Terabit – 20 Examples, Conversion Chart, Uses
A terabit is a unit of data measurement that equals one trillion bits. In the era of cloud computing and digital communication, the need for high-speed data transfer is critical. Communication technology advancements have made it possible to manage and transfer vast amounts of data efficiently. This capability is essential for modern applications, ensuring seamless and rapid data exchange.
What is Terabit?
A terabit is a unit of digital information equal to one trillion bits. It is commonly used to measure data transfer speeds and storage capacity in high-capacity networks and devices.
Examples of Terabit
- Internet Backbone: Large-scale networks that form the core of the internet often use terabit-level connections to handle massive data flows.
- Data Centers: Major data centers use terabit connections to ensure fast and efficient data storage and retrieval.
- Telecommunications Networks: Telecom companies employ terabit speeds to support high-volume data transmission across vast distances.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): HPC systems, used in scientific research and simulations, require terabit connections for data-intensive tasks.
- Cloud Computing Services: Providers like AWS and Google Cloud use terabit links to connect their global data centers and manage data traffic.
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and YouTube rely on terabit networks to deliver high-definition and 4K content seamlessly to millions of users.
- Financial Services: Stock exchanges and financial institutions use terabit speeds to execute high-frequency trading and manage large databases.
- Smart Cities: Infrastructure in smart cities utilizes terabit connections for real-time data processing from sensors, cameras, and IoT devices.
- Online Gaming: Gaming networks, especially those supporting VR and AR, use terabit speeds to reduce latency and enhance user experience.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI systems that process large datasets and perform complex computations benefit from terabit connections.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR applications require terabit speeds for immersive and responsive experiences.
- 5G Networks: Advanced 5G networks use terabit technology to support high-speed mobile data and connect billions of devices.
- Scientific Research: Research institutions and universities use terabit connections to share and analyze large datasets across the globe.
- Government Operations: Governments use terabit networks for secure and efficient communication and data management.
- Military and Defense: Defense networks use terabit speeds for secure and rapid data transfer in intelligence and operational systems.
- E-commerce Platforms: Large e-commerce sites like Amazon use terabit connections to manage traffic and ensure quick data processing.
- Social Media Platforms: Companies like Facebook and Twitter use terabit connections to handle vast amounts of user-generated content.
- Healthcare Systems: Hospitals and medical research facilities use terabit networks for telemedicine, medical imaging, and patient data management.
- Education and E-learning: Universities and online learning platforms use terabit connections for live streaming lectures and managing educational content.
- Broadcasting Networks: TV and radio networks use terabit connections to distribute high-quality broadcasts to a global audience.
Conversion of Terabit
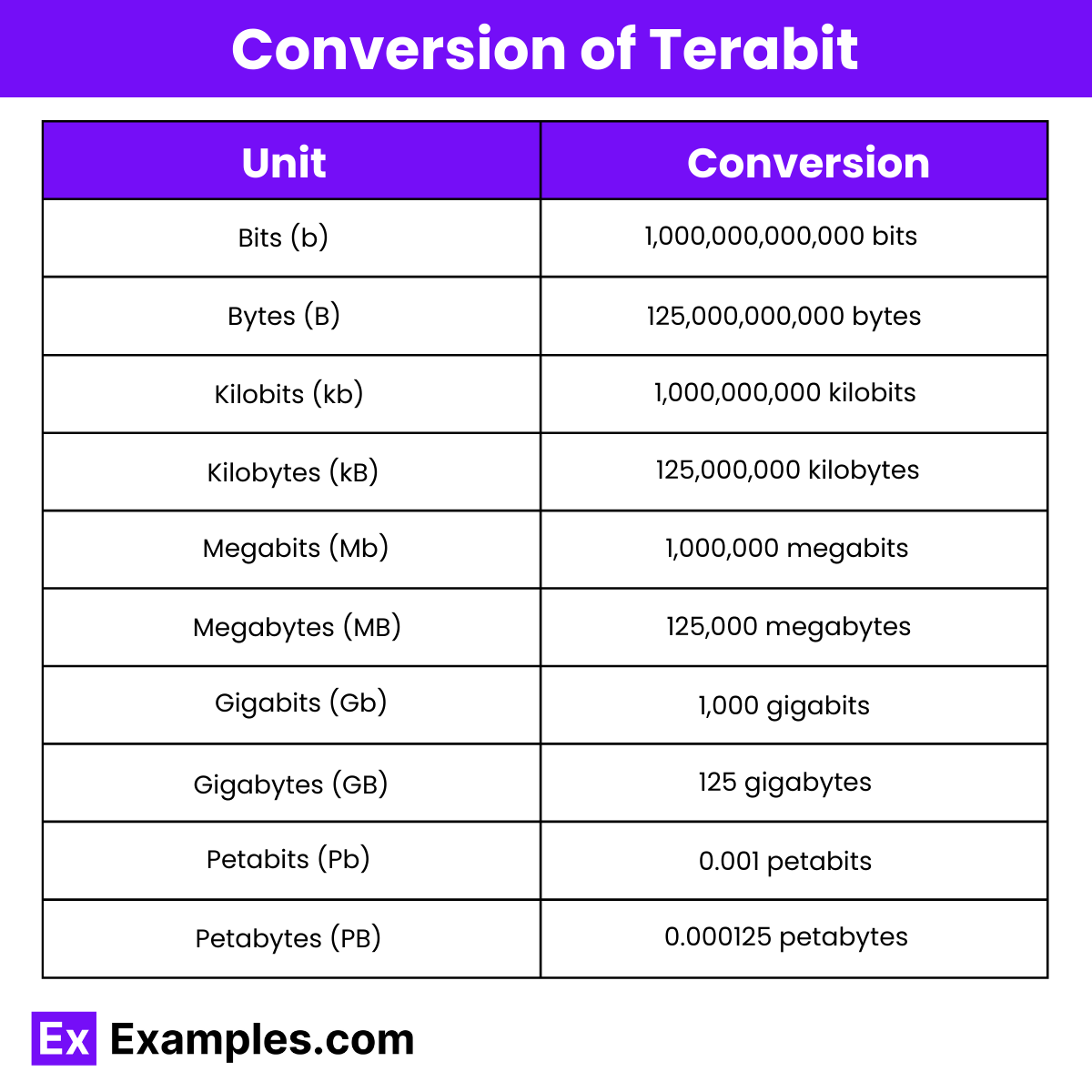
| Unit (Symbol) | Equivalent Value |
|---|---|
| Bits (b) | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000,000 bits |
| Bytes (B) | 1 Terabit = 125,000,000,000 bytes |
| Kilobits (kb) | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000 kilobits |
| Kilobytes (kB) | 1 Terabit = 125,000,000 kilobytes |
| Megabits (Mb) | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000 megabits |
| Megabytes (MB) | 1 Terabit = 125,000 megabytes |
| Gigabits (Gb) | 1 Terabit = 1,000 gigabits |
| Gigabytes (GB) | 1 Terabit = 125 gigabytes |
| Petabits (Pb) | 1 Terabit = 0.001 petabits |
| Petabytes (PB) | 1 Terabit = 0.000125 petabytes |
Terabit to Bits (b)
The smallest unit of digital information. One terabit equals 1,000,000,000,000 bits. This unit is often used to describe data transfer rates.
Terabit to Bytes (B)
There are 8 bits in a byte. One terabit equals 125,000,000,000 bytes. Bytes are used to measure file sizes and storage capacity.
Terabit to Kilobits (kb)
A kilobit is 1,000 bits. One terabit equals 1,000,000,000 kilobits. This unit is used for lower-speed data transfer rates, like certain internet speeds.
Terabit to Kilobytes (kB)
A kilobyte is 1,000 bytes. One terabit equals 125,000,000 kilobytes. This unit measures smaller file sizes.
Terabit to Megabits (Mb)
A megabit is 1,000,000 bits. One terabit equals 1,000,000 megabits. This unit is often used for higher-speed internet connections.
Terabit to Megabytes (MB)
A megabyte is 1,000,000 bytes. One terabit equals 125,000 megabytes. This unit measures medium-sized files, such as images and music files.
Terabit to Gigabits (Gb)
A gigabit is 1,000,000,000 bits. One terabit equals 1,000 gigabits. This unit measures high-speed data transfer rates.
Terabit to Gigabytes (GB)
A gigabyte is 1,000,000,000 bytes. One terabit equals 125 gigabytes. This unit measures larger files, such as HD videos and software applications.
Terabit to Petabits (Pb)
A petabit is 1,000,000,000,000,000 bits. One terabit equals 0.001 petabits. This unit is used for extremely large data quantities.
Terabit to Petabytes (PB)
A petabyte is 1,000,000,000,000,000 bytes. One terabit equals 0.000125 petabytes. This unit measures massive storage capacities, like those in large data centers.
Importance of Terabit
High-Speed Data Transmission
1. Technological Advancements: Terabit networks enable the rapid transmission of large amounts of data, essential for the growth of technologies like 5G, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- These advancements rely on high-speed and high-capacity data channels to function effectively.
2. Enhanced Connectivity: Faster data transfer rates provided by terabit technology ensure smooth and uninterrupted connectivity.
- This is particularly important for real-time applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and telemedicine.
Data Storage and Management
1. Massive Data Storage: Terabit capacity is crucial for data centers that handle enormous volumes of data generated by businesses, governments, and individuals.
- It supports cloud storage solutions, allowing users to store and access large datasets efficiently.
2. Efficient Data Management: Managing data at the terabit scale improves the efficiency of data retrieval and processing.
- This is vital for sectors like finance, healthcare, and research, where large datasets are regularly analyzed and utilized.
Economic and Industrial Impact
1. Boost to Economies: Countries and businesses investing in terabit infrastructure can experience significant economic growth.
- Improved data capabilities can lead to innovations, better services, and more competitive industries.
2. Industrial Applications: Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing benefit from terabit technology through improved design, simulation, and production processes.
- Enhanced data handling capabilities support the development of smarter, more efficient machines and systems.
Research and Development
1. Scientific Research: Researchers in fields like genomics, astronomy, and climate science rely on the ability to store and process terabits of data.
- High-capacity data storage and transmission facilitate groundbreaking discoveries and innovations.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML algorithms require large datasets to train and improve models.
- Terabit technology supports the storage and processing needs of these data-intensive applications, driving advancements in AI and ML.
Future Prospects
1. Exponential Data Growth: As the digital universe expands, the demand for terabit-scale data handling will continue to rise.
- Innovations in technology and infrastructure will be necessary to meet this growing demand.
2. Global Connectivity: The development of terabit networks can bridge digital divides, providing high-speed internet access to remote and underserved areas.
- This can lead to more inclusive global connectivity and economic development.
Where do you use of Terabit
Networking and Telecommunications
- High-Speed Internet: Terabit per second (Tbps) speeds are increasingly relevant in high-speed internet infrastructure, especially in backbone networks that form the core of the internet.
- Fiber Optic Networks: Fiber optic technology leverages terabit speeds to provide high-capacity data transmission over long distances. These networks are essential for handling the growing demand for data.
- Data Centers: Terabit speeds are used in data center interconnects, enabling efficient and fast data transfers between servers, storage systems, and other network components.
Data Storage and Transfer
- Mass Data Storage: Large-scale data storage systems, especially in enterprises and research institutions, may measure storage capacities in terabits. This is particularly relevant for systems handling massive datasets.
- Backup Solutions: Terabit capacities are used in backup and disaster recovery solutions to ensure large volumes of data can be stored and retrieved efficiently.
Cloud Computing
- Cloud Storage Services: Cloud providers use terabits to describe the bandwidth and capacity of their storage and data transfer services, supporting high-volume data operations.
- Big Data Processing: In big data environments, terabit speeds and capacities are crucial for processing and analyzing large datasets rapidly.
Media and Entertainment
- High-Definition Content: Streaming services that offer high-definition (HD), 4K, and even 8K content require high data transfer rates, often measured in terabits, to deliver smooth and uninterrupted viewing experiences.
- Live Broadcasting: Live broadcasts of events, such as sports and concerts, use terabit-capacity networks to handle the large data streams involved.
Scientific Research
- Large Hadron Collider (LHC): Research facilities like the LHC generate enormous amounts of data from experiments. Terabit-capacity networks are used to transfer this data for analysis and storage.
- Astronomy: Telescopes and observatories capture vast amounts of data that need to be processed and stored efficiently, often utilizing terabit data transfer rates.
Government and Defense
- Surveillance Systems: Government and defense agencies use terabit capacities for storing and analyzing large volumes of surveillance data.
- Satellite Communications: High-speed data links between satellites and ground stations often operate at terabit speeds to ensure efficient data transmission.
Enterprise Applications
- Corporate Networks: Large enterprises use terabit-capacity networks for internal communications and data transfers, ensuring smooth and efficient operations across multiple locations.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions require high-speed data transfer capabilities to process transactions and conduct real-time trading, often leveraging terabit networks.
Educational Institutions
- Research Universities: Universities engaged in cutting-edge research use terabit networks to facilitate collaboration and data sharing among researchers globally.
- Digital Libraries: Large digital libraries and repositories store vast amounts of data and require high-capacity networks to manage and access this information.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- Smart Cities: Smart city infrastructures use terabit networks to handle data from numerous sensors and devices, enabling efficient management of urban services.
- Industrial IoT: Industries implementing IoT solutions use terabit networks for real-time data processing and monitoring of equipment and processes.
What is the difference between Terabit and Terabyte
| Aspect | Terabit (Tb) | Terabyte (TB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1 Terabit = 1 trillion (10^12) bits | 1 Terabyte = 1 trillion (10^12) bytes |
| Units | Bits | Bytes |
| Binary Equivalent | 1 Terabit = 1,024 Gigabits (Gb) | 1 Terabyte = 1,024 Gigabytes (GB) |
| Decimal Equivalent | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000,000 bits | 1 Terabyte = 1,000,000,000,000 bytes |
| Usage | Network bandwidth, data transfer rates | Data storage capacities |
| Measurement Context | Typically used for measuring data transfer speed or network capacity | Typically used for measuring data storage and capacity |
| Volume Comparison | 1 Terabit = 0.125 Terabytes (TB) | 1 Terabyte = 8 Terabits (Tb) |
| Symbol | Tb | TB |
| Common Applications | High-speed internet, data center interconnects, telecommunications | Data storage systems, hard drives, SSDs, cloud storage |
How do terabits benefit data centers?
Terabits enable efficient data transfers and interconnects between servers.
Why are terabits important in telecommunications?
They support massive data handling and high-speed communications.
Are terabits used in cloud computing?
Yes, terabits measure bandwidth and data transfer capabilities in cloud services.
How do terabits aid scientific research?
They facilitate large data analysis in projects like climate modeling and genomics.
How do terabits enhance streaming services?
They provide bandwidth for high-definition and 4K content delivery.
Why are terabits crucial for global corporations?
They ensure fast data exchange across international offices and data centers.
How do terabits improve network performance?
They enable high-speed data transfer and low-latency communication.
What role do terabits play in high-performance computing?
Terabits support rapid data transfer between supercomputers and storage systems.
Are terabits used in financial services?
Yes, for fast data processing in high-frequency trading and transaction records.
How do terabits support content delivery networks?
They provide the necessary bandwidth for seamless global content distribution.
Terabit – 20 Examples, Conversion Chart, Uses
A terabit is a unit of data measurement that equals one trillion bits. In the era of cloud computing and digital communication, the need for high-speed data transfer is critical. Communication technology advancements have made it possible to manage and transfer vast amounts of data efficiently. This capability is essential for modern applications, ensuring seamless and rapid data exchange.
What is Terabit?
A terabit is a unit of digital information equal to one trillion bits. It is commonly used to measure data transfer speeds and storage capacity in high-capacity networks and devices.
Examples of Terabit
Internet Backbone: Large-scale networks that form the core of the internet often use terabit-level connections to handle massive data flows.
Data Centers: Major data centers use terabit connections to ensure fast and efficient data storage and retrieval.
Telecommunications Networks: Telecom companies employ terabit speeds to support high-volume data transmission across vast distances.
High-Performance Computing (HPC): HPC systems, used in scientific research and simulations, require terabit connections for data-intensive tasks.
Cloud Computing Services: Providers like AWS and Google Cloud use terabit links to connect their global data centers and manage data traffic.
Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and YouTube rely on terabit networks to deliver high-definition and 4K content seamlessly to millions of users.
Financial Services: Stock exchanges and financial institutions use terabit speeds to execute high-frequency trading and manage large databases.
Smart Cities: Infrastructure in smart cities utilizes terabit connections for real-time data processing from sensors, cameras, and IoT devices.
Online Gaming: Gaming networks, especially those supporting VR and AR, use terabit speeds to reduce latency and enhance user experience.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI systems that process large datasets and perform complex computations benefit from terabit connections.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR applications require terabit speeds for immersive and responsive experiences.
5G Networks: Advanced 5G networks use terabit technology to support high-speed mobile data and connect billions of devices.
Scientific Research: Research institutions and universities use terabit connections to share and analyze large datasets across the globe.
Government Operations: Governments use terabit networks for secure and efficient communication and data management.
Military and Defense: Defense networks use terabit speeds for secure and rapid data transfer in intelligence and operational systems.
E-commerce Platforms: Large e-commerce sites like Amazon use terabit connections to manage traffic and ensure quick data processing.
Social Media Platforms: Companies like Facebook and Twitter use terabit connections to handle vast amounts of user-generated content.
Healthcare Systems: Hospitals and medical research facilities use terabit networks for telemedicine, medical imaging, and patient data management.
Education and E-learning: Universities and online learning platforms use terabit connections for live streaming lectures and managing educational content.
Broadcasting Networks: TV and radio networks use terabit connections to distribute high-quality broadcasts to a global audience.
Conversion of Terabit
Unit (Symbol) | Equivalent Value |
|---|---|
Bits (b) | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000,000 bits |
Bytes (B) | 1 Terabit = 125,000,000,000 bytes |
Kilobits (kb) | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000 kilobits |
Kilobytes (kB) | 1 Terabit = 125,000,000 kilobytes |
Megabits (Mb) | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000 megabits |
Megabytes (MB) | 1 Terabit = 125,000 megabytes |
Gigabits (Gb) | 1 Terabit = 1,000 gigabits |
Gigabytes (GB) | 1 Terabit = 125 gigabytes |
Petabits (Pb) | 1 Terabit = 0.001 petabits |
Petabytes (PB) | 1 Terabit = 0.000125 petabytes |
Terabit to Bits (b)
1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000,000 bits
The smallest unit of digital information. One terabit equals 1,000,000,000,000 bits. This unit is often used to describe data transfer rates.
Terabit to Bytes (B)
1 Terabit = 125,000,000,000 bytes
There are 8 bits in a byte. One terabit equals 125,000,000,000 bytes. Bytes are used to measure file sizes and storage capacity.
Terabit to Kilobits (kb)
1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000 kilobits
A kilobit is 1,000 bits. One terabit equals 1,000,000,000 kilobits. This unit is used for lower-speed data transfer rates, like certain internet speeds.
Terabit to Kilobytes (kB)
1 Terabit = 125,000,000 kilobytes
A kilobyte is 1,000 bytes. One terabit equals 125,000,000 kilobytes. This unit measures smaller file sizes.
Terabit to Megabits (Mb)
1 Terabit = 1,000,000 megabits
A megabit is 1,000,000 bits. One terabit equals 1,000,000 megabits. This unit is often used for higher-speed internet connections.
Terabit to Megabytes (MB)
1 Terabit = 125,000 megabytes
A megabyte is 1,000,000 bytes. One terabit equals 125,000 megabytes. This unit measures medium-sized files, such as images and music files.
Terabit to Gigabits (Gb)
1 Terabit = 1,000 gigabits
A gigabit is 1,000,000,000 bits. One terabit equals 1,000 gigabits. This unit measures high-speed data transfer rates.
Terabit to Gigabytes (GB)
1 Terabit = 125 gigabytes
A gigabyte is 1,000,000,000 bytes. One terabit equals 125 gigabytes. This unit measures larger files, such as HD videos and software applications.
Terabit to Petabits (Pb)
1 Terabit = 0.001 petabits
A petabit is 1,000,000,000,000,000 bits. One terabit equals 0.001 petabits. This unit is used for extremely large data quantities.
Terabit to Petabytes (PB)
1 Terabit = 0.000125 petabytes
A petabyte is 1,000,000,000,000,000 bytes. One terabit equals 0.000125 petabytes. This unit measures massive storage capacities, like those in large data centers.
Importance of Terabit
High-Speed Data Transmission
1. Technological Advancements: Terabit networks enable the rapid transmission of large amounts of data, essential for the growth of technologies like 5G, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
These advancements rely on high-speed and high-capacity data channels to function effectively.
2. Enhanced Connectivity: Faster data transfer rates provided by terabit technology ensure smooth and uninterrupted connectivity.
This is particularly important for real-time applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and telemedicine.
Data Storage and Management
1. Massive Data Storage: Terabit capacity is crucial for data centers that handle enormous volumes of data generated by businesses, governments, and individuals.
It supports cloud storage solutions, allowing users to store and access large datasets efficiently.
2. Efficient Data Management: Managing data at the terabit scale improves the efficiency of data retrieval and processing.
This is vital for sectors like finance, healthcare, and research, where large datasets are regularly analyzed and utilized.
Economic and Industrial Impact
1. Boost to Economies: Countries and businesses investing in terabit infrastructure can experience significant economic growth.
Improved data capabilities can lead to innovations, better services, and more competitive industries.
2. Industrial Applications: Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing benefit from terabit technology through improved design, simulation, and production processes.
Enhanced data handling capabilities support the development of smarter, more efficient machines and systems.
Research and Development
1. Scientific Research: Researchers in fields like genomics, astronomy, and climate science rely on the ability to store and process terabits of data.
High-capacity data storage and transmission facilitate groundbreaking discoveries and innovations.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML algorithms require large datasets to train and improve models.
Terabit technology supports the storage and processing needs of these data-intensive applications, driving advancements in AI and ML.
Future Prospects
1. Exponential Data Growth: As the digital universe expands, the demand for terabit-scale data handling will continue to rise.
Innovations in technology and infrastructure will be necessary to meet this growing demand.
2. Global Connectivity: The development of terabit networks can bridge digital divides, providing high-speed internet access to remote and underserved areas.
This can lead to more inclusive global connectivity and economic development.
Where do you use of Terabit
Networking and Telecommunications
High-Speed Internet: Terabit per second (Tbps) speeds are increasingly relevant in high-speed internet infrastructure, especially in backbone networks that form the core of the internet.
Fiber Optic Networks: Fiber optic technology leverages terabit speeds to provide high-capacity data transmission over long distances. These networks are essential for handling the growing demand for data.
Data Centers: Terabit speeds are used in data center interconnects, enabling efficient and fast data transfers between servers, storage systems, and other network components.
Data Storage and Transfer
Mass Data Storage: Large-scale data storage systems, especially in enterprises and research institutions, may measure storage capacities in terabits. This is particularly relevant for systems handling massive datasets.
Backup Solutions: Terabit capacities are used in backup and disaster recovery solutions to ensure large volumes of data can be stored and retrieved efficiently.
Cloud Computing
Cloud Storage Services: Cloud providers use terabits to describe the bandwidth and capacity of their storage and data transfer services, supporting high-volume data operations.
Big Data Processing: In big data environments, terabit speeds and capacities are crucial for processing and analyzing large datasets rapidly.
Media and Entertainment
High-Definition Content: Streaming services that offer high-definition (HD), 4K, and even 8K content require high data transfer rates, often measured in terabits, to deliver smooth and uninterrupted viewing experiences.
Live Broadcasting: Live broadcasts of events, such as sports and concerts, use terabit-capacity networks to handle the large data streams involved.
Scientific Research
Large Hadron Collider (LHC): Research facilities like the LHC generate enormous amounts of data from experiments. Terabit-capacity networks are used to transfer this data for analysis and storage.
Astronomy: Telescopes and observatories capture vast amounts of data that need to be processed and stored efficiently, often utilizing terabit data transfer rates.
Government and Defense
Surveillance Systems: Government and defense agencies use terabit capacities for storing and analyzing large volumes of surveillance data.
Satellite Communications: High-speed data links between satellites and ground stations often operate at terabit speeds to ensure efficient data transmission.
Enterprise Applications
Corporate Networks: Large enterprises use terabit-capacity networks for internal communications and data transfers, ensuring smooth and efficient operations across multiple locations.
Financial Services: Financial institutions require high-speed data transfer capabilities to process transactions and conduct real-time trading, often leveraging terabit networks.
Educational Institutions
Research Universities: Universities engaged in cutting-edge research use terabit networks to facilitate collaboration and data sharing among researchers globally.
Digital Libraries: Large digital libraries and repositories store vast amounts of data and require high-capacity networks to manage and access this information.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Smart Cities: Smart city infrastructures use terabit networks to handle data from numerous sensors and devices, enabling efficient management of urban services.
Industrial IoT: Industries implementing IoT solutions use terabit networks for real-time data processing and monitoring of equipment and processes.
What is the difference between Terabit and Terabyte
Aspect | Terabit (Tb) | Terabyte (TB) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | 1 Terabit = 1 trillion (10^12) bits | 1 Terabyte = 1 trillion (10^12) bytes |
Units | Bits | Bytes |
Binary Equivalent | 1 Terabit = 1,024 Gigabits (Gb) | 1 Terabyte = 1,024 Gigabytes (GB) |
Decimal Equivalent | 1 Terabit = 1,000,000,000,000 bits | 1 Terabyte = 1,000,000,000,000 bytes |
Usage | Network bandwidth, data transfer rates | Data storage capacities |
Measurement Context | Typically used for measuring data transfer speed or network capacity | Typically used for measuring data storage and capacity |
Volume Comparison | 1 Terabit = 0.125 Terabytes (TB) | 1 Terabyte = 8 Terabits (Tb) |
Symbol | Tb | TB |
Common Applications | High-speed internet, data center interconnects, telecommunications | Data storage systems, hard drives, SSDs, cloud storage |
How do terabits benefit data centers?
Terabits enable efficient data transfers and interconnects between servers.
Why are terabits important in telecommunications?
They support massive data handling and high-speed communications.
Are terabits used in cloud computing?
Yes, terabits measure bandwidth and data transfer capabilities in cloud services.
How do terabits aid scientific research?
They facilitate large data analysis in projects like climate modeling and genomics.
How do terabits enhance streaming services?
They provide bandwidth for high-definition and 4K content delivery.
Why are terabits crucial for global corporations?
They ensure fast data exchange across international offices and data centers.
How do terabits improve network performance?
They enable high-speed data transfer and low-latency communication.
What role do terabits play in high-performance computing?
Terabits support rapid data transfer between supercomputers and storage systems.
Are terabits used in financial services?
Yes, for fast data processing in high-frequency trading and transaction records.
How do terabits support content delivery networks?
They provide the necessary bandwidth for seamless global content distribution.

