What is the formula for calculating density?
Density = Mass × Volume
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
Density = Volume ÷ Mass
Density = Mass + Volume

Density is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the mass of a substance per unit volume. It is crucial in understanding material properties and behavior. The density formula is expressed as p = M/V where ( P ) is density, ( m ) is mass, and ( V ) is volume. In electrochemistry, charge density is important, defined as the electric charge per unit area or volume, calculated using the charge density formula σ = Q/A or P = Q/V
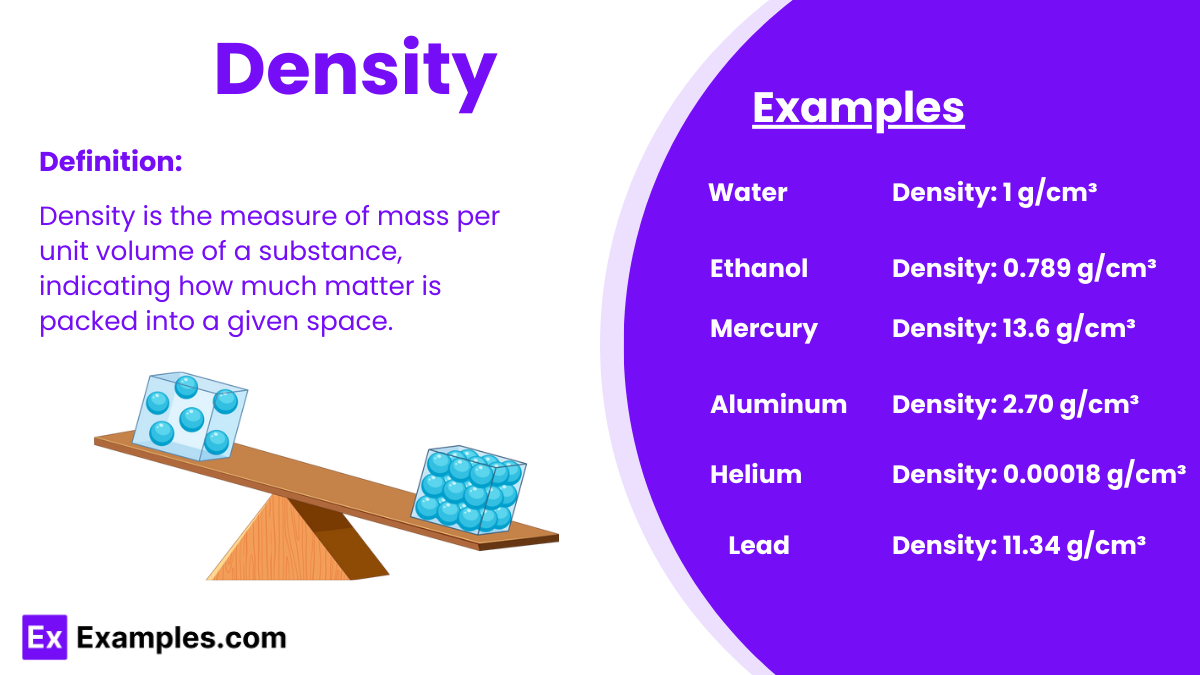
Density is a measure of mass per unit volume of a substance. It is calculated by dividing an object’s mass by its volume and is typically expressed in units of grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).

Density(ρ) = Mass(m)/Volume(V)
Determine the mass (( m )) of the object using a balance or scale. Ensure the mass is measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
Determine the volume (( V )) of the object. For regular shapes, use mathematical formulas (e.g., ( V = l x w x h ) for a rectangular prism). For irregular shapes, use water displacement in a graduated cylinder to find the volume in cubic centimeters (cm³) or cubic meters (m³).
Ensure that the mass and volume are in compatible units. For example, if mass is in grams, volume should be in cubic centimeters (cm³). If mass is in kilograms, volume should be in cubic meters (m³).
Use the density formula:
[ p = m/v ]
Where:
Divide the mass by the volume to obtain the density. Ensure the result is in the appropriate units (e.g., g/cm³ or kg/m³).
The units of density indicate how much mass is contained within a given volume. Common units include kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) in the International System of Units (SI) and grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) in the metric system. Other units like pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft³) are also used in specific contexts.
The density of water is a critical reference value in science and engineering. At standard temperature and pressure (STP), the density of water is:
This value is essential for various calculations and experiments, serving as a benchmark for comparing the densities of other substances.
| Substance | Density (g/cm³) | Aspects |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.00 | Basis for comparison, essential for life |
| Air | 0.0012 | Varies with temperature and pressure, low density |
| Gold | 19.32 | High density, valuable, used in jewelry and finance |
| Iron | 7.87 | Common metal, used in construction and manufacturing |
| Aluminum | 2.70 | Lightweight, used in aerospace and packaging |
| Mercury | 13.53 | Only liquid metal at room temperature, dense |
| Ice | 0.92 | Less dense than water, floats, important in climates |
| Granite | 2.75 | Common rock, used in construction |
| Lead | 11.34 | Dense, used in batteries and radiation shielding |
| Ethanol | 0.79 | Alcohol, less dense than water, used in fuels |
Density is calculated by dividing mass by volume.
Density is commonly expressed in g/cm³ or kg/m³.
Density helps identify substances and determine their properties.
The density of water is 1.00 g/cm³.
Yes, density typically decreases as temperature increases.
The density of air is approximately 0.0012 g/cm³.
Density increases with increasing pressure.
The density of gold is 19.32 g/cm³.
Ice is less dense than water.
The density of aluminum is 2.70 g/cm³.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for calculating density?
Density = Mass × Volume
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
Density = Volume ÷ Mass
Density = Mass + Volume
If an object has a mass of 50 grams and a volume of 10 cm³, what is its density?
1 g/cm³
2 g/cm³
5 g/cm³
0.5 g/cm³
What happens to the density of an object if its mass increases but its volume remains constant?
Density decreases
Density increases
Density remains the same
Density becomes zero
Which of the following units can be used to express density?
kg/m³
m/s²
Newton
Joule
An object has a mass of 120 grams and a density of 6 g/cm³. What is its volume?
20 cm³
30 cm³
40 cm³
50 cm³
If two objects have the same mass but different volumes, which one has the higher density?
The object with larger volume
The object with smaller volume
Both have the same density
It depends on the shape of the objects
A cube has a volume of 8 cm³ and a mass of 32 grams. What is the density of the cube?
1 g/cm³
2 g/cm³
3 g/cm³
4 g/cm³
Which material typically has the highest density?
Air
Water
Lead
Wood
What is the relationship between temperature and the density of most materials?
As temperature increases, density increases
As temperature decreases, density decreases
As temperature increases, density decreases
There is no relationship between temperature and density
Which of the following objects will float in water (density of water = 1 g/cm³)?
An object with a density of 0.5 g/cm³
An object with a density of 1.5 g/cm³
An object with a density of 2 g/cm³
An object with a density of 1 g/cm³
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

