What is the primary function of cobalamin in the body?
Energy production
DNA synthesis
Bone growth
Immune response

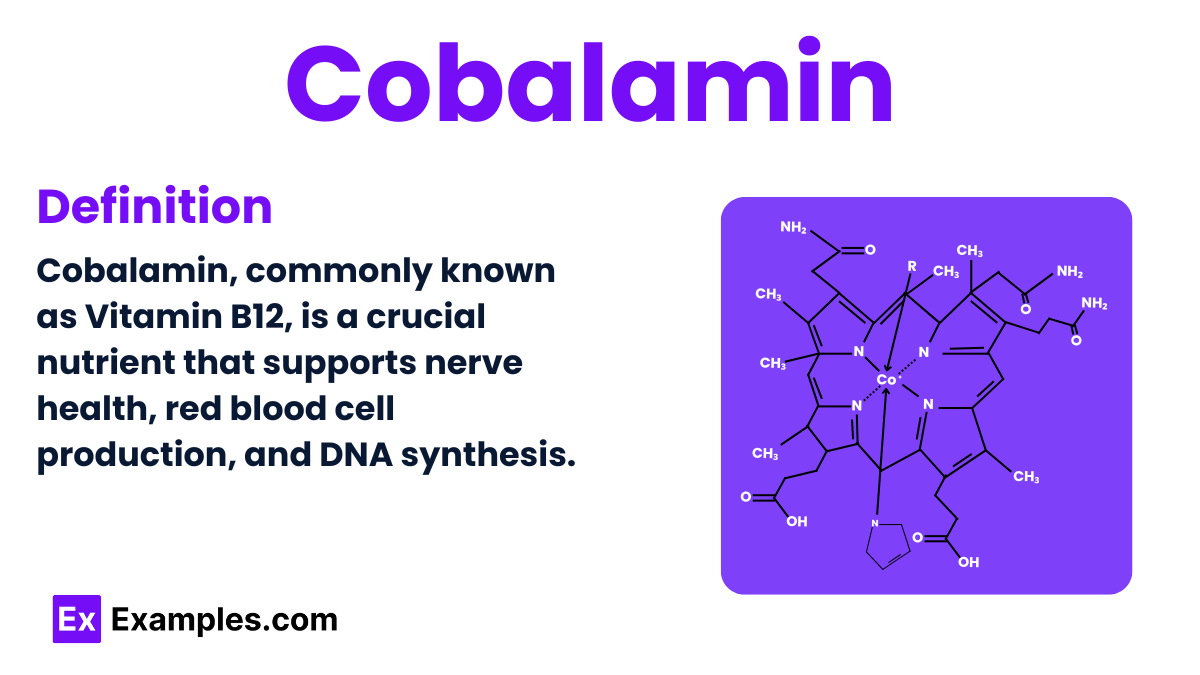
Cobalamin, commonly known as Vitamin B12, is a crucial nutrient in human health and a complex compound that plays a vital role in many bodily functions. This chemical is essential for making red blood cells and maintaining healthy nerve cells. Found naturally in animal products like meat, eggs, and dairy, cobalamin is a key topic in chemistry because of its intricate structure and impact on metabolism. Its absence can lead to serious health issues, making it a critical component of our diet.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | C₆₂CoH₈₈N₁₃O₁₄P |
| Hill formula | C₆₂H₈₈CoN₁₃O₁₄P |
| Name | Cobalamin |
| Alternate Names | DMBC Coenzyme, Hydroxomin, Rubivite, Rubramin PC, Rubratope-57, Rubratope-60, Ruvite |
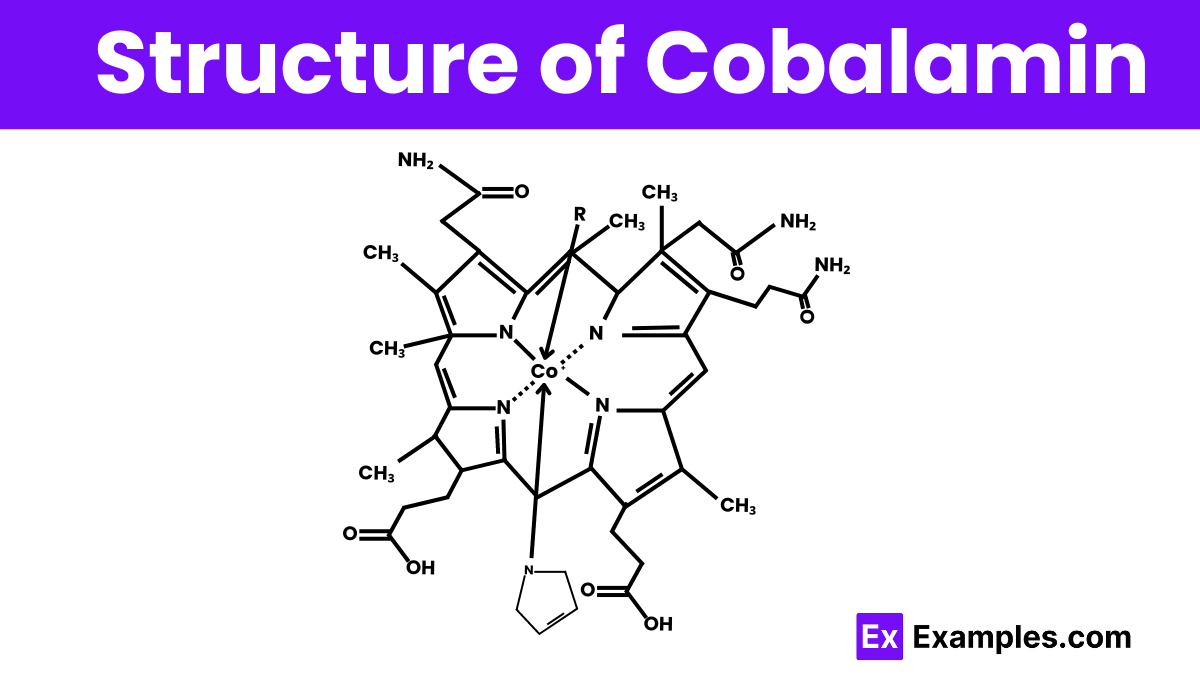
Cobalamin, also known as Vitamin B12. It is molecular formula
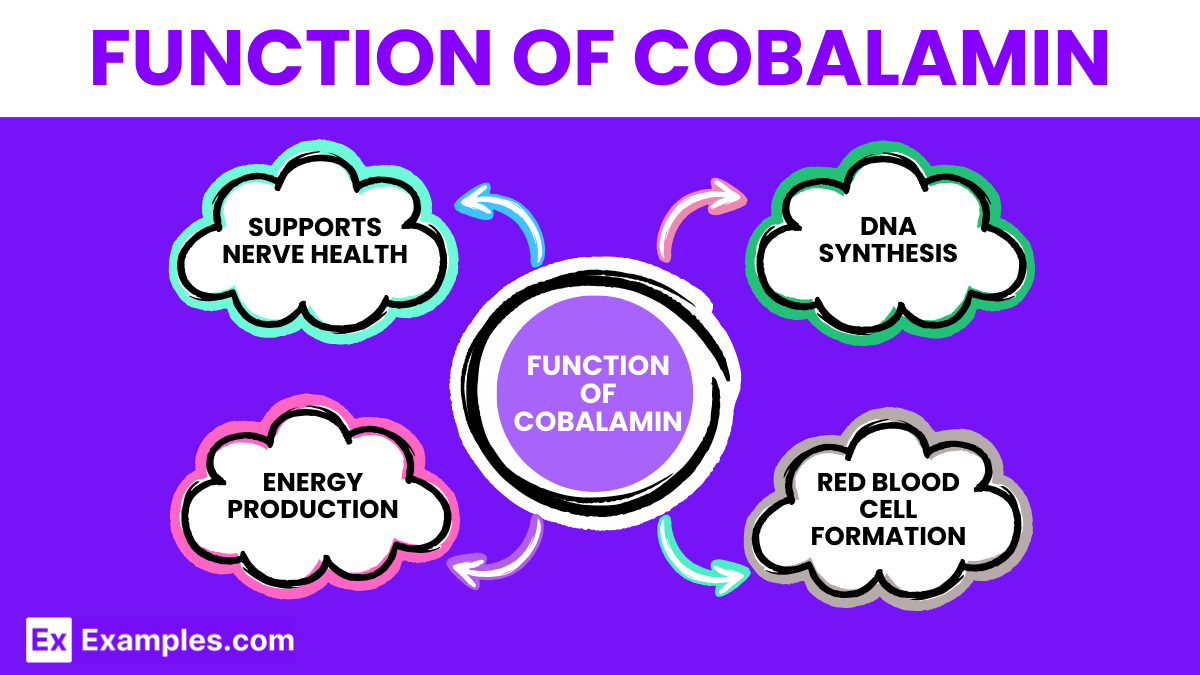
Cobalamin helps maintain the health of nerve cells by aiding in the formation of the protective covering around nerves, known as the myelin sheath. This covering is crucial for effective nerve impulse transmission.
Cobalamin plays a critical role in the production of red blood cells. By participating in the process of cell division, cobalamin ensures that the body can produce healthy red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
Cobalamin is vital for DNA synthesis, the process that creates new DNA molecules. This is essential for all cellular functions and growth.
It is involved in energy production within the body by being part of the metabolism of every cell. It helps in converting carbohydrates into glucose, which the body uses for energy.
Cobalamin plays a key role in converting food into glucose, which is the body’s main source of energy. This process helps boost overall energy levels, keeping you active and alert.
By aiding in the maintenance of nerve cells and the formation of the nerve-protecting myelin sheath, cobalamin supports brain health and cognitive functions, reducing the risk of memory loss and other brain-related issues.
Cobalamin contributes to the production of serotonin, a chemical responsible for regulating mood. Adequate levels of Vitamin B12 can improve mood and help prevent disorders related to mood swings, such as depression and anxiety.
Cobalamin is essential for the production of red blood cells. Adequate intake prevents megaloblastic anemia, a condition that makes people tired and weak due to the production of abnormally large red blood cells that do not function properly.
Yes, cobalamin is another name for Vitamin B12, an essential nutrient that supports nerve health and red blood cell production.
Cobalamin levels are measured to assess Vitamin B12 status in the body, crucial for diagnosing deficiencies affecting nerve function and anemia.
Cobalamin is generally good, essential for brain function, DNA synthesis, and energy production. Over-supplementation can cause mild side effects.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of cobalamin in the body?
Energy production
DNA synthesis
Bone growth
Immune response
Which of the following is a common dietary source of cobalamin?
Citrus fruits
Leafy green vegetables
Meat and dairy products
Whole grains
A deficiency in cobalamin can lead to which of the following conditions?
Scurvy
Pellagra
Anemia
Rickets
Which condition is associated with a lack of intrinsic factor, affecting cobalamin absorption?
Celiac disease
Crohn's disease
Pernicious anemia
Ulcerative colitis
What is the recommended method for diagnosing cobalamin deficiency?
Blood pressure test
Serum vitamin B12 levels
Urine analysis
Skin biopsy
Which population is at higher risk for cobalamin deficiency?
Children
Pregnant women
Vegetarians and vegans
Athletes
Cobalamin is essential for the metabolism of which amino acid?
Methionine
Glycine
Glutamine
Serine
What form of cobalamin is commonly used in dietary supplements?
Methylcobalamin
Folate
Pyridoxine
Retinol
How does a cobalamin deficiency affect nerve function?
Causes nerve damage
Enhances nerve function
Has no effect on nerves
Improves nerve regeneration
Which test is often used to check for cobalamin deficiency in patients with neurological symptoms?
X-ray
MRI scan
Homocysteine levels
Liver function test
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

