50+ Swot Examples to Download
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of an organization. This framework helps businesses like a Warehouse, a Gym, or a Manager to assess their internal and external environments. By conducting a Warehouse SWOT Analysis, businesses can optimize storage and distribution processes. Similarly, a Gym SWOT Analysis can help fitness centers enhance member experiences and services. For managers, a Manager SWOT Analysis is essential to improve leadership skills and team performance.
What is Swot?
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a strategic tool used to evaluate these four aspects in a business or project to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
Examples of Swot
1. Opportunities
- Emerging markets – Potential for growth in new regions.
- Technological advancements – New tools and systems to improve operations.
- Strategic partnerships – Collaborations with other businesses.
- Market expansion – Entering new segments or demographics.
- Product diversification – Expanding the range of offerings.
- Increased online sales – Boosting e-commerce presence.
- Sustainability initiatives – Adopting green practices.
- Government incentives – Tax breaks or grants.
- Changing consumer preferences – Adapting to new trends.
- Mergers and acquisitions – Opportunities to buy or merge with other companies.
2. Threats
- Economic downturns – Recession or slow economic growth.
- Increased competition – New or stronger competitors.
- Regulatory changes – New laws or regulations.
- Technological changes – New technologies that disrupt the industry.
- Supply chain disruptions – Issues with suppliers or logistics.
- Negative publicity – Bad press or social media backlash.
- Market saturation – Too many competitors in the market.
- Cybersecurity threats – Risk of data breaches or cyberattacks.
- Changing consumer behavior – Shifts in customer preferences.
- Environmental issues – Natural disasters or sustainability concerns.
3. Warehouse SWOT Analysis
- Strength: Efficient inventory management system.
- Weakness: Limited storage capacity.
- Opportunity: Adoption of automation technology.
- Threat: Rising real estate costs.
4. Manager SWOT Analysis
- Strength: Strong leadership skills.
- Weakness: Lack of industry-specific experience.
- Opportunity: Professional development programs.
- Threat: High employee turnover in the team.
5. Gym SWOT Analysis
- Strength: State-of-the-art equipment.
- Weakness: High membership fees.
- Opportunity: Growing trend in fitness and wellness.
- Threat: Competition from budget gyms.
Swot Examples for Students
1. Strengths
- Strong academic performance – Consistently high grades and test scores.
- Good time management skills – Ability to balance schoolwork, extracurricular activities, and personal time.
- Effective study habits – Proven methods for retaining and understanding information.
- Strong communication skills – Ability to express ideas clearly and effectively.
- Active participation in class – Engages in discussions and contributes to group work.
2. Weaknesses
- Procrastination – Tendency to delay starting assignments.
- Poor note-taking skills – Difficulty in capturing important information during lectures.
- Test anxiety – High levels of stress and anxiety during exams.
- Lack of focus – Easily distracted, leading to reduced study efficiency.
- Limited subject interest – Difficulty staying motivated in subjects that are less interesting.
What does SWOT stand for?
SWOT stands for
S – Strengths
W – Weaknesses
O – Opportunities
T – Threats
Why is a SWOT Important?
1. Identifies Strengths:
- Helps organizations understand their internal strengths.
- Highlights unique advantages and resources.
2. Recognizes Weaknesses:
- Points out internal weaknesses that need improvement.
- Provides a clear picture of areas that require attention.
3. Uncovers Opportunities:
- Identifies external opportunities for growth and expansion.
- Helps in leveraging market trends and emerging possibilities.
4. Anticipates Threats:
- Detects potential external threats that could impact the organization.
- Aids in developing strategies to mitigate risks.
5. Informed Decision-Making:
- Provides a comprehensive view of internal and external factors.
- Helps in making well-informed strategic decisions.
6. Strategic Planning:
- Assists in setting realistic goals and objectives.
- Guides the development of effective action plans.
7. Competitive Advantage:
- Enables organizations to capitalize on strengths and opportunities.
- Helps in staying ahead of competitors by addressing weaknesses and threats.
8. Resource Allocation:
- Aids in prioritizing resources and efforts where they are needed most.
- Ensures efficient use of time, money, and human resources.
9. Enhanced Performance:
- Improves overall organizational performance by focusing on key areas.
- Encourages continuous improvement and innovation.
10. Stakeholder Communication:
- Provides a clear framework for communicating strategic insights to stakeholders.
- Enhances transparency and understanding among team members and stakeholders.
When should you use a SWOT?
1. Strategic Planning:
- During the development of long-term goals and objectives.
- To inform and guide the strategic planning process.
2. New Project or Initiative:
- At the start of a new project or business venture.
- To assess feasibility and potential success.
3. Competitive Analysis:
- When analyzing competitors and market position.
- To identify competitive advantages and areas for improvement.
4. Organizational Change:
- During times of significant change or restructuring.
- To understand the impact of changes on the organization.
5. Performance Evaluation:
- For periodic reviews of business or project performance.
- To identify areas of success and areas needing improvement.
6. Market Expansion:
- When considering entering new markets or launching new products.
- To evaluate the potential and challenges of new opportunities.
7. Risk Management:
- To identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- As part of a comprehensive risk management plan.
8. Resource Allocation:
- When deciding where to allocate resources most effectively.
- To prioritize projects and initiatives based on strengths and opportunities.
9. Problem-Solving:
- To address specific challenges or issues within the organization.
- To develop targeted solutions based on identified weaknesses and threats.
10. Partnership Evaluation:
- When considering mergers, acquisitions, or strategic partnerships.
- To assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats involved.
SWOT: Pros and Cons
Pros of SWOT Analysis
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and use.
- Comprehensive View: Provides a holistic view of internal and external factors.
- Versatility: Applicable to any industry or organization.
- Strategic Insights: Identifies strengths to leverage.
- Improved Decision-Making: Informs and guides strategic decisions.
- Engages Stakeholders: Encourages participation and input from various stakeholders.
Cons of SWOT Analysis
- Subjectivity: Relies on the perspectives of the individuals conducting the analysis.
- Over-Simplification: May oversimplify complex issues.
- Static Snapshot: Represents a specific point in time.
- Lack of Prioritization: Does not inherently prioritize the factors identified.
- Resource Intensive: Can be time-consuming to gather and analyze data.
- Implementation Challenges: Identifying factors is only the first step; implementing strategies based on the analysis can be challenging.
SWOT vs. SWOT Analysis
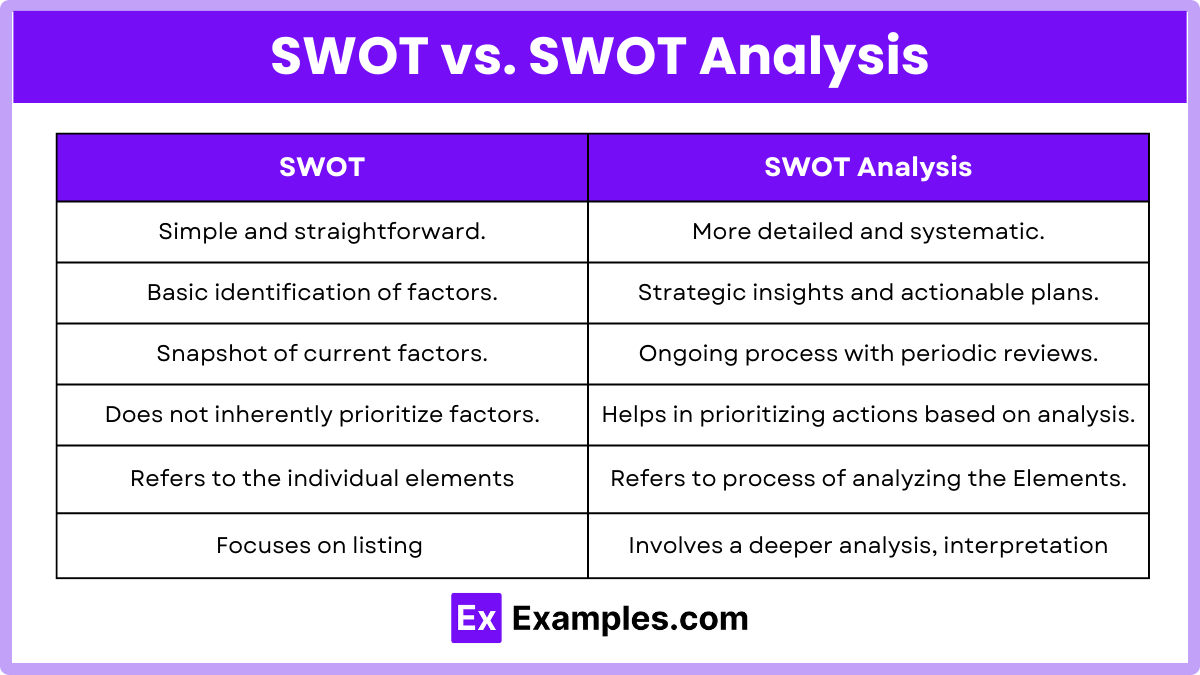
| Aspect | SWOT | SWOT Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. | A strategic planning tool used to identify and evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business or project. |
| Usage | Refers to the individual elements (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats). | Refers to the process of analyzing these elements in a structured manner. |
| Purpose | Identifies the four key areas impacting an organization or project. | Provides a comprehensive framework for strategic planning and decision-making. |
| Scope | Focuses on listing and understanding the four components. | Involves a deeper analysis, interpretation, and application of the four components. |
| Complexity | Simple and straightforward. | More detailed and systematic. |
| Outcome | Basic identification of factors. | Strategic insights and actionable plans. |
| Application | Used as a checklist or a starting point. | Used for detailed strategic planning, problem-solving, and decision-making. |
| Time Frame | Snapshot of current factors. | Ongoing process with periodic reviews. |
| Stakeholder Involvement | Can be done individually or with minimal input. | Typically involves multiple stakeholders for a comprehensive view. |
| Prioritization | Does not inherently prioritize factors. | Helps in prioritizing actions based on the analysis. |
How often should SWOT Analysis be conducted?
Regularly, or when significant changes occur in the organization or market.
Who should be involved in SWOT Analysis?
Key stakeholders, including management, employees, and sometimes external consultants.
Can SWOT Analysis be used for personal development?
Yes, it helps individuals identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
What are common strengths in a SWOT Analysis?
Strong brand, skilled workforce, and advanced technology.
What are typical weaknesses in a SWOT Analysis?
Poor customer service, high production costs, and outdated technology.
What opportunities might a SWOT Analysis reveal?
Market expansion, technological advancements, and strategic partnerships.
What threats are often identified in SWOT Analysis?
Economic downturns, increased competition, and regulatory changes.
How does SWOT Analysis aid strategic planning?
By providing insights to develop effective strategies and make informed decisions.
Can SWOT Analysis help in risk management?
Yes, it identifies potential threats and helps develop mitigation strategies.
Is SWOT Analysis useful for startups?
Absolutely, it helps startups understand their market position and plan effectively.
50+ Swot Examples to Download

SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of an organization. This framework helps businesses like a Warehouse, a Gym, or a Manager to assess their internal and external environments. By conducting a Warehouse SWOT Analysis, businesses can optimize storage and distribution processes. Similarly, a Gym SWOT Analysis can help fitness centers enhance member experiences and services. For managers, a Manager SWOT Analysis is essential to improve leadership skills and team performance.
What is Swot?
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a strategic tool used to evaluate these four aspects in a business or project to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
Examples of Swot
1. Opportunities
Emerging markets – Potential for growth in new regions.
Technological advancements – New tools and systems to improve operations.
Strategic partnerships – Collaborations with other businesses.
Market expansion – Entering new segments or demographics.
Product diversification – Expanding the range of offerings.
Increased online sales – Boosting e-commerce presence.
Sustainability initiatives – Adopting green practices.
Government incentives – Tax breaks or grants.
Changing consumer preferences – Adapting to new trends.
Mergers and acquisitions – Opportunities to buy or merge with other companies.
2. Threats
Economic downturns – Recession or slow economic growth.
Increased competition – New or stronger competitors.
Regulatory changes – New laws or regulations.
Technological changes – New technologies that disrupt the industry.
Supply chain disruptions – Issues with suppliers or logistics.
Negative publicity – Bad press or social media backlash.
Market saturation – Too many competitors in the market.
Cybersecurity threats – Risk of data breaches or cyberattacks.
Changing consumer behavior – Shifts in customer preferences.
Environmental issues – Natural disasters or sustainability concerns.
3. Warehouse SWOT Analysis
Strength: Efficient inventory management system.
Weakness: Limited storage capacity.
Opportunity: Adoption of automation technology.
Threat: Rising real estate costs.
4. Manager SWOT Analysis
Strength: Strong leadership skills.
Weakness: Lack of industry-specific experience.
Opportunity: Professional development programs.
Threat: High employee turnover in the team.
5. Gym SWOT Analysis
Strength: State-of-the-art equipment.
Weakness: High membership fees.
Opportunity: Growing trend in fitness and wellness.
Threat: Competition from budget gyms.
Swot Examples for Students
1. Strengths
Strong academic performance – Consistently high grades and test scores.
Good time management skills – Ability to balance schoolwork, extracurricular activities, and personal time.
Effective study habits – Proven methods for retaining and understanding information.
Strong communication skills – Ability to express ideas clearly and effectively.
Active participation in class – Engages in discussions and contributes to group work.
2. Weaknesses
Procrastination – Tendency to delay starting assignments.
Poor note-taking skills – Difficulty in capturing important information during lectures.
Test anxiety – High levels of stress and anxiety during exams.
Lack of focus – Easily distracted, leading to reduced study efficiency.
Limited subject interest – Difficulty staying motivated in subjects that are less interesting.
What does SWOT stand for?
SWOT stands for
S – Strengths
W – Weaknesses
O – Opportunities
T – Threats
Why is a SWOT Important?
1. Identifies Strengths:
Helps organizations understand their internal strengths.
Highlights unique advantages and resources.
2. Recognizes Weaknesses:
Points out internal weaknesses that need improvement.
Provides a clear picture of areas that require attention.
3. Uncovers Opportunities:
Identifies external opportunities for growth and expansion.
Helps in leveraging market trends and emerging possibilities.
4. Anticipates Threats:
Detects potential external threats that could impact the organization.
Aids in developing strategies to mitigate risks.
5. Informed Decision-Making:
Provides a comprehensive view of internal and external factors.
Helps in making well-informed strategic decisions.
6. Strategic Planning:
Assists in setting realistic goals and objectives.
Guides the development of effective action plans.
7. Competitive Advantage:
Enables organizations to capitalize on strengths and opportunities.
Helps in staying ahead of competitors by addressing weaknesses and threats.
8. Resource Allocation:
Aids in prioritizing resources and efforts where they are needed most.
Ensures efficient use of time, money, and human resources.
9. Enhanced Performance:
Improves overall organizational performance by focusing on key areas.
Encourages continuous improvement and innovation.
10. Stakeholder Communication:
Provides a clear framework for communicating strategic insights to stakeholders.
Enhances transparency and understanding among team members and stakeholders.
When should you use a SWOT?
1. Strategic Planning:
During the development of long-term goals and objectives.
To inform and guide the strategic planning process.
2. New Project or Initiative:
At the start of a new project or business venture.
To assess feasibility and potential success.
3. Competitive Analysis:
When analyzing competitors and market position.
To identify competitive advantages and areas for improvement.
4. Organizational Change:
During times of significant change or restructuring.
To understand the impact of changes on the organization.
5. Performance Evaluation:
For periodic reviews of business or project performance.
To identify areas of success and areas needing improvement.
6. Market Expansion:
When considering entering new markets or launching new products.
To evaluate the potential and challenges of new opportunities.
7. Risk Management:
To identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
As part of a comprehensive risk management plan.
8. Resource Allocation:
When deciding where to allocate resources most effectively.
To prioritize projects and initiatives based on strengths and opportunities.
9. Problem-Solving:
To address specific challenges or issues within the organization.
To develop targeted solutions based on identified weaknesses and threats.
10. Partnership Evaluation:
When considering mergers, acquisitions, or strategic partnerships.
To assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats involved.
SWOT: Pros and Cons
Pros of SWOT Analysis
Simplicity: Easy to understand and use.
Comprehensive View: Provides a holistic view of internal and external factors.
Versatility: Applicable to any industry or organization.
Strategic Insights: Identifies strengths to leverage.
Improved Decision-Making: Informs and guides strategic decisions.
Engages Stakeholders: Encourages participation and input from various stakeholders.
Cons of SWOT Analysis
Subjectivity: Relies on the perspectives of the individuals conducting the analysis.
Over-Simplification: May oversimplify complex issues.
Static Snapshot: Represents a specific point in time.
Lack of Prioritization: Does not inherently prioritize the factors identified.
Resource Intensive: Can be time-consuming to gather and analyze data.
Implementation Challenges: Identifying factors is only the first step; implementing strategies based on the analysis can be challenging.
SWOT vs. SWOT Analysis
Aspect | SWOT | |
|---|---|---|
Definition | An acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. | A strategic planning tool used to identify and evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business or project. |
Usage | Refers to the individual elements (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats). | Refers to the process of analyzing these elements in a structured manner. |
Purpose | Identifies the four key areas impacting an organization or project. | Provides a comprehensive framework for strategic planning and decision-making. |
Scope | Focuses on listing and understanding the four components. | Involves a deeper analysis, interpretation, and application of the four components. |
Complexity | Simple and straightforward. | More detailed and systematic. |
Outcome | Basic identification of factors. | Strategic insights and actionable plans. |
Application | Used as a checklist or a starting point. | Used for detailed strategic planning, problem-solving, and decision-making. |
Time Frame | Snapshot of current factors. | Ongoing process with periodic reviews. |
Stakeholder Involvement | Can be done individually or with minimal input. | Typically involves multiple stakeholders for a comprehensive view. |
Prioritization | Does not inherently prioritize factors. | Helps in prioritizing actions based on the analysis. |
How often should SWOT Analysis be conducted?
Regularly, or when significant changes occur in the organization or market.
Who should be involved in SWOT Analysis?
Key stakeholders, including management, employees, and sometimes external consultants.
Can SWOT Analysis be used for personal development?
Yes, it helps individuals identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
What are common strengths in a SWOT Analysis?
Strong brand, skilled workforce, and advanced technology.
What are typical weaknesses in a SWOT Analysis?
Poor customer service, high production costs, and outdated technology.
What opportunities might a SWOT Analysis reveal?
Market expansion, technological advancements, and strategic partnerships.
What threats are often identified in SWOT Analysis?
Economic downturns, increased competition, and regulatory changes.
How does SWOT Analysis aid strategic planning?
By providing insights to develop effective strategies and make informed decisions.
Can SWOT Analysis help in risk management?
Yes, it identifies potential threats and helps develop mitigation strategies.
Is SWOT Analysis useful for startups?
Absolutely, it helps startups understand their market position and plan effectively.

