What is the chemical formula of borax?
Na2B4O7·10H2O
Na3BO3·4H2O
Na2CO3·10H2O
K2SO4·6H2O


Borax, also known as sodium borate, is a versatile inorganic compound that plays a significant role in chemistry and various industrial applications. This white powder is not only fundamental in creating cleaning products and detergents but also serves as an essential ingredient in glassmaking and ceramics. Easily soluble in water, borax exhibits unique properties that make it valuable in both household and laboratory settings. Its chemical stability and low toxicity provide a safe and effective solution for many chemical reactions and processes, making it a staple in the study of chemistry and the production of various inorganic materials.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O |
| Hill Formula | B₄H₂₀Na₂O₁₇ |
| Name | Sodium borate decahydrate |
| IUPAC Name | Disodium 3,7-dioxido-2,4,6,8,9-pentaoxa-1,3,5,7-tetraborabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane decahydrate |
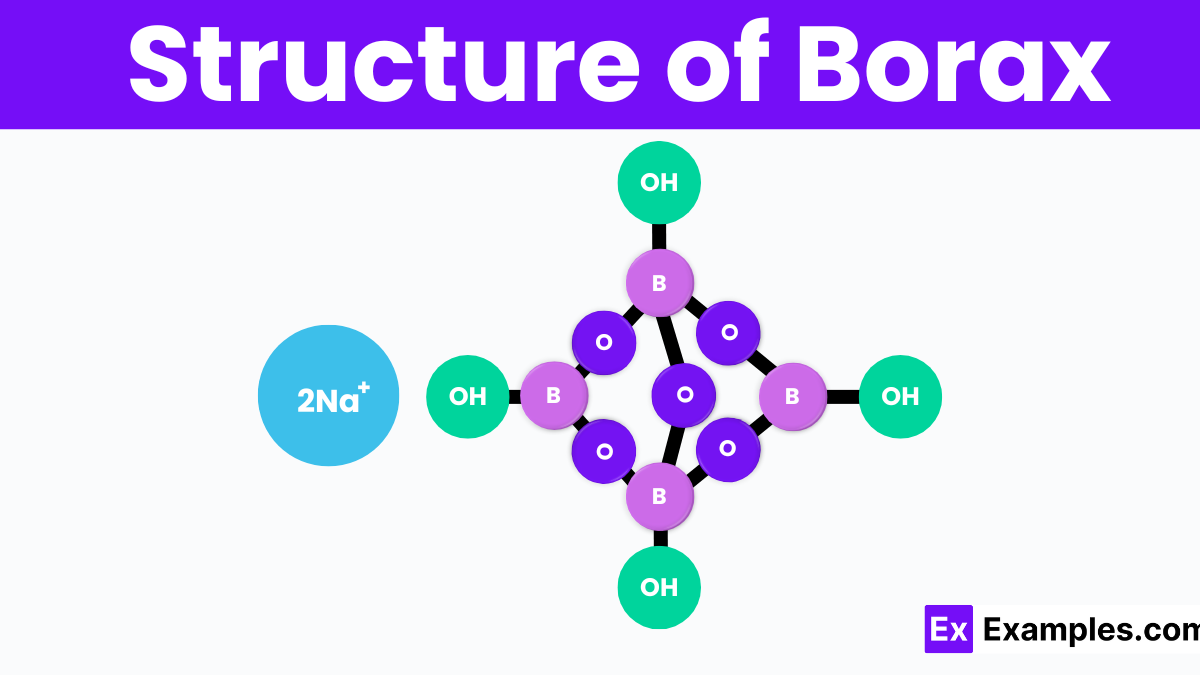
Borax, scientifically known as sodium tetraborate decahydrate, has a unique crystal structure that includes four boron atoms, ten water molecules, and two sodium atoms. In this structure, the boron atoms are linked together in a symmetrical pattern, forming a part of the compound called the borate ion. Each boron atom is connected to oxygen atoms, creating a network that holds the sodium ions in place. This arrangement results in a solid, yet easily dissolvable, structure in water. Understanding borax’s structure helps explain its effectiveness in various cleaning and household tasks.
Borax is typically prepared through a process involving the mineral colemanite, a borate mineral rich in calcium. This process starts with the reaction of colemanite with sodium carbonate (soda ash). During this reaction, colemanite reacts with sodium carbonate in hot water, resulting in the formation of borax and calcium carbonate as a by-product. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
Here, Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O represents borax (sodium tetraborate decahydrate), and 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂₃ stands for calcium carbonate, which precipitates out. The mixture is then filtered to separate the borax from the calcium carbonate sediment. The resulting solution is cooled, allowing the borax to crystallize. This method is widely used in industry due to its efficiency in producing borax from natural sources.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, crystalline powder or granular solid |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble, especially at higher temperatures |
| Melting Point | 743°C (dehydrates), 1575°C (anhydrous) |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm³ (solid) |
| pH | About 9.3 (alkaline when dissolved in water) |
| Odor | Odorless |
Borax reacts with strong acids such as hydrochloric acid to produce boric acid and sodium chloride. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
This reaction is particularly useful for producing boric acid, which is employed in various applications including antiseptics and insecticides.
Upon heating, borax undergoes thermal decomposition. It first loses its water molecules to form anhydrous sodium tetraborate at about 320°C. Further heating results in the formation of boron oxide (B2O3), sodium oxide (Na2O), and additional water. The reactions involved are:
Na₂B₄O₇ → 2NaBO₂ + B₂O₃
This decomposition is crucial for its role as a flux in the manufacture of glass and ceramics.
Borax can create a buffer solution when dissolved in water. This buffered solution is valuable for maintaining a stable pH, which is crucial in both chemical and biochemical lab settings for sustaining the necessary conditions for various reactions.
Borax can form complexes with different molecules. An important example is its ability to react with methylene blue to form a borate complex, used as a pH indicator. This property of complexation makes borax a useful component in laboratory experiments and tests.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 1303-96-4 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 16211214 |
| SMILES Identifier | B1(OB2OB(OB(O1)O2)[O-])[O-].O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.[Na+].[Na+] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/B4O7.2Na.10H2O/c5-1-7-3-9-2(6)10-4(8-1)11-3;;;;;;;;;;;;/h;;;101H2/q-2;2+1;;;;;;;;;; |
| RTECS Number | VZ2275000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00149193 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 2 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 0 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
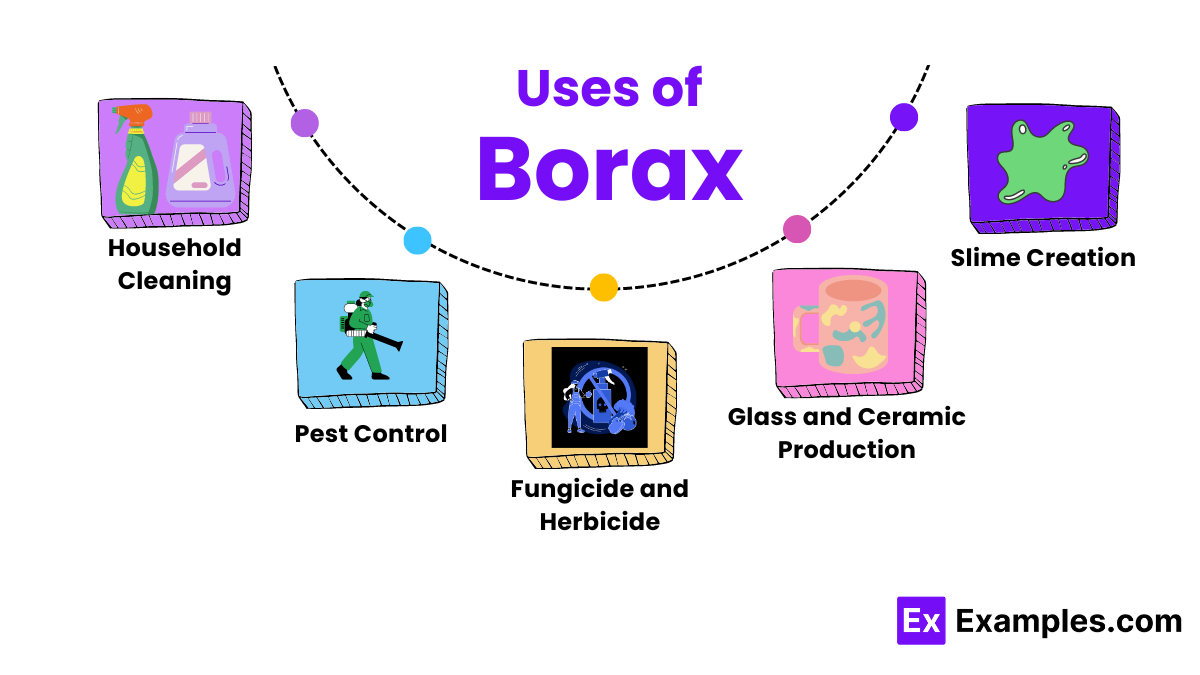
Borax is commonly used in household cleaning products due to its ability to enhance the effectiveness of detergents. It helps to break down stains and odors, making it excellent for laundry and general household cleaning.
In areas with hard water, borax can act as a water softener. It binds to the minerals in hard water, such as calcium and magnesium, preventing them from interfering with the cleaning power of soaps and detergents.
Borax also functions as a pH buffer, maintaining a stable alkaline environment in solutions. This property is crucial in pools, cosmetics, and various industrial applications to control acidity and alkalinity.
Due to its antifungal properties, borax is used in some over-the-counter creams and sprays to treat fungal infections like athlete’s foot. It also has mild antiseptic qualities for preventing the growth of microorganisms.
In the ceramics industry, borax is used to improve the quality of glazes and enamels on pottery and ceramics. It helps to create smooth and glossy surfaces that are more durable.
Another significant function of borax is its role as a flame retardant. It is applied to materials like wood and fabric to reduce their flammability and slow the spread of fire in case of an emergency.
Borax is a popular ingredient in many cleaning products due to its ability to enhance the cleaning power of laundry detergents. It helps remove tough stains, neutralizes odors, and disinfects surfaces effectively.
Due to its toxic properties to insects, borax is often used in homemade pest control recipes. It is particularly effective against ants and cockroaches when mixed with sweeteners that attract these pests.
Borax serves as a fungicide and herbicide, controlling the growth of mold, mildew, and weeds. It’s especially useful in gardens and lawns to manage fungal diseases and unwanted plants.
In the realm of fire safety, borax is used as a fire retardant. It’s applied to wood and fabrics to reduce their flammability and slow down the spread of fire.
In manufacturing, borax is a vital component in the production of glass and ceramics. It lowers the melting point of glass and improves the gloss and durability of glazed ceramics.
A fun and educational use of borax is in making slime. It acts as a cross-linking agent that binds polymer molecules in glue to create stretchy, gooey slime, which is a popular science activity for kids.
Yes, borax can be harmful if ingested, inhaled, or if it contacts skin, causing irritation, respiratory issues, and toxicity.
No, borax and baking soda are different substances; borax is sodium tetraborate, while baking soda is sodium bicarbonate.
Borax is less used due to safety concerns about its potential toxicity and environmental impact, leading to restricted use in some countries.
Borax effectively kills household pests like ants, cockroaches, fleas, and silverfish when used as a pesticide.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula of borax?
Na2B4O7·10H2O
Na3BO3·4H2O
Na2CO3·10H2O
K2SO4·6H2O
Borax is commonly used in which of the following household applications?
Air fresheners
Laundry detergents
Air conditioners
Dishwashers
Which property of borax makes it useful in glassmaking?
Its acidity
Its viscosity
Its fluxing ability
Its density
Borax can be used as a natural remedy for which of the following?
Allergies
Skin infections
Joint pain
Headaches
Which industry makes use of borax for fire retardant applications?
Textile industry
Aerospace industry
Food industry
Automotive industry
Borax can be used to soften water because it reacts with which type of ions?
Calcium and magnesium ions
Sodium and potassium ions
Iron and zinc ions
Chlorine and fluorine ions
Which of the following is a common name for borax?
Sodium borate
Potassium chloride
Calcium carbonate
Magnesium sulfate
In which form is borax typically found for use in cleaning products?
Liquid
Solid powder
Gas
Gel
What effect does borax have on pests like ants and cockroaches?
It repels them
It attracts them
It dehydrates and kills them
It makes them larger
Borax is a common ingredient in which type of DIY craft?
Metalworking
Ceramics
Candle making
Wood carving
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

