What defines isotopes of an element?
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons
Same number of neutrons, different number of protons
Different number of protons and neutrons
Same number of protons and neutrons
Some elements have different forms when scientists find them in nature or through scientific manufacturing. Researchers have categorized some forms of these elements into a category called isotopes.
Isotopes are a category of a family of elements that all share the same amount of protons but have different numbers of neutrons or energy. Elements that can have isotopes will basically have different stable and unstable forms that their subatomic particles and structure will affect.
Atomic mass is the overall amount of atomic matter inside a specific atom of an element. The average atomic mass uses the mass of the isotopes and the abundance of said isotopes of a specific element.
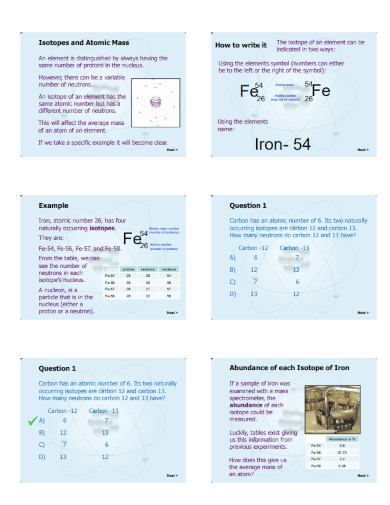
Begin by obtaining the formula for atomic mass, which will act as the outline format for the whole equation. The formula for atomic mass is Average Atomic Mass = (Mass of Isotope 1 x Fractional Abundance of Isotope 1) + (Mass of Isotope 2 x Fractional Abundance of Isotope 2), you may extend the formula to accommodate more isotopes.
After obtaining the formula for atomic mass, you must obtain the values the question provides. Be sure that the values for the isotopes are using the correct form of measurement, which is an atomic mass unit or amu. If the measurement is wrong, convert the values accordingly.
After you have obtained the given values and have ensured that it is using the correct measurements, you must now substitute them for the correct variables in the formula. Doing this will help detail the various steps you will undergo to solve the overall equation.
When you have finished substituting all the values in the formula, you will have a working equation you can use to obtain the atomic weight. Solve the equation, which will give you an answer that will be measured in amu. If the question is asking for a different measurement, be sure to convert the answer to the desired measurement.
Radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes are a type of isotope that has an unstable collection of protons and neutrons that will later balance back to create a stable isotope. A radioactive isotope will transform back into a stable isotope through radioactive decay, which will cause it to shed the excess proton, neutron, or potential energy. Examples of radioactive isotopes include carbon-14, the longest-living radioactive isotope, and cobalt-60, a radioactive isotope that doctors use as a product in their service to treat cancer through radiation therapy.
Carbon-12 is the most stable isotope one can find in nature and acts as the standard form or the standard model researchers use to measure other isotopes. This isotope is very unique for having an isotope mass of 12 da, which is composed of six protons, six neutrons, and six electrons. This type of isotope makes up 98 to 99% of most organic beings and organisms in the biosphere.
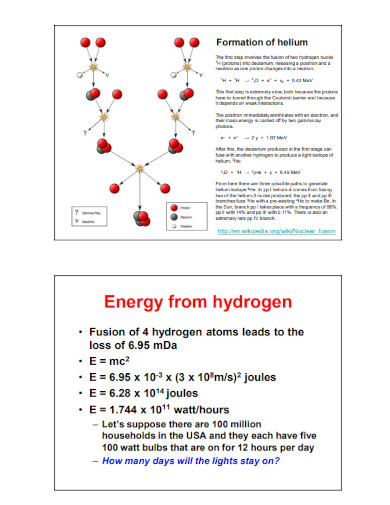
Uranium 235 is a radioactive isotope that is known for the amount of nuclear energy it releases through nuclear fission. Atomic bombs make use of uranium-235 or plutonium-239 as their main ingredient. Current nuclear reactors use an enhanced form of uranium-235 as a commodity to be refined in the reactor to obtain nuclear and chemical energy and convert it to electrical energy or electricity.
Isotopes are a subtype or category of an element all of which has the same amount of protons and different numbers of neutrons, and energy making up the subatomic particles. People need to understand the concept of isotopes as this chemical property will dictate the form the element will take.

Some elements have different forms when scientists find them in nature or through scientific manufacturing. Researchers have categorized some forms of these elements into a category called isotopes.
springtownisd.net
Details
File Format
Size: 60 KB

annualreviews.org
Details
File Format
Size: 119 KB

ias.ac.in
Details
File Format
Size: 58 KB

luna.cas.usf.edu
Details
File Format
Size: 85 KB

large.stanford.edu
Details
File Format
Size: 69 KB

ldeo.columbia.edu
Details
File Format
Size: 64 KB

usitc.gov
Details
File Format
Size: 92 KB
uab.edu
Details
File Format
Size: 56 KB

nios.ac.in
Details
File Format
Size: 49 KB

eolss.net
Details
File Format
Size: 71 KB

flinnsci.com
Details
File Format
Size: 78 KB

scholarworks.wm.edu
Details
File Format
Size: 67 KB
web.viu.ca
Details
File Format
Size: 55 KB
Isotopes are a category of a family of elements that all share the same amount of protons but have different numbers of neutrons or energy. Elements that can have isotopes will basically have different stable and unstable forms that their subatomic particles and structure will affect.
Atomic mass is the overall amount of atomic matter inside a specific atom of an element. The average atomic mass uses the mass of the isotopes and the abundance of said isotopes of a specific element.
Begin by obtaining the formula for atomic mass, which will act as the outline format for the whole equation. The formula for atomic mass is Average Atomic Mass = (Mass of Isotope 1 x Fractional Abundance of Isotope 1) + (Mass of Isotope 2 x Fractional Abundance of Isotope 2), you may extend the formula to accommodate more isotopes.
After obtaining the formula for atomic mass, you must obtain the values the question provides. Be sure that the values for the isotopes are using the correct form of measurement, which is an atomic mass unit or amu. If the measurement is wrong, convert the values accordingly.
After you have obtained the given values and have ensured that it is using the correct measurements, you must now substitute them for the correct variables in the formula. Doing this will help detail the various steps you will undergo to solve the overall equation.
When you have finished substituting all the values in the formula, you will have a working equation you can use to obtain the atomic weight. Solve the equation, which will give you an answer that will be measured in amu. If the question is asking for a different measurement, be sure to convert the answer to the desired measurement.
Radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes are a type of isotope that has an unstable collection of protons and neutrons that will later balance back to create a stable isotope. A radioactive isotope will transform back into a stable isotope through radioactive decay, which will cause it to shed the excess proton, neutron, or potential energy. Examples of radioactive isotopes include carbon-14, the longest-living radioactive isotope, and cobalt-60, a radioactive isotope that doctors use as a product in their service to treat cancer through radiation therapy.
Carbon-12 is the most stable isotope one can find in nature and acts as the standard form or the standard model researchers use to measure other isotopes. This isotope is very unique for having an isotope mass of 12 da, which is composed of six protons, six neutrons, and six electrons. This type of isotope makes up 98 to 99% of most organic beings and organisms in the biosphere.
Uranium 235 is a radioactive isotope that is known for the amount of nuclear energy it releases through nuclear fission. Atomic bombs make use of uranium-235 or plutonium-239 as their main ingredient. Current nuclear reactors use an enhanced form of uranium-235 as a commodity to be refined in the reactor to obtain nuclear and chemical energy and convert it to electrical energy or electricity.
Isotopes are a subtype or category of an element all of which has the same amount of protons and different numbers of neutrons, and energy making up the subatomic particles. People need to understand the concept of isotopes as this chemical property will dictate the form the element will take.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What defines isotopes of an element?
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons
Same number of neutrons, different number of protons
Different number of protons and neutrons
Same number of protons and neutrons
Which of the following pairs are isotopes?
Carbon-12 and Carbon-14
Oxygen-16 and Nitrogen-16
Helium-4 and Helium-3
Uranium-235 and Uranium-238
What is the common use of the isotope Carbon-14?
Medical imaging
Radiocarbon dating
Cancer treatment
Power generation
Which isotope is used in nuclear reactors as fuel?
Uranium-238
Plutonium-239
Uranium-235
Thorium-232
Isotopes of the same element have the same:
Mass number
Number of neutrons
Atomic number
Number of electrons
How are isotopes represented?
By the chemical symbol only
By the chemical symbol and atomic number
By the chemical symbol and mass number
By the chemical symbol and neutron number
Which of the following is a stable isotope of hydrogen?
Tritium
Deuterium
Protium
Both b and c
What is the main difference between isotopes that affects their physical properties?
Number of electrons
Number of protons
Number of neutrons
Number of ions
Which isotope of iodine is commonly used in medical imaging?
Iodine-123
Iodine-124
Iodine-125
Iodine-131
Which of the following isotopes is used in PET scans?
Fluorine-18
Carbon-12
Oxygen-16
Nitrogen-14
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

