulnerabilities in digital systems and data assets to strengthen cybersecurity defenses and prevent cyber threats. |
| Project Risk Assessment | Identifies and manages risks affecting project success, including budget overruns, delays, and stakeholder conflicts. |
| Supply Chain Risk Assessment | Assesses risks within the supply chain, such as disruptions in materials flow or transportation delays, to ensure continuity. |
| Operational Risk Assessment | Evaluates risks associated with internal processes and systems to enhance operational resilience and efficiency. |
Performing Risk Assessment in Five Steps
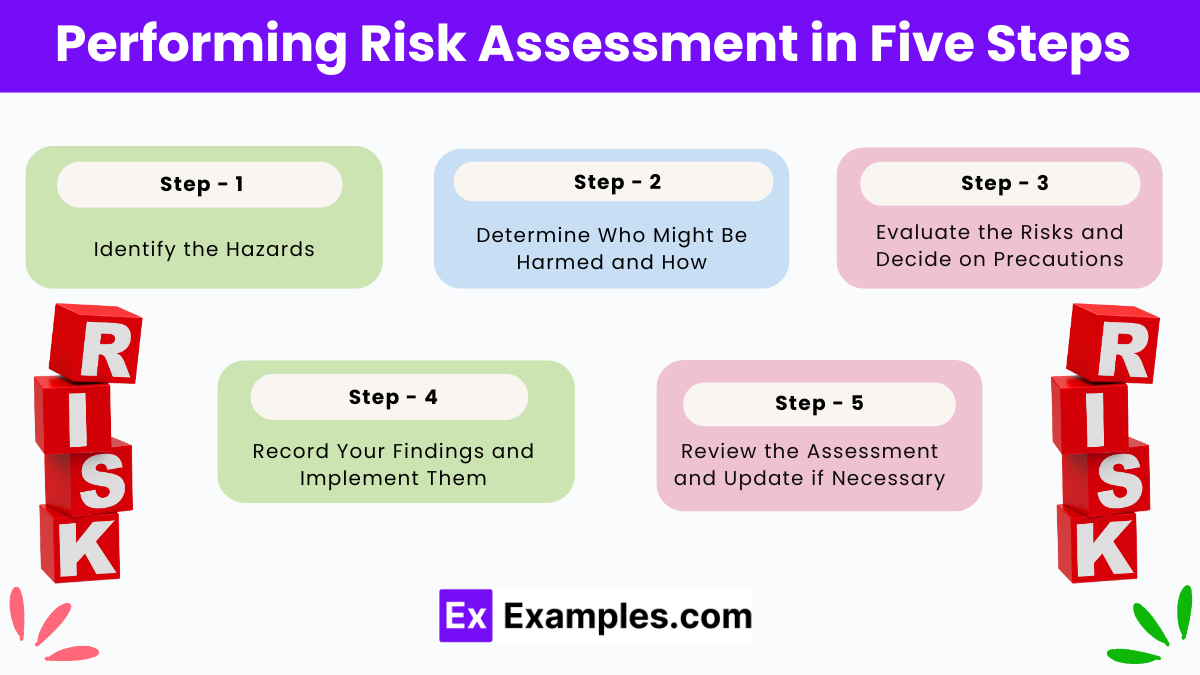
How to use a Risk Matrix?
A risk matrix is a visual tool used to assess and prioritize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. Here’s how to use a risk matrix effectively:
- Identify Risks: Start by identifying potential risks relevant to your project, process, or activity. These could be identified through brainstorming sessions, historical data, or risk assessment techniques.
- Define Criteria: Establish criteria for assessing risks, typically involving two dimensions: likelihood (probability of occurrence) and impact (severity of consequences). Define specific rating scales for each dimension, such as low, medium, and high.
- Plot Risks: Plot each identified risk on the risk matrix based on its likelihood and impact. Use the defined rating scales to determine the position of each risk within the matrix.
- Assess and Prioritize: Assess the position of each risk on the matrix to determine its overall risk level. Risks located in the high likelihood and high impact quadrant pose the greatest risk and should be prioritized for mitigation.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Based on the prioritized risks, develop appropriate mitigation strategies to reduce their likelihood or impact. These strategies may include risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk reduction, or risk acceptance.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor and review the effectiveness of mitigation measures and reassess risks as circumstances change. Update the risk matrix accordingly to reflect any changes in risk levels.
- Communicate and Document: Communicate the findings of the risk assessment and the resulting mitigation strategies to relevant stakeholders. Document the risk matrix and associated mitigation actions for future reference and accountability.
Risk assessment examples mental health
- Suicide Risk Assessment: This assessment evaluates an individual’s risk of suicide by assessing factors such as suicidal ideation, intent, plan, access to means, and history of suicide attempts.
- Self-Harm Risk Assessment: This assessment focuses on evaluating the risk of self-harming behaviors, such as cutting or burning, by considering factors such as triggers, frequency, severity, and underlying emotional distress.
- Violence Risk Assessment: This assessment examines the risk of violence towards self or others, including physical aggression, threats, or property damage. It considers factors such as history of violence, impulsivity, substance use, and current stressors.
- Substance Use Risk Assessment: This assessment evaluates the risk associated with substance use or addiction, including the potential for overdose, withdrawal symptoms, impaired judgment, and risky behaviors.
- Psychosocial Risk Assessment: This assessment assesses various psychosocial factors that may impact an individual’s mental health and well-being, such as social support, family dynamics, housing stability, employment status, and financial stressors.
- Trauma Risk Assessment: This assessment evaluates the risk of trauma-related symptoms or disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), by considering factors such as trauma history, severity, and current coping mechanisms.
- Crisis Risk Assessment: This assessment assesses an individual’s immediate risk of crisis or acute mental health deterioration, including factors such as current symptoms, level of distress, coping skills, and availability of support.
How to Assess Consequences?
Assessing consequences involves evaluating the potential outcomes or impacts of a risk event occurring. Here’s how to assess consequences effectively:
- Identify Potential Consequences: Start by identifying all possible consequences that could result from the occurrence of a risk event. Consider both direct and indirect consequences across various dimensions, such as financial, operational, reputational, legal, and health and safety.
- Quantify Severity: Assess the severity or magnitude of each consequence based on its potential impact on the organization, project, or activity. Consider factors such as the extent of damage, duration of impact, and number of stakeholders affected.
- Assign Ratings: Use a predefined rating scale or scoring system to assign ratings to each consequence based on its severity. This scale could range from low to high or be numerically graded, depending on the specific context and criteria.
- Consider Probability: Take into account the likelihood or probability of each consequence occurring in conjunction with the associated risk event. A consequence may be severe, but if it has a low probability of occurrence, its overall risk level may be lower.
- Weight Importance: Consider the relative importance or priority of different consequences based on organizational objectives, stakeholder interests, and strategic goals. Some consequences may carry greater significance than others and warrant more attention in risk assessment and management efforts.
- Aggregate Overall Impact: Calculate the overall impact or significance of each risk event by combining the severity of consequences with their respective probabilities. This can be done using techniques such as qualitative risk analysis, quantitative risk analysis, or scenario analysis.
- Document Findings: Document the results of consequence assessment, including the identified consequences, severity ratings, probability assessments, and overall impact analysis. This documentation provides a basis for decision-making, risk treatment prioritization, and risk communication.
What is risk mitigation?
Risk mitigation involves taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk.
What is the difference between a hazard and a risk?
A hazard is a potential source of harm, while a risk is the likelihood and impact of the harm occurring.
How does risk assessment help in compliance?
It ensures that organizations meet regulatory and safety standards, reducing legal and financial penalties.
Can risk assessment be used in all industries?
Yes, risk assessment is applicable across various industries, including healthcare, construction, finance, and IT.
What is a risk assessment template?
A risk assessment template is a standardized form used to document and assess risks systematically.
What are inherent and residual risks?
Inherent risk is the risk before any mitigation measures are applied, while residual risk is the risk remaining after mitigation.
What role does communication play in risk assessment?
Effective communication ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the risks and the measures in place to manage them.
How do you prioritize risks?
Risks are prioritized based on their potential impact and likelihood, often using a risk matrix.
What is a risk appetite?
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
What is risk transfer?
Risk transfer involves shifting the risk to another party, often through insurance or contracts.
How do you measure the effectiveness of a risk assessment?
Effectiveness can be measured by the accuracy of risk identification, the success of mitigation strategies, and the reduction in adverse outcomes.
10 Risk Assessment Examples

Risk assessment is a fundamental aspect of risk management, essential for identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential hazards and their impacts. It involves a systematic process that integrates needs assessment and specific domains like food safety risk assessment, needs assessment determines the scope and objectives of risk assessment activities, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. In the context of food safety, risk assessment evaluates potential risks associated with food production, handling, and consumption, aiming to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure consumer safety. Effective risk assessment facilitates informed decision-making and the implementation of proactive measures to mitigate identified risks.
What is Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks to understand their likelihood and potential impact. It involves systematically assessing hazards, vulnerabilities, and exposures, considering various factors such as severity, frequency, and consequences. By quantifying risks, organizations can prioritize mitigation strategies and allocate resources effectively. Risk assessment enables informed decision-making, proactive risk management, and the implementation of preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of adverse events and their associated consequences.
Risk assessment examples
Financial Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential financial losses due to market fluctuations, credit defaults, or investment risks.
Operational Risk Assessment: Identifying risks associated with internal processes, systems, and procedures that may impact business operations.
Health and Safety Risk Assessment: Assessing workplace hazards to prevent accidents, injuries, and occupational health issues.
Cybersecurity Risk Assessment: Analyzing vulnerabilities in digital systems and networks to protect against cyber threats such as data breaches and malware attacks.
Environmental Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential environmental impacts of activities, projects, or developments to mitigate harm to ecosystems and human health.
Project Risk Assessment: Identifying and managing risks that may affect the successful completion of a project, including budget overruns, delays, and resource constraints.
Supply Chain Risk Assessment: Assessing risks within the supply chain, such as disruptions in the flow of materials, transportation delays, and supplier dependencies.
Legal and Regulatory Risk Assessment: Identifying compliance risks related to laws, regulations, and industry standards to ensure adherence and avoid legal liabilities.
Reputational Risk Assessment: Evaluating risks that may damage an organization’s reputation, such as negative publicity, ethical lapses, or customer dissatisfaction.
Natural Disaster Risk Assessment: Assessing the likelihood and potential impacts of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires to implement appropriate mitigation measures.
Why is it Important?
Risk assessment is crucial for various aspects of life, including home safety and health, as it helps identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate risks. Conducting a home risk assessment enables homeowners to identify safety hazards such as tripping hazards, fire risks, or faulty electrical wiring, thereby reducing the likelihood of accidents or injuries within the household. Similarly, health risk assessments evaluate individual health status, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures to identify potential health risks and prevent or manage chronic diseases. By systematically assessing risks, individuals can take preventive actions, such as installing safety devices at home or making lifestyle changes to improve health outcomes. Overall, risk assessment empowers individuals to make informed decisions, prioritize resources effectively, and promote safety and well-being in both home and health environments.
When Do You Perform a Risk Assessment?
A risk assessment is typically performed at various stages depending on the context and purpose. In general, risk assessments are conducted:
Before Initiating a Project: To identify potential risks and plan risk management strategies before starting a new project or endeavor.
During Project Planning: To assess risks associated with project objectives, timelines, resources, and stakeholders, ensuring effective risk mitigation and contingency planning.
Regularly and Periodically: To review and update risk assessments as circumstances change, such as changes in project scope, external factors, or regulatory requirements.
Before Implementing Changes: To evaluate the potential risks and impacts of any significant changes to processes, systems, or operations before implementation.
After Incidents or Near-Misses: To analyze the root causes of incidents, accidents, or near-misses and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
As Part of Compliance Requirements: To comply with regulatory standards or industry best practices that mandate regular risk assessments in specific domains such as health and safety, cybersecurity, or environmental management.
Types of Risk Assessments
Type of Risk Assessment | Description |
|---|---|
Health Risk Assessment | Evaluates individual health status, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures for preventive healthcare. |
Safety Risk Assessment | Identifies workplace hazards and evaluates risks to prevent accidents, injuries, and ensure occupational safety. |
Financial Risk Assessment | Analyzes potential financial losses from market fluctuations, credit defaults, or mismanagement for effective planning. |
Environmental Risk Assessment | Assesses impacts of activities on ecosystems, resources, and human health to ensure compliance and minimize harm. |
Cybersecurity Risk Assessment | Evaluates vulnerabilities in digital systems and data assets to strengthen cybersecurity defenses and prevent cyber threats. |
Project Risk Assessment | Identifies and manages risks affecting project success, including budget overruns, delays, and stakeholder conflicts. |
Supply Chain Risk Assessment | Assesses risks within the supply chain, such as disruptions in materials flow or transportation delays, to ensure continuity. |
Operational Risk Assessment | Evaluates risks associated with internal processes and systems to enhance operational resilience and efficiency. |
Performing Risk Assessment in Five Steps

How to use a Risk Matrix?
A risk matrix is a visual tool used to assess and prioritize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. Here’s how to use a risk matrix effectively:
Identify Risks: Start by identifying potential risks relevant to your project, process, or activity. These could be identified through brainstorming sessions, historical data, or risk assessment techniques.
Define Criteria: Establish criteria for assessing risks, typically involving two dimensions: likelihood (probability of occurrence) and impact (severity of consequences). Define specific rating scales for each dimension, such as low, medium, and high.
Plot Risks: Plot each identified risk on the risk matrix based on its likelihood and impact. Use the defined rating scales to determine the position of each risk within the matrix.
Assess and Prioritize: Assess the position of each risk on the matrix to determine its overall risk level. Risks located in the high likelihood and high impact quadrant pose the greatest risk and should be prioritized for mitigation.
Develop Mitigation Strategies: Based on the prioritized risks, develop appropriate mitigation strategies to reduce their likelihood or impact. These strategies may include risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk reduction, or risk acceptance.
Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor and review the effectiveness of mitigation measures and reassess risks as circumstances change. Update the risk matrix accordingly to reflect any changes in risk levels.
Communicate and Document: Communicate the findings of the risk assessment and the resulting mitigation strategies to relevant stakeholders. Document the risk matrix and associated mitigation actions for future reference and accountability.
Risk assessment examples mental health
Suicide Risk Assessment: This assessment evaluates an individual’s risk of suicide by assessing factors such as suicidal ideation, intent, plan, access to means, and history of suicide attempts.
Self-Harm Risk Assessment: This assessment focuses on evaluating the risk of self-harming behaviors, such as cutting or burning, by considering factors such as triggers, frequency, severity, and underlying emotional distress.
Violence Risk Assessment: This assessment examines the risk of violence towards self or others, including physical aggression, threats, or property damage. It considers factors such as history of violence, impulsivity, substance use, and current stressors.
Substance Use Risk Assessment: This assessment evaluates the risk associated with substance use or addiction, including the potential for overdose, withdrawal symptoms, impaired judgment, and risky behaviors.
Psychosocial Risk Assessment: This assessment assesses various psychosocial factors that may impact an individual’s mental health and well-being, such as social support, family dynamics, housing stability, employment status, and financial stressors.
Trauma Risk Assessment: This assessment evaluates the risk of trauma-related symptoms or disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), by considering factors such as trauma history, severity, and current coping mechanisms.
Crisis Risk Assessment: This assessment assesses an individual’s immediate risk of crisis or acute mental health deterioration, including factors such as current symptoms, level of distress, coping skills, and availability of support.
How to Assess Consequences?
Assessing consequences involves evaluating the potential outcomes or impacts of a risk event occurring. Here’s how to assess consequences effectively:
Identify Potential Consequences: Start by identifying all possible consequences that could result from the occurrence of a risk event. Consider both direct and indirect consequences across various dimensions, such as financial, operational, reputational, legal, and health and safety.
Quantify Severity: Assess the severity or magnitude of each consequence based on its potential impact on the organization, project, or activity. Consider factors such as the extent of damage, duration of impact, and number of stakeholders affected.
Assign Ratings: Use a predefined rating scale or scoring system to assign ratings to each consequence based on its severity. This scale could range from low to high or be numerically graded, depending on the specific context and criteria.
Consider Probability: Take into account the likelihood or probability of each consequence occurring in conjunction with the associated risk event. A consequence may be severe, but if it has a low probability of occurrence, its overall risk level may be lower.
Weight Importance: Consider the relative importance or priority of different consequences based on organizational objectives, stakeholder interests, and strategic goals. Some consequences may carry greater significance than others and warrant more attention in risk assessment and management efforts.
Aggregate Overall Impact: Calculate the overall impact or significance of each risk event by combining the severity of consequences with their respective probabilities. This can be done using techniques such as qualitative risk analysis, quantitative risk analysis, or scenario analysis.
Document Findings: Document the results of consequence assessment, including the identified consequences, severity ratings, probability assessments, and overall impact analysis. This documentation provides a basis for decision-making, risk treatment prioritization, and risk communication.
What is risk mitigation?
Risk mitigation involves taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk.
What is the difference between a hazard and a risk?
A hazard is a potential source of harm, while a risk is the likelihood and impact of the harm occurring.
How does risk assessment help in compliance?
It ensures that organizations meet regulatory and safety standards, reducing legal and financial penalties.
Can risk assessment be used in all industries?
Yes, risk assessment is applicable across various industries, including healthcare, construction, finance, and IT.
What is a risk assessment template?
A risk assessment template is a standardized form used to document and assess risks systematically.
What are inherent and residual risks?
Inherent risk is the risk before any mitigation measures are applied, while residual risk is the risk remaining after mitigation.
What role does communication play in risk assessment?
Effective communication ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the risks and the measures in place to manage them.
How do you prioritize risks?
Risks are prioritized based on their potential impact and likelihood, often using a risk matrix.
What is a risk appetite?
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
What is risk transfer?
Risk transfer involves shifting the risk to another party, often through insurance or contracts.
How do you measure the effectiveness of a risk assessment?
Effectiveness can be measured by the accuracy of risk identification, the success of mitigation strategies, and the reduction in adverse outcomes.

