What is the chemical formula of potassium nitrate?
KNO2
KNO₃
K2O
K2CO₃


Potassium nitrate is commonly known as saltpeter and it is a chemical compound with the formula KNO₃. This white to dirty gray crystalline solid is a key ingredient in various applications, most notably in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and potassium – two vital nutrients for plants. It is also historically significant in the production of gunpowder. Found naturally in mineral deposits, potassium nitrate is water-soluble and has properties that make it valuable in food preservation and even in fireworks, where it acts as an oxidizer to produce vivid colors. Its versatility makes it an interesting subject of study in chemistry, especially for students exploring chemical reactions and compound applications.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | KNO₃ |
| Name | Potassium Nitrate |
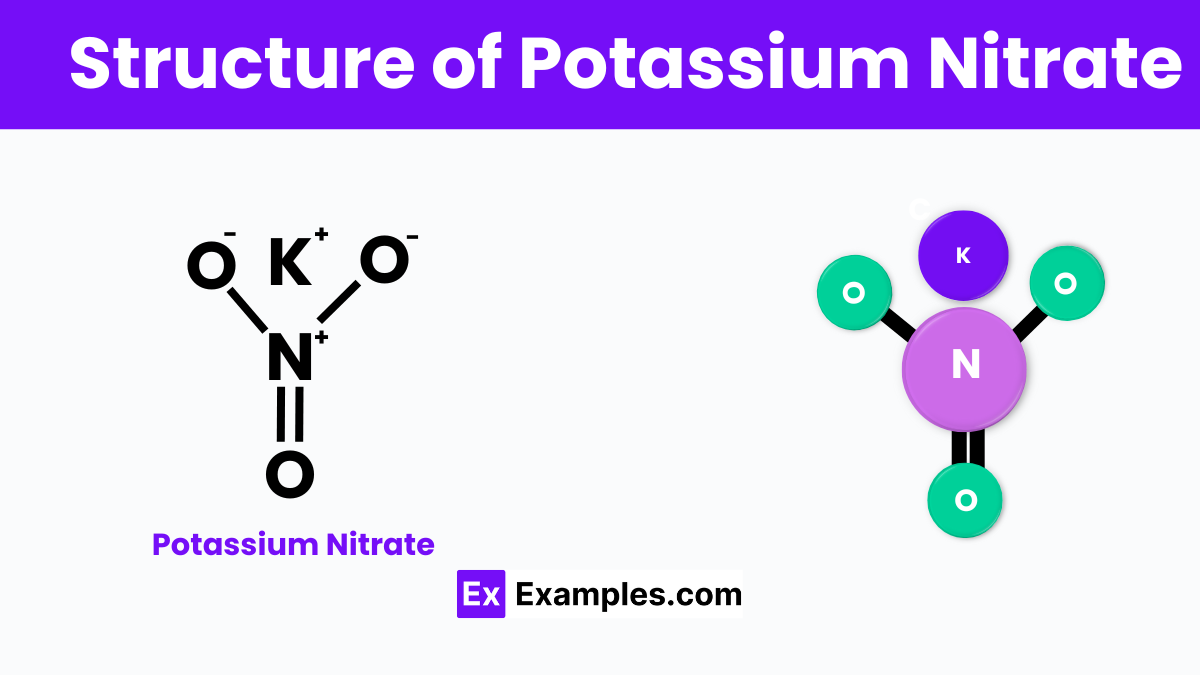
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound made up of potassium (K), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O) atoms. Its indicates that each molecule consists of one potassium atom, one nitrogen atom, and three oxygen atoms. Structurally, the potassium ion (K⁺) and the nitrate ion (NO₃⁻) are bonded together through ionic bonds. This means that the potassium atom gives up one electron to achieve a stable electronic arrangement, and this electron is gained by the nitrate group, creating a stable ionic structure. In solid form, potassium nitrate typically forms a crystalline structure where each potassium ion is surrounded by multiple nitrate ions, and vice versa, aligning in a repeating pattern to form the solid crystal lattice. This structure is crucial for its various uses, from fertilizers to gunpowder, as it ensures the compound is stable yet reactive under the right conditions.
Potassium nitrate can be prepared through a simple chemical reaction that involves combining potassium chloride (KCl) with ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). This process is commonly referred to as the double decomposition method. When these two compounds are dissolved in water, they interact and exchange ions to form potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). The reaction can be represented by the chemical equation:
In a laboratory setting, the mixture is heated until the salts dissolve completely. Upon cooling, Potassium nitrate, which is less soluble in cold water compared to Ammonium chloride, crystallizes out of the solution and can be collected by filtration. The remaining solution contains ammonium chloride. This method is popular due to its straightforward approach and the purity of potassium nitrate that can be achieved. Potassium nitrate produced in this way is often used in various applications, including in fertilizers and pyrotechnics, due to its high quality and reactive properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White to dirty gray crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Molecular Formula | KNO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 101.10 g/mol |
| Density | 2.109 g/cm³ at 25°C |
| Melting Point | 334 °C (633 °F) |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes at 400 °C (752 °F) before boiling |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble, with increasing solubility at higher temperatures |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 334 °C; decomposes at higher temperatures |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7757-79-1 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 24434 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24852201 |
| SMILES Identifier | N+([O-])[O-].[K+] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/K.NO3/c;2-1(3)4/q+1;-1 |
| RTECS Number | TT3700000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00011409 |
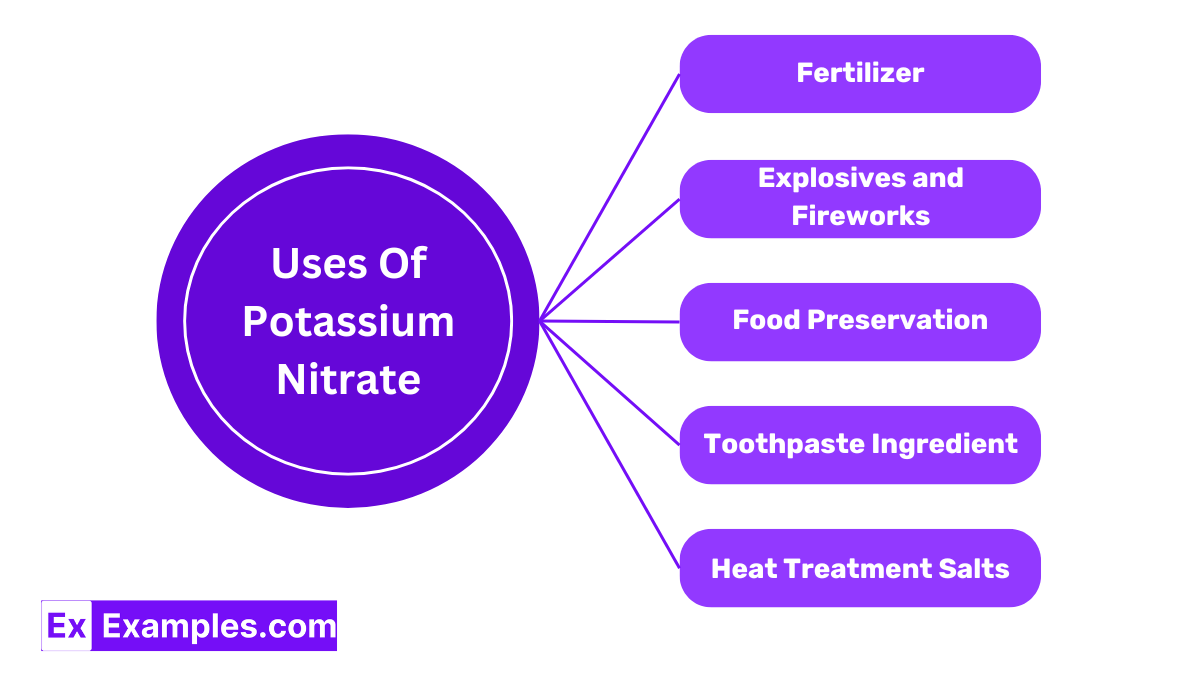
Potassium nitrate is widely used as a fertilizer in agriculture. It provides plants with potassium and nitrogen, two essential nutrients that support plant growth and improve fruit quality. This makes it ideal for gardens, commercial crops, and greenhouses.
Due to its oxidizing properties, Potassium nitrate is a key component in gunpowder and fireworks. When heated, it releases oxygen that helps burn other materials in the mixture, creating the explosive reactions needed for fireworks and ammunition.
Potassium nitrate has been historically used in the curing of meats. It helps preserve the meat, prevents bacterial growth, and maintains the pink coloring in cured products like salami and ham.
In dental care, potassium nitrate is used as a desensitizing agent in toothpaste. It helps reduce tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, acidic, or sweet stimuli by calming the nerves in the teeth.
In the production of glass, Potassium nitrate is used as a flux, which helps reduce the melting temperature of the glass mix and improves the glass’s optical properties.
Potassium nitrate is used in heat treatment salts where it’s mixed with sodium nitrite to make a molten bath for the surface hardening of steel. This process enhances the toughness and wear resistance of steel components.
Beyond fireworks, Potassium nitrate is used in other pyrotechnic applications such as smoke bombs and flares, where it acts as an oxidizer to produce dense smoke and vivid colors.
Potassium nitrate is used in enamels and glazes. It acts as an oxidizing agent and helps improve the finish and coloration of ceramic products.
Yes, potassium nitrate can be purchased over the counter at pharmacies and garden supply stores, primarily used for fertilizers and toothpaste.
Saltpeter, or Potassium nitrate, is not naturally present in foods but may be added in small amounts to some cured meats for preservation.
Potassium nitrate does not clarify teeth but is used in toothpaste to reduce sensitivity by stopping pain signals from the tooth to the nerve.

Potassium nitrate is commonly known as saltpeter and it is a chemical compound with the formula KNO₃. This white to dirty gray crystalline solid is a key ingredient in various applications, most notably in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and potassium – two vital nutrients for plants. It is also historically significant in the production of gunpowder. Found naturally in mineral deposits, potassium nitrate is water-soluble and has properties that make it valuable in food preservation and even in fireworks, where it acts as an oxidizer to produce vivid colors. Its versatility makes it an interesting subject of study in chemistry, especially for students exploring chemical reactions and compound applications.
Potassium nitrate is also known as saltpeter, is a chemical compound with the formula KNO₃. This white to dirty gray crystalline solid is one of the most common nitrates, which are salts of nitric acid. It is a naturally occurring mineral and plays a crucial role in both agriculture and industry. In agriculture, potassium nitrate is valued as a fertilizer because it provides essential nutrients, potassium and nitrogen, to plants. In industry, it is used in the manufacture of gunpowder and fireworks due to its ability to produce oxygen when heated, enhancing combustion. Potassium nitrate is also used in food preservation, particularly in curing meats.
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Formula | KNO₃ |
Name | Potassium Nitrate |
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound made up of potassium (K), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O) atoms. Its indicates that each molecule consists of one potassium atom, one nitrogen atom, and three oxygen atoms. Structurally, the potassium ion (K⁺) and the nitrate ion (NO₃⁻) are bonded together through ionic bonds. This means that the potassium atom gives up one electron to achieve a stable electronic arrangement, and this electron is gained by the nitrate group, creating a stable ionic structure. In solid form, potassium nitrate typically forms a crystalline structure where each potassium ion is surrounded by multiple nitrate ions, and vice versa, aligning in a repeating pattern to form the solid crystal lattice. This structure is crucial for its various uses, from fertilizers to gunpowder, as it ensures the compound is stable yet reactive under the right conditions.
Potassium nitrate can be prepared through a simple chemical reaction that involves combining potassium chloride (KCl) with ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). This process is commonly referred to as the double decomposition method. When these two compounds are dissolved in water, they interact and exchange ions to form potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). The reaction can be represented by the chemical equation:
KCl + NH₄NO₃ → KNO₃ + NH₄Cl
In a laboratory setting, the mixture is heated until the salts dissolve completely. Upon cooling, Potassium nitrate, which is less soluble in cold water compared to Ammonium chloride, crystallizes out of the solution and can be collected by filtration. The remaining solution contains ammonium chloride. This method is popular due to its straightforward approach and the purity of potassium nitrate that can be achieved. Potassium nitrate produced in this way is often used in various applications, including in fertilizers and pyrotechnics, due to its high quality and reactive properties.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Appearance | White to dirty gray crystalline solid |
Odor | Odorless |
Molecular Formula | KNO3 |
Molecular Weight | 101.10 g/mol |
Density | 2.109 g/cm³ at 25°C |
Melting Point | 334 °C (633 °F) |
Boiling Point | Decomposes at 400 °C (752 °F) before boiling |
Solubility in Water | Soluble, with increasing solubility at higher temperatures |
Thermal Stability | Stable up to 334 °C; decomposes at higher temperatures |
Potassium nitrate acts as a strong oxidizing agent. This means it can provide oxygen to support the combustion of other materials. This property is crucial in its use in fireworks and gunpowder. For example, when potassium nitrate is heated in gunpowder, it decomposes to produce oxygen, which then fuels the combustion of charcoal and sulfur in the mixture.
Equation: 2KNO₃ → 2KNO₂ + O₂
When potassium nitrate is mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄ ), it forms nitric acid (HNO₃) and potassium bisulfate (KHSO₄). This is a way to produce nitric acid in the lab.
Equation: KNO₃ + H₂SO₄ → HNO₃ + KHSO₄
Upon heating, potassium nitrate undergoes thermal decomposition. This process is used to produce Nitrogen oxides, which are important industrial chemicals.
Equation: 2KNO₃ → 2KNO₂ + O₂
Property | Value |
|---|---|
CAS Registry Number | 7757-79-1 |
PubChem Compound ID | 24434 |
PubChem Substance ID | 24852201 |
SMILES Identifier | N+([O-])[O-].[K+] |
InChI Identifier | InChI=1/K.NO3/c;2-1(3)4/q+1;-1 |
RTECS Number | TT3700000 |
MDL Number | MFCD00011409 |
Potassium nitrate is widely used as a fertilizer in agriculture. It provides plants with potassium and nitrogen, two essential nutrients that support plant growth and improve fruit quality. This makes it ideal for gardens, commercial crops, and greenhouses.
Due to its oxidizing properties, Potassium nitrate is a key component in gunpowder and fireworks. When heated, it releases oxygen that helps burn other materials in the mixture, creating the explosive reactions needed for fireworks and ammunition.
Potassium nitrate has been historically used in the curing of meats. It helps preserve the meat, prevents bacterial growth, and maintains the pink coloring in cured products like salami and ham.
In dental care, potassium nitrate is used as a desensitizing agent in toothpaste. It helps reduce tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, acidic, or sweet stimuli by calming the nerves in the teeth.
In the production of glass, Potassium nitrate is used as a flux, which helps reduce the melting temperature of the glass mix and improves the glass’s optical properties.
Potassium nitrate is used in heat treatment salts where it’s mixed with sodium nitrite to make a molten bath for the surface hardening of steel. This process enhances the toughness and wear resistance of steel components.
Beyond fireworks, Potassium nitrate is used in other pyrotechnic applications such as smoke bombs and flares, where it acts as an oxidizer to produce dense smoke and vivid colors.
Potassium nitrate is used in enamels and glazes. It acts as an oxidizing agent and helps improve the finish and coloration of ceramic products.
Irritation: Potassium nitrate can irritate your skin, eyes, and lungs. Contact may cause redness and a burning feeling.
Toxicity: Eating too much potassium nitrate is harmful. Symptoms include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It can also hurt your kidneys or affect your heartbeat.
Reduced Oxygen Transport: This chemical can make it hard for your blood to carry oxygen, causing shortness of breath, blue-tinged skin, and dizziness.
Allergic Reactions: Some people may have allergies to potassium nitrate, showing up as skin rashes, itching, or breathing problems like wheezing.
Dental Sensitivity Reduction: Potassium nitrate is good in toothpaste for sensitive teeth as it helps reduce tooth pain.
Skin and Eye Irritation: Touching potassium nitrate can make your skin and eyes red and itchy. Wear safety gear to prevent this.
Respiratory Problems: Breathing in potassium nitrate dust can cause coughing and a sore throat. It can also make it hard to breathe.
Gastrointestinal Distress: Eating potassium nitrate can cause stomach upset, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Methemoglobinemia: This chemical can turn your blood into a type that doesn’t carry oxygen well, causing symptoms like blue-gray skin, breathlessness, tiredness, and confusion.
Allergic Reactions: Some people may get allergic reactions like hives, itching, and swelling from potassium nitrate. In severe cases, it can be life-threatening.
Increased Heart Rate: Large amounts of potassium nitrate can speed up your heart rate and affect your heart health.
Yes, potassium nitrate can be purchased over the counter at pharmacies and garden supply stores, primarily used for fertilizers and toothpaste.
Saltpeter, or Potassium nitrate, is not naturally present in foods but may be added in small amounts to some cured meats for preservation.
Potassium nitrate does not clarify teeth but is used in toothpaste to reduce sensitivity by stopping pain signals from the tooth to the nerve.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula of potassium nitrate?
KNO2
KNO₃
K2O
K2CO₃
What is the common name for potassium nitrate?
Baking soda
Epsom salt
Saltpeter
Bleach
Potassium nitrate is most commonly used in which application?
Fertilizers
Food preservatives
Antifreeze
Plastic production
Which of the following is a property of potassium nitrate?
It is acidic
It is a strong oxidizer
It is a reducing agent
It is a non-metal
Potassium nitrate is used in the production of:
Glass
Gunpowder
Soap
Dyes
What is the solubility of potassium nitrate in water at 20°C?
31.6 g/100 mL
13.9 g/100 mL
42.7 g/100 mL
64.2 g/100 mL
Which ion is responsible for the oxidizing property of potassium nitrate?
Potassium ion
Nitrate ion
Nitrite ion
Chloride ion
What is the molar mass of potassium nitrate?
101 g/mol
85 g/mol
71 g/mol
101.1 g/mol
In which of the following industries is potassium nitrate NOT commonly used?
Fireworks
Food preservation
Textiles
Pharmaceuticals
Which element is present in the highest percentage by mass in potassium nitrate?
Potassium
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Hydrogen
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

