36+ UX Design Examples to Download
UX Design focuses on creating intuitive and enjoyable user experiences for websites and applications. It involves understanding user behavior, conducting research, and implementing design principles that enhance usability and satisfaction. By leveraging tools like Chat GPT, web designers can generate creative ideas and solutions, streamline their design process, and improve communication with clients. Chat GPT prompts for web designers can inspire innovative designs and help create more effective and user-friendly digital products.
What is UX Design?
User Experience (UX) Design is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users, focusing on usability, accessibility, and enhancing user satisfaction through intuitive and efficient interactions.
UX design examples
- Airbnb: Simple, intuitive interface with high-quality images and easy booking process.
- Google Search: Clean layout, fast performance, and relevant search results.
- Apple’s iOS: Consistent design, smooth animations, and intuitive touch interactions.
- Slack: User-friendly messaging platform with customizable notifications and integrations.
- Duolingo: Engaging gamification for language learning with clear progress tracking.
- Spotify: Personalized music recommendations and easy-to-navigate interface.
- Amazon: Efficient search functionality and personalized product recommendations.
- Netflix: Intuitive navigation, personalized content, and seamless streaming experience.
- Trello: Visual task management with drag-and-drop functionality and customizable boards.
- Mailchimp: Simplified email marketing tools with clear step-by-step guidance.
- Asana: Project management with an intuitive interface and collaborative features.
- Uber: Easy ride-booking process with real-time tracking and transparent pricing.
- Pinterest: Visually appealing design with easy content discovery and organization.
- Dropbox: Simple file sharing and cloud storage with intuitive drag-and-drop.
- Medium: Clean reading experience with a focus on high-quality content.
- Stripe: Developer-friendly payment processing with clear documentation and APIs.
- Canva: User-friendly design tools with a wide range of templates and customization options.
UX design examples in real life
- Multi-Purpose Water Dispenser: Designed by Global Tap, this dispenser at the California Academy of Sciences allows easy access to water for drinking and filling bottles, including lower taps for pets, enhancing user convenience.
- Fly in Urinal (Amsterdam Schiphol Airport): Implemented a small image of a fly in urinals to improve aim and reduce spillage, leading to an 80% reduction in cleaning costs.
- Anti-Pee Wall (Hamburg, Germany): Used a water-repellent coating on walls to bounce urine back at offenders, successfully deterring public urination.
- Accessible Bathrooms: Examples include poorly designed bathrooms that are inaccessible to wheelchair users, highlighting the importance of thoughtful, inclusive design.
- Body Lotion Bottles: Pump bottles often leave residue at the bottom, while squeeze bottles with narrow openings allow easy use of every last drop, demonstrating good UX in product packaging.
- OYAKATA Instant Noodles: The packaging allows for easy preparation and draining of water through built-in holes in the lid, ensuring a hassle-free cooking experience.
- Gym Studio Design: Studios with obstructive columns or poor visibility of the instructor highlight the impact of physical design on user experience during fitness classes.
- Rjukan Mirrors (Norway): Installed mirrors to reflect sunlight into a town hidden from direct sunlight during winter, improving the living experience for residents.
- Google Classroom: Saw a significant increase in users, providing an intuitive and effective platform for remote education, making it easier for teachers and students to adapt to online learning.
- Spotify’s Harmonious User Flow: Offers a seamless music streaming experience with personalized recommendations and an intuitive interface.
Mobile UX design examples
- Spotify’s Mobile App: Features an intuitive interface with easy navigation, personalized playlists, and seamless integration across devices, providing a consistent and enjoyable user experience.
- Instagram: Offers a user-friendly layout with simple navigation, engaging visual content, and interactive features like stories and reels, enhancing social media interaction.
- Duolingo: Utilizes gamification elements and a clean, straightforward design to make language learning engaging and accessible on mobile devices.
- Uber: Provides a seamless ride-booking experience with clear, easy-to-use features for locating drivers, tracking rides, and making payments, incorporating user feedback for continuous improvement.
- Google Maps: Delivers accurate, real-time navigation and location information with a simple interface, ensuring ease of use while on the go.
- Apple Pay: Ensures a secure and efficient payment process with an intuitive setup, easy authentication, and widespread acceptance at numerous retailers.
- WhatsApp: Facilitates communication with a clean design, easy navigation, and reliable messaging features, including multimedia sharing and end-to-end encryption.
- Amazon: Offers a streamlined shopping experience with an intuitive search dashboard, personalized recommendations, and easy checkout processes..
- TikTok: Provides an engaging video-sharing platform with a user-friendly interface, easy content discovery, and interactive features like filters and effects.
- Airbnb: Simplifies the booking process with a clean design, easy-to-navigate property listings, and integrated messaging with hosts.
why UX Design is important?
- Enhances User Satisfaction: A well-designed user experience ensures that products are intuitive and enjoyable to use, leading to increased user satisfaction and loyalty. When users find it easy to navigate and interact with a product, they are more likely to have a positive perception of the brand.
- Improves Accessibility: Good UX design considers the needs of all users, including those with disabilities, ensuring that products are accessible to a broader audience. This inclusivity not only helps in complying with legal standards but also enhances the brand’s reputation.
- Increases Conversion Rates: Effective UX design can significantly improve conversion rates by making it easier for users to complete desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service. Streamlined processes and clear calls-to-action reduce friction and increase the likelihood of conversions.
- Reduces Development Costs: Investing in UX design early in the development process can save time and money by identifying and addressing usability issues before they become costly problems. A user-centered design approach helps in creating more efficient and effective solutions.
- Boosts User Engagement: Products with engaging and intuitive designs encourage users to interact more frequently and deeply. Features that are easy to understand and use keep users coming back, fostering long-term engagement.
- Supports Brand Loyalty and Trust: Consistent and pleasant user experiences build trust and loyalty. Users are more likely to return to and recommend products that they find reliable and enjoyable to use, strengthening the brand’s market position.
- Facilitates Effective Problem Solving: UX design focuses on understanding user needs and pain points, leading to more effective problem-solving. By empathizing with users, designers can create solutions that address real issues, improving overall user satisfaction.
UX Design is User-Centered
- Empathy and Understanding: UX designers conduct extensive research to understand user needs, preferences, and pain points. Methods such as user interviews, surveys, and usability testing help gather insights that inform design decisions.
- Iterative Design Process: UX design follows an iterative process where user feedback is continually integrated into the design. Prototypes are tested with real users, and their feedback is used to refine and improve the product. This ensures that the final product aligns closely with user expectations.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: User-centered design strives to make products accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. By considering diverse user needs, UX designers create inclusive products that everyone can use comfortably.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: Products designed with a user-centered approach tend to be more successful because they meet the actual needs of users. This leads to higher user satisfaction, increased engagement, and greater loyalty.
- Problem Solving: UX design addresses real user problems through thoughtful, research-driven solutions. By focusing on user needs, designers can create products that solve specific issues effectively, improving overall usability and user satisfaction.
UI UX design examples for beginners
Creating Wireframes for a Blog: Beginners can start with designing wireframes for a simple blog layout, focusing on structure, navigation, and content placement, using tools like Figma or Sketch.
Designing a Login Page: Practice by designing a user-friendly login page with clear input fields, accessible buttons, and error messages that guide users through the process.
Building a To-Do List App: Create a basic to-do list application with features like task addition, completion status, and categorization, emphasizing ease of use and intuitive interactions.
Redesigning a Website Homepage: Take an existing website and redesign its homepage to improve layout, readability, and user engagement, ensuring a cleaner and more modern look.
Developing a Mobile App Prototype: Start with a simple mobile app prototype, such as a weather app, incorporating essential design elements like icons, typography, and navigation.
Why is UX design important for product teams?
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: UX design focuses on creating intuitive and enjoyable user experiences, which directly leads to higher user satisfaction and loyalty. When users find a product easy to use and navigate, they are more likely to continue using it and recommend it to others.
- Improved Usability: By incorporating UX principles, product teams can ensure that their products are user-friendly and accessible. This reduces the learning curve for new users and makes it easier for existing users to perform tasks efficiently.
- Reduced Development Costs: Integrating UX design early in the product development process helps identify and resolve usability issues before they become expensive problems, aligning with the budget plan to reduce costly redesigns and fixes later in the development cycle.
- Increased Conversion Rates: Effective UX design can significantly improve conversion rates by streamlining user journeys and minimizing friction points. Clear calls-to-action and a well-thought-out interface guide users toward completing desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service.
- Competitive Advantage: A product with superior UX stands out in the market. Users are more likely to choose and stick with a product that provides a better experience over competitors. This competitive edge can lead to increased market share and brand loyalty.
- Better User Engagement: Products designed with a focus on UX tend to have higher user engagement. Engaging features and an intuitive interface keep users interacting with the product, increasing usage frequency and duration.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: UX design involves gathering user feedback and conducting usability testing. This data-driven approach helps product teams make informed decisions that align with user needs and preferences, ensuring the product evolves in the right direction.
The UX design process in 5 steps
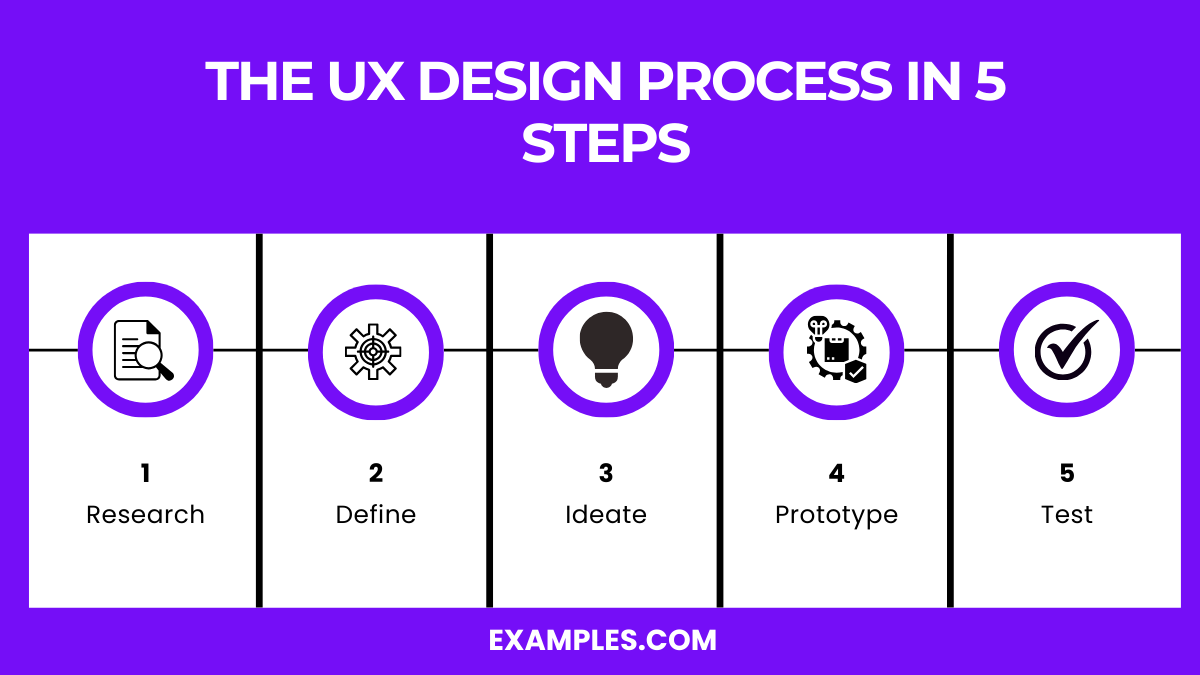
Research: Begin by gathering information about users through various methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing. This step is crucial for understanding user needs, behaviors, and pain points. Analyzing this data helps in creating user personas and identifying key requirements for the design, while also aligning with current marketing trends to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
Define: Synthesize the research data to define the core problems that need to be addressed. Develop clear problem statements and user personas to guide the design process. This step ensures that the design team is aligned on the goals and objectives, setting a solid foundation for ideation.
Ideate: Brainstorm a wide range of ideas and potential solutions to the defined problems. Techniques like sketching, mind mapping, and brainstorming sessions help generate creative solutions. Narrow down the ideas to the most feasible and effective ones, ensuring they align with user needs and business goals.
Prototype: Create low-fidelity prototypes, such as wireframes or mockups, to visualize the design solutions. These prototypes allow for early testing and feedback without significant time or resources investment. Iteratively refine the prototypes based on user feedback and usability testing results, ensuring the payment process is smooth and user-friendly.
Test: Conduct usability testing with real users to evaluate the effectiveness of the prototypes. Gather feedback on how users interact with the design and identify any usability issues. Use this feedback to make necessary adjustments and improvements, ensuring the final product meets user needs and expectations, while collaborating with Human Resources to recruit participants and manage the testing process.
What Skills Are Required for a UX/UI Designer?
- User Research: Conduct interviews, surveys, and usability tests to understand user needs and behaviors accurately.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Create low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes to visualize design concepts and test usability.
- Interaction Design: Develop intuitive interfaces focusing on user interactions, ensuring a seamless and engaging experience.
- Visual Design: Apply principles of color, typography, and layout to create aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.
- Information Architecture: Organize and structure content logically, making it easy for users to find information.
- Usability Testing: Conduct tests to identify usability issues and gather feedback for improving the design.
- Collaboration: Work effectively with cross-functional teams, including developers, product managers, and other designers.
- Communication: Clearly convey design ideas and decisions through sketches, presentations, and documentation.
- Problem-Solving: Address user pain points with innovative solutions, enhancing overall user satisfaction.
- Attention to Detail: Ensure every aspect of the design is polished and meets quality standards.
- Empathy: Understand and prioritize user needs, creating designs that provide meaningful experiences.
- Analytical Thinking: Use data and user feedback to inform design decisions and iterate on solutions.
- Adaptability: Stay updated with industry trends and continuously improve skills to adapt to new challenges.
- Coding Knowledge: Basic understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to communicate effectively with developers.
- Project Management: Manage time and resources efficiently to meet deadlines and deliver high-quality designs.
Key Differences Between UX and UI Design
| Aspect | UX Design (User Experience) | UI Design (User Interface) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Overall experience of the user | Visual elements and interaction touchpoints |
| Objective | Enhance user satisfaction and usability | Create visually appealing and functional interfaces |
| Scope | Entire user journey, including research, prototyping, testing | Specific to the look and feel of the product |
| Tasks | User research, creating personas, wireframing, usability testing | Designing buttons, icons, spacing, typography, color schemes |
| Outcome | Functional and enjoyable user interactions | Aesthetic and interactive interfaces |
| Skills Required | Research, problem-solving, empathy, analytical thinking | Visual design, color theory, typography, branding |
| Deliverables | User personas, user journey maps, wireframes, prototypes | High-fidelity mockups, style guides, UI kits |
| Tools Used | Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD, Balsamiq | Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma, InVision, Illustrator |
| Role in Development | Informing the design process with user needs and feedback | Bringing the visual aspects to life according to UX guidelines |
| User Interaction | How users feel and experience the product | How users interact with the visual elements of the product |
| Design Approach | User-centered, focusing on solving user problems | Aesthetic-centered, focusing on creating a visually pleasing layout |
| Evaluation Criteria | Usability, accessibility, user satisfaction | Visual consistency, clarity, attractiveness |
| Collaboration | Works closely with researchers and product managers | Works closely with graphic designers and developers |
| Example Tasks | Conducting usability studies, creating user flows | Designing the look of buttons, creating icons, setting typographic styles |
| Key Question | Is this product easy and enjoyable to use? | Does this product look good and function visually as intended? |
What does a UX designer do?
A UX designer conducts user research, creates personas, wireframes, and prototypes, and tests designs for usability.
Why is UX design important?
UX design enhances user satisfaction, improves usability, and increases engagement and conversion rates.
What is the difference between UX and UI design?
UX design focuses on the overall user experience, while UI design focuses on the visual and interactive elements.
What are user personas?
User personas are fictional characters created based on user research to represent different user types.
What is a wireframe?
A wireframe is a low-fidelity visual representation of a website or app’s layout and structure.
Why is UX design important?
UX design enhances user satisfaction, improves usability, and increases engagement and conversion rates.
What is usability testing?
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a product to identify any issues and improve the design.
How does user research inform UX design?
User research provides insights into user needs, behaviors, and pain points, guiding the design process.
What is prototyping?
Prototyping is the creation of an interactive model of a design to test and refine its functionality and usability.
What is the goal of UX design?
The goal of UX design is to create products that are easy to use, effective, and enjoyable for users.


