6+ Trial Balance Examples to Download
Trial balance is a crucial accounting tool used to ensure that the total debits and credits in a company’s financial records are equal. This is done by listing all of the company’s accounts and their balances in two columns – debit and credit. The purpose of the trial balance is to identify any errors in the accounting records before the preparation of financial statements.
1. Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
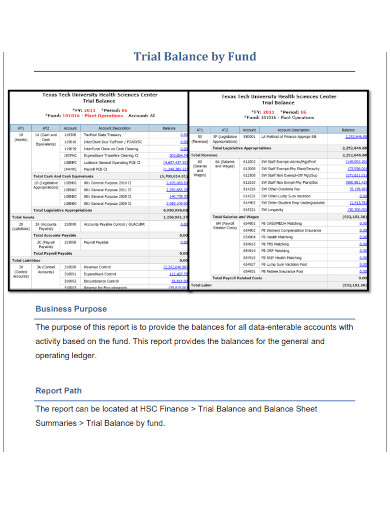
2. Trial Balance by Fund
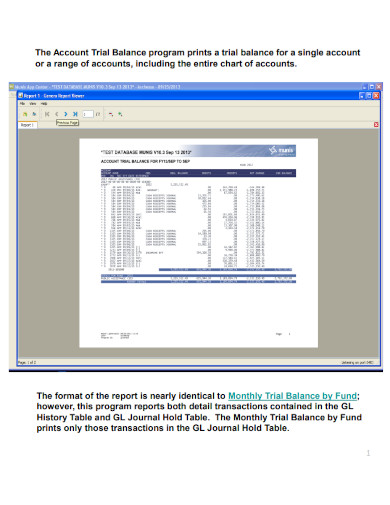
3. Account Trial Balance Report
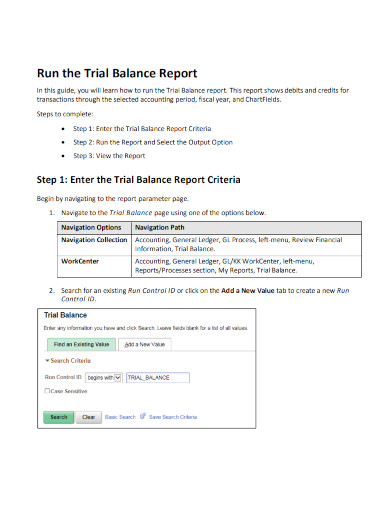
4. Run the Trial Balance Report
5. Digital Trial Balance Template
7. Quick Trial Balance
What is a Trial Balance?
A trial balance is a statement of all the ledger accounts of a business and their balances. The purpose of the trial balance is to ensure that the total debits in the accounting system are equal to the total credits. It is prepared at the end of an accounting period and serves as the basis for creating financial statements. The trial balance includes all accounts such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. The balances of these accounts are separated into debit and credit columns. If the debits and credits are equal, the trial balance is said to be balanced, indicating that the accounting records are accurate. However, if the trial balance is not balanced, it indicates an error in the accounting records that need to be corrected before the preparation of financial statements.
How to do a trial balance
By following these steps, a trial balance can be prepared accurately, helping to ensure that the financial statements prepared from the accounting records are accurate as well. Here’s how to do a trial balance:
Step 1: Collect all the ledger accounts
Collect all the ledger accounts from the general ledger of the company.
Step 2: List all the accounts
List all the accounts in the trial balance worksheet. The accounts should be listed in a specific order, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses.
Step 3: Enter the balances
Enter the balances of each account in the trial balance worksheet. The balance of an account is the difference between its total debits and total credits.
Step 4: Total the debit and credit columns
Total the debit and credit columns separately. This will help ensure that the total debits are equal to the total credits.
Step 5: Verify the trial balance
Verify that the total debits and credits are equal. If they are equal, the trial balance is balanced. If they are not equal, there is an error in the accounting records that need to be corrected.
Step 6: Investigate the errors
Investigate the errors that caused the trial balance to be unbalanced. Common errors include incorrect posting of transactions, mathematical errors, and transposition errors.
Step 7: Correct the errors
Correct the errors in the accounting records and re-calculate the trial balance.
Step 8: Re-verify the trial balance
Re-verify the trial balance to ensure that the errors have been corrected and the trial balance is now balanced.
FAQs
Why is a trial balance important?
A trial balance is important because it helps ensure the accuracy of the accounting records. If the total debits and credits in the trial balance are equal, it indicates that the accounting records are accurate. If they are not equal, it indicates an error that needs to be corrected before the preparation of financial statements. This is a key aspect of the importance of financial accounting in decision-making.
What are the common errors that can be identified through a trial balance?
Common errors that can be identified through a trial balance include incorrect posting of transactions, mathematical errors, transposition errors, and errors in the ledger account balances.
What is the difference between a trial balance and a balance sheet?
A trial balance is a statement of all the ledger accounts of a business and their balances, while a balance sheet is a financial statement that shows the assets, liabilities, and equity of a business at a specific point in time.
To conclude, a trial balance is an essential tool in accounting that summarizes all ledger account balances and ensures that the total debits and credits are equal. It plays a critical role in identifying and correcting errors in accounting records, helping to ensure that the financial statements accurately reflect the financial position of a business. By using a trial balance, businesses can maintain accurate financial records and make informed decisions based on reliable financial information.