What is the atomic number of Cesium?
54
55
56
57
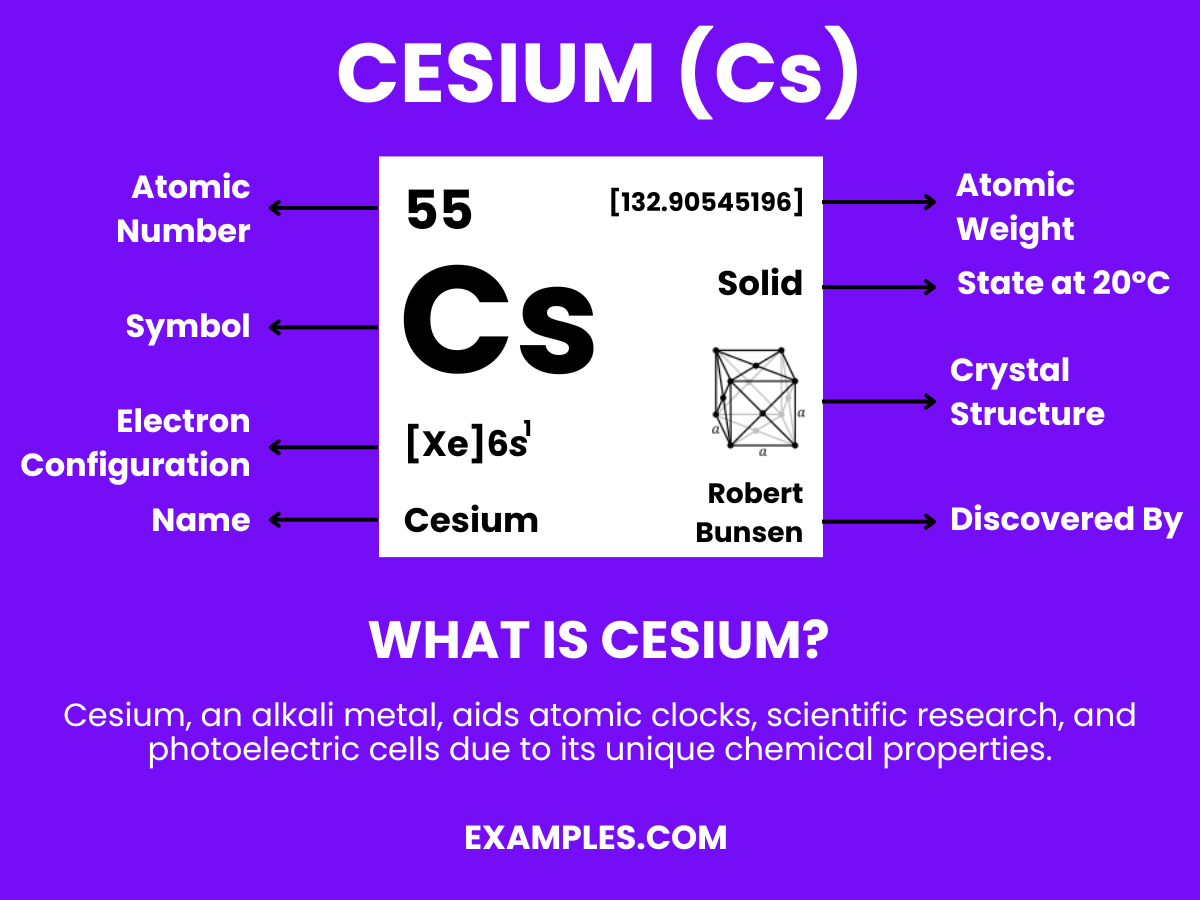
Cesium, a fascinating element on the periodic table, plays a crucial role in various applications. This guide delves into its intriguing properties and practical uses, offering a comprehensive understanding for teachers and students alike. Enhance your chemistry lessons with engaging examples and insights into Cesium’s world, making science more accessible and exciting.
Cesium, often symbolized as Cs, is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with atomic number 55. It’s known for its high reactivity and low melting point. This element is used in various industries, including electronics, atomic clocks, and even as a catalyst in the hydrogenation of certain organic compounds. Understanding Cesium’s properties and uses can enrich chemistry lessons, making them more relevant and engaging for students.
| Lithium |
| Sodium |
| Potassium |
| Rubidium |
| Francium |

| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Silvery-gold, soft metal. |
| Atomic Number | 55 |
| Density | About 1.93 g/cm³, one of the least dense metals. |
| Melting Point | Low, at 28.5°C, near room temperature. |
| Boiling Point | 671°C. |
| State at Room Temperature | Liquid (near melting point) or soft solid depending on ambient temperature. |
| Conductivity | Excellent conductor of electricity. |
| Malleability | Extremely malleable and can be easily cut with a knife. |
Cesium is a highly reactive alkali metal, characterized by its readiness to lose its single valence electron. This behavior is evident in its chemical properties:
| Property | Value with Unit |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 671 °C |
| Melting Point | 28.5 °C |
| Critical Temperature | Not Available |
| Critical Pressure | Not Available |
| Heat of Vaporization | 63.9 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Fusion | 2.09 kJ/mol |
| Specific Heat Capacity (at 25°C) | 0.242 J/g·K |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35.9 W/m·K |
| Property | Value with Unit |
|---|---|
| Density (at 20°C) | 1.93 kg/m³ |
| Viscosity (at melting point) | Not Available |
| Solubility | Reacts with water, soluble in anhydrous alcohol |
| Color | Silvery gold |
| Phase at Room Temperature | Solid |
| Property | Value with Unit |
|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity (at 20°C) | 20.5 nΩ·m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35.9 W/m·K |
| Magnetic Susceptibility | -28.0 × 10^-6 cm^3/mol |
| Electronegativity (Pauling scale) | 0.79 |
| Property | Value with Unit |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 55 |
| Atomic Mass | 132.90545196 amu |
| Isotopes | ^133Cs (100%) |
| Nuclear Spin (for ^133Cs) | 7/2 ℏ |
| Neutron Cross Section (for ^133Cs) | 29 barns |
| Nuclear Magnetic Moment (for ^133Cs) | 2.582 µN |
| Isotope | Natural Abundance | Half-Life | Type of Decay | Use/Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cs-133 | 100% (stable) | Stable | N/A | Used as a standard in atomic clocks |
| Cs-134 | Trace | ~2 years | Beta decay | Used in hydrology and geology |
| Cs-135 | Trace | ~2.3 million years | Beta decay | Studied for waste management |
| Cs-136 | Trace | ~13 days | Beta decay | Used in environmental studies |
| Cs-137 | Trace | ~30 years | Beta decay | Used in medical and industrial applications, also a product of nuclear fission |
| Cs-138 | Trace | ~33 minutes | Beta decay | Rare, used in nuclear physics research |

The commercial production of cesium involves several key steps:
Cesium, particularly in its radioactive isotopes (like Cesium-137), can have significant health effects:
Cesium, especially its radioactive forms, can have various impacts on the environment:
Cesium is primarily used in atomic clocks, oil drilling fluids, and photoelectric cells, enhancing precision and efficiency in various industries.
Cesium can be toxic, especially its radioactive isotopes, causing radiation sickness. However, stable isotopes pose less risk in small quantities.
Cesium itself is not an explosive, but it reacts explosively with water due to its high reactivity, releasing hydrogen gas.
Cesium’s value lies in its unique properties: it’s vital in high-precision atomic clocks, and its reactivity makes it useful in various chemical applications.
Cesium impacts the body by mimicking potassium, potentially disrupting electrolyte balance and muscle function, especially when radioactive isotopes are involved.
Understanding cesium’s unique properties and applications, from atomic clocks to chemical processes, is crucial. When writing about cesium, emphasize its reactivity, value in precision technology, and potential health impacts. Always highlight its dual nature of utility and caution, providing a well-rounded perspective on this fascinating element in your guides and tips.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
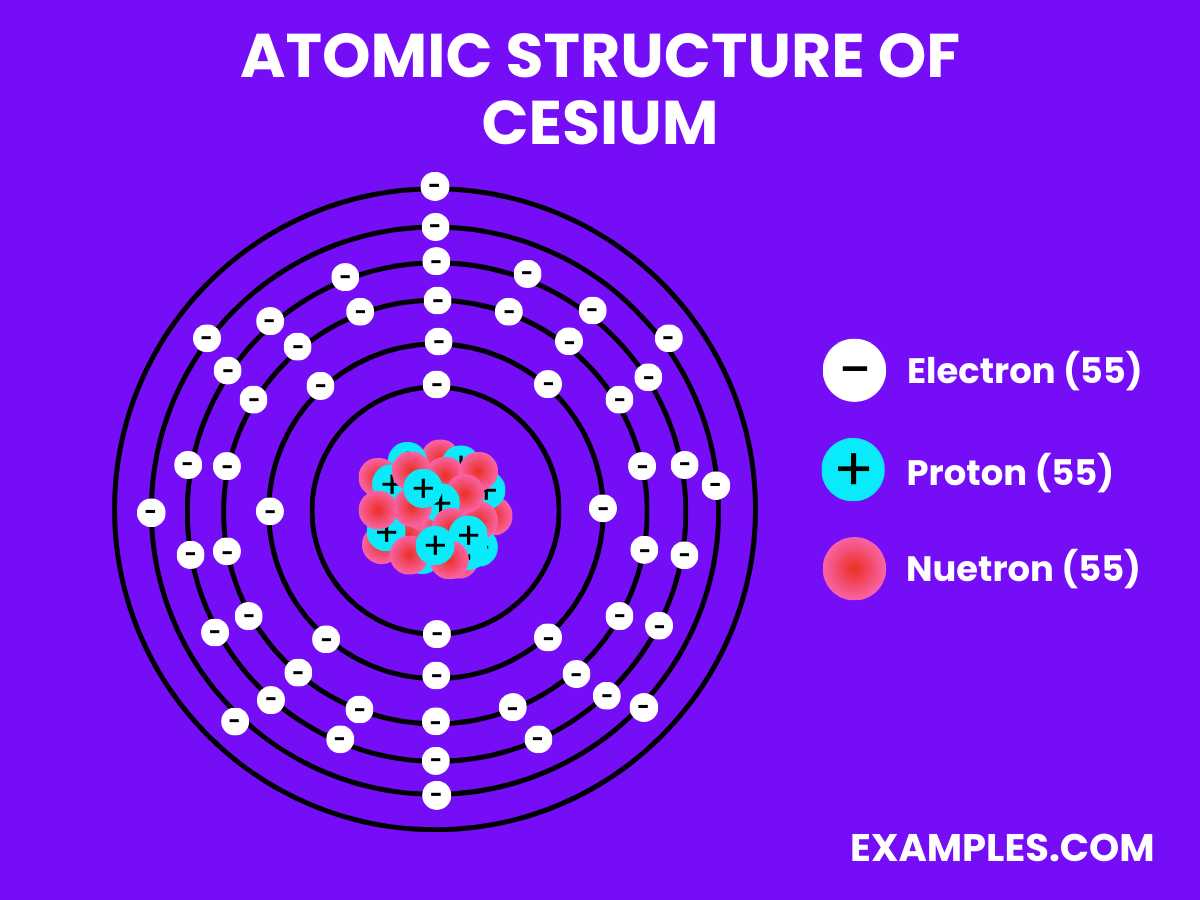
Electrons
Neutrons
Protons
What is the atomic number of Cesium?
54
55
56
57
What is the symbol for Cesium on the periodic table?
Cs
Ce
C
Ca
In which group of the periodic table is Cesium found?
Group 1
Group 2
Group 13
Group 14
What is the most common oxidation state of Cesium?
+0
+1
+2
+3
What is the standard atomic weight of Cesium?
132.91
133.91
134.91
135.91
Cesium has a melting point that is closest to which of the following temperatures?
28.5°C
50.5°C
78.5°C
100.5°C
Cesium is most commonly used in which of the following applications?
Construction materials
Atomic clocks
Food preservation
Textile manufacturing
Which property is NOT associated with Cesium?
Softness
High reactivity
Low density
High melting point
Cesium reacts explosively with which of the following substances?
Oxygen
Water
Nitrogen
Carbon dioxide
What color does Cesium emit in a flame test?
Red
Blue
Green
Violet
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

