14+ Solution Examples
When you mix the pancake mix with water and eggs, it will create a pancake batter that you can use to cook pancakes. This is a real-life example of the practical uses of solutions.
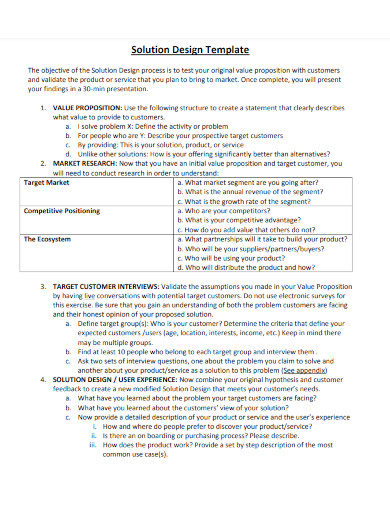
1. Solution Design Template
2. Conceptual Solution Architecture Model
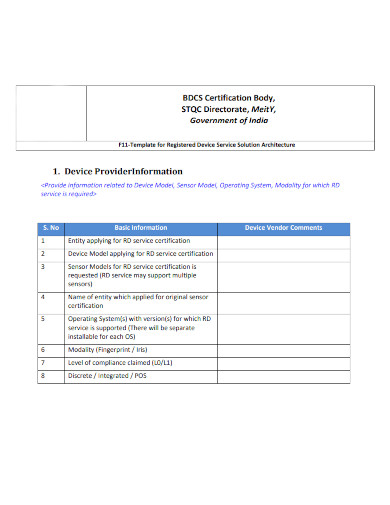
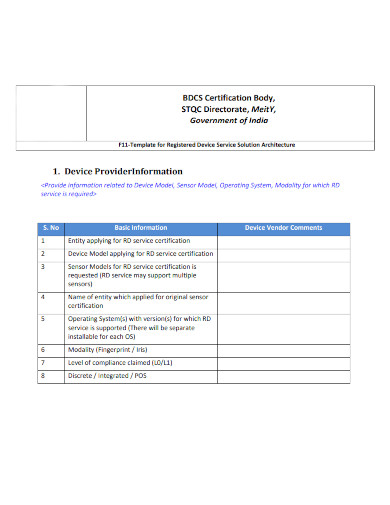
3. Solutions Architecture Template
4. Baseline Analytics Solution Portfolio Template
5. Cloud Migration Solution Template
6. Polycom Solution Sheet Template
7. Solution Statement Template
8. Solution Architect Template
9. Solution Approach For Design & Development
10. Blue Solutions Template
11. Laboratory Solution Preparation
12. Solution Competency Guide
13. Solution Premier Service
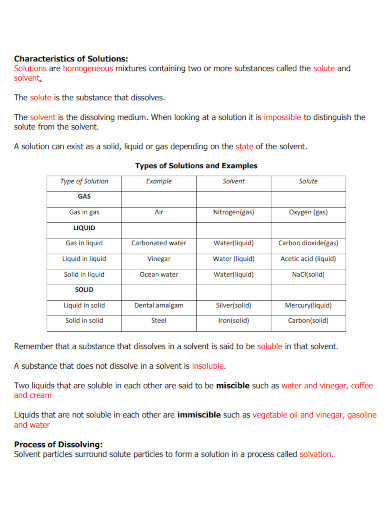
14. Characteristics of Solutions
15. Business Solution Services Objective
What Is a Solution
A solution can refer to many things which ultimately depend on the overall context of the subject. A solution can refer to a collection of steps to solve a problem or an issue about a specific theme or outline format. This article focuses on solutions in the context of chemistry and the chemical properties, chemical reactions, and elements.
How to Distinguish Solutions from Chemical Mixtures
People tend to conflate solutions from chemical mixtures as both of these objects are very similar in definition. Laboratories use both solutions and mixtures in their everyday experiments, therefore future chemists need to understand the difference between solutions and chemical mixtures.
1.) Check the Ingredients of the Investigated Object
One of the best ways to distinguish between solutions and mixtures is to first check the substances added to the mixture. If the substances in the solution or mixture are composed of three or more substances then the object is a chemical mixture. But if two substances compose the investigated object then it is a solution instead.
2.) Observe The Method of Mixing
The method of mixing in the investigated object will also determine whether the object is investigating is either a mixture or a solution. If the main method used in the creation of the object is a chemical reaction then the object is a solution, not a chemical mixture.
3.) Check the Ratio of the Investigated Object
When people make solutions the solvent and the solute is often made in a fixed ratio. This is juxtaposed with a chemical mixture whose components are not in a fixed ratio. If possible, check the ratio of the ingredients or substances in the mixture.
4.) Observe if There Are any Physical or Chemical Changes
Most solutions will have and show a visible chemical change or physical change, often manifesting new characteristics in the object, while chemical mixtures will retain the characteristics of their substances.
FAQs
What are the 3 types of solutions?
Solutions can be divided into supersaturated, unsaturated, and saturated solutions based on how well the solute dissolves in the solvent. The excess solute will crystallize fast in a supersaturated solution because it contains a lot of solutes at a temperature where it will be decreased. A solvent may dissolve any additional solute in an unsaturated solution at a specific temperature. While a saturated solution is one in which a solvent can no longer dissolve any more solute at a certain temperature.
What are the differences between solutions and chemical mixtures?
A mixture is the combining of two different things. Here, the elements are physically combined rather than reacting chemically. Mixtures can be categorized as homogeneous or heterogeneous depending on the nature of their constituent parts. The mixture known as a solution is one in which two or more ingredients have been dissolved. While compounds in a solution are entirely dissolved and cannot be filtered out, substances in a mixture are often only combined and not completely dissolved.
What is a true solution?
A real result has all the necessary element patches at the right rate and has experienced the necessary dissolution. A homogenous combination with predictable rates makes up a real result. In a real result, filtration is unfit to distinguish the solute from the result. The detergent and solute both pass through the sludge paper at about the same rate since their flyspeck sizes are analogous.
A solution is a product of a chemical reaction or physical reaction, where the solvent is completely dissolved in the solution. There are many examples of solutions that we can observe in our everyday lives, one of which is the making of coffee through the mixing of water and coffee powder.