What is condensation?
The process of a liquid turning into a gas
The process of a gas turning into a liquid
The process of a solid turning into a liquid
The process of a liquid turning into a solid

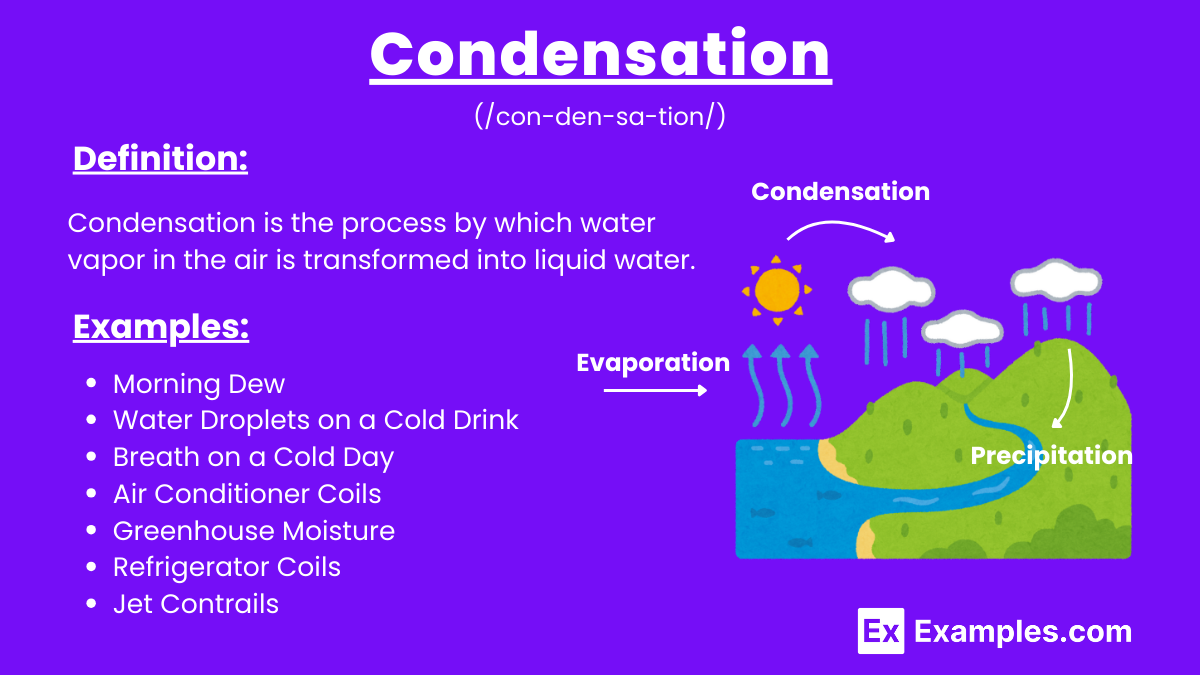
Condensation is the process by which water vapor in the air is transformed into liquid water. This occurs when the air is cooled to its dew point, the temperature at which it becomes saturated and can no longer hold all of the moisture in the form of vapor. As a result, the excess water vapor condenses into tiny droplets, forming clouds, fog, dew, or frost, depending on the environmental conditions. Condensation is a crucial part of the water cycle, playing a significant role in weather patterns and climate regulation. It is the opposite of evaporation, where liquid water is converted into water vapor. The process of condensation is closely related to units of humidity, which measure the amount of moisture in the air.
Condensation is the process by which water vapor in the air is transformed into liquid water. This transformation occurs when the air is cooled to its dew point, causing the water vapor to lose energy and form tiny droplets. Condensation is a crucial part of the water cycle, as it is responsible for the formation of clouds and precipitation.
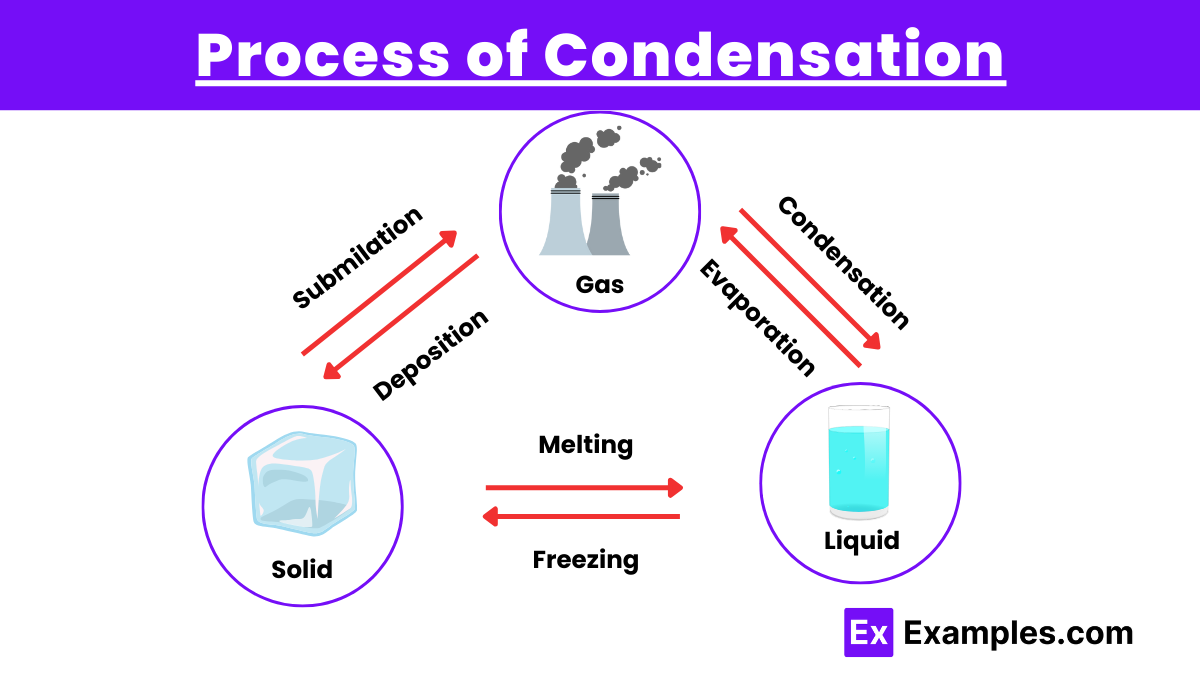
Condensation is a crucial component of the water cycle, involving the transformation of water vapor into liquid water. The process can be broken down into several key steps:
Condensation is a vital process in the water cycle, where water vapor in the air transforms into liquid water. This phase is essential for the formation of clouds and precipitation, which are crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Here are the key points about condensation within the water cycle:
Condensation occurs in various forms, depending on the environmental conditions and surfaces involved. Here are the primary types of condensation:
Condensation occurs when warm, moist air comes into contact with a cold surface, causing the water vapor to cool and turn into liquid.
Common examples include dew forming on grass, water droplets on a cold glass, and foggy mirrors after a shower.
Cold surfaces lower the temperature of the air around them, causing the water vapor in the air to lose energy and condense into liquid.
Temperature affects condensation by cooling warm air, which reduces the air’s capacity to hold water vapor, leading to the formation of liquid droplets.
Condensation is a physical change because it involves a change in the state of matter from gas to liquid without altering the chemical composition.
In the water cycle, condensation is the process that forms clouds when water vapor rises, cools, and changes into liquid water droplets.
Condensation is the change from gas to liquid, while evaporation is the change from liquid to gas.
Condensation can occur at any temperature where the air reaches its dew point, which is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture.
The dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor and condensation begins.
Windows fog up in winter because the warm, moist indoor air comes into contact with the cold window surface, causing condensation.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is condensation?
The process of a liquid turning into a gas
The process of a gas turning into a liquid
The process of a solid turning into a liquid
The process of a liquid turning into a solid
What happens to the temperature of a gas during condensation?
It increases
It decreases
It remains constant
It fluctuates randomly
Where is condensation commonly observed in daily life?
When boiling water
When ice melts
When dew forms on a cold surface
When water evaporates from a lake
What is the role of condensation in the water cycle?
To form clouds
To increase evaporation
To decrease precipitation
To heat the atmosphere
In air conditioning systems, what happens to the air as it cools?
It condenses
It evaporates
It freezes
It stays the same
Which of the following factors primarily affects the rate of condensation?
The volume of the liquid
The temperature of the gas
The color of the surface
The shape of the container
What is a common example of condensation in the home?
Ice forming in the freezer
Water droplets on the inside of a window
A boiling kettle
Drying clothes on a line
What state of matter does water vapor change into during condensation?
Solid
Gas
Liquid
Plasma
How does condensation differ from evaporation?
Condensation involves cooling, while evaporation involves heating
Evaporation involves cooling, while condensation involves heating
Condensation and evaporation are identical processes
Evaporation produces solid, while condensation produces liquid
Which process releases latent heat, condensation or evaporation?
Condensation
Evaporation
Both processes release the same amount of heat
Neither process releases heat
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

