What is the chemical formula of Potassium Bromide?
KBr
KCl
K2Br
KBr2

Potassium Bromide, symbolized as KBr, is an ionic compound. It consists of potassium ions and bromine ions. This compound appears as a white crystalline substance. Historically significant as a sedative and an epilepsy treatment, its solubility and chemical properties have paved the way for diverse applications. Currently, KBr serves important roles in the production of synthetic fibers, photographic processes, analytical chemistry, and as a component of drilling fluids in the oil and gas industry. This compound’s transition from a medical remedy to a staple in various industries highlights its enduring relevance and versatility.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | KBr |
| Hill Formula | BrK |
| Name | Potassium Bromide |
| Alternate Names | Bromide salt of potassium, Hydrobromic acid potassium salt, Tripotassium tribromide |
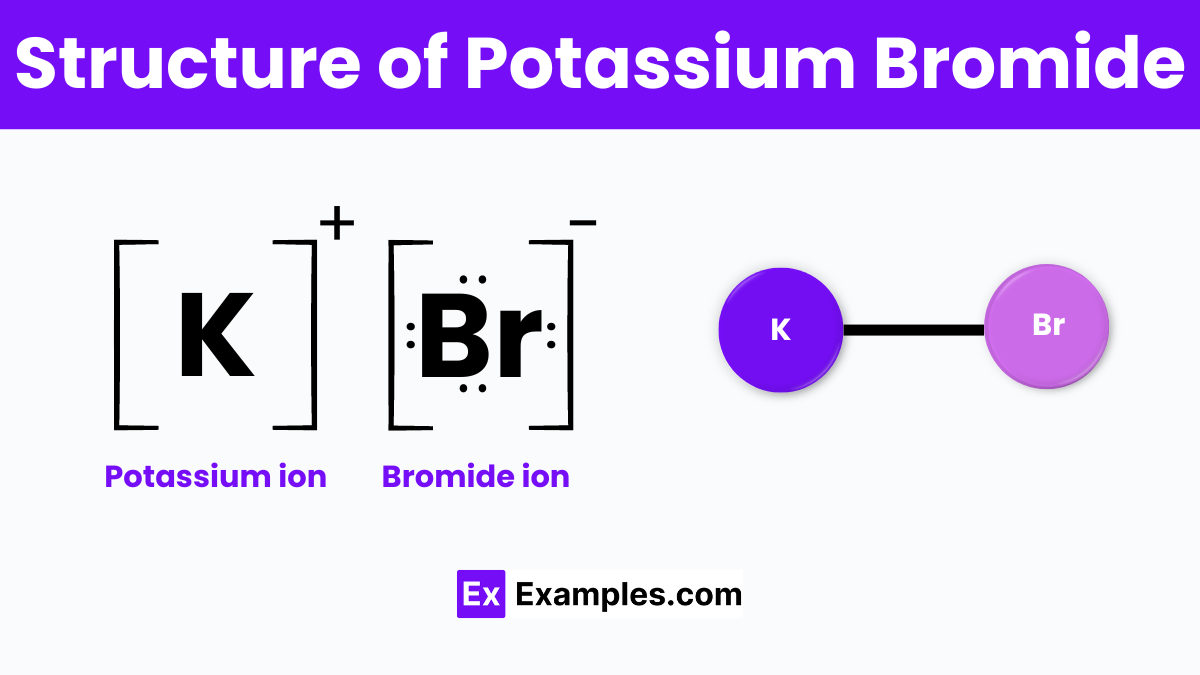
Potassium Bromide (KBr) has a simple yet significant structure characteristic of ionic compounds. In its solid form, KBr arranges itself in a cubic crystal lattice, which is a highly organized structure that repeats in three dimensions. This lattice is made up of potassium ions (K⁺) and bromide ions (Br⁻), which are held together by ionic bonds. Potassium atoms donate one electron to bromide atoms, forming bonds that create positively charged potassium ions and negatively charged bromide ions.. Their opposite charges attract each other, creating a stable, solid structure.
This ionic arrangement allows Potassium Bromide to have high melting and boiling points, typical of ionic compounds. Additionally, its structure is responsible for its solubility in water; when KBr is dissolved, the water molecules work to separate the potassium ions from the bromide ions, allowing it to dissolve effectively. This structural attribute of KBr underpins its varied applications in the medical, industrial, and scientific fields.
Potassium Bromide (KBr) is commonly prepared by mixing two things: potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) and hydrobromic acid (HBr). When they react with this chemicals they produce Potassium Bromide, water (H₂O), and a gas called carbon dioxide (CO₂). The balanced chemical equation is
After this reaction, the mix is heated to get rid of the water, leaving behind solid potassium bromide. To make sure it’s really clean and pure, this solid is dissolved in hot water, filtered to take out any dirt, and then left to cool down. As it cools, pure KBr crystals form. These crystals are then dried to take away any water left, giving you pure potassium bromide. This method is simple and uses easy-to-find materials, making it a good way to make potassium bromide for things like medicine and photography.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White powder or crystals |
| Taste | Slightly bitter |
| Smell | No smell |
| Solubility in Water | Dissolves easily in water |
| Melting Point | About 734°C (1,353°F) |
| Boiling Point | About 1,435°C (2,615°F) |
| Density | 2.75 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, like tiny boxes stacked together |
KBr can react with strong acids like sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to produce bromine (Br₂), water (H₂O), and potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄).
Equation: 2KBr+H₂SO₄ → K₂SO₄+H₂O+Br₂
Mixing KBr with a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO₃) results in the formation of a creamy white precipitate composed of silver bromide (AgBr) and potassium nitrate (KNO3).
Equation: 3KBr+AgNO₃ →AgBr(s)+KNO₃
KBr can react with chlorine (Cl₂) to form potassium chloride (KCl) and bromine (Br₂). This reaction shows how chlorine can replace the bromide part of KBr.
Equation: 2KBr+Cl₂→KCl+Br₂
KBr easily dissolves in water, separating into potassium ( K+) and bromide (Br−) ions. This property makes it useful in solutions for various industrial and medical applications.
Equation for Dissolving: KBr→K++Br− in water.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7758-02-3 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 253877 |
| SMILES Identifier | [K+].[Br-] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/BrH.K/h1H;/q;+1/p-1/fBr.K/h1h;/q-1;m |
| RTECS Number | TS7650000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00011358 |
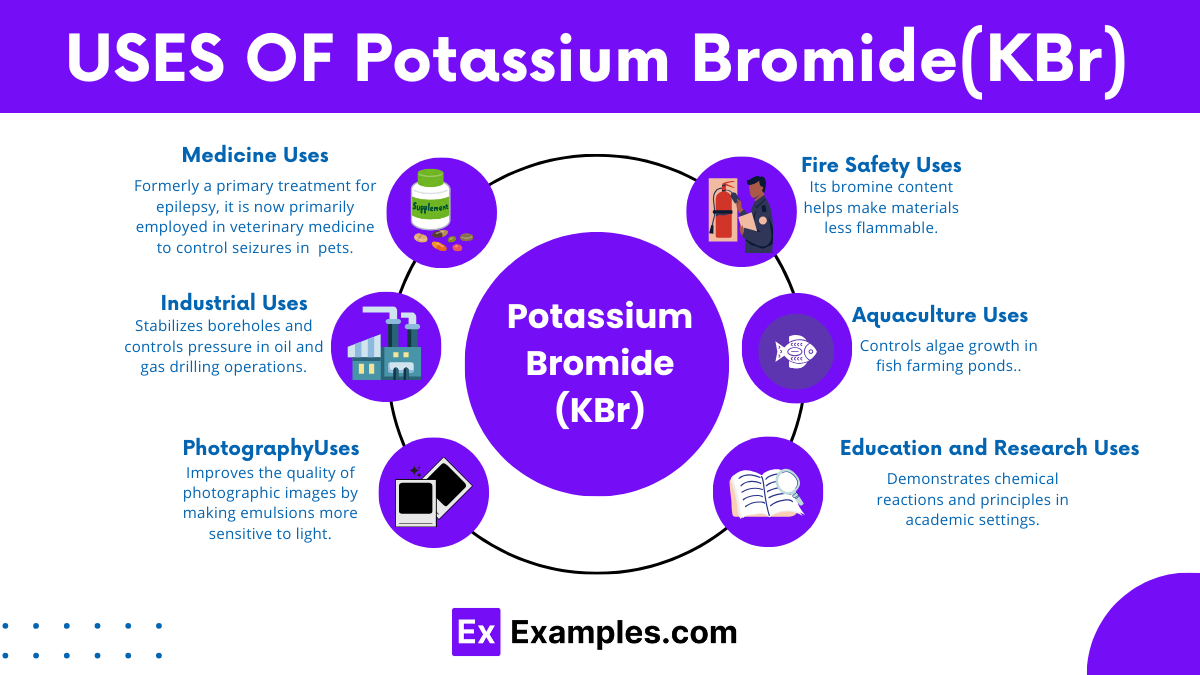
Potassium bromide serves to manage seizures in dogs, particularly when alternative medications prove ineffective or induce intolerable side effects.
Quizlet may provide flashcards or study materials on potassium bromide, aiding learners in understanding its uses, side effects, and administration in veterinary medicine.
Potassium bromide can cause adverse effects in dogs if not properly administered or monitored, including vomiting, lethargy, and rarely, severe reactions like pancreatitis or bromism.
In some cases, abrupt changes in potassium bromide dosage or inadequate monitoring may trigger seizures in dogs. Proper veterinary guidance and monitoring are crucial for seizure management.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula of Potassium Bromide?
KBr
KCl
K2Br
KBr2
What type of bond is primarily found in Potassium Bromide?
Covalent bond
Metallic bond
Ionic bond
Hydrogen bond
What is the primary use of Potassium Bromide in the field of medicine?
Antibiotic
Anticonvulsant
Pain reliever
Antipyretic
119.0 g/mol
137.3 g/mol
149.0 g/mol
153.3 g/mol
In which state of matter is Potassium Bromide most commonly found at room temperature?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Plasma
What is the solubility of Potassium Bromide in water at 25°C?
31 g/100 mL
53 g/100 mL
65 g/100 mL
75 g/100 mL
What is the common use of Potassium Bromide in photography?
Film developer
Fixing agent
Toning agent
Emulsion stabilizer
Which property of Potassium Bromide makes it useful in infrared spectroscopy?
High melting point
High electrical conductivity
Transparency to infrared light
High refractive index
What is the boiling point of Potassium Bromide?
1347°C
1472°C
1537°C
1627°C
Which of the following is a potential side effect of Potassium Bromide use?
Hypoglycemia
Hyperkalemia
Sedation
Insomnia
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

