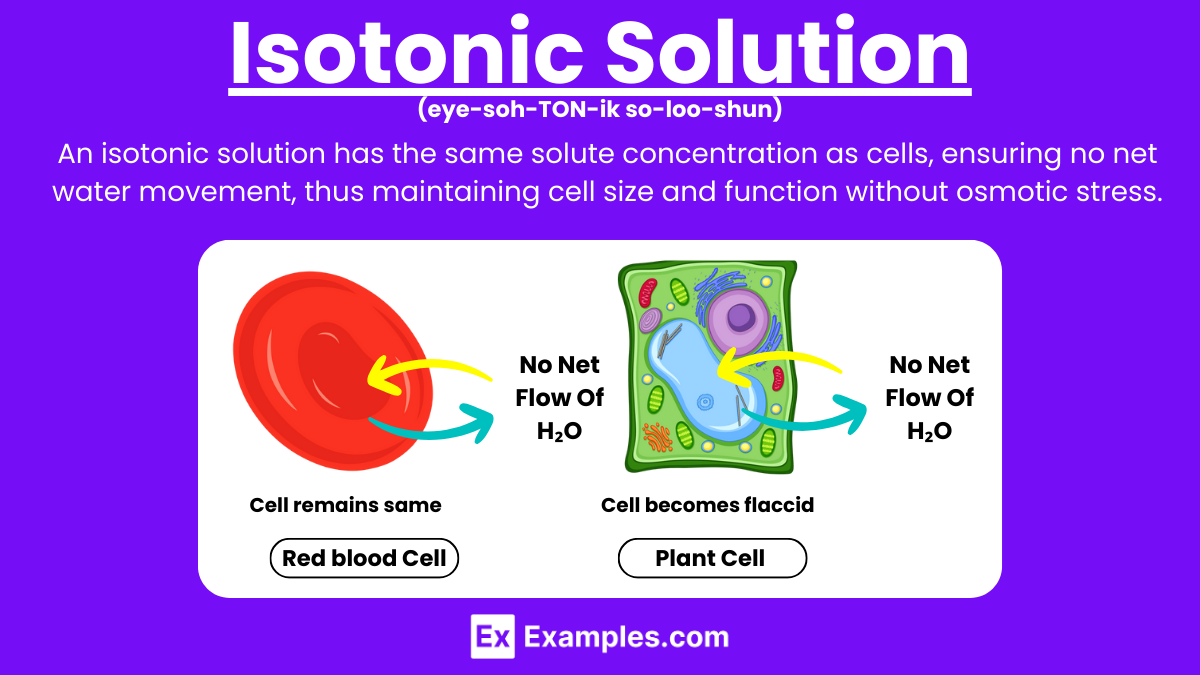
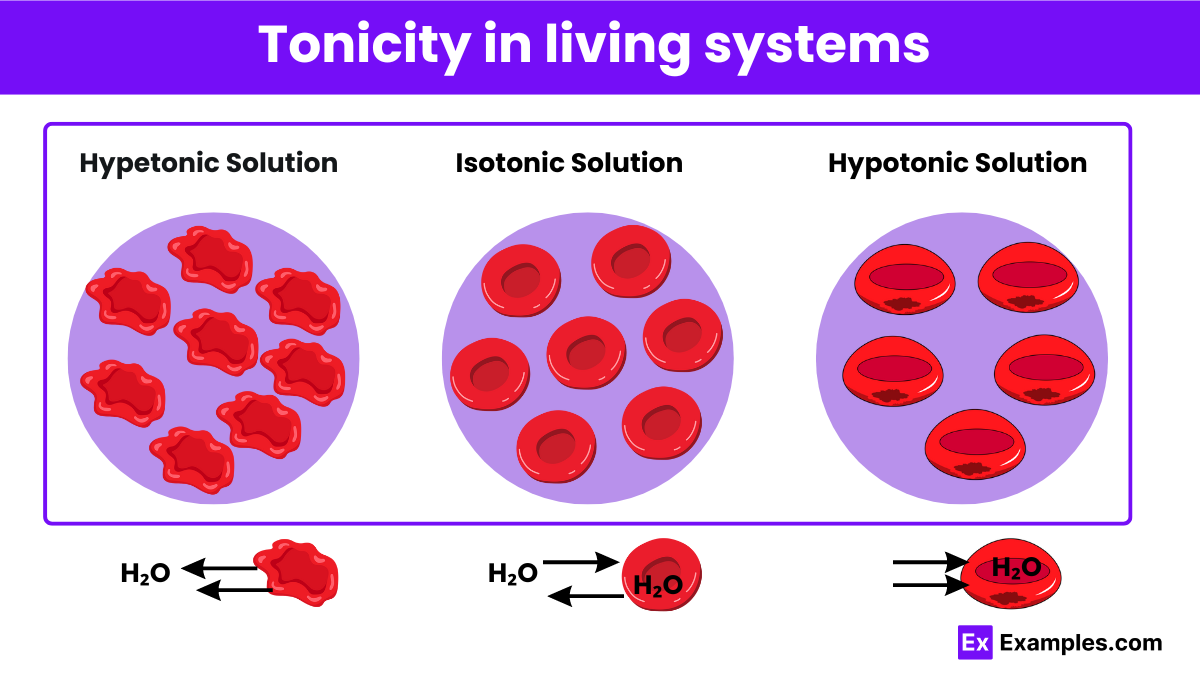
What is the definition of an isotonic solution?
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes than the cell
A solution with the same concentration of solutes as the cell
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes than the cell
A solution with no solutes