Which of the following is a strong acid?
HCl
CH₃COOH
H₂CO₃
NH₄OH

Acids are fascinating substances that play a vital role in the world of chemistry and in our daily lives. They’re found in everything from the food we eat to the batteries that power our devices. In simple terms, acids are substances that taste sour and can turn blue litmus paper red, indicating their acidic nature. They’re known for their ability to react with bases to form water and salts, a fundamental reaction in chemistry. Understanding acids is not just a crucial part of chemistry; it’s also a window into understanding the chemical reactions that occur all around us, every day.
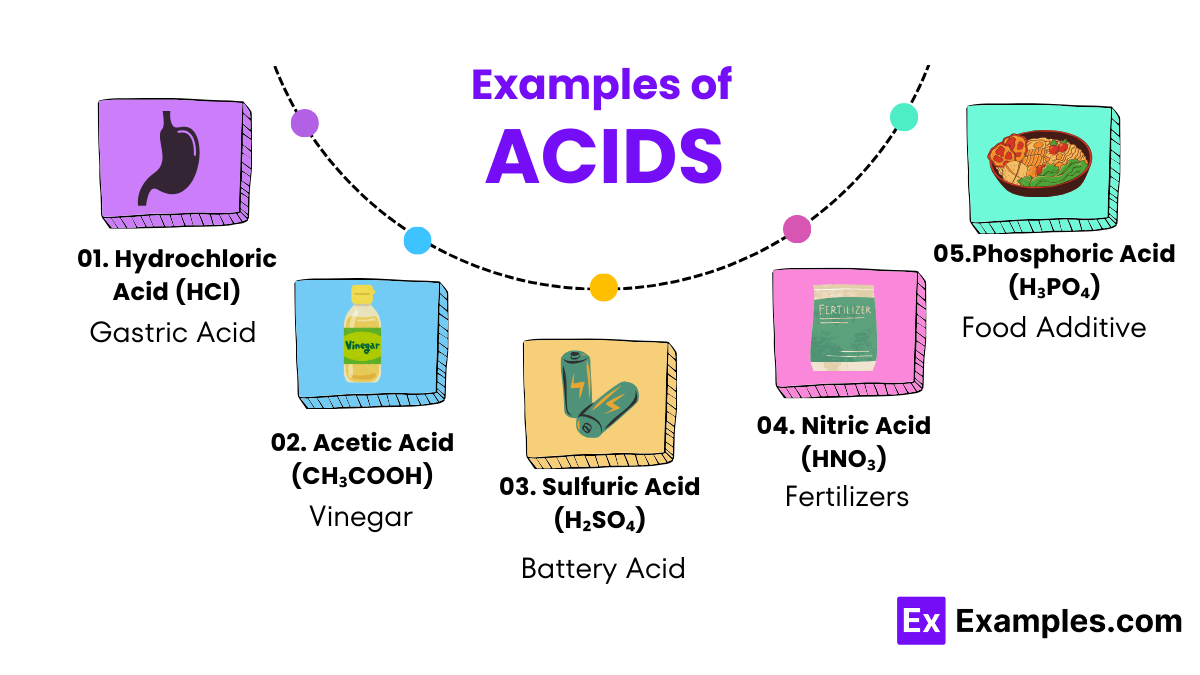
These are the superheroes of the acid world. Once in water, they don’t hold back; they give away all their hydrogen ions quickly, like a sprinter racing to the finish line. Examples include hydrochloric acid (HCl), used in cleaning agents, and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), found in car batteries.
These acids are more like marathon runners, slowly releasing their hydrogen ions over time. They don’t give away all their hydrogen ions as strong acids do. Vinegar, which contains acetic acid (CH₃COOH), is a familiar weak acid used in cooking and cleaning.
These are primarily found in living organisms. They often contain carbon atoms and have a wide range of uses, from preserving food to making medicines. Citric acid, present in citrus fruits, is a well-known organic acid.
Unlike organic acids, these don’t have carbon. They’re usually derived from minerals and are often strong acids, like hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid. These acids are key players in industrial processes and manufacturing.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Taste | Sour |
| Touch | Can be corrosive |
| State at Room Temperature | Mostly liquid |
| Conductivity | Good conductors of electricity in solution |
| pH Value | Below 7 |
| Reaction with Metals | Produce hydrogen gas |
Taste: Acids have a sour taste, which is why foods like lemons and vinegar have that tangy flavor. However, tasting chemicals in a lab to identify them is not a safe practice!
Touch: Many acids can feel corrosive if they come into contact with skin, leading to irritation or burns. This property necessitates careful handling, using protective gear like gloves.
State at Room Temperature: Most acids are liquid at room temperature. This liquid nature makes acids adaptable for use in a wide range of products, from household cleaners to industrial solvents.
Conductivity: When dissolved in water, acids break apart into ions, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. This property is useful in batteries, where acids help generate electrical power.
pH Level: All acids have a pH lesser than 7. The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is on a scale of 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
Reaction with Metals: Acids react with most metals, producing hydrogen gas in the process. This reaction is not only fascinating to observe but also serves as a key characteristic for identifying acids.
Acids like citric acid and acetic acid are key to adding that tangy flavor to our foods. Citric acid, present in citrus fruits, not only flavors beverages and candies but also acts as a preservative. Acetic acid gives vinegar its characteristic sour taste, widely used in culinary practices for salad dressings and as a natural food preservative.
Acids are indispensable in the pharmaceutical industry. Aspirin, a derivative of salicylic acid, is a common medication used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Various acids are foundational in synthesizing numerous other medicinal compounds and vitamins, contributing significantly to health and wellness.
Hydrochloric acid is a powerful cleaning agent found in many household cleaning products, effectively tackling tough stains and mineral deposits. Similarly, vinegar, which contains acetic acid, is a versatile and eco-friendly cleaning solution for a sparkling home.
The agricultural sector benefits greatly from acids such as sulfuric and phosphoric acid, crucial in manufacturing fertilizers. These acids help in providing essential nutrients to plants, enhancing growth and agricultural productivity.
Nitric acid is vital in producing fertilizers, plastics, dyes, and even explosives, underscoring its significant industrial utility. Its ability to participate in various chemical reactions makes it a cornerstone substance in manufacturing processes.
Sulfuric acid serves as the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, such as those used in vehicles. Its role is crucial in conducting electricity, thereby powering engines and electrical systems in cars and trucks.
In educational settings, acids are fundamental for demonstrating a wide array of chemical reactions and principles, making them essential tools for teaching chemistry and inspiring future scientists.
When considering the strength of an acid, one typically looks at its ability to donate protons (hydrogen ions) in an aqueous solution. By this measure, Fluoroantimonic Acid (HSbF₆) is often cited as the strongest acid known. It’s a super acid, meaning it has an acidity greater than that of 100% sulfuric acid. This extreme reactivity makes Fluoroantimonic Acid highly effective at protonating substances, even those that are generally considered non-reactive. Its applications, therefore, are specialized and handled with extreme care, primarily within scientific research environments. This super acid exemplifies the extraordinary capabilities of acids at the extreme end of the pH scale, demonstrating the profound impact that these substances have in the realm of chemistry.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is a strong acid?
HCl
CH₃COOH
H₂CO₃
NH₄OH
What is the pH value of a neutral solution at 25°C?
0
7
14
3
Which of the following acids is found in vinegar?
Sulfuric acid
Nitric acid
Acetic acid
Hydrochloric acid
Which of the following acids is commonly used in car batteries?
Phosphoric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Sulfuric acid
Nitric acid
What is the common name for hydrochloric acid?
Muriatic acid
Aqua regia
Vinegar
Lactic acid
Which of the following acids is produced in the stomach to aid digestion?
Lactic acid
Acetic acid
Hydrochloric acid
Citric acid
Which acid is commonly found in citrus fruits?
Lactic acid
Malic acid
Citric acid
Tartaric acid
What is the name of the acid present in sour milk?
Citric acid
Tartaric acid
Lactic acid
Acetic acid
Which acid is a component of acid rain?
Hydrochloric acid
Nitric acid
Lactic acid
Acetic acid
Which of the following acids is used in the production of fertilizers?
Hydrochloric acid
Nitric acid
Acetic acid
Phosphoric acid
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

