Work Breakdown Structure Examples to Download
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a critical tool in project management that outlines a project’s tasks in a hierarchical format. By breaking down complex projects into manageable sections, the WBS ensures clarity and efficiency. It’s essential for a business project plan as it helps in resource allocation, tracking progress, and identifying potential risks. The WBS promotes better communication among team members and stakeholders, ensuring all aspects of the project are covered and executed effectively.
What is Work Breakdown structure?
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of a project into smaller, manageable tasks. It organizes and defines the total scope of the project, ensuring all deliverables are identified and facilitating better planning, execution, and monitoring of the project.
Work Breakdown Structure Examples
- Construction Project: Breaking down into phases like foundation, framing, plumbing, and electrical work.
- Software Development: Dividing tasks into design, coding, testing, and deployment stages.
- Event Planning: Categorizing into venue booking, catering, invitations, and entertainment.
- Marketing Campaign: Segmenting into research, content creation, distribution, and analysis.
- Product Launch: Splitting into market research, product development, marketing, and sales strategy.
Types of Work Breakdown Structure
- Deliverable-Based WBS: Focuses on project deliverables, breaking them down into smaller components.
- Phase-Based WBS: Organizes tasks according to project phases or stages.
- Function-Based WBS: Divides the project by functional areas, such as design, development, and testing.
- Organizational WBS: Aligns tasks with different departments or teams responsible for the work.
- Geographic WBS: Splits the project based on geographic locations or regions where work will be performed.
Types of WBS Charts
- Tree Structure Chart: Visualizes the hierarchical breakdown of tasks in a tree-like format.
- Tabular View: Lists tasks and their sub-tasks in a table format for easy reference and organization.
- Gantt Chart: Combines the WBS with a timeline, showing task dependencies and durations.
- Mind Map: Uses a central idea with branches for each major task, promoting a visual and flexible breakdown.
- Flowchart: Depicts tasks and their relationships using a flowchart format, ideal for process-oriented projects.
Work Breakdown Structure Elements
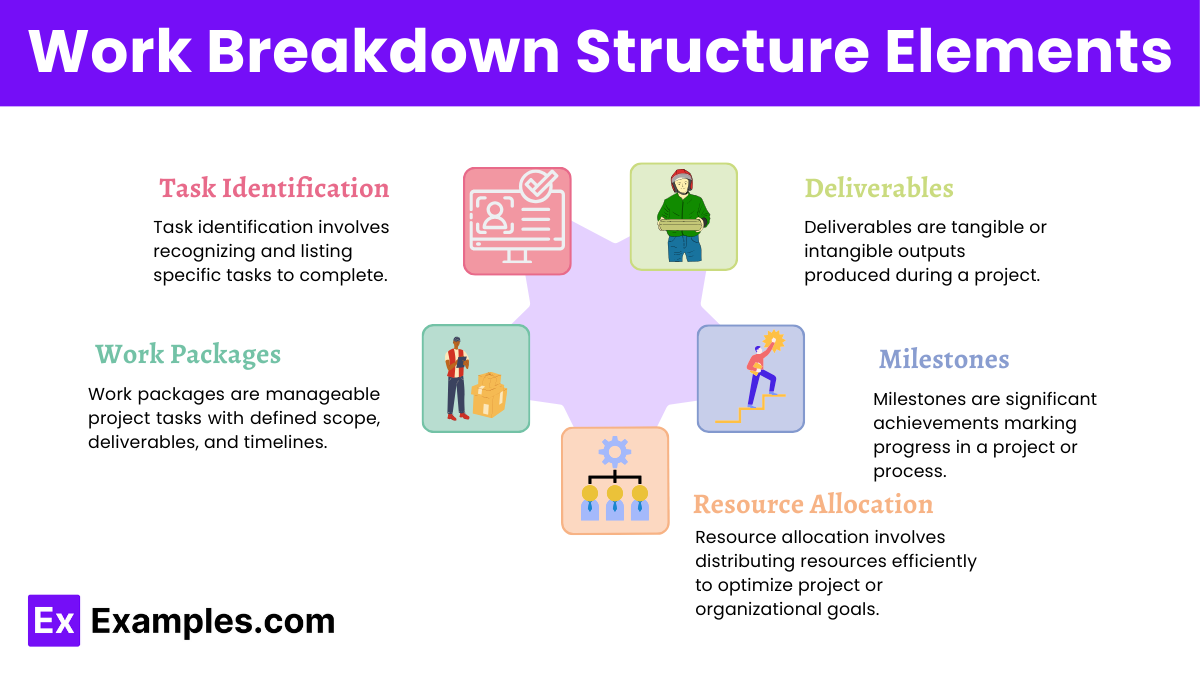
- Task Identification: Define and list all tasks required for the project, including creating a maintenance strategy plan.
- Deliverables: Specify the expected outputs, such as an event quotation for planning purposes.
- Work Packages: Break down tasks into smaller units, like developing a salary schedule for the project team.
- Milestones: Identify key project milestones, ensuring each major phase is completed on time.
- Resource Allocation: Assign resources to tasks, ensuring efficient use of time, money, and personnel.
Key Characteristics and Components of the WBS
- Hierarchical Structure: Breaks down project scope into manageable sections, aiding in qualitative research plan development.
- Deliverable-Oriented: Focuses on outputs rather than activities, essential for defining the scope of work for home projects.
- Levels of Detail: Provides varying levels of task detail, crucial for creating an accurate fee proposal.
- Unique Identifiers: Assigns codes to tasks for easy tracking within the qualitative research plan.
- Work Packages: Smallest units of work in the WBS, facilitating detailed scope of work for home projects.
- Scope Definition: Clearly defines project scope, ensuring comprehensive coverage in the fee proposal.
- Integration with Plans: Aligns with qualitative research plan and fee proposal for seamless project execution.
Why a WBS Is Helpful for Project Management
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is essential for project management as it provides a clear framework for organizing and managing project tasks. It enhances clarity and focus, ensuring every aspect of the project is covered. By breaking down tasks into manageable sections, the WBS helps in resource allocation and progress tracking. For instance, in creating a home-based employee checklist, a WBS would list all necessary steps, from setting up a home office to establishing communication protocols. This systematic approach ensures nothing is overlooked, promoting efficiency and effectiveness in project execution. Additionally, WBS aids in risk identification and management, further ensuring the project’s success.
Why to Use a WBS In Project Management?
Using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in project management is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it supports a detailed scope management plan, helping to define and control the project scope, ensuring all deliverables are identified and managed. Additionally, it provides clarity and focus by breaking down complex projects into manageable tasks, making them easier to understand and execute. The WBS also facilitates efficient resource allocation and management, ensuring all tasks have the necessary support. Moreover, it enables better progress tracking, helping to identify any issues early on, and aids in risk management by identifying potential risks and allowing for proactive mitigation strategies.
Work Breakdown Structure in Project Management
- Task Identification: List all tasks required for the project, including obtaining a project quotation.
- Deliverables: Define the expected outputs to ensure all deliverables are accounted for.
- Work Packages: Break down tasks into smaller, manageable units for easier execution.
- Milestones: Identify key project milestones to track progress effectively.
- Resource Allocation: Assign resources to tasks to ensure efficient use of time and personnel.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and plan mitigation strategies to avoid project delays.
- Scope Management: Ensure a clear and controlled scope management plan to prevent scope creep.
Work Breakdown Structure in Software Project Management
- Requirements Gathering: Identify and document all software requirements, including user stories and system specifications.
- System Design: Develop the overall architecture and design, detailing the software components and their interactions.
- Development: Break down the coding tasks into modules, features, and functions to be developed by the team.
- Testing: Plan and execute unit tests, integration tests, and system tests to ensure software quality and functionality.
- Deployment: Prepare for software deployment, including setting up the environment and performing final checks.
- Maintenance: Develop a maintenance strategy plan for post-deployment support and updates.
- Documentation: Create comprehensive documentation, including user manuals, technical guides, and a project quotation for clients.
- Training: Provide training sessions for end-users and support staff to ensure smooth software adoption and usage.
Work Breakdown Structure Benefits
- Improved Clarity: A WBS provides a clear and detailed breakdown of all project tasks, making it easier for team members to understand their responsibilities.
- Better Planning: It enhances project planning by outlining all necessary tasks and deliverables, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently assigns resources, ensuring each task has the necessary personnel, budget, and materials.
- Progress Tracking: Facilitates monitoring project progress, making it easier to identify and address any issues promptly.
- Enhanced Communication: Improves communication among team members and stakeholders by providing a common understanding of the project’s scope and tasks.
- Risk Management: Aids in identifying potential risks early, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies.
- Scope Management: Helps in creating a comprehensive scope management plan, preventing scope creep and ensuring the project stays on track.
- Cost Control: By detailing tasks and resources, it helps in accurately estimating and controlling project costs, including obtaining accurate project quotations.
Why is a WBS important?
A WBS ensures clarity, better planning, and efficient resource allocation.
How does a WBS improve project management?
It organizes tasks, tracks progress, and identifies potential risks.
What are the main elements of a WBS?
Task identification, deliverables, work packages, milestones, resource allocation, risk management, and scope management.
Can a WBS be used in any project?
Yes, a WBS is versatile and can be applied to any project, regardless of size or industry.
How does a WBS help in resource allocation?
It assigns resources efficiently to ensure each task has the necessary support.
What is the difference between a WBS and a project plan?
A WBS breaks down tasks, while a project plan outlines how the project will be executed.
How does a WBS aid in risk management?
It helps identify potential risks early, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies.
What is a deliverable-based WBS?
It focuses on project deliverables, breaking them down into smaller components.
What is a phase-based WBS?
It organizes tasks according to the project’s phases or stages.
How does a WBS facilitate progress tracking?
It provides a clear framework for monitoring and tracking project progress.