What primarily drives the process of evaporation?
Air pressure
Chemical reactions
Heat energy
Magnetic fields

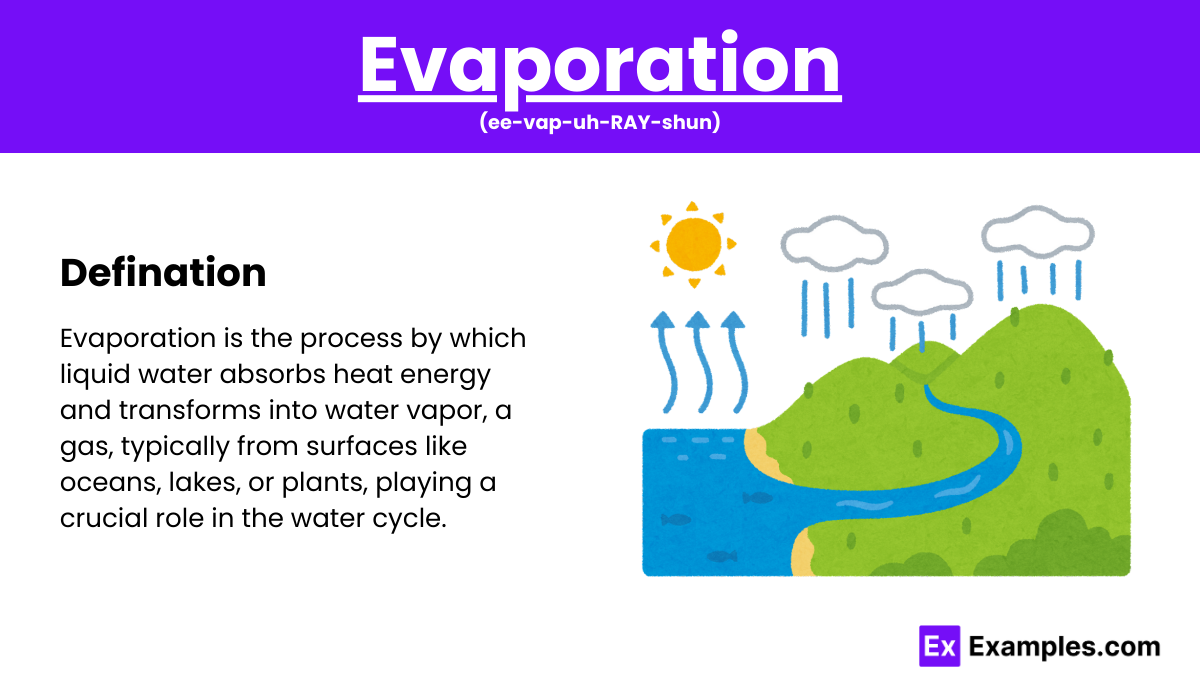
Evaporation is the process where liquid water transforms into water vapor, a gas. This occurs when water molecules gain enough energy to break free from the liquid’s surface. Evaporation is a crucial part of the water cycle, influencing weather and climate. Factors like temperature, wind, and surface area affect the evaporation rate. This natural process is essential for distributing heat and maintaining the Earth’s hydrological balance.
Evaporation is the process where liquid water turns into water vapor. This occurs when water molecules absorb enough energy to escape from the liquid’s surface into the air, significantly influenced by temperature, surface area, and air movement. It’s essential in the water cycle.
| Aspect | Evaporation | Condensation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where liquid turns into gas. | Process where gas turns into liquid. |
| Energy Transfer | Absorbs heat energy from the surroundings. | Releases heat energy to the surroundings. |
| Temperature | Occurs at any temperature, faster at higher temperatures. | Occurs when gas cools down to its dew point. |
| Example | Water evaporating from a puddle. | Dew forming on grass in the morning. |
| Process | Increases kinetic energy of molecules. | Decreases kinetic energy of molecules. |
| Surface Area | Larger surface area increases rate. | Can occur on various surfaces (e.g., windows). |
| Humidity Effect | Lower humidity accelerates rate. | Higher humidity slows rate. |
| Occurrence | Common in dry, warm environments. | Common in cool, humid environments. |
| Role in Water Cycle | Moves water from Earth’s surface to atmosphere. | Returns water from atmosphere to Earth’s surface. |
| Impact on Climate | Cools the environment by absorbing heat. | Warms the environment by releasing heat. |
Evaporation is caused by the absorption of heat energy by water molecules.
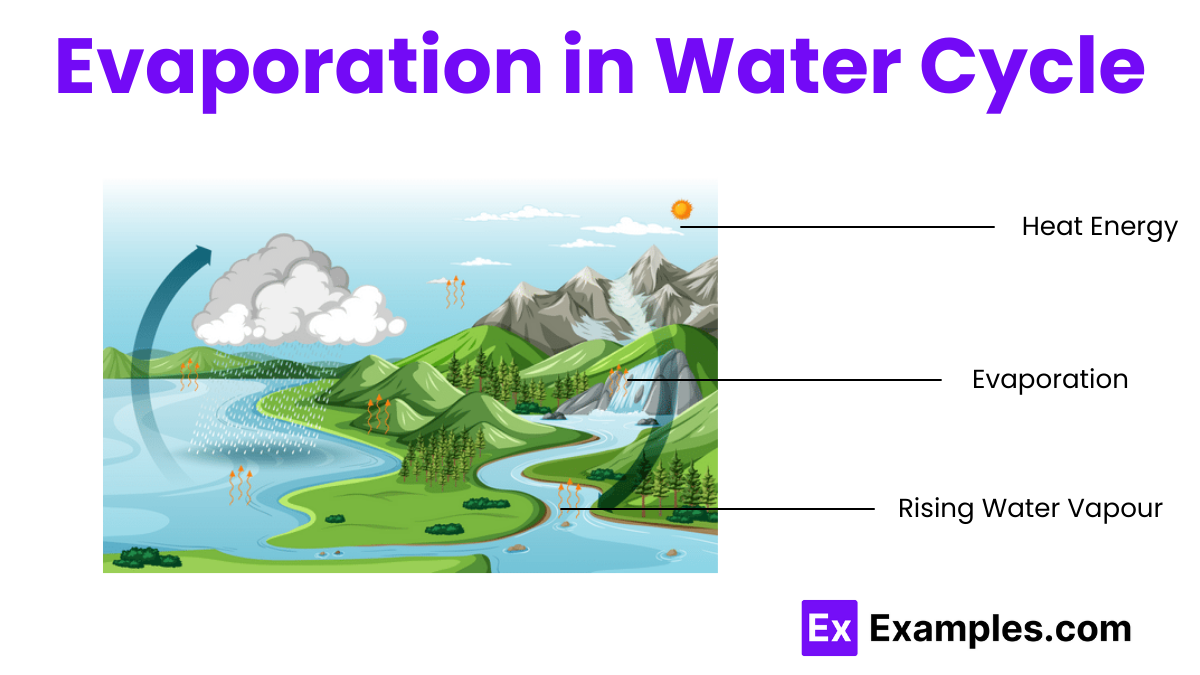
Evaporation occurs in oceans, lakes, rivers, and other bodies of water.
Higher temperatures increase the rate of evaporation.
Yes, higher wind speeds enhance evaporation by removing water vapor from the surface.
Sweat evaporates to cool the body by removing heat.
Yes, evaporation can occur at all temperatures, though it is faster at higher temperatures.
Evaporation transfers water from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere.
Lower humidity levels increase the rate of evaporation.
Evaporation occurs at any temperature, while boiling occurs at a specific temperature.
Larger surface areas increase the rate of evaporation.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What primarily drives the process of evaporation?
Air pressure
Chemical reactions
Heat energy
Magnetic fields
How does increasing the surface area of a liquid affect its evaporation rate?
It decreases the rate of evaporation
It has no effect
It increases the rate of evaporation
It stops evaporation
Which of the following factors does not affect the rate of evaporation?
Temperature
Humidity
Surface area
Color of the liquid
In which situation will evaporation occur most rapidly?
On a cold, humid day
In a warm, dry environment
Under a vacuum
In the dark
How does humidity impact evaporation?
Higher humidity speeds up evaporation
Higher humidity slows down evaporation
Humidity has no effect
Humidity causes evaporation to stop completely
Which of the following liquids will evaporate the fastest under the same conditions?
Water
Alcohol
Honey
Oil
What happens to the temperature of a liquid as it evaporates?
The temperature increases
The temperature stays the same
The temperature decreases
The temperature fluctuates
Why do clothes dry faster on a sunny day compared to a cloudy day?
Higher temperatures increase evaporation rates
Lower temperatures decrease evaporation rates
Sunlight directly dries clothes
Clouds cause increased humidity
What role does wind play in the evaporation process?
Wind decreases the rate of evaporation
Wind has no effect on evaporation
Wind increases the rate of evaporation
Wind causes condensation
Which of the following processes is most similar to evaporation?
Melting
Condensation
Freezing
Sublimation
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

