What are disaccharides composed of?
One sugar molecule
Two sugar molecules
Three sugar molecules
Four sugar molecules

Sugar is a basic composition of various foods that provide potential energy or chemical energy to the entity should they consume the sugar. Complex forms of sugars include complex carbohydrates and disaccharides, which will provide energy depending on the context, tone, and theme of the environment when the person will digest the food.
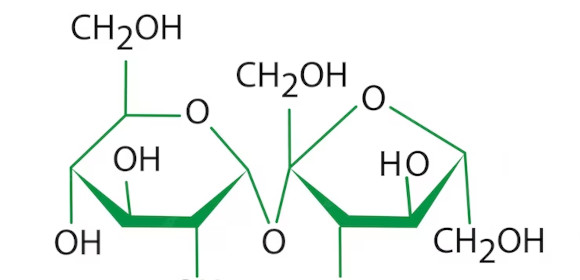
Disaccharide is one of the complex forms sugar can take as it is a compound of two monosaccharides linked by a specific formation or chain. Two or more disaccharides create complex carbohydrates. One of the most common examples of disaccharides is table sugar, which is also known as sucrose. If you want to learn more about disaccharides and other forms of sugar you may use any of the references and links in the examples above.
Disaccharides have a very unique structure because two monosaccharides link together to form said substance. Not only that but disaccharides have specific unique elements that a person can conduct observations on.
Disaccharides and monosaccharides are water soluble, this means that when a person introduces water to the substance, it is immediately mixed. If the substance doesn’t fully disappear or mix with the whole solution then it is not a disaccharide or a monosaccharide.
Disaccharides often present themselves as a powder or crystalline-like substance that will taste sweet or remotely sweet. If the pure form of the substance doesn’t have the same characteristics as a disaccharide, then it isn’t one.
A benedict test is a scientific tool people use to detect simple sugars in a specific substance or object. It will produce results that will identify the presence of reducing sugars, which are either monosaccharides or disaccharides. Note, there are specific disaccharides that do not present themselves as reducing sugars like maltase; you must be keen and vigilant when using the benedict test to determine the type of sugar.
The basic structure of the disaccharide will have two monosaccharides that have a glycosidic linkage. You can easily examine this structure by observing it through a microscope or any other investigatory tools available. You must also have a reference of the basic structure of a disaccharide, so you will know what you will compare and contrast the sample with.
Lactose is a disaccharide that is present in cow milk, which requires a specific enzyme to properly digest said sugars. Lactose has a lot of sugar, which will provide the person with chemical energy through the bloodstream. People who cannot digest lactose have a condition called lactose intolerance.
Starch is a carbohydrate that has a composition of multiple disaccharides. These complex sugars make up most bodies of vegetables, fruits, and grapes, which will create a fibrous body for said structure.
Maltase or malt sugar is a type of disaccharide that people can primarily find in grains and wheat seeds. The process of malting allows people to create beer, whiskey, milk, and vinegar. This is because of the water-soluble nature of disaccharides, which will germinate the seed when submerged in water. The germination will stop when the person will dry the germinating seed.
Disaccharides are a type of sugar structure that has two monosaccharides fused together with a specific linking structure. It is important to know what disaccharides are, as these compounds have various real-life applications. Not only that but some people cannot properly digest specific forms of disaccharides, which will cause health issues and problems that might become lethal if improperly treated. Therefore it is important to know what substances disaccharides can present themselves as.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What are disaccharides composed of?
One sugar molecule
Two sugar molecules
Three sugar molecules
Four sugar molecules
Which of the following is a common disaccharide found in milk?
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
Glucose
Which disaccharide is commonly known as table sugar?
Lactose
Maltose
Sucrose
Cellulose
What is the primary sugar in maltose?
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Sucrose
How is sucrose hydrolyzed in the human body?
By amylase
By lactase
By sucrase
By maltase
What is the primary role of disaccharides in the diet?
Provide fiber
Provide vitamins
Provide energy
Aid digestion
Which disaccharide is formed from glucose and fructose?
Lactose
Maltose
Sucrose
Trehalose
What enzyme breaks down lactose in the digestive system?
Amylase
Lactase
Sucrase
Maltase
Which of these is not a disaccharide?
Sucrose
Lactose
Fructose
Maltose
What is the primary function of disaccharides in plants?
Store genetic information
Store energy
Provide structural support
Transport nutrients
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

