Preparing for the CFA Exam requires a comprehensive understanding of “Investment Manager Selection,” a crucial component of portfolio management. Mastery of evaluating managers based on performance, investment process, and risk management strategies is essential. This knowledge provides insights into optimal manager selection, aligning with client objectives and enhancing portfolio performance, critical for achieving a high CFA score.
Learning Objective
In studying “Investment Manager Selection” for the CFA Exam, you should learn to understand the criteria and processes involved in evaluating and selecting investment managers. Analyze how quantitative performance measures, investment styles, and risk management strategies influence the selection process. Evaluate the principles behind due diligence, including assessments of organizational structure, track record, and investment philosophy. Additionally, explore how client-specific needs, such as investment objectives and risk tolerance, align with manager capabilities. Apply this knowledge to case studies and real-world scenarios, enhancing your ability to choose managers who can effectively contribute to the achievement of strategic investment goals.
Introduction to Investment Manager Selection

Investment manager selection involves choosing a professional or firm to oversee and manage an investment portfolio. The goal is to select a manager who aligns with the investor’s financial goals, risk tolerance, investment strategy, and expectations. This process is critical because the chosen investment manager will have a significant impact on the performance of the investment portfolio.
Key Factors in Choosing an Investment Manager
- Experience and Track Record:
- Look for managers with a proven track record of managing investments similar to your needs.
- Analyze past performance, but consider it in light of market conditions during those periods.
- Investment Philosophy and Strategy:
- Ensure the manager’s investment philosophy aligns with your objectives and risk tolerance.
- Evaluate how they plan to achieve returns and manage risks.
- Fees and Compensation:
- Understand all fees involved, including management fees, performance fees, and other charges.
- Consider how the fee structure affects your potential net return.
- Client Servicing and Communication:
- Assess the manager’s approach to client service and the frequency and quality of communications.
- Ensure there is a strong alignment in service expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance and Reputation:
- Check the manager’s regulatory compliance and any past violations or issues.
- Consider the firm’s reputation in the industry as part of your decision-making process.
Evaluation Criteria for Investment Managers

Evaluating investment managers involves analyzing various qualitative and quantitative factors to ensure they align with your financial goals and investment strategy. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the essential criteria you should consider when assessing investment managers:
1. Performance Metrics
- Assess historical returns against benchmarks and peers.
- Evaluate risk-adjusted returns and consistency across different market conditions.
2. Investment Philosophy and Strategy
- Ensure the manager’s investment approach (active or passive) matches your risk tolerance.
- Analyze their asset allocation strategies and research capabilities.
3. Manager Experience and Expertise
- Consider the qualifications and track record of the manager and their team.
- Check for specialization relevant to your needs and team stability.
4. Operational Efficiency and Infrastructure
- Examine the use of technology, operational structure, and client servicing capabilities.
5. Fees and Expenses
- Analyze the fee structure for transparency and alignment with industry standards.
- Consider cost efficiency and how fees impact net returns.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Reputation
- Investigate the manager’s compliance record and overall reputation in the market.
- Ensure they uphold high ethical standards and prioritize client interests.
7. Client Compatibility and Flexibility
- Confirm alignment with your investment goals and the ability for customization.
- Evaluate the manager’s adaptability to changes in market conditions or your investment objectives.
Manager Selection Process
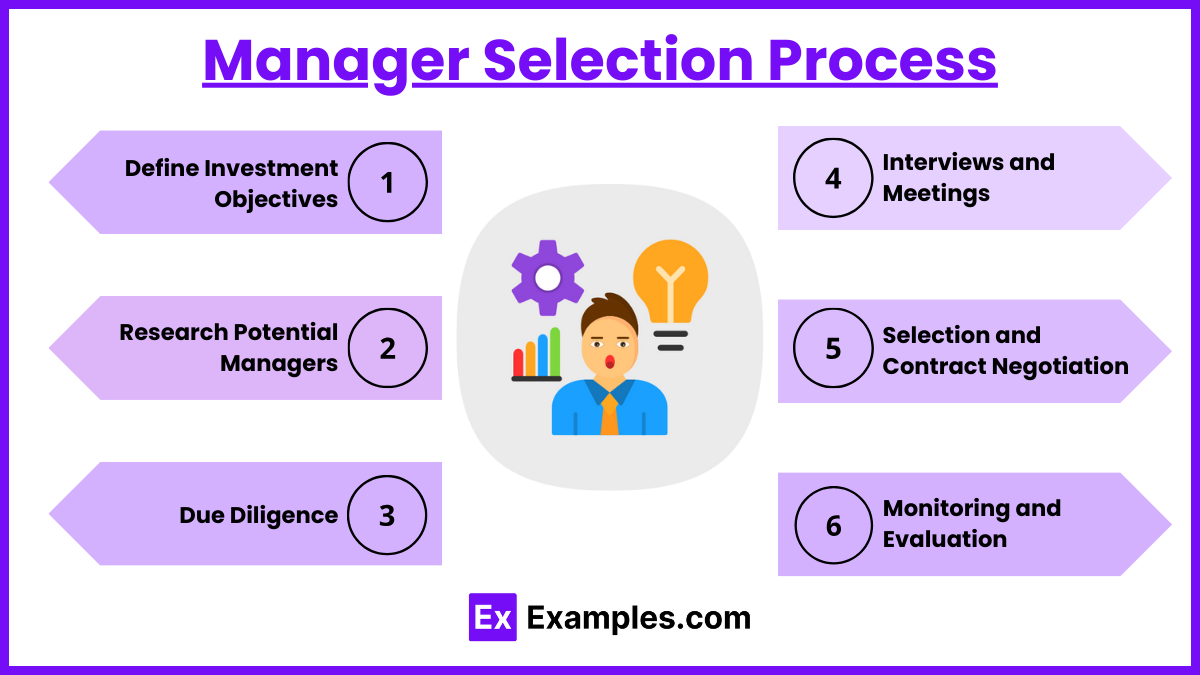
Selecting the right investment manager is a critical process that involves careful consideration and evaluation to ensure alignment with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Here’s a detailed overview of the steps involved in the manager selection process:
Step 1: Define Investment Objectives
- Identify Goals: Clearly define your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
- Establish Criteria: Determine the necessary qualifications and expertise for potential managers.
Step 2: Research Potential Managers
- Source Candidates: Compile a list of potential managers from referrals, industry publications, and databases.
- Initial Screening: Filter candidates based on their experience, performance records, and specialization.
Step 3: Due Diligence
- Qualitative Analysis: Evaluate investment philosophy, team stability, and compliance with ethical and regulatory standards.
- Quantitative Analysis: Analyze historical performance, consistency, and risk-adjusted returns.
Step 4: Interviews and Meetings
- Personal Interaction: Meet with top candidates to discuss strategies and assess communication skills.
- Reference Checks: Contact current and former clients to verify satisfaction levels and experiences.
Step 5: Selection and Contract Negotiation
- Choose the Manager: Select the best-fit manager based on alignment with your investment goals.
- Negotiate Terms: Finalize terms regarding fees, services, and performance expectations.
Step 6: Monitoring and Evaluation
- Performance Review: Regularly assess the manager’s performance against benchmarks.
- Reevaluation: Periodically reassess the manager’s suitability based on performance and any changes in your goals or the market.
Client-Specific Considerations
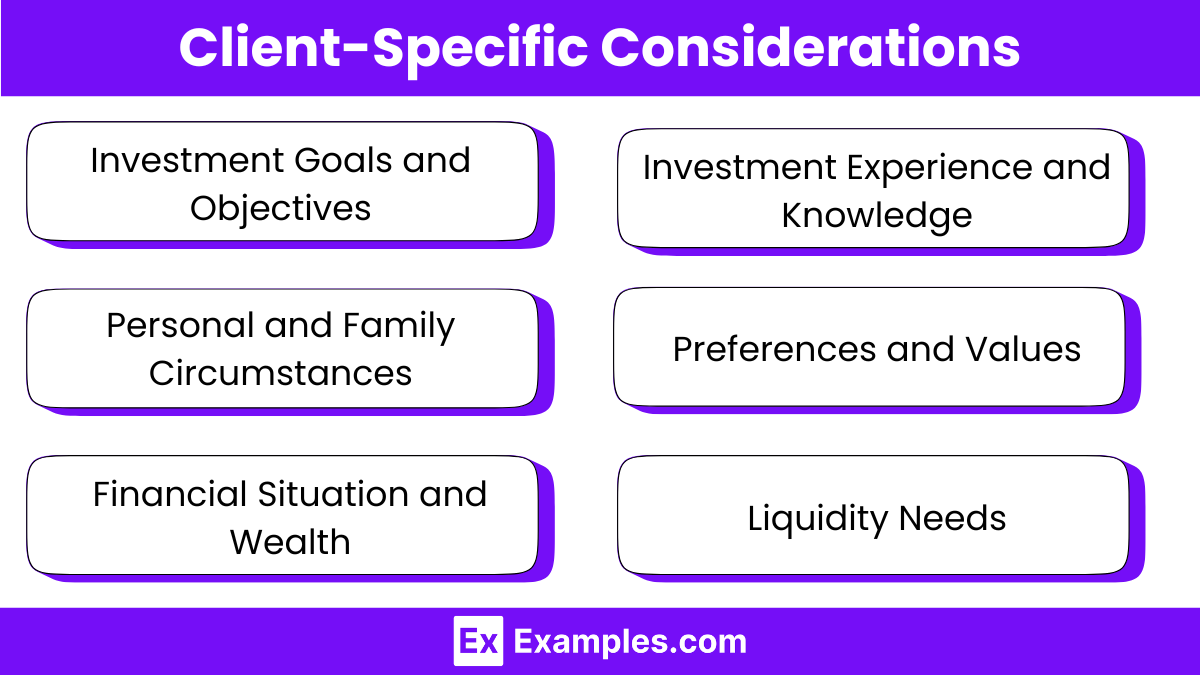
When selecting an investment manager, considering client-specific factors is crucial to ensure that the manager’s approach and services align with the individual needs and expectations of the client. Here’s a breakdown of key client-specific considerations:
1. Investment Goals and Objectives
- Understand the client’s specific financial targets, risk tolerance, and investment time horizon.
2. Personal and Family Circumstances
- Assess the client’s age, life stage, family structure, and any health considerations that may impact investment choices.
3. Financial Situation and Wealth
- Review the client’s current financial status, including assets, liabilities, and tax considerations.
- Differentiate between wealth preservation and growth priorities.
4. Investment Experience and Knowledge
- Gauge the client’s understanding of and experience with financial markets to tailor the complexity of the proposed strategies.
5. Preferences and Values
- Consider the client’s ethical values, such as ESG preferences, and their expectations for communication and service levels.
6. Liquidity Needs
- Evaluate the client’s need for liquidity and regular income to meet immediate and ongoing expenses.
Examples
Example 1: Retirement Planning
- Client Profile: A couple in their early 50s aiming to retire in 15 years.
- Considerations: Adjust investment strategy to gradually reduce exposure to high-risk assets, increase allocation to bonds and stable income sources, and plan for possible health-related expenses.
Example 2: College Fund
- Client Profile: Young family with newborn children planning for future educational expenses.
- Considerations: Invest in a mix of stocks and bonds through a 529 college savings plan to optimize growth with a decreasing risk approach as college nears.
Example 3: High Net Worth Individual
- Client Profile: Wealthy individual interested in wealth preservation and estate planning.
- Considerations: Diversify investments across various asset classes, including real estate and international markets, focus on tax-efficient strategies, and utilize trusts and other estate tools.
Example 4: Socially Responsible Investor
- Client Profile: An environmentally conscious investor looking to impact social and environmental change.
- Considerations: Prioritize ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) compliant investments, screen out sectors that conflict with personal values (like fossil fuels), and engage in shareholder advocacy.
Example 5: Entrepreneur with Irregular Cash Flow
- Client Profile: A startup owner with fluctuating income and significant capital needs for business expansion.
- Considerations: Create a liquidity buffer with easily accessible cash reserves, invest in low-volatility stocks and bonds for stability, and plan for strategic withdrawals without significant penalties.
Practice Questions
When selecting an investment manager, what is the most important factor to consider to ensure alignment with ethical standards?
A. The manager’s historical financial performance
B. The manager’s adherence to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct
C. The cost of the investment management services
D. The manager’s brand reputation in the market
Answer:
B. The manager’s adherence to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct
Explanation:
While all the factors listed are important in the selection of an investment manager, adherence to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct is crucial for ensuring that the manager’s practices align with ethical guidelines and professional standards. This adherence helps ensure that the manager operates with integrity, transparency, and in the best interest of clients, which is foundational to ethical investment practices.
Question 2
Which action by an asset manager would most likely raise ethical concerns during the selection process?
A. Reporting performance that closely tracks the benchmark
B. Utilizing advanced algorithms to optimize trade execution
C. Charging a performance fee on top of a management fee
D. Failing to disclose a conflict of interest related to investment allocations
Answer:
D. Failing to disclose a conflict of interest related to investment allocations
Explanation:
Failing to disclose a conflict of interest, especially one that could affect investment allocations, is a significant ethical violation. It compromises the manager’s duty to act fairly and in the best interests of all clients. This lack of transparency and potential breach of trust is a critical red flag during the manager selection process.
Question 3
What must be evaluated during the due diligence process of an investment manager to ensure ethical compliance?
A. The geographical location of the manager’s operations
B. The size of the manager’s investment team
C. The manager’s policies and procedures for handling insider information
D. The types of clients the manager typically services
Answer:
C. The manager’s policies and procedures for handling insider information
Explanation:
During the due diligence process, it is essential to evaluate the manager’s policies and procedures for handling insider information to ensure they comply with ethical standards and regulatory requirements. This evaluation helps ascertain the manager’s commitment to maintaining market integrity and protecting client interests against unethical practices like insider trading.


