What is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element?
Molecule
Atom
Proton
Electron

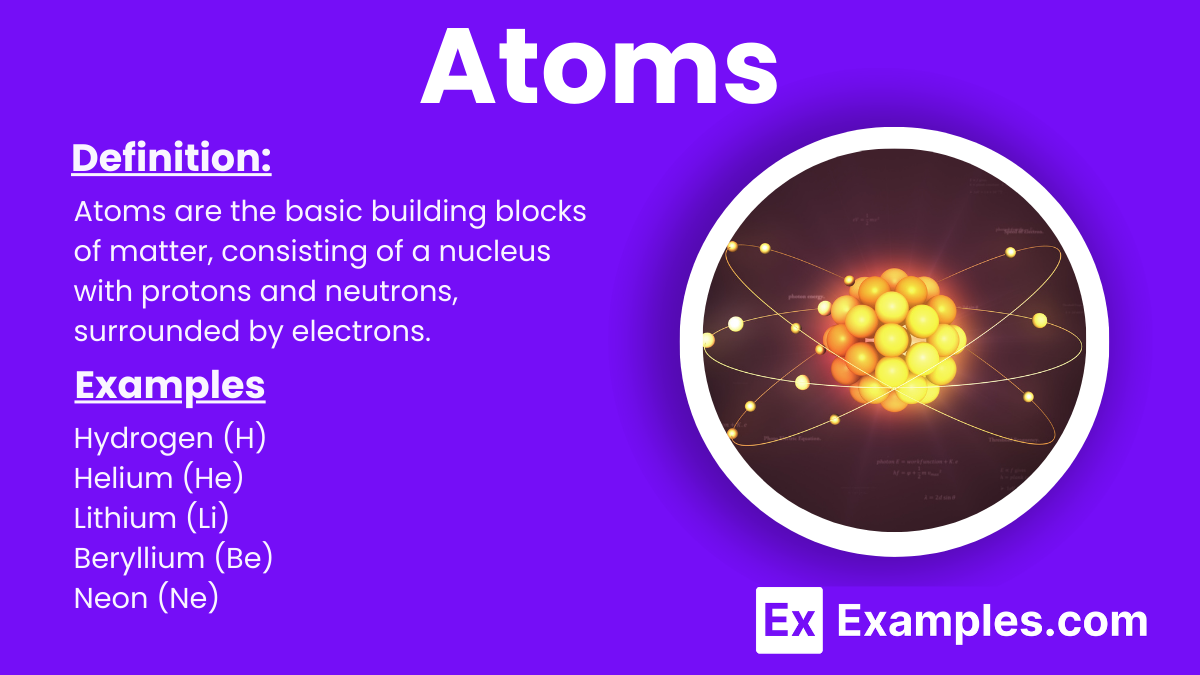
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter in chemistry. They are tiny particles that make up everything around us, including the air we breathe, the food we eat, and even our own bodies. Each atom consists of a nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons that orbit the nucleus. Atoms combine in various ways to form molecules and compounds, which are the substances we study in chemistry to understand the properties and behaviors of different materials.
To calculate the number of atoms in a sample, you use the formula:
First, divide the mass of your sample by the molar mass of the element or compound. Then, multiply the result by Avogadro’s number, which is 6.022×10²³. This formula helps you determine how many individual atoms are present in a given amount of substance.
Atoms come in different types based on the number of protons in their nucleus, which defines the element. Here are the main types:
The history of the atom begins in ancient Greece around 450 BCE when philosopher Democritus proposed that matter consists of small, indivisible particles called atoms. However, it wasn’t until the early 19th century that the atomic theory gained scientific footing. In 1803, John Dalton revived the concept, suggesting that each element is composed of unique atoms and that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of these atoms.
In the early 20th century, discoveries accelerated. J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in 1897, revealing that atoms were divisible and contained smaller particles. Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment in 1911 uncovered the nucleus, a dense central core within the atom. Later, Niels Bohr proposed a model in 1913 where electrons orbit the nucleus in defined paths. This model laid the groundwork for the modern quantum mechanical model of the atom, which describes electrons in probabilistic terms rather than fixed orbits.
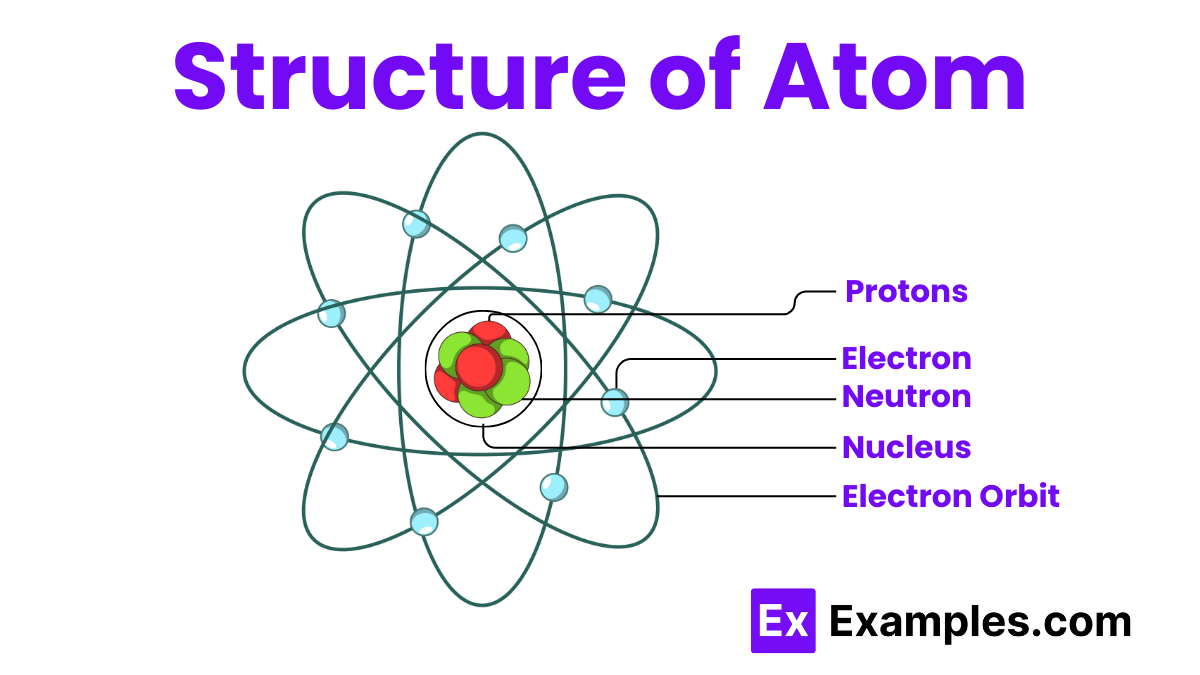
An atom has a nucleus at its center, which contains protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles, while neutrons have no charge. Electrons, which are negatively charged, orbit the nucleus in regions called electron shells or energy levels. The number of protons defines the element, while the arrangement of electrons determines the atom’s chemical properties. This simple structure—nucleus with protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons—forms the basis of all matter in the universe.
Atoms are incredibly small, typically measuring about 0.1 to 0.5 nanometers in diameter. To put this in perspective, a single nanometer is one-billionth of a meter. Despite their minuscule size, atoms consist of even smaller particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. The nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, is about 100,000 times smaller than the atom itself, while the electrons occupy the vast empty space around the nucleus. This tiny size makes individual atoms invisible to the naked eye, yet they are the fundamental building blocks of all matter.
An atom is the smallest building block of everything around us. It has a nucleus in the center with tiny electrons orbiting around it.
Atoms were formed in the early universe after the Big Bang and continue to be created in stars through nuclear reactions.
Atoms work by combining with other atoms to form molecules through chemical bonds, creating all substances we see and use.
An atom is made of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting around the nucleus in electron shells.
Atoms are matter, but they also contain energy within their particles and bonds.
Subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons are smaller than an atom.
Quarks and leptons are currently considered the smallest known particles in the universe.
The rarest atoms include astatine and francium, which are naturally occurring but very unstable and scarce.
Yes, atoms are 99.9% empty space, with electrons orbiting far from the nucleus, creating this vast empty space.
A baby contains approximately 10²⁷ atoms, which is a billion times a trillion atoms.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element?
Molecule
Atom
Proton
Electron
What particles are found in the nucleus of an atom?
Electrons and protons
Neutrons and electrons
Protons and neutrons
Electrons only
Which particle has a negative charge?
Proton
Neutron
Electron
Nucleus
What is the charge of a neutron?
Positive
Neutral
Negative
Variable
Which element has an atomic number of 1?
Helium
Hydrogen
Lithium
Beryllium
What is the mass number of an atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons?
6
12
18
24
Which of the following particles is found outside the nucleus?
Proton
Neutron
Electron
Quark
What term describes atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons?
Isotopes
Ions
Molecules
Compounds
Which subatomic particle determines the identity of an element?
Proton
Neutron
Electron
Quark
What is the atomic mass unit (amu) based on?
Carbon-12
Hydrogen-1
Oxygen-16
Nitrogen-14
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

