What is the molecular formula of ethane?
CH₄
C₂H₄
C2H₆
C₃H₈

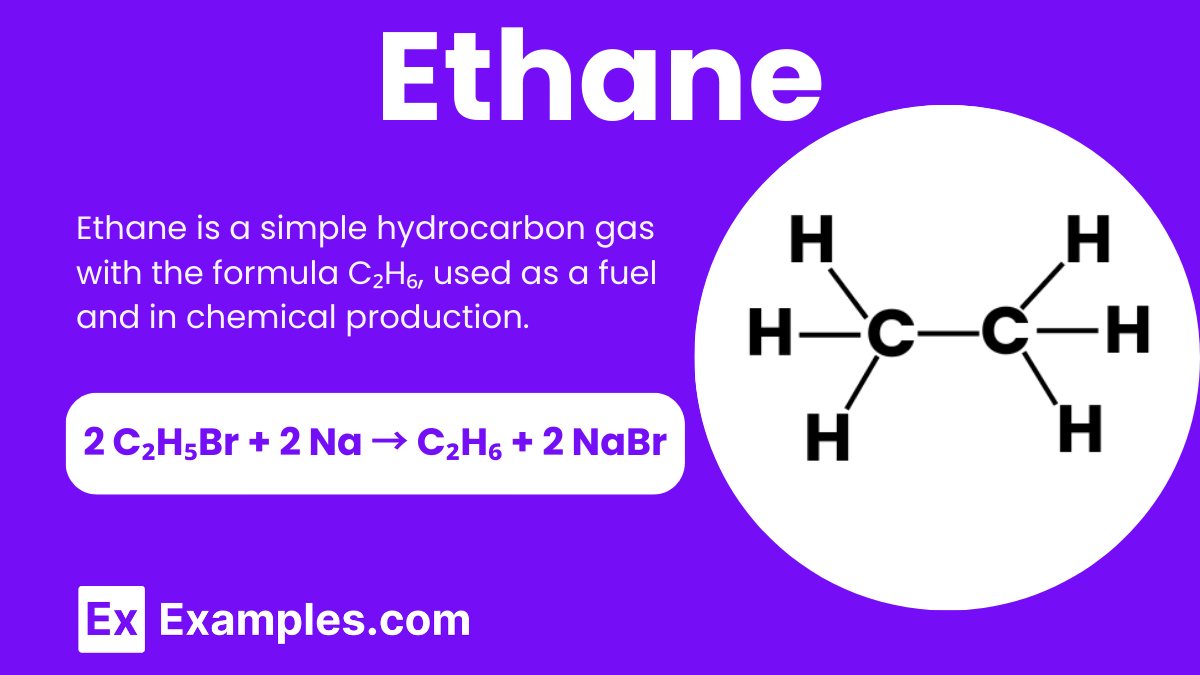
Ethane is a simple chemical compound that plays an essential role in chemistry. It consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms, making its molecular formula C₂H₆. Ethane is a colorless, odorless gas found in natural gas and petroleum. It is a key building block in the production of various chemicals and plastics. Understanding ethane helps us to grasp basic concepts in organic chemistry, as it represents one of the simplest hydrocarbons in the alkane family.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | CH₃CH₃ |
| Hill Formula | C₂H₆ |
| Name | Ethane |
| Alternate Names | Bimethyl, Dimethyl, Ethyl Hydride, Freon 170, Methylmethane, R-170 |
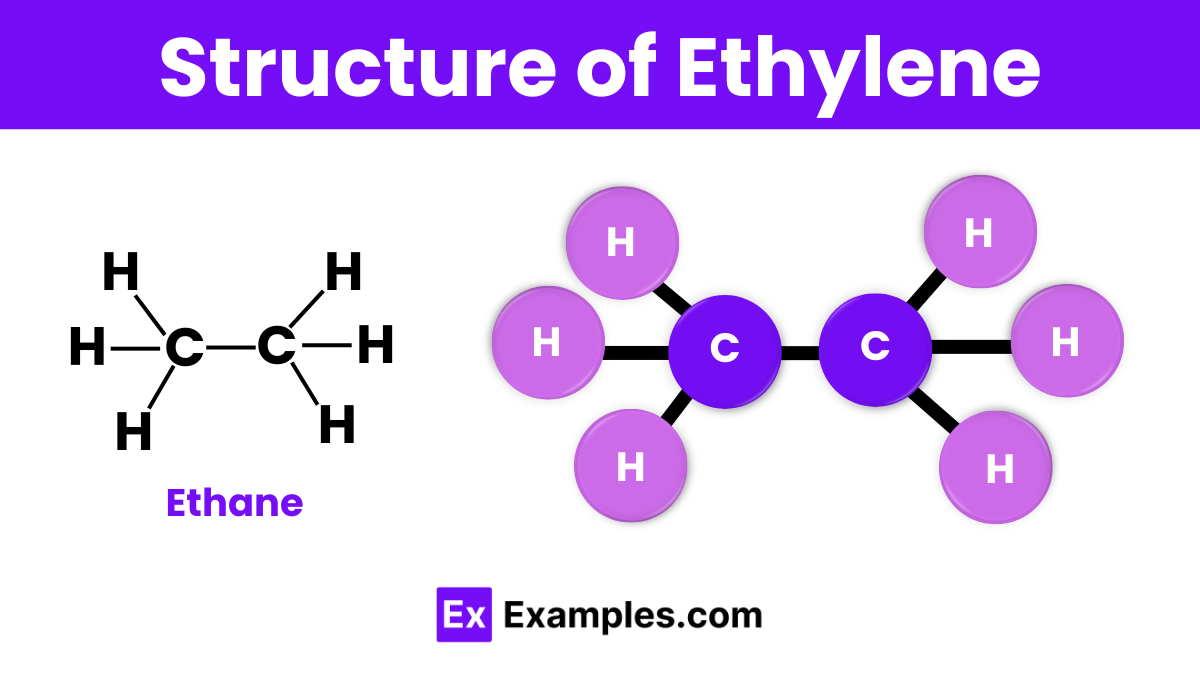
Ethane has a simple structure where two carbon atoms are bonded together, and each carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms. The carbon atoms form a single covalent bond between them, making the formula C₂H₆. The structure is often represented as H₃C-CH₃, showing that each carbon atom is surrounded by three hydrogen atoms. This arrangement creates a tetrahedral shape around each carbon, giving ethane its stable structure.
You can prepare ethane in the laboratory through a process called Wurtz reaction. In this method, you react bromoethane (C₂H₅Br) with sodium (Na) in the presence of dry ether. The reaction combines two bromoethane molecules, resulting in the formation of ethane and sodium bromide.
The chemical equation for this reaction is:
In this equation, two molecules of bromoethane react with two sodium atoms to produce one molecule of ethane and two molecules of sodium bromide. This method is commonly used in organic chemistry to create simple alkanes like ethane
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| State at Room Temperature | Gas |
| Color | Colorless |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Boiling Point | -88.6°C |
| Melting Point | -182.8°C |
| Density | 1.26 kg/m³ (at 15°C) |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble |
| Molecular Weight | 30.07 g/mol |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 74-84-0 |
| Beilstein Number | 1730716 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 6324 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24857772 |
| SMILES Identifier | CC |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C2H6/c1-2/h1-2H3 |
| RTECS Number | KH3800000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00009023 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 1 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 4 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
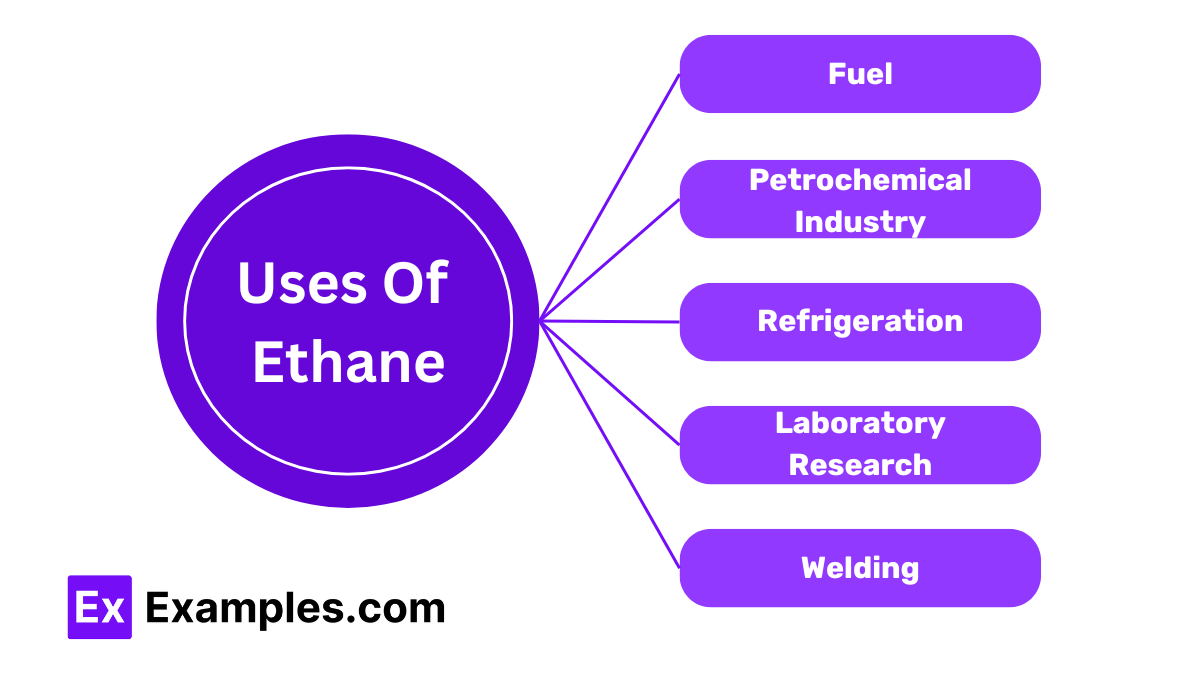
Ethane is used as a fuel in power plants and heating systems. It burns cleanly, producing energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
Ethane is a key raw material in the petrochemical industry. It is cracked to produce ethylene, which is used to make plastics, antifreeze, and detergents.
Ethane is used as a refrigerant in cryogenic refrigeration systems due to its low boiling point. It helps in cooling processes that require very low temperatures.
Ethane is used in welding and cutting metals. Its high heat of combustion makes it effective for these applications.
Ethane is used in laboratories for various research purposes. It serves as a standard gas for calibrating equipment and studying reactions.
Ethane can be converted into ethanol, a valuable industrial and fuel chemical. This conversion is achieved through a series of chemical reactions.
Ethane gas is not considered highly toxic, but inhaling large quantities can cause dizziness, headaches, and respiratory issues.
Ethane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. It can be liquefied under high pressure or low temperatures.
The common name for ethane is “methyl methane.” It is a simple hydrocarbon in the alkane family.
Ethane is not highly toxic to humans, but excessive inhalation can cause respiratory problems and central nervous system effects.
Ethane is commonly found in natural gas and petroleum. It is also present in small amounts in volcanic gases and some plants.
Ethane is not used directly for food. It is mainly utilized in industrial processes and as a feedstock in chemical production.
Ethane is a major component of natural gas, burns cleanly, and can be used to produce ethylene, a key ingredient in plastics.
Farmers use ethene (ethylene) to ripen fruits and regulate plant growth. It accelerates the ripening process and enhances crop yield.
Ethene is commonly found in ripening fruits, vehicle emissions, and as a byproduct of industrial processes. It is also present in natural gas.
Farmers use ethene (ethylene) to ripen fruits and regulate plant growth. It accelerates the ripening process and enhances crop yield.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the molecular formula of ethane?
CH₄
C₂H₄
C2H₆
C₃H₈
Ethane belongs to which category of hydrocarbons?
Alkenes
Alkynes
Alkanes
Aromatics
What type of bond exists between the carbon atoms in an ethane molecule?
Single bond
Double bond
Triple bond
Ionic bond
Which of the following is a common use of ethane?
Solvent
Fuel
Plastic production
Lubricant
What is the boiling point of ethane at standard atmospheric pressure?
-88°C
-42°C
0°C
25°C
Ethane can be obtained from which natural source?
Petroleum
Coal
Biomass
Water
How many sigma bonds are present in an ethane molecule?
5
6
7
8
The structural formula of ethane can be represented as:
H-C≡C-H
H₂C=CH₂
H₃C-CH₃
HC≡CH
Which process is used to separate ethane from natural gas?
Distillation
Electrolysis
Filtration
Crystallization
In which state of matter is ethane at room temperature?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Plasma
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

