Preparing for the CFA Exam requires a comprehensive understanding of “Economics of Regulations,” a crucial aspect of economic policy analysis. Mastery of how regulations influence market dynamics, corporate behavior, and economic efficiency is essential. This knowledge provides insights into policy impacts, compliance, and the regulatory environment, critical for achieving a high CFA score.
Learning Objective
In studying “Economics of Regulations” for the CFA Exam, you should learn to understand the principles behind regulatory frameworks and their influence on market behavior and economic outcomes. Analyze the role of government regulations in promoting market stability, protecting consumers, and mitigating systemic risks. Evaluate the impacts of various types of regulations, such as financial, environmental, and antitrust regulations, on corporate strategies and economic efficiency. Additionally, explore how regulations affect economic growth, innovation, and competition, while considering the balance between regulatory benefits and compliance costs. Apply this knowledge to assess policy changes and regulatory risk in investment analysis and decision-making.
Introduction of Regulations and Their Purpose

Regulations are rules or directives established by authorities, such as governments or regulatory bodies, to oversee the operations of industries, protect consumers, maintain fair markets, and ensure public welfare. These regulations can apply to various sectors, including finance, healthcare, environment, and business, and they serve several key purposes. Here’s an overview of the role of regulations and their primary objectives:
Purpose of Regulations
- Consumer Protection
- Safeguards consumers from unsafe products, unfair practices, and fraud. Ensures that products and services meet safety standards and provide transparent information to consumers.
- Market Stability and Fairness
- Creates a level playing field for businesses and prevents monopolistic practices. Includes antitrust laws that promote competition and prevent price-fixing.
- Environmental Protection
- Mitigates the negative impact of industrial and commercial activities on the environment. Sets standards for emissions, waste management, and sustainable use of resources.
- Financial Security and Economic Stability
- Ensures the soundness of financial institutions and protects the economy from systemic risks. Requires financial transparency and ethical practices within banking and investment sectors.
- Public Health and Safety
- Protects the health and safety of the public by regulating industries such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food production.
- Workplace Standards
- Ensures fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and equitable treatment of employees. Governs wages, working hours, and occupational safety.
Types of Regulations
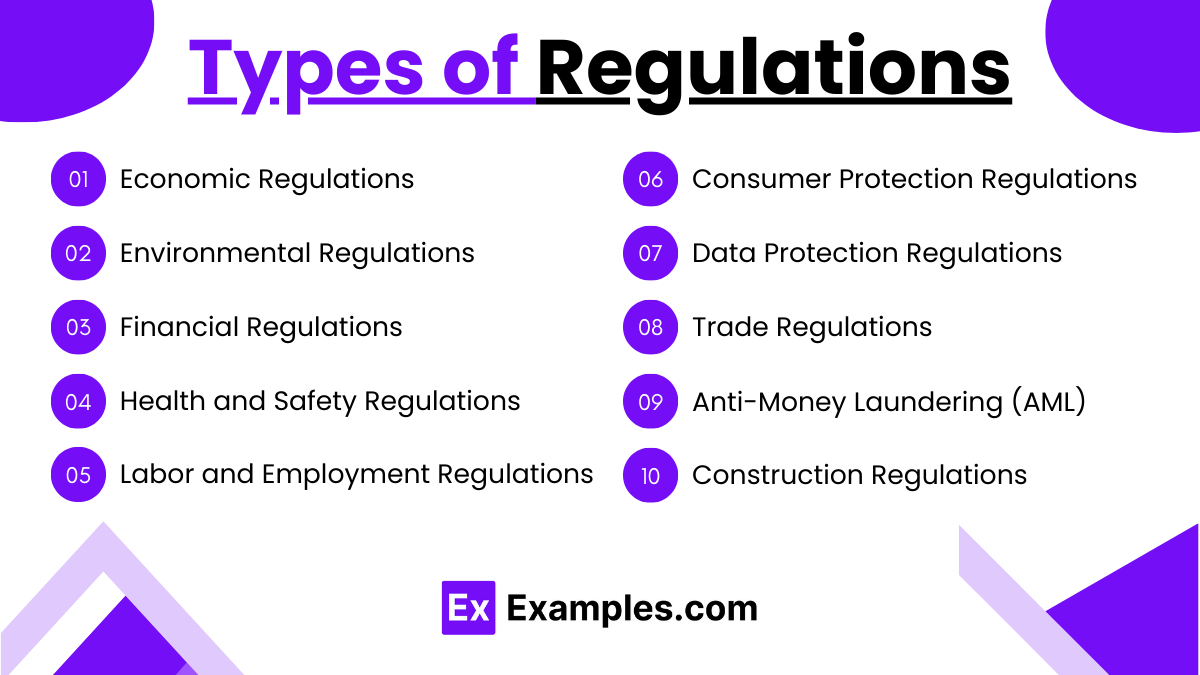
Regulations can be broadly categorized based on the areas they govern and the objectives they aim to achieve. Here’s an overview of the main types of regulations:
1. Economic Regulations
- Govern economic activities by controlling prices, wages, competition, and market entry to promote fairness and efficiency.
- Often involve antitrust laws to prevent monopolies and practices that restrict free trade and competition.
2. Environmental Regulations
- Aim to protect the environment by managing pollution levels, waste disposal, resource conservation, and the impact of industrial activities.
- Include rules on emissions, energy efficiency, and environmental impact assessments.
3. Financial Regulations
- Ensure the integrity, stability, and transparency of financial markets and institutions.
- Include laws that oversee banking practices, capital markets, and the conduct of financial service providers.
4. Health and Safety Regulations
- Focus on protecting public health and ensuring the safety of products, services, and workplaces.
- Cover industries like healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food production, setting standards for safety protocols and product approvals.
5. Labor and Employment Regulations
- Govern working conditions, labor rights, and employer-employee relationships.
- Include minimum wage laws, working hours, anti-discrimination measures, and occupational safety standards.
6. Consumer Protection Regulations
- Protect consumers from fraudulent, misleading, and harmful business practices.
- Require businesses to provide clear, accurate information about products and services, ensuring consumer rights are upheld.
7. Data Protection and Privacy Regulations
- Safeguard personal data and privacy in the digital age.
- Include laws that require organizations to collect, use, and store data responsibly, such as data breach notifications and consent protocols.
8. Trade Regulations
- Govern international and domestic trade practices to ensure fair competition and protect local industries.
- Include tariffs, trade agreements, and import/export restrictions.
9. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Financial Crime Regulations
- Combat financial crimes by preventing practices like money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing.
- Require financial institutions to implement checks such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and monitor suspicious activities.
10. Building and Construction Regulations
- Ensure the safety, stability, and sustainability of buildings and infrastructure.
- Cover zoning laws, building codes, and safety requirements for construction projects.
Impacts of Regulations on Market Behavior
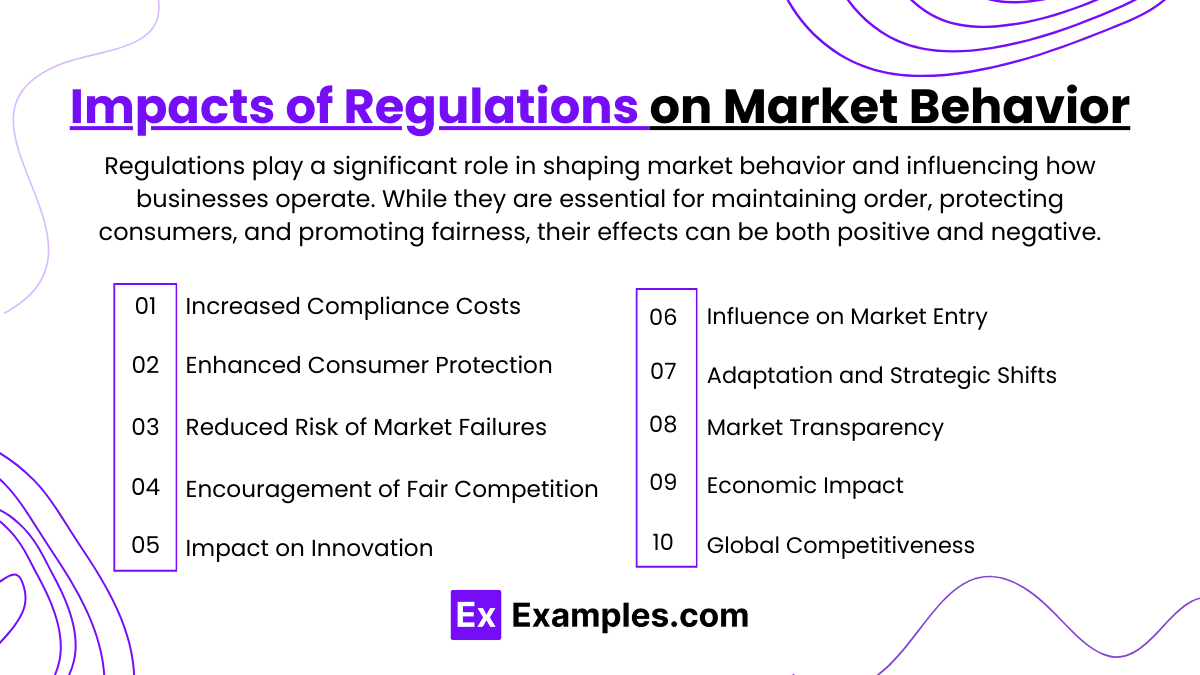
Regulations play a significant role in shaping market behavior and influencing how businesses operate. While they are essential for maintaining order, protecting consumers, and promoting fairness, their effects can be both positive and negative. Here’s an overview of the impacts of regulations on market behavior:
1. Increased Compliance Costs
- Regulations often require businesses to implement changes, maintain certain standards, or report specific data, leading to increased operational and administrative expenses. Small businesses, in particular, may face challenges due to the costs of meeting regulatory requirements.
2. Enhanced Consumer Protection
- Regulations ensure that consumers have access to safe products and truthful information. This leads to increased consumer confidence and trust in the market, which can boost sales and support long-term economic growth.
3. Reduced Risk of Market Failures
- By setting rules that prevent monopolistic practices, protect against fraud, and promote competition, regulations can reduce the risk of market failures. This helps maintain market efficiency and stability.
4. Encouragement of Fair Competition
- Anti-trust laws and competition regulations prevent dominant firms from engaging in anti-competitive practices like price-fixing or market monopolization. This promotes a level playing field where smaller and new entrants have the opportunity to compete.
5. Impact on Innovation
- Regulations can have mixed effects on innovation. While stringent regulations can stifle innovation by creating high compliance barriers, well-designed regulations can encourage innovation, particularly in areas like renewable energy, health, and safety technologies.
6. Influence on Market Entry
- Regulations can act as barriers to entry for new businesses due to the high costs of compliance and complexity. However, they can also ensure that only serious and capable entities enter the market, maintaining quality and safety standards.
7. Adaptation and Strategic Shifts
- Companies often adapt their strategies to align with regulations. For example, businesses may focus on developing more sustainable practices or integrating data privacy measures to comply with environmental or digital regulations.
8. Market Transparency
- Financial and consumer protection regulations often require greater transparency from companies, leading to a more informed and confident market. This can attract more investors and enhance economic stability.
9. Economic Impact and Growth Constraints
- Overly stringent or poorly designed regulations can constrain economic growth by placing excessive burdens on businesses, slowing down operations, or discouraging investment. On the other hand, balanced regulations can promote sustainable growth and prevent economic crises.
10. Global Competitiveness
- Regulatory environments can affect a country’s global competitiveness. Countries with efficient, clear, and supportive regulations may attract more foreign investments. However, excessively strict regulations can deter companies from operating within those markets.
Balancing Regulation Benefits and Compliance Costs
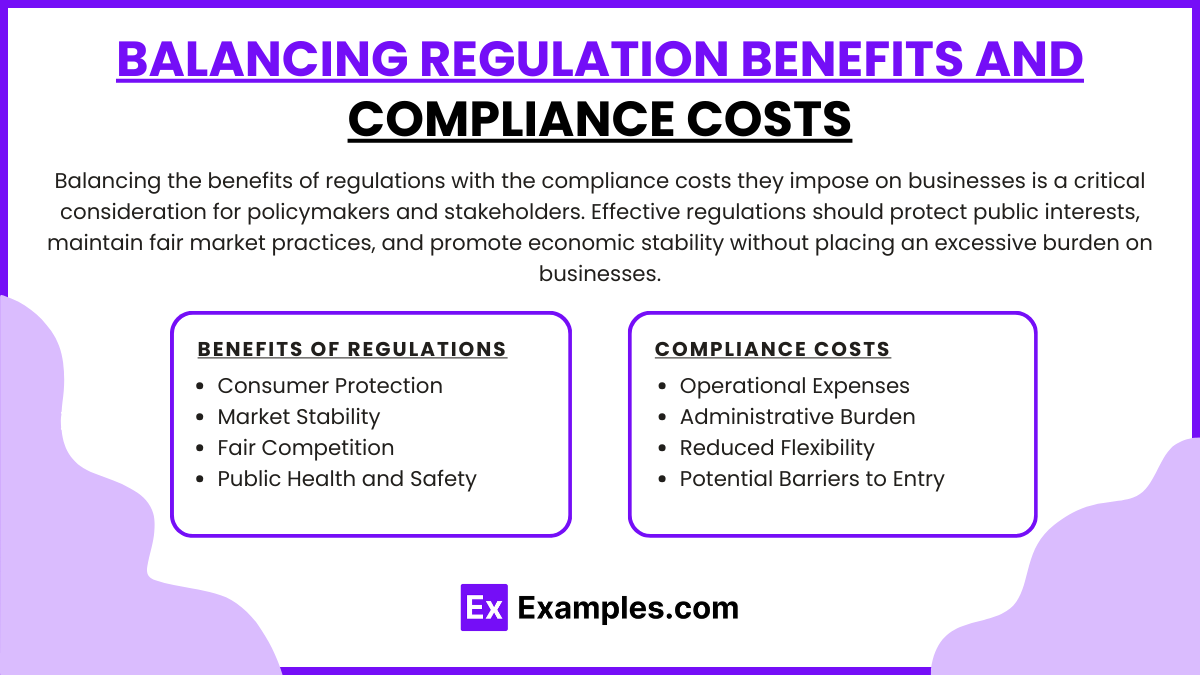
Balancing the benefits of regulations with the compliance costs they impose on businesses is a critical consideration for policymakers and stakeholders. Effective regulations should protect public interests, maintain fair market practices, and promote economic stability without placing an excessive burden on businesses. Here’s a look at how to achieve this balance:
Benefits of Regulations
- Consumer Protection: Regulations ensure products and services meet safety and quality standards, fostering consumer trust and confidence.
- Market Stability: They reduce the risk of financial crises by enforcing standards that promote transparency, ethical practices, and responsible behavior in financial markets.
- Fair Competition: Regulations prevent monopolistic behavior and promote a level playing field, encouraging healthy competition and innovation.
- Public Health and Safety: Health, safety, and environmental regulations protect communities and ensure long-term societal welfare.
Compliance Costs
- Operational Expenses: Meeting regulatory requirements often involves significant financial investment in infrastructure, technology, and training.
- Administrative Burden: Businesses must allocate resources to manage and document compliance efforts, which can be particularly taxing for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Reduced Flexibility: Strict regulations may limit a company’s ability to innovate or pivot quickly in response to market changes.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: High compliance costs can discourage new businesses from entering the market, reducing competition and innovation.
Examples
Example 1: Impact of Dodd-Frank Act on Financial Institutions
Analyze how the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, implemented after the 2008 financial crisis, affected the banking industry. Discuss how stricter capital requirements and enhanced oversight influenced risk management, lending practices, and financial stability in the U.S.
Example 2: European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS)
Study the EU ETS as an example of environmental regulation that incentivizes companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Explore how the cap-and-trade system impacts businesses, investment in clean technology, and the cost of compliance for companies operating in the European Union.
Example 3: Antitrust Case Study: U.S. vs. Microsoft
Review the landmark antitrust case where the U.S. government sued Microsoft for monopolistic practices. Examine how regulatory actions influenced competition within the software industry and set precedents for future technology sector regulations.
Example 4: Financial Reporting and Transparency Under Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
Explore the effects of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act on corporate governance and financial reporting. Discuss how SOX improved transparency and investor confidence but also increased compliance costs for publicly traded companies.
Example 5: Healthcare Regulations and Investment Opportunities
Analyze the impact of healthcare regulations, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), on the healthcare industry. Evaluate how regulations affected healthcare providers, insurers, and pharmaceutical companies, as well as investment opportunities and challenges arising from changes in policy.
Practice Questions
Question 1
What is the primary objective of antitrust regulations?
A. To increase tax revenues for the government
B. To ensure fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices
C. To support mergers and acquisitions for economic growth
D. To regulate currency exchange rates
Answer:
B. To ensure fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices
Explanation:
Antitrust regulations aim to prevent monopolies and anti-competitive practices to ensure that markets remain competitive and consumer interests are protected. This fosters innovation, ensures fair pricing, and encourages better quality of products and services.
Question 2
How do environmental regulations, such as emissions trading systems, primarily influence businesses?
A. By allowing companies to avoid compliance costs entirely
B. By incentivizing companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
C. By increasing the number of firms in the industry
D. By reducing operational transparency requirements
Answer:
B. By incentivizing companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Explanation:
Environmental regulations, such as emissions trading systems (e.g., cap-and-trade programs), encourage companies to lower their greenhouse gas emissions by placing a limit on total emissions and allowing firms to buy or sell emission permits. This incentivizes companies to adopt cleaner technologies to stay within limits or profit from selling excess allowances.
Question 3
What is one potential negative consequence of overly stringent regulations on industries?
A. Increased innovation due to higher compliance
B. Improved consumer trust and market transparency
C. Reduced economic growth and stifled business expansion
D. Enhanced ability for businesses to attract foreign investment
Answer:
C. Reduced economic growth and stifled business expansion
Explanation:
Overly stringent regulations can lead to higher compliance costs and operational constraints, which can limit a company’s ability to expand and innovate. While regulations are designed to protect stakeholders and ensure market fairness, excessive regulatory burdens can hinder economic growth and reduce competitive advantage.


