99+ Scientific Method Examples
Before Copernicus asserted the idea that the Earth revolved around the stars, the ancient people believed that the celestial bodies in space revolved around Earth. The scientific method allows us to use observation and data gathering to understand the inner workings of our world.
1. Scientific Method Worksheet
2. The Scientific Method
3. Scientific Method Sample
4. General Scientific Method
5. Using the Scientific Method
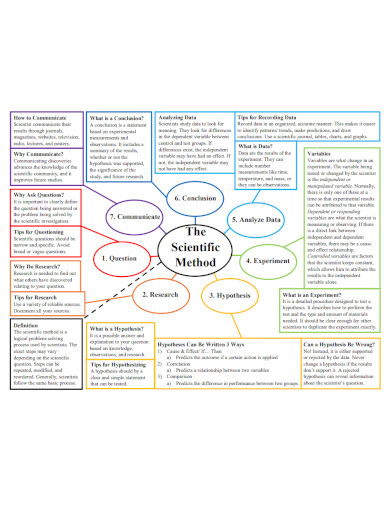
6. Scientific Method Mind Mapping
7. General Scientific Method Example
8. Nature of Science and Scientific Method
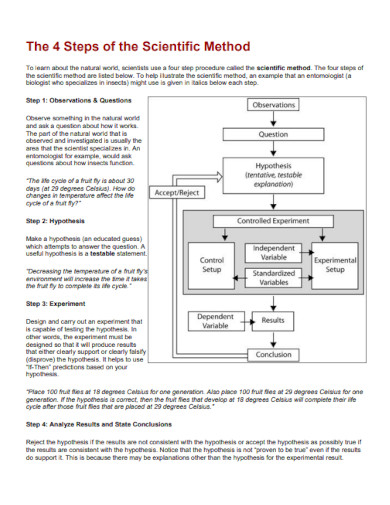
9. Scientific Method Steps
10. Printable Scientific Method
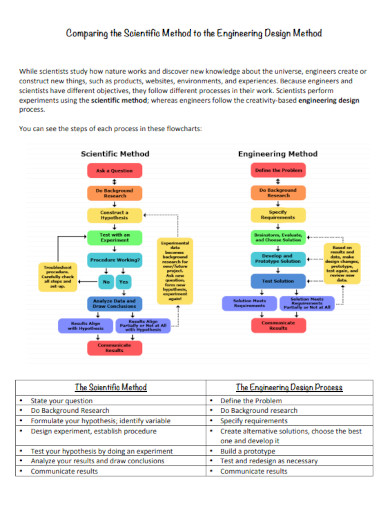
11. Comparing the Scientific Method
12. Scientific Method in PDF Example
13. Scientific Method in the Social Sciences
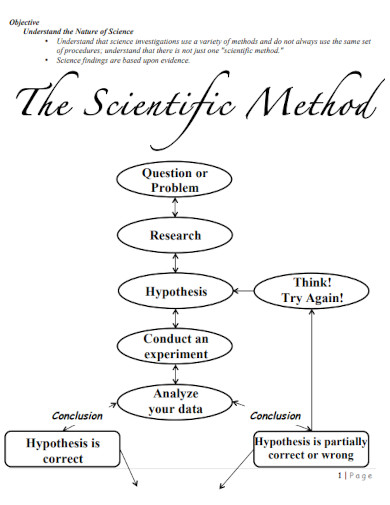
14. Scientific Method
15. Scientific Method Document
16. Scientific Method Unit
17. Statistics and the Scientific Method
18. Scientific Method in Practise
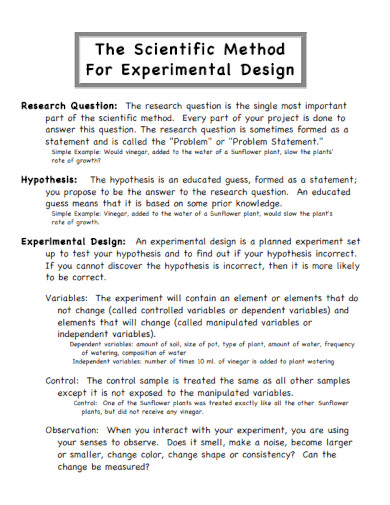
19. Scientific Method For Experimental Design
20. Scientific Method Format
21. The Scientific Method in PDF
22. Printable Scientific Method Example
23. Scientific Method Introduction
24. Scientific Method Planning Sheet
25. Scientific Method Handout
26. Simple Scientific Methods
27. Scientific Method Steps and Examples
28. Scientific Method for Elementary
29. Editable Scientific Method
30. The Elements of Scientific Method
31. Whats Scientific Method
32. Classical Scientific Method
33. Science and the Scientific Method
34. Scientific Method Investigation
35. Scientific Method Activity Example
36. Scientific Method Reading
37. The Scientific Method and the Creative Process
38. Introduction to Science and the Scientific Method
39. Defining Scientific Method
40. Scientific Method in Lab
41. Scientific Method Diagram
42. Case History in Scientific Method
43. Exploring the Scientific Method
44. Scientific Method and its Types
45. Scientific Method Notes
46. Scientific Method Sample PDF
47. Scientific Method and Observations
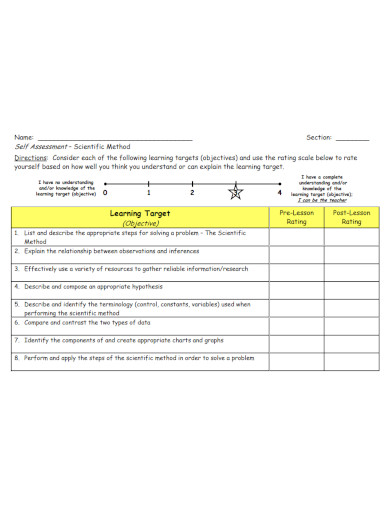
48. Scientific Method Self Assessment
49. Scientific Method Experiment Sheet
50. Scientific Method Biology
51. The Level of Scientific Methods
52. Introduction to the Scientific Method
53. Theory of Scientific Method
54. Scientific Methodology
55. Scientific Method and Observations
56. Example Scientific Method in PDF
57. Scientific Method and Critical Thinking
58. Scientific Method Lesson
59. Scientific Methods in Computer Science
60. Scientific Method Approach
62. Scientific Method Activity Example
63. Scientific Method in Practise
64. Scientific Method Short Lesson
65. Scientific Method and Scientific Notation
66. Fourth Grade Scientific Method
67. The Scientific Method Made Easy
68. Scientific Method Exercise
69. The Scientific Method of Practicing
70. Scientific Method in Project Plan
71. Scientific Method Rubric
72. Scientific Method in Vaccine History
73. Graphical View of the Scientific Method
74. Scientific Method with Example
75. Scientific Method Draft Example
76. The Scientific Method Sample PDF
77. Vocabulary for Scientific Method
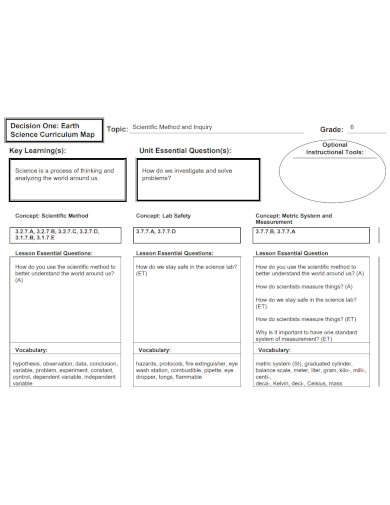
78. Scientific Methods in Earth Science
79. Theory of Scientific Method
80. Linguistics and Scientific Method
81. Recognized Scientific Method
82. Using the Scientific Method Example
83. Scientific Method and Inquiry
84. Scientific Method in Daily Life
85. Sample Introduction to Scientific Method
86. Scientific Method Quiz
87. Scientific Method Fact Sheet
88. Scientific Method Ideas
89. Scientific Method Vocabulary Test
90. Scientific Method Lesson Topic
91. Scientific Method Practice PDF
92. A Transformed Scientific Method
93. Student Handout Scientific Method
94. Scientific Method for Prevention Intervention Research
95. Scientific Method for Students
96. Scientific Method Unit Overview
97. Historical Scientific Method
98. Scientific Method Lab Report
99. Michael Crichton’s Scientific Method
100. Scientific Method Unit Plan
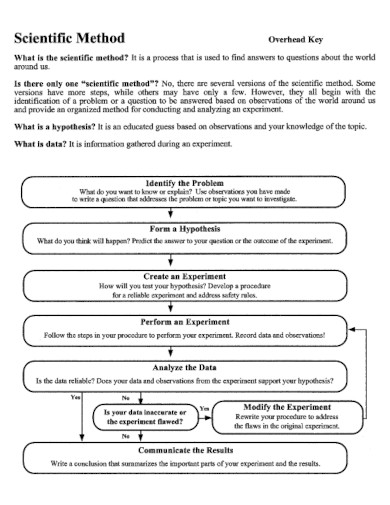
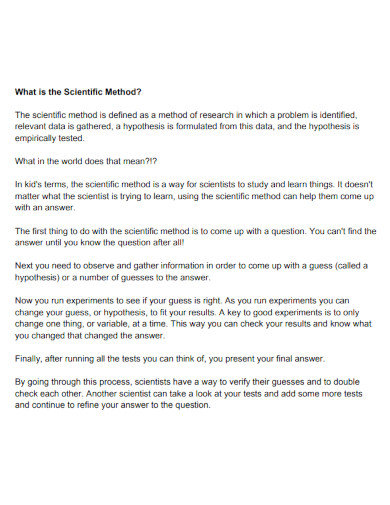
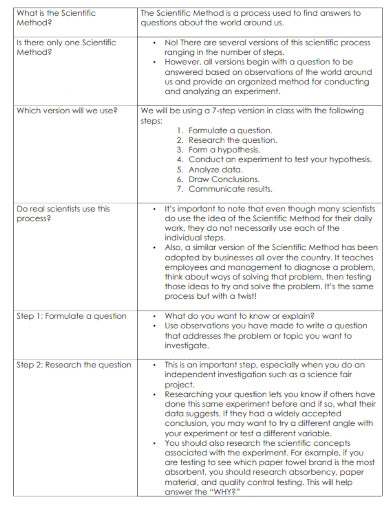
What Is the Scientific Method
The scientific method is the structured process or approach that all scientists and researchers must adhere to so that the board or commission will consider their research valid. The nature of the scientific method is objective, which will distance the researcher from their research to prevent bias.
How to Use the Scientific Method
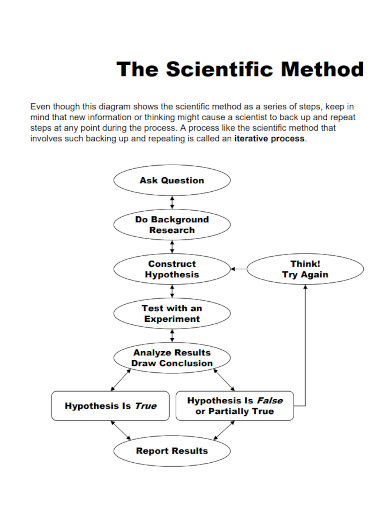
The scientific method has a process that should be followed step by step. When using the scientific method, you must have an interest in the field or topic adjacent to the problem or the phenomenon. The scientific method steps should be done in order as each step will cascade into the next.
1.) Identify the Problem or Phenomenon
Begin by identifying the problem or phenomenon you want to investigate. This will act as the overall topic of the research you are conducting or undertaking.
2.) Read and Review any Related Literature and Studies
After you have identified the problem or phenomenon, you must read and review any previous literature or study that is adjacent and related to the problem or phenomenon you have chosen. This will create relevance and indicate whether any previous studies tried to investigate the problem or phenomenon you have chosen.
3.) Formulate the Hypothesis, and Design the Experiment
Formulate the hypothesis and research question. This will decide the specific type of research you will have to do. If inductive reasoning is required then you must do a qualitative approach to your research. If deductive reasoning is required then you must fo a quantitative approach instead. Design the experiment and data collection with the appropriate approach.
4.) Collect, Organize, and Analyze the Data
After designing the experiment, begin to obtain data through various methods appropriate to the type of research you are conducting. These data can come in the form of numerical statistics, real numbers, or paragraphs and phrases. When you have the data, organize and analyze the data to obtain codes for interpretation.
5.) Interpret the Data
Through analyzing the data, you will be able to obtain codes that you can use to interpret the data you have collected. This will form the basis of the conclusion you will be able to make. Not only that but the researcher will use the data to determine whether or not the phenomenon or problem has been explained or solved.
6.) Create a Conclusion
Using the interpretation, you will be able to create a conclusion that will close off your research. This should also include a brief explanation of the implications of the data and a short call to action
FAQs
Why is the scientific method important?
The scientific method allows the researcher to approach their research and thesis systematically. The scientific method eliminates the existence of bias by implementing a structured approach. This means that the scientific method acts as the standardized approach that all researchers, new or old, will have to adhere to the steps laid out by the scientific method. It is important because all researchers have a bias toward a specific outcome, which may lead to botched or doctored results. Because of the scientific method, researches are more likely to be credible and reliable.
Who created the scientific method?
There are many contributors to the current state and processes that are integrated into the scientific method. During the golden age of Islam, mathematician Ibn al-Haytham posited that an inductive hypothesis must be accompanied and supported by confirmable mathematical evidence. Not only did Ibn al-Haytham assert what a hypothesis should have, but he also developed a process of observation and experimentation. Later on, Francis Bacon refined the inductive process of research and produced the following steps: empirical observation, systematic experimentation, analysis of experimental evidence, and inductive reasoning. Descartes instead, felt that a deductive research approach will lead to a higher understanding of the world, and developed a deductive research process. This will lead to the modern state of the scientific method, where Isaac Newton contributed to the idea that induction and deduction are needed to understand and figure out the various phenomena of our world. In the end, the scientific method is an ever-evolving part of science that has no single creator.
How does the scientific method relate to quantitative and qualitative research?
The scientific method is composed of two different approaches, each with its topics, methodology, and results. These two approaches are quantitative and qualitative research. Quantitative research uses deductive reasoning and thinking to obtain data and an understanding of specific phenomena. This approach utilizes a quantity over quality approach and requires numerous amounts of data gathered through surveys and group interviews. Qualitative research on the other hand utilizes quantitative inductive reasoning and thinking to understand more subjective and personal phenomena. This approach adopts the quality over quantity approach and will have different methods. This means that the scientific method is ingrained into these two types of research.
The scientific method is a standardized and structured approach to research that all researchers and scientists adhere to. Not only does it provide structure to the whole research process, but it also allows the researchers to objectively approach their research with minimal or no bias.