Dive into the fascinating world of chemistry with Examples.com comprehensive resources. Designed for both educators and students, our platform offers interactive guides, detailed concept explanations, practical examples, and essential equations, all powered by AI and created by chemistry experts. These resources are easily editable and printable, making chemistry more accessible and engaging. From basic principles to complex chemical reactions, our free materials are an excellent tool for learning and teaching chemistry effectively.
Chemistry is the branch of science that studies the composition, structure, properties, and changes of matter. It explores how substances interact, combine, and transform through chemical reactions, forming the foundation of everything in the universe, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. With applications in medicine, engineering, environmental science, and technology, chemistry plays a crucial role in advancing human life. From understanding atoms and molecules to developing life-saving drugs and sustainable materials, chemistry helps us innovate and solve real-world problems, making it one of the most essential sciences in our daily lives.
What is Chemistry?
Chemistry is the scientific study of matter, its composition, properties, and the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. It explains how atoms and molecules interact to form different substances, influencing everything from the food we eat to the medicines we use. As a central science, chemistry connects physics, biology, and environmental science, playing a vital role in industries like healthcare, energy, and manufacturing. Whether developing new materials, improving agriculture, or creating sustainable solutions, chemistry is essential to understanding and transforming the world around us.
Chemistry Examples in Real Life
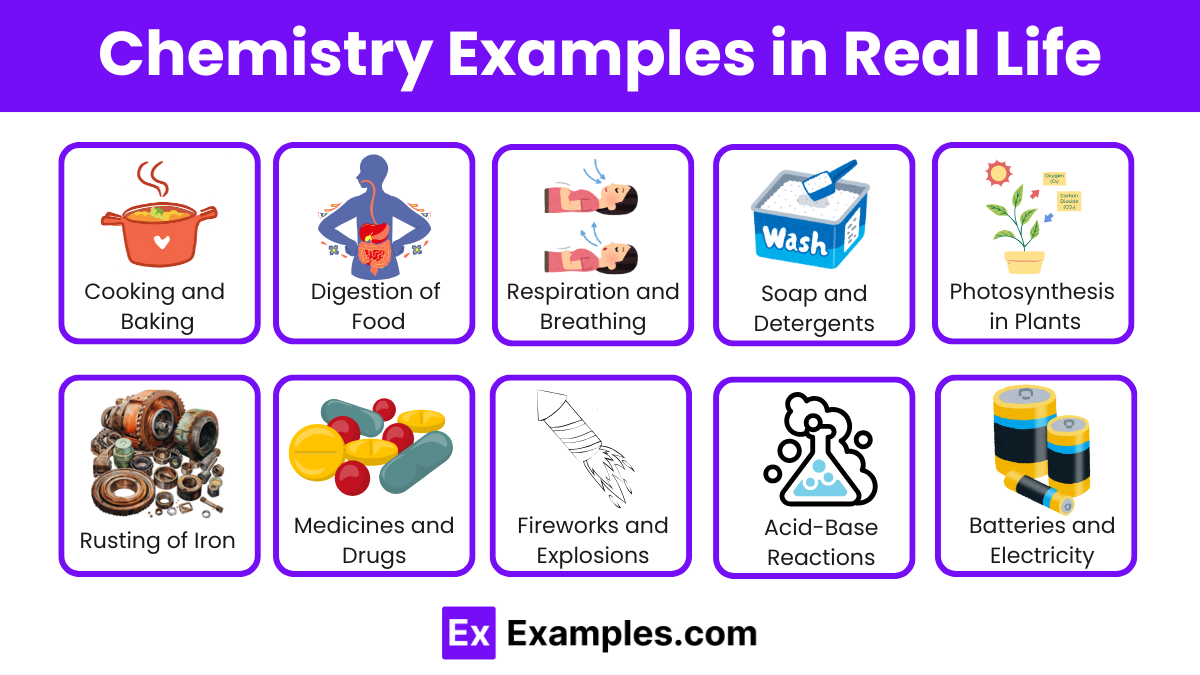
1. Cooking and Baking
- Chemical reactions like caramelization, fermentation, and Maillard reaction occur while cooking food.
- Baking soda reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide, making cakes and bread rise.
2. Digestion of Food
- Enzymes and stomach acid break down food into nutrients through chemical reactions.
- Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats undergo hydrolysis to provide energy.
3. Respiration and Breathing
- Oxygen reacts with glucose in cells to produce energy through cellular respiration.
- Hemoglobin in blood binds with oxygen and carries it throughout the body.
4. Soap and Detergents
- Soap molecules break down grease and dirt through emulsification.
- Saponification is the chemical process used to make soap from fats and alkali.
5. Photosynthesis in Plants
- Plants convert sunlight into energy by turning carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll absorbs light to drive the chemical reaction.
6. Rusting of Iron
- Iron reacts with oxygen and moisture in the air to form iron oxide (rust).
- This is an example of an oxidation reaction.
7. Medicines and Drugs
- Painkillers, antibiotics, and vaccines are created using chemical compounds.
- Chemical reactions in the body allow medicines to work effectively.
8. Fireworks and Explosions
- Fireworks display bright colors due to the burning of different metal salts.
- Combustion reactions release heat, light, and sound.
9. Acid-Base Reactions
- Mixing vinegar (acid) with baking soda (base) creates carbon dioxide bubbles.
- Antacids neutralize stomach acid through acid-base reactions.
10. Fermentation in Alcohol and Dairy
- Yeast converts sugar into alcohol through fermentation in brewing.
- Bacteria help produce yogurt and cheese by fermenting milk.
11. Cleaning with Vinegar and Baking Soda
- Vinegar (acetic acid) reacts with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) to form carbon dioxide and water, useful for cleaning.
- Chemical reactions help remove stains and odors.
12. Fuel Combustion in Vehicles
- Gasoline burns in an engine through a combustion reaction, releasing energy.
- Carbon dioxide and water are byproducts of fuel combustion.
13. Bleaching Clothes
- Bleach breaks down stains through oxidation reactions.
- Hydrogen peroxide and chlorine-based bleaches are commonly used.
14. Water Purification
- Chlorination kills bacteria and viruses in drinking water.
- Chemical processes like filtration and ion exchange remove impurities.
15. Batteries and Electricity
- Chemical reactions in batteries produce electrical energy.
- Rechargeable batteries undergo reversible chemical reactions.
Chemistry Examples at Home
1. Cooking and Boiling Water
- When water is heated, it undergoes a physical change from liquid to gas (steam).
- The boiling point varies with atmospheric pressure.
2. Refrigeration and Food Preservation
- Cooling slows down bacterial growth and chemical reactions, keeping food fresh.
- Freezing changes the physical state of food without altering its composition.
3. Non-Stick Cookware (Teflon Coating)
- Non-stick pans use a polymer called polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to prevent food from sticking.
- This material is resistant to heat and chemical reactions.
4. Cutting Onions and Tears
- Cutting onions releases sulfur compounds that react with the eyes to form sulfuric acid, causing tears.
- This is a chemical reaction between enzymes and amino acids.
5. Making Coffee or Tea
- Hot water extracts caffeine, tannins, and flavors from tea leaves or coffee grounds.
- Brewing involves solubility and diffusion processes.
6. Dishwashing and Grease Removal
- Detergents break down oils and grease using surfactants.
- Hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts of soap molecules help in cleaning.
7. Air Fresheners and Diffusers
- Air fresheners release volatile compounds that react with odor molecules.
- Essential oils in diffusers evaporate due to chemical properties.
8. Baking Potatoes or Vegetables
- Starch in potatoes undergoes gelatinization, making them soft.
- Heat-induced Maillard reaction enhances flavor and color.
9. Cooking with Pressure Cookers
- High pressure raises the boiling point of water, cooking food faster.
- Steam builds up inside, leading to a chemical and physical change in food.
10. Plastic Containers and Microwave Reactions
- Some plastics release chemicals when heated, affecting food safety.
- Microwaves heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate.
11. Formation of Ice Cubes
- Water molecules slow down and arrange in a solid structure when frozen.
- The freezing point can be altered by adding salt or sugar.
12. Toothpaste and Oral Care
- Fluoride in toothpaste strengthens enamel through remineralization.
- Abrasive compounds help remove plaque and stains.
13. Shampoo and Hair Washing
- Surfactants in shampoo trap oil and dirt, allowing them to be rinsed away.
- Conditioners contain silicones that coat and smooth hair strands.
14. Dyeing Clothes
- Fabric dyes chemically bond with textile fibers to produce permanent colors.
- Some dyes react with fabric under heat for better absorption.
15. Cooking Rice or Pasta
- Starches absorb water and swell, undergoing a physical and chemical change.
- The heat breaks down complex carbohydrates for easier digestion.
Chemistry Examples of Mixtures
A mixture in chemistry is a physical combination of two or more substances where each retains its properties. Mixtures can be classified into homogeneous mixtures (uniform composition) and heterogeneous mixtures (non-uniform composition). Here are some examples of mixtures categorized based on their type:
Homogeneous Mixtures (Solutions)
These mixtures have a uniform composition throughout and appear as a single phase.
- Saltwater – A solution of salt (sodium chloride) dissolved in water.
- Air – A mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and argon.
- Vinegar – A solution of acetic acid in water.
- Brass – An alloy of copper and zinc.
- Steel – An alloy of iron and carbon with small amounts of other elements.
- Rubbing Alcohol – A solution of isopropyl alcohol and water.
- Lemonade – A mixture of lemon juice, sugar, and water.
- Coffee – A solution of coffee powder, water, and sometimes milk.
- Tea – A mixture of tea leaves extract and water.
- Soft Drinks (Soda) – A carbonated solution of water, sugar, and flavoring agents.
Heterogeneous Mixtures
These mixtures have a non-uniform composition and can have distinguishable components.
- Sand and Water – Sand particles do not dissolve in water, forming a suspension.
- Oil and Water – Two immiscible liquids that form distinct layers.
- Salad – A mixture of vegetables, dressing, and toppings where each ingredient is visible.
- Mud – A mixture of soil and water, forming a suspension.
- Smoke – A mixture of solid particles and gases in the air.
- Milk – A colloidal mixture of fat droplets dispersed in water.
- Concrete – A mixture of cement, sand, gravel, and water.
- Granite – A natural mixture of different minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and mica.
- Trail Mix – A mixture of nuts, dried fruits, and chocolate pieces.
- Blood – A heterogeneous mixture of plasma, red and white blood cells, and platelets.
Special Types of Mixtures
Colloids
These mixtures have microscopic particles dispersed evenly but do not settle over time.
- Mayonnaise – A colloid of oil, egg yolk, and vinegar.
- Fog – Tiny water droplets suspended in air.
- Butter – A colloidal dispersion of fat and water.
- Whipped Cream – Air bubbles dispersed in a liquid.
- Ink – A colloidal mixture of pigments and a solvent.
Suspensions
These mixtures contain larger particles that settle over time.
- Orange Juice with Pulp – Pulp particles settle over time in the juice.
- Chalk and Water – Chalk particles settle at the bottom.
- Dust in Air – Solid dust particles suspended in air.
Mixtures are found everywhere in our daily lives, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. Understanding mixtures helps in separating substances, analyzing materials, and creating new compounds for industrial and scientific applications.
Chemistry Examples Physical Change
1. Changes in State of Matter
- Melting of Ice – Solid ice turns into liquid water without changing its chemical composition (H₂O).
- Boiling of Water – Liquid water turns into water vapor (gas), but remains H₂O.
- Freezing of Water – Liquid water becomes solid ice without a chemical change.
- Condensation of Steam – Water vapor turns back into liquid water.
- Sublimation of Dry Ice – Solid carbon dioxide (CO₂) changes directly into gas without becoming liquid.
2. Mechanical Changes
- Breaking a Glass – The shape changes, but the material remains glass.
- Cutting Paper – Paper is physically altered but remains the same chemically.
- Crushing a Can – The can is deformed but still made of the same metal.
- Grinding Salt into Powder – The salt particles get smaller, but their composition (NaCl) remains unchanged.
- Shredding Wood – The wood is cut into smaller pieces but retains its properties.
3. Mixing and Separation Processes
- Dissolving Sugar in Water – Sugar molecules spread throughout the water but do not chemically change.
- Dissolving Salt in Water – Salt (NaCl) dissolves but retains its identity.
- Separating Sand from Water – Sand can be filtered out without a chemical reaction.
- Mixing Oil and Water – They do not chemically react but remain separate phases.
- Magnetizing Iron – The iron can be attracted by a magnet, but its chemical composition remains the same.
4. Expansion and Contraction
- Expansion of Metal in Heat – Metals expand when heated but do not change chemically.
- Shrinking of Plastic in Cold – Some plastics shrink in cold temperatures but do not chemically alter.
5. Changes in Appearance
- Polishing a Metal – The surface becomes shinier without a chemical reaction.
- Changing the Shape of Clay – Clay can be molded into different shapes without a chemical change.
- Bending a Copper Wire – The shape changes but the copper remains the same.
Chemistry Examples of Compounds
A compound is a substance formed when two or more different elements chemically bond together in a fixed ratio. Compounds have unique properties that differ from the elements that make them up. They can be classified into organic and inorganic compounds.
1. Common Inorganic Compounds
These compounds do not contain carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds and are often found in minerals, rocks, and salts.
Examples of Inorganic Compounds
- Water (H₂O) – A compound made of hydrogen and oxygen, essential for life.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl) – Common table salt, formed from sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl).
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – A gas produced by respiration and combustion.
- Ammonia (NH₃) – A nitrogen-hydrogen compound used in fertilizers and cleaning agents.
- Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) – A strong acid used in batteries and industrial processes.
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) – Found in stomach acid and used in cleaning.
- Calcium Carbonate (CaCO₃) – Found in limestone, marble, and eggshells.
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO) – Used in medicine and as a fire-resistant material.
- Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) – Also known as baking soda, used in cooking and medicine.
- Iron Oxide (Fe₂O₃) – Rust, formed when iron reacts with oxygen and moisture.
2. Common Organic Compounds
Organic compounds contain carbon and are found in living organisms and synthetic materials.
Examples of Organic Compounds
- Methane (CH₄) – A simple hydrocarbon and a major component of natural gas.
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) – A sugar that provides energy in living organisms.
- Ethanol (C₂H₅OH) – Found in alcoholic beverages and used as a fuel additive.
- Acetic Acid (CH₃COOH) – The main component of vinegar.
- Benzene (C₆H₆) – A hydrocarbon used in chemical synthesis.
- Proteins (Composed of amino acids like C, H, O, N, S) – Essential for body structure and function.
- Lipids (Fats and Oils, C, H, O) – Provide energy storage and insulation.
- Cellulose (C₆H₁₀O₅)n – A structural component of plant cell walls.
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid, composed of C, H, O, N, P) – Carries genetic information.
- Plastic (Polyethylene – C₂H₄)n – A synthetic polymer used in packaging and manufacturing.
3. Types of Compounds Based on Bonding
Ionic Compounds (Metal + Non-metal)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl) – Table salt.
- Calcium Fluoride (CaF₂) – Found in toothpaste and dental treatments.
- Potassium Nitrate (KNO₃) – Used in fertilizers and fireworks.
Covalent Compounds (Non-metal + Non-metal)
- Water (H₂O) – A universal solvent.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – A greenhouse gas.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) – Released by burning fossil fuels.
Chemistry Examples of Solutions
A solution is a homogeneous mixture where a solute dissolves in a solvent to form a single-phase mixture. Solutions can be found in different states—solid, liquid, and gas.
1. Common Liquid Solutions
Liquid Solvent with Solid, Liquid, or Gas Solutes
- Saltwater (NaCl + H₂O) – Salt dissolves in water to form a homogeneous solution.
- Sugar in Water (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ + H₂O) – A sweet solution used in beverages.
- Vinegar (Acetic Acid + Water, CH₃COOH + H₂O) – A solution of acetic acid in water.
- Alcoholic Beverages (Ethanol + Water, C₂H₅OH + H₂O) – Ethanol is dissolved in water.
- Tea (Tea Extract + Water) – Tea components dissolve in hot water.
- Coffee (Coffee Extract + Water) – Coffee solubles dissolve to make a beverage.
- Soft Drinks (Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sugar + Flavoring) – Carbonated drinks contain CO₂ dissolved under pressure.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Solution (H₂O₂ + H₂O) – A disinfectant solution with hydrogen peroxide dissolved in water.
- Lemonade (Lemon Juice + Sugar + Water) – A flavored liquid solution.
- Mouthwash (Antiseptic Agents + Water) – A disinfecting solution with multiple solutes.
2. Common Gaseous Solutions
Gas Solvent with One or More Gases as Solutes
- Air (O₂ + N₂ + CO₂ + Other Gases) – A natural solution of multiple gases.
- Oxygen in Water (O₂ + H₂O) – Dissolved oxygen helps aquatic life survive.
- Carbonated Beverages (CO₂ + Water) – Carbon dioxide dissolves in soft drinks under pressure.
- Smog (Pollutants + Air) – A solution of smoke particles and gases in the air.
- Natural Gas (Methane + Other Gases) – A mixture of gases used as fuel.
3. Common Solid Solutions
Solid Solvent with Solid, Liquid, or Gas Solutes
- Brass (Copper + Zinc, Cu + Zn) – A solid alloy used in hardware and musical instruments.
- Steel (Iron + Carbon, Fe + C) – A strong metal alloy used in construction.
- Bronze (Copper + Tin, Cu + Sn) – Used in sculptures and machinery.
- Gold Jewelry (Gold + Copper/Silver, Au + Cu/Ag) – 18K and 14K gold contain metals in solid solution.
- Amalgam (Mercury + Silver/Tin, Hg + Ag/Sn) – A dental filling material.
- Glass (SiO₂ + Other Oxides) – A transparent solid solution.
- Rubber (Polymer + Additives) – A solid solution with elastic properties.
- Air in Ice (O₂ + H₂O Solid) – Small air bubbles trapped in frozen water.
- Semiconductors (Silicon + Phosphorus/Boron, Si + P/B) – Used in electronics.
- Plastic (Polymers + Additives) – A solid solution with added stabilizers.
4. Special Types of Solutions
Colloidal Solutions
- Milk (Fat + Water) – A colloidal emulsion of fat in water.
- Paint (Pigments + Solvent) – A suspension of color particles.
- Blood (Plasma + Cells + Proteins) – A biological solution.
- Fog (Water Droplets + Air) – A colloidal suspension of tiny water droplets.
Suspensions (Temporary Solutions)
- Orange Juice with Pulp – The pulp settles over time.
- Chalk in Water – Chalk powder settles in water but can be temporarily mixed.
Chemistry Examples of Bases
A base is a substance that accepts protons (H⁺) or donates hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in a solution. Bases have a pH greater than 7, feel slippery, and taste bitter. They are widely used in cleaning products, medicine, food, and industry.
1. Common Strong Bases
Strong bases fully dissociate in water, releasing OH⁻ ions completely.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) – Lye or Caustic Soda
- Used in soap making, drain cleaners, and paper production.
- Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) – Caustic Potash
- Used in fertilizers, biodiesel production, and alkaline batteries.
- Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) – Slaked Lime
- Used in cement, plaster, and food processing.
- Barium Hydroxide (Ba(OH)₂)
- Used in plastics, lubricants, and alkaline solutions.
- Lithium Hydroxide (LiOH)
- Used in battery production and CO₂ absorption in spacecraft.
2. Common Weak Bases
Weak bases do not fully dissociate in water and have a lower concentration of OH⁻ ions.
- Ammonia (NH₃)
- Used in cleaning products, fertilizers, and refrigeration.
- Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) – Baking Soda
- Used in baking, medicine (antacid), and cleaning.
- Magnesium Hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) – Milk of Magnesia
- Used as an antacid and laxative.
- Aluminum Hydroxide (Al(OH)₃)
- Used in antacids and water purification.
- Methylamine (CH₃NH₂)
- Used in chemical manufacturing and pharmaceuticals.
3. Household and Industrial Examples of Bases
Household Bases
- Soap (Contains NaOH or KOH) – Removes grease and dirt.
- Toothpaste (Contains Sodium Bicarbonate or Fluoride Bases) – Neutralizes acids in the mouth.
- Bleach (Contains Sodium Hypochlorite, NaClO) – A disinfectant and stain remover.
- Detergents (Contain Ammonia or Other Alkaline Compounds) – Used for cleaning clothes and dishes.
- Baking Powder (Contains Sodium Bicarbonate, NaHCO₃) – A leavening agent in baking.
Industrial Bases
- Cement and Concrete (Contain Ca(OH)₂ and Mg(OH)₂) – Used in construction.
- Fertilizers (Contain Ammonium Hydroxide, NH₄OH) – Supplies nitrogen to plants.
- Paper Manufacturing (Uses NaOH and KOH) – Breaks down wood pulp.
- Alkaline Batteries (Contain KOH or NaOH) – Provides electrical energy.
4. Biological and Natural Examples of Bases
- Blood (Slightly Basic, pH ~7.4) – Maintains homeostasis in the body.
- Seawater (Contains Dissolved Bases Like NaOH and Mg(OH)₂, pH ~8.1) – Alkaline due to dissolved minerals.
- Egg Whites (Contain Weak Bases, pH ~8–9) – Help in food preservation.
- Bile (Contains Bicarbonates, pH ~7.6–8.6) – Helps in fat digestion.
5. Bases vs. Acids
| Property |
Bases |
Acids |
| pH Level |
Greater than 7 |
Less than 7 |
| Taste |
Bitter |
Sour |
| Feel |
Slippery |
Corrosive |
| Ion Released in Water |
OH⁻ (Hydroxide ions) |
H⁺ (Hydrogen ions) |
| Example |
NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide) |
HCl (Hydrochloric Acid) |
Bases are essential in daily life, medicine, industries, and nature. They play a key role in neutralization reactions, maintaining biological balance, and are vital in various chemical processes.
Uses of Chemistry in our Daily Life
Chemistry plays a crucial role in our everyday lives, from the food we eat to the air we breathe. It helps us understand how substances interact and enables advancements in medicine, technology, food, and environmental protection. Below are some essential ways chemistry impacts our daily lives.
1. Chemistry in Food and Cooking
- Preservatives (Sodium Benzoate, BHT, BHA) – Prevent food from spoiling.
- Food Additives (Artificial Flavors, Colors, and Sweeteners) – Enhance taste and appearance.
- Baking (Sodium Bicarbonate, Yeast Reactions) – Help dough rise.
- Emulsifiers (Lecithin, Egg Yolks, Mustard) – Keep ingredients like oil and water mixed in dressings and sauces.
- Fermentation (Ethanol Production in Alcohol and Yogurt Making) – Used in dairy and beverage industries.
2. Chemistry in Medicine and Healthcare
- Pharmaceuticals (Aspirin, Paracetamol, Antibiotics) – Relieve pain and treat diseases.
- Vaccines (mRNA, Inactivated Virus, Live Attenuated) – Protect against infections.
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants (Hydrogen Peroxide, Iodine, Alcohol) – Kill germs.
- Medical Tests (Blood Sugar Test, Pregnancy Test) – Use chemical reactions for diagnosis.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy – Target and treat cancer cells.
3. Chemistry in Personal Care Products
- Soap and Detergents (Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Potassium Hydroxide) – Remove dirt and oil.
- Shampoo and Conditioners (Silicones, Surfactants) – Clean and soften hair.
- Perfumes and Deodorants (Ethanol, Essential Oils, Aluminum Compounds) – Provide fragrance and control sweating.
- Toothpaste (Fluoride, Baking Soda, Hydrogen Peroxide) – Strengthen teeth and whiten enamel.
- Cosmetics (Lipstick, Foundations, Nail Polish, Sunscreen) – Contain chemical compounds for beauty and skincare.
4. Chemistry in Household Cleaning
- Laundry Detergents (Enzymes, Bleaching Agents, Surfactants) – Remove stains and odors.
- Dishwashing Liquid (Ammonia, Sodium Hydroxide) – Cuts grease and removes food particles.
- Bleach (Sodium Hypochlorite, Hydrogen Peroxide) – Disinfects and whitens clothes.
- Glass Cleaners (Ammonia, Isopropyl Alcohol) – Provide streak-free shine.
- Pesticides and Insect Repellents (DEET, Permethrin) – Protect against insects and pests.
5. Chemistry in Transportation and Energy
- Fuels (Petrol, Diesel, Natural Gas, Hydrogen Fuel Cells) – Power vehicles.
- Lubricants (Motor Oil, Grease) – Reduce friction in engines.
- Battery Technology (Lithium-Ion, Lead-Acid, Alkaline Batteries) – Store and provide energy.
- Solar Panels (Silicon-Based Compounds) – Convert sunlight into electricity.
- Biofuels (Ethanol, Biodiesel, Methanol) – Provide renewable energy sources.
6. Chemistry in Clothing and Textiles
- Synthetic Fibers (Polyester, Nylon, Acrylic, Spandex) – Durable, lightweight clothing.
- Natural Fibers (Cotton, Wool, Silk, Rayon) – Enhanced through chemical treatment for strength.
- Dyes and Pigments (Azo Dyes, Indigo, Synthetic Colors) – Provide long-lasting fabric colors.
- Waterproofing Agents (Teflon, Silicone-Based Coatings) – Protect against moisture.
- Flame Retardants (Brominated Compounds, Phosphates) – Reduce flammability.
7. Chemistry in Agriculture
- Fertilizers (NPK Fertilizers – Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) – Improve soil fertility.
- Pesticides and Herbicides (DDT, Glyphosate, Malathion) – Protect crops from pests.
- GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms) – Enhance crop resistance and yield.
- Soil pH Testing (Lime for Acidic Soil, Sulfur for Alkaline Soil) – Balance nutrients for optimal growth.
- Irrigation Chemicals (Water Treatment, pH Stabilizers) – Maintain water quality.
8. Chemistry in Environmental Protection
- Water Purification (Chlorine, Ozone, Activated Carbon Filters) – Remove harmful contaminants.
- Air Pollution Control (Catalytic Converters, Scrubbers) – Reduce harmful emissions.
- Biodegradable Plastics (PLA, PHA, Starch-Based Plastics) – Reduce environmental waste.
- Recycling Processes (Metals, Plastics, Paper, Glass) – Conserve natural resources.
- Acid Rain Neutralization (Limestone Treatment, Alkaline Reactions) – Reduce environmental damage.
9. Chemistry in Electronics and Technology
- Semiconductors (Silicon, Germanium, Gallium Arsenide) – Used in microchips and processors.
- LED Lights (Gallium Nitride, Phosphors) – Provide energy-efficient lighting.
- Smartphone Batteries (Lithium-Ion, Graphene-Based Tech) – Store energy efficiently.
- Touchscreens (Indium Tin Oxide, Conductive Polymers) – Allow smooth interaction.
- Fiber Optics (Glass, Plastic, Silica-Based Materials) – Enable high-speed internet.
10. Chemistry in Space and Aviation
- Rocket Fuels (Liquid Hydrogen, Hydrazine, RP-1 Kerosene) – Power spacecraft.
- Spacesuit Materials (Kevlar, Polyurethane, Mylar, Neoprene) – Provide thermal and radiation protection.
- Oxygen Generation Systems (Electrolysis of Water) – Provide breathable air in space.
- Heat Shields (Ceramic Tiles, Carbon-Carbon Composites) – Protect spacecraft from high temperatures.
- GPS and Satellite Components (Rare Earth Metals, Semiconductor Materials) – Enable communication and navigation.
Basic concepts of chemical reactions
1. Definition of a Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction occurs when reactants undergo a transformation to form products. This involves bond-breaking, bond-forming, and energy changes.
Example of a Chemical Reaction:
Here, hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) are reactants, and water (H₂O) is the product.
2. Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions can be classified into different types based on how reactants are transformed.
1. Combination (Synthesis) Reactions
- Two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
- Example: Formation of water
- Example: Formation of carbon dioxide
2. Decomposition Reactions
- A single reactant breaks down into two or more simpler products.
- Example: Breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen gas
- Example: Decomposition of calcium carbonate
3. Displacement (Single Replacement) Reactions
- A more reactive element replaces a less reactive element in a compound.
- Example: Zinc replaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid
4. Double Displacement (Metathesis) Reactions
- Two compounds exchange their ions to form new compounds.
- Example: Reaction of silver nitrate and sodium chloride
5. Combustion Reactions
- A substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
- Example: Burning of methane
6. Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reactions
- Involves the transfer of electrons between species.
- Example: Rusting of iron
3. Chemical Equation Representation
Chemical reactions are represented using chemical equations that show reactants and products.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced equation has equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides.
- Example (Balanced Equation):
- Example (Unbalanced Equation):
Types of Symbols in Chemical Equations
| Symbol |
Meaning |
| (s) |
Solid |
| (l) |
Liquid |
| (g) |
Gas |
| (aq) |
Aqueous (dissolved in water) |
| Δ |
Heat applied |
| ↑ |
Gas released |
| ↓ |
Precipitate formed |
4. Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve energy changes due to bond breaking and bond formation.
1. Exothermic Reactions
- Release heat energy.
- Example: Combustion of fuel
2. Endothermic Reactions
- Absorb heat energy.
- Example: Photosynthesis
5. Factors Affecting Chemical Reactions
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on several factors:
1. Temperature
- Increasing temperature increases the reaction rate by providing more energy to molecules.
2. Concentration
- Higher concentration of reactants increases the chances of collisions.
3. Surface Area
- Smaller particle sizes (larger surface area) speed up reactions.
4. Catalysts
- Catalysts speed up reactions without being consumed.
- Example: Enzymes in biological reactions.
5. Pressure (For Gases)
- Higher pressure increases reaction rates in gaseous systems.
6. Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. The total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products.
Example:
Mass of reactants = Mass of products
7. Importance of Chemical Reactions in Daily Life
Chemical reactions are essential in various fields:
- Medicine – Drug synthesis and metabolism.
- Cooking – Baking, fermentation, and food processing.
- Environment – Photosynthesis, respiration, and decomposition.
- Industry – Production of plastics, fertilizers, and fuels.
- Energy – Combustion in engines and power plants.
Branches of Chemistry
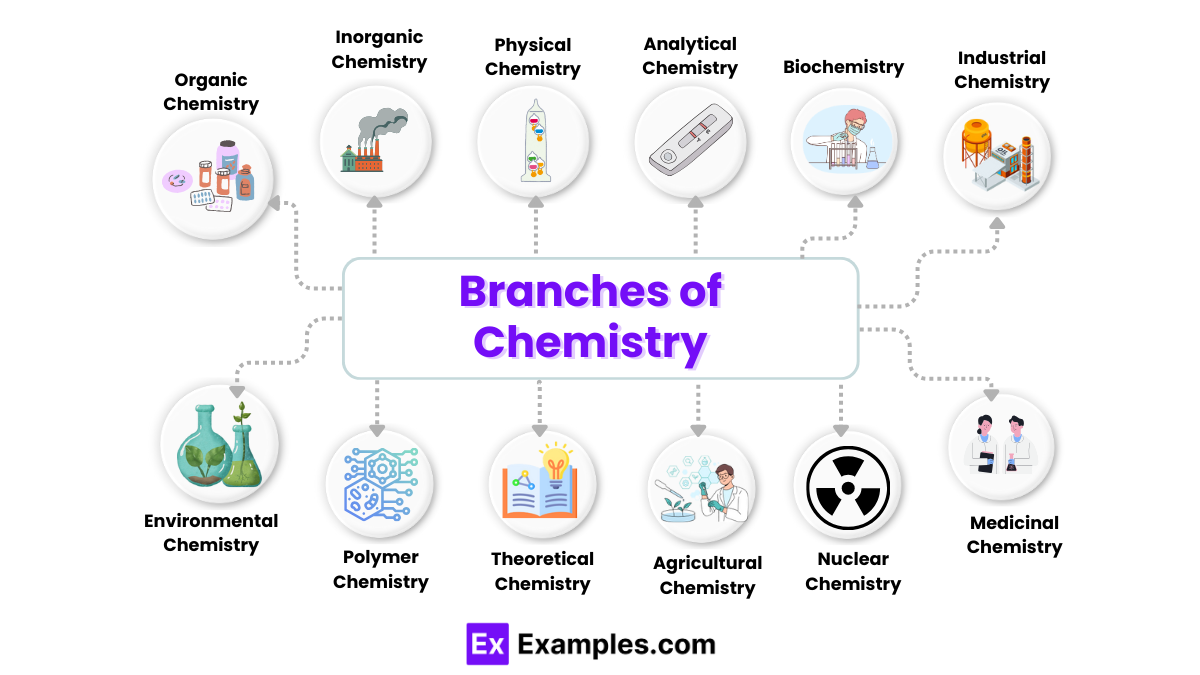
1. Organic Chemistry
- Definition: The study of carbon-containing compounds, including hydrocarbons and their derivatives.
- Focus Areas: Structure, bonding, synthesis, and reactions of organic molecules.
- Applications:
- Pharmaceuticals (drugs, vaccines)
- Plastics and polymers
- Petrochemicals (gasoline, diesel)
- Food and flavor chemistry
🔹 Example: The synthesis of aspirin (C₉H₈O₄) in medicine.
2. Inorganic Chemistry
- Definition: The study of non-carbon-based compounds, including metals, minerals, and salts.
- Focus Areas: Properties, reactions, and structures of inorganic substances.
- Applications:
- Industrial catalysts (platinum, nickel)
- Ceramics and glass materials
- Corrosion prevention
- Battery technology
🔹 Example: The use of sodium chloride (NaCl) as table salt.
3. Physical Chemistry
- Definition: The study of how matter behaves on a molecular and atomic level and how chemical reactions occur.
- Focus Areas: Thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, reaction kinetics.
- Applications:
- Development of new materials
- Battery and fuel cell research
- Nanotechnology
- Spectroscopy (used in forensic science)
🔹 Example: Understanding how enzymes speed up biochemical reactions.
4. Analytical Chemistry
- Definition: The study of techniques used to analyze substances and determine their composition.
- Focus Areas: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of chemical compounds.
- Applications:
- Drug testing and quality control
- Environmental monitoring (pollution analysis)
- Food safety testing
- Forensic investigations
🔹 Example: Detecting lead (Pb) in drinking water.
5. Biochemistry
- Definition: The study of chemical processes occurring in living organisms.
- Focus Areas: Enzymes, DNA, metabolism, and cellular processes.
- Applications:
- Medical research and disease treatment
- Biotechnology (genetic engineering, CRISPR)
- Agriculture (GMOs, fertilizers)
- Nutrition science
🔹 Example: The role of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels.
6. Industrial Chemistry
- Definition: The study of chemical processes in large-scale manufacturing.
- Focus Areas: Chemical production, process engineering, and materials science.
- Applications:
- Production of plastics and polymers
- Fertilizers and pesticides
- Pharmaceuticals and petrochemicals
- Textile and paint industries
🔹 Example: The large-scale production of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) for fertilizers.
7. Environmental Chemistry
- Definition: The study of chemical processes in the environment and their effects on ecosystems.
- Focus Areas: Pollution, climate change, and sustainable chemistry.
- Applications:
- Water purification and waste treatment
- Air quality monitoring
- Renewable energy solutions
- Green chemistry initiatives
🔹 Example: Studying the impact of carbon dioxide (CO₂) on global warming.
8. Polymer Chemistry
- Definition: The study of large molecules (polymers) and their applications.
- Focus Areas: Plastics, synthetic fibers, and biodegradable materials.
- Applications:
- Rubber and plastic industries
- Biomedical implants and prosthetics
- Packaging materials
- Textile production
🔹 Example: The development of biodegradable plastics to reduce pollution.
9. Theoretical Chemistry
- Definition: The study of mathematical and computational models to predict chemical behavior.
- Focus Areas: Quantum chemistry, molecular modeling, reaction mechanisms.
- Applications:
- Drug discovery and design
- Computational simulations in nanotechnology
- Understanding fundamental chemical reactions
🔹 Example: Using computer simulations to design new drugs.
10. Agricultural Chemistry
- Definition: The study of chemical processes related to soil, crops, and fertilizers.
- Focus Areas: Soil chemistry, plant growth, pest control.
- Applications:
- Fertilizer and pesticide development
- Genetic modification of crops
- Soil testing and improvement
🔹 Example: Using ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃) as a fertilizer.
11. Nuclear Chemistry
- Definition: The study of radioactive elements, nuclear reactions, and their applications.
- Focus Areas: Radiation, nuclear fission and fusion, isotopes.
- Applications:
- Nuclear power generation
- Medical imaging and cancer treatment (radiotherapy)
- Radioactive dating (carbon-14 dating)
🔹 Example: Using Uranium-235 in nuclear reactors to generate electricity.
12. Medicinal Chemistry
- Definition: The study of chemical compounds used in medicine and drug development.
- Focus Areas: Drug design, pharmacology, and biocompatibility.
- Applications:
- Development of painkillers, antibiotics, and vaccines
- Research on anti-cancer drugs
- Drug testing and formulation
🔹 Example: Synthesis of paracetamol (C₈H₉NO₂) for pain relief.