What is the common name for sodium carbonate?
Baking soda
Washing soda
Table salt
Epsom salt


Sodium carbonate, also known as soda ash or washing soda, is a chemical compound often used in household cleaning. In chemistry, sodium carbonate belongs to a group of compounds known as salts. It appears as a white, odorless powder that dissolves easily in water, creating an alkaline solution. This versatile compound is not only essential in cleaning products but also in processes like glass making and water treatment, making it a valuable substance in both household and industrial applications.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | Na2CO3 |
| Hill Formula | CNa2O3 |
| Name | Soda Ash |
| IUPAC Name | Disodium Carbonate |
| Alternate Names | Crystol Carbonate, Soda, Sodium Carbonate |
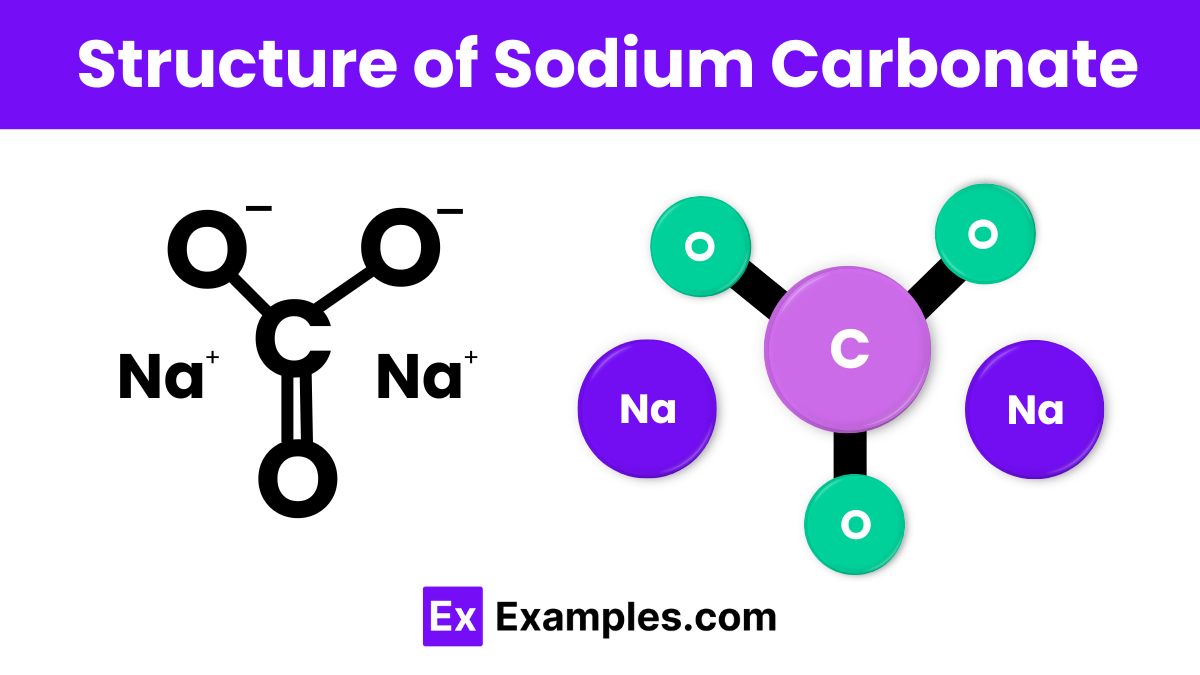
The structure of sodium carbonate consists of two sodium (Na) atoms, one carbon (C) atom, and three oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms form a stable, ionic compound where the sodium ions (Na⁺) bond with the carbonate ion (CO₃²⁻). In this structure, the carbon atom is centrally located and bonded to three oxygen atoms, forming a triangular arrangement. This configuration helps sodium carbonate dissolve easily in water.
To prepare sodium carbonate, we use the Solvay process, which involves several steps. First, we combine sodium chloride (NaCl) with ammonia (NH₃) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) in water. This reaction forms sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) and ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl).
Next, we heat the sodium bicarbonate, causing it to decompose into sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide.
This process efficiently produces sodium carbonate, which we then collect and use in various applications, such as cleaning and glass-making.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | 851°C (1564°F) |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble, dissolves easily |
| Density | 2.54 g/cm³ |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Alkaline, mildly bitter |
| Hygroscopic | Absorbs moisture from the air |
Sodium carbonate reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide, water, and a salt. For example, when it reacts with hydrochloric acid, it forms sodium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water.
Na₂CO₃ + 2HCl → 2NaCl + CO₂ + H₂O
In water, sodium carbonate dissolves and forms an alkaline solution, releasing hydroxide ions (OH⁻) and carbonate ions (CO₃²⁻).
Na₂CO₃ → 2Na⁺ + CO₃²⁻
Sodium carbonate does not react with strong bases like sodium hydroxide, as both are already basic in nature. However, it can react with weak bases, neutralizing them and forming carbonates or bicarbonates.
Upon heating, sodium carbonate remains stable up to its melting point. Beyond this, it decomposes to form sodium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Na₂CO₃ → Na₂O + CO₂
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 497-19-8 |
| Beilstein Number | 4154566 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 10340 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24852265 |
| SMILES Identifier | C(=O)([O-])[O-].[Na+].[Na+] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/CH2O3.2Na/c2-1(3)4;;/h(H2,2,3,4);;/q;2*+1/p-2/fCO3.2Na/q-2;2m |
| RTECS Number | VZ4050000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00003494 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 0 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
| Property | Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃) | Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Na₂CO₃ | NaHCO₃ |
| Common Names | Soda ash, washing soda | Baking soda, bicarbonate of soda |
| Appearance | White, crystalline powder | White, crystalline powder |
| pH in Solution | Strongly alkaline (pH ~ 11.5) | Mildly alkaline (pH ~ 8.3) |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble | Moderately soluble |
| Uses | Glass making, cleaning, water softening | Baking, antacid, fire extinguishers |
| Thermal Stability | Stable at high temperatures | Decomposes above 50°C |
| Reaction with Acids | Produces carbon dioxide, water, and a salt | Produces carbon dioxide, water, and a salt |
| Reaction with Bases | Does not react with strong bases | Reacts with acids to form carbonates |
| Molecular Weight | 105.99 g/mol | 84.01 g/mol |
| Decomposition Products | Sodium oxide and carbon dioxide upon strong heating | Sodium carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide on heating |
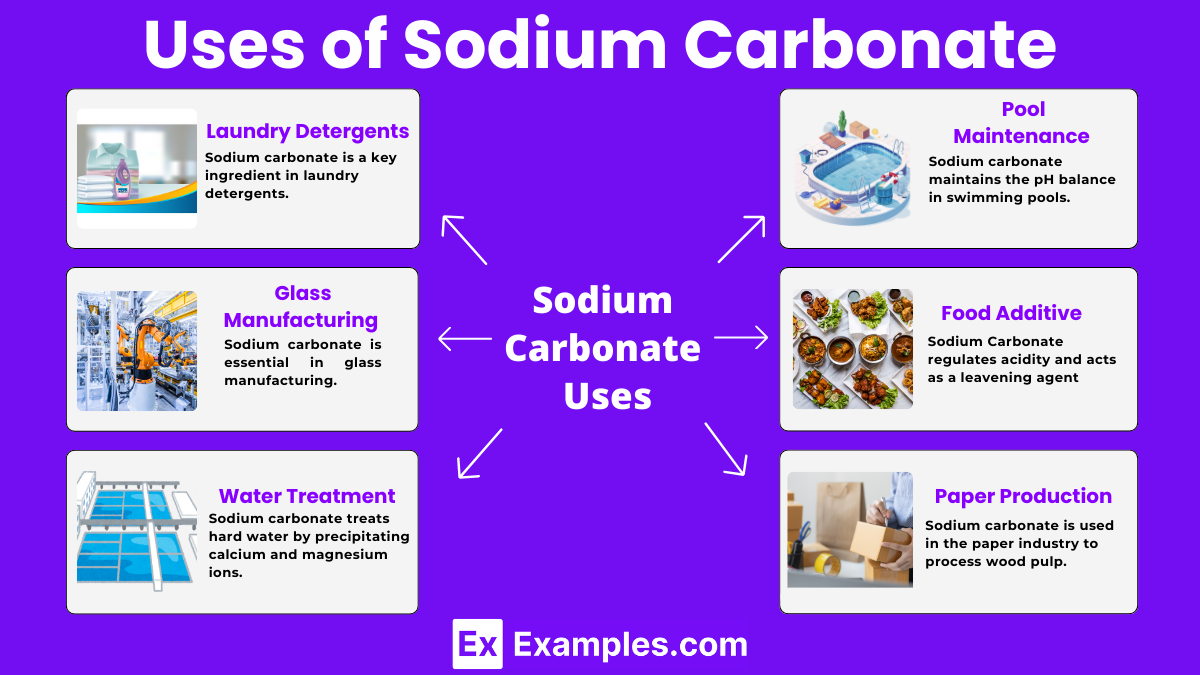
Sodium carbonate is a key ingredient in laundry detergents. It helps remove stains and soften water, making the detergent more effective at cleaning clothes.
Sodium carbonate is essential in glass manufacturing. It lowers the melting point of silica, making the glass-making process more efficient and cost-effective.
Sodium carbonate treats hard water by precipitating calcium and magnesium ions. This process softens the water, making it suitable for industrial and household use.
In the food industry, sodium carbonate regulates acidity and acts as a leavening agent. It helps baked goods rise and improves their texture.
Sodium carbonate maintains the pH balance in swimming pools. It raises the pH levels, ensuring the water remains safe and comfortable for swimmers.
Sodium carbonate is used in the paper industry to process wood pulp. It breaks down the fibers and aids in the production of paper, acting as a buffering agent.
Sodium carbonate is a versatile cleaning agent. It is used in various household cleaners to break down grease, dirt, and stains, making surfaces cleaner and brighter.
No, sodium carbonate is not baking soda. Sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) is also known as soda ash, while baking soda is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃).
Sodium carbonate is safe in small amounts for household use but can cause irritation or health issues if inhaled, ingested, or contacted in large quantities.
Yes, sodium carbonate raises the pH in pools, helping to balance the water’s acidity and maintain safe swimming conditions.
The common name of sodium carbonate is soda ash.
When sodium carbonate is added to water, it dissolves and forms an alkaline solution, releasing sodium ions (Na⁺) and carbonate ions (CO₃²⁻).
Na₂CO₃ (sodium carbonate) is a base. It increases the pH of solutions, making them more alkaline.
Yes, baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) increases pH, making solutions less acidic.
In water, sodium carbonate has a pH of approximately 11, making the solution highly alkaline.
The pH level of sodium carbonate is around 11, indicating it is a strongly alkaline substance.
Soda ash is used in glass manufacturing, water treatment, cleaning products, and as a pH regulator in pools and various industrial processes.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the common name for sodium carbonate?
Baking soda
Washing soda
Table salt
Epsom salt
What is the chemical formula for sodium carbonate?
NaCl
NaHCO₃
Na₂CO₃
NaOH
Sodium carbonate is often used in the manufacture of which of the following?
Glass
Paint
Batteries
Pharmaceuticals
What type of reaction does sodium carbonate typically undergo in water?
Neutralization
Acid-base reaction
Oxidation
Decomposition
In which of the following household products might you find sodium carbonate?
Shampoo
Dishwashing detergent
Toothpaste
Air freshener
What happens when sodium carbonate is heated strongly?
It decomposes into sodium chloride and carbon dioxide
It dissolves completely in water
It forms sodium bicarbonate
It decomposes into sodium oxide and carbon dioxide
Sodium carbonate is a salt formed from which acid and base?
Sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide
Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide
Carbonic acid and sodium hydroxide
Acetic acid and sodium hydroxide
What is one industrial use of sodium carbonate in water treatment?
As a coagulant
As a disinfectant
To neutralize acidic water
To soften hard water
What is the role of sodium carbonate in baking?
It acts as a leavening agent
It preserves food
It adds flavor
It thickens the mixture
Which of the following is a safety precaution when handling sodium carbonate?
Avoid contact with skin
Store in a refrigerator
Keep away from sunlight
Mix with strong acids
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

