30+ Article Summary Examples
When writing an article summary, the goal is to distill the most essential points of the original text into a concise and clear format. This process involves identifying the main ideas and supporting details, then presenting them in a streamlined manner that retains the essence of the article while making it accessible and quick to read. Whether for academic purposes, professional use, or personal reference, mastering the art of summarizing articles can enhance comprehension and save time, providing a valuable skill in today’s information-rich world.
What is Article Summary?

Article Summary Examples Bundle
Article Summary Format
Title
Start with a title that reflects the main topic or objective of the original article.
Introduction
Briefly introduce the main theme or purpose of the article.
Main Points
List the key points or arguments presented in the article. Use bullet points or a numbered list for clarity.
Supporting Details
Add important facts, statistics, or examples the author uses to back up the main points.
Conclusion
Summarize the article’s findings or the author’s final thoughts. Highlight any conclusions drawn or implications suggested by the article.
References
Include a citation of the original article, formatted according to the appropriate style guide (APA, MLA, etc.).
Article Summary Example
Title: Impact of Social Media on Modern Communication
Introduction: This summary discusses the main points from an article that explores how social media has transformed ways of communication in the modern era, emphasizing both positive and negative impacts.
Social Media as a Communication Tool: The article identifies social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram as pivotal in facilitating instantaneous communication and information sharing globally.
Enhancement of Business Marketing: Businesses leverage social media to reach a broader audience more effectively and at a lower cost compared to traditional marketing methods.
Impact on Personal Interactions: While social media helps maintain relationships over distances, it may also reduce face-to-face interactions and potentially weaken interpersonal communication skills.
- The article cites studies showing that 62% of businesses report increased engagement with their customers via social media.
- Psychological research mentioned in the article suggests a rise in feelings of isolation and anxiety correlated with high usage of social media platforms.
The article concludes that social media has fundamentally altered communication, offering valuable tools for both personal and professional interactions, but it also presents challenges that require careful management to prevent negative social impacts.
Doe, J. (2021). The Changing Landscape of Social Communication. Journal of Media Studies, 58(2), 134-145.
Article Summary Examples
Article Summary of the Constitution

Article Summary for Students

Scientific Article Summary

More on Article Summary Examples
- Research Article Summary
- APA Article Summary
- Journal Article Summary
- Short Article Summary
- News Article Summary
- Academic Article Summary
Article Summary Samples
Extra Credit Article Summary

Article Summary Active Learning

Medical Article Summary

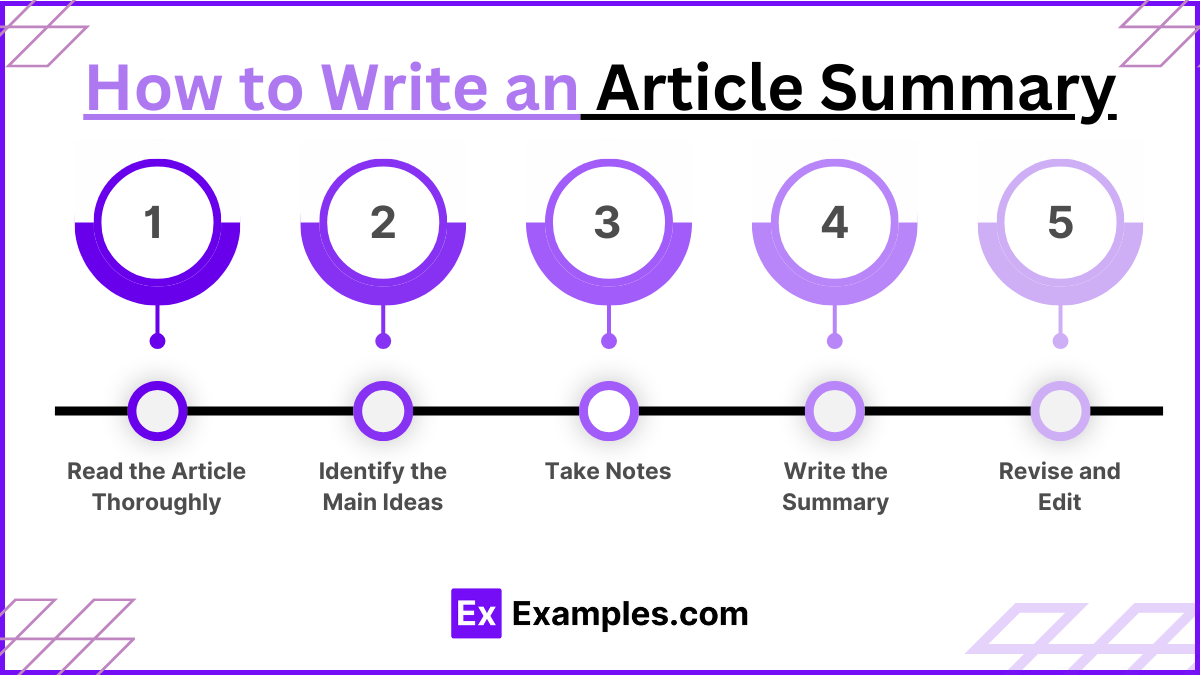
How to Write an Article Summary
Writing an article summary involves condensing the main ideas of a longer text into a shorter, concise version. This skill is essential for students, educators, and professionals who need to understand and communicate key points quickly. Follow these steps to write an effective article summary:
Read the Article Thoroughly
Initial Reading: Read the article from start to finish without taking notes. This helps you understand the overall message and tone.
Second Reading: Read the article again, this time highlighting key points, main arguments, and significant details.Identify the Main Ideas
Thesis Statement: Locate the thesis statement or the main argument of the article. This is usually found in the introduction.
Supporting Points: Identify the primary supporting points that the author uses to back up the thesis. These are typically found in the body paragraphs.
Conclusion: Note any conclusions or final thoughts the author presents.Take Notes
Create an outline of the main ideas and supporting details. Use bullet points for clarity.
Write down any significant quotes or data that are crucial to the article’s argument.Write the Summary
Introduction: Start with an introductory sentence that includes the article’s title, author, and the main point.
Body Paragraphs: Summarize each main idea in a separate paragraph. Combine supporting points to create a concise version of the article.
Conclusion: End with a concluding sentence that reflects the author’s final thoughts or conclusions.Revise and Edit
Check for Clarity: Ensure your summary clearly conveys the main ideas without adding your interpretations.
Eliminate Redundancies: Remove any repetitive or unnecessary information.
Grammar and Style: Proofread for grammatical errors and ensure the summary is written in a consistent style.
Common mistakes to avoid in Article Summarization
1. Including Too Much Detail
- Overly Detailed: Avoid adding too many specific details, examples, or anecdotes from the original article.
- Lengthy Summaries: Keep your summary concise, focusing only on the main points.
2. Omitting Key Points
- Missing Main Ideas: Ensure you include all the key points and main arguments.
- Incomplete Picture: Avoid leaving out critical information that is necessary for understanding the article’s main idea.
3. Using the Same Words as the Article
- Plagiarism: Refrain from copying sentences or phrases directly from the article.
- Lack of Paraphrasing: Use your own words to explain the main ideas and key points.
4. Adding Personal Opinions
- Subjective Views: Do not include your own opinions, interpretations, or analysis in the summary.
- Bias: Maintain an objective tone, reflecting the original author’s intent and perspective.
5. Misinterpreting the Main Idea
- Inaccurate Summary: Make sure you correctly understand the article’s thesis and main arguments before summarizing.
- Confusion: Avoid confusing the reader by misrepresenting the article’s core message.
6. Neglecting the Article’s Structure
- Ignoring Organization: Follow the structure of the original article, summarizing each section systematically.
- Disorganized Summary: Ensure your summary is organized and flows logically.
7. Failing to Mention the Title and Author
- Lack of Attribution: Always include the title of the article and the author’s name to provide proper context.
- Context Omission: This helps the reader understand the source and context of the summary.
8. Overlooking the Conclusion
- Incomplete Summary: Don’t forget to summarize the conclusion and any final thoughts of the article.
- Missing Closure: Ensure the summary reflects the article’s ending to provide a complete overview.
FAQs
How long should an article summary be?
An article summary should be concise, typically one-third of the original article length, focusing on the main points and key arguments without unnecessary details.
What is the main purpose of summarizing an article?
The main purpose is to condense the article’s key points and main ideas, providing a clear and concise understanding of the content without reading the entire text.
How can I ensure my summary is accurate?
Ensure accuracy by thoroughly reading the article multiple times, taking notes on key points, and comparing your summary with the original to check for completeness and correctness.
Should I include quotes in my summary?
Include quotes only if they encapsulate a key idea or argument succinctly. Otherwise, paraphrase the information in your own words to maintain brevity.
Can I add my own opinion in the summary?
No, a summary should be objective and free from personal opinions. It should only reflect the author’s ideas and arguments presented in the article.
How do I handle complex information in a summary?
Simplify complex information by breaking it down into key points and summarizing them clearly. Avoid technical jargon unless it’s essential to the main ideas.
Is it necessary to follow the article’s structure in my summary?
Yes, follow the article’s structure to maintain logical flow and coherence. Summarize each section or paragraph systematically to ensure all main points are covered.
How do I summarize an article if it has multiple authors?
Mention all authors at the beginning of the summary. For example, “The article by Jane Doe, John Smith, and Emily Johnson discusses…”
What should I do if the article has no clear thesis?
Identify the main theme or overall message of the article. Focus on summarizing the central ideas and key points that support this theme.
How can I improve my summarization skills?
Practice regularly by summarizing various articles, seeking feedback, and refining your ability to identify key points and convey them concisely and accurately.



