What is the atomic number of Strontium?
36
38
40
42
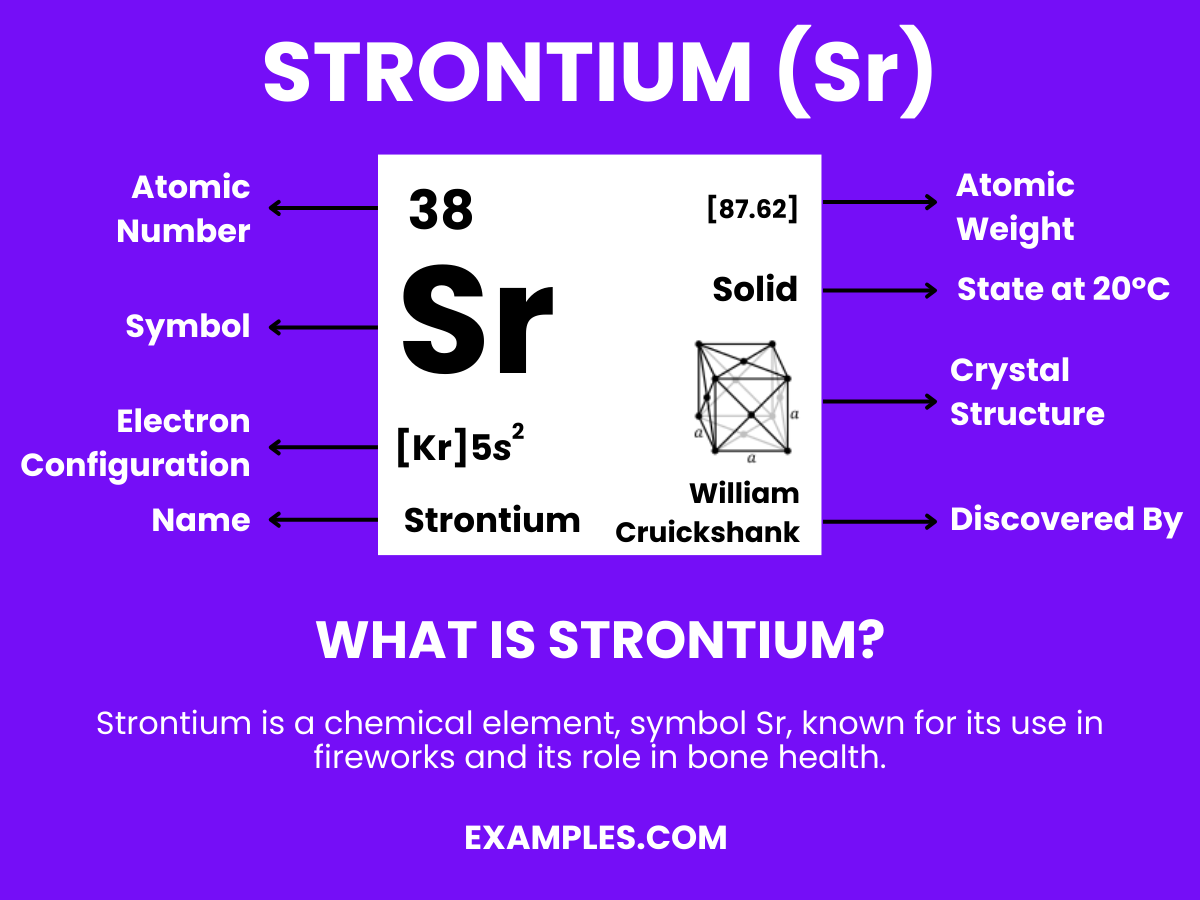
Strontium, a key player in the periodic table, is more than just a chemical element. It’s a gateway to a world of scientific exploration and understanding. For teachers looking to enrich their classroom, Strontium offers a unique opportunity to delve into the realms of chemistry and physics. This guide will illuminate the intricate details of Strontium, from its fundamental properties to its varied applications in everyday life and scientific research. As educators, understanding Strontium’s role in the world around us not only enhances our knowledge but also empowers us to inspire our students with real-world examples.
Strontium is an element found in the Earth’s crust. Known for its bright red flames in fireworks and flares, it’s much more than a spectacle. In its pure form, Strontium is a silvery-white metal that reacts with air and water. It has applications ranging from making TV screens to strengthening bones in osteoporosis treatments. Understanding Strontium’s properties and uses helps us appreciate its role in both nature and technology. For teachers, this knowledge is invaluable in making chemistry relatable and engaging for students.
| Beryllium(Be) |
| Magnesium(Mg) |
| Calcium(Ca) |
| Barium(Ba) |
| Radium(Ra) |
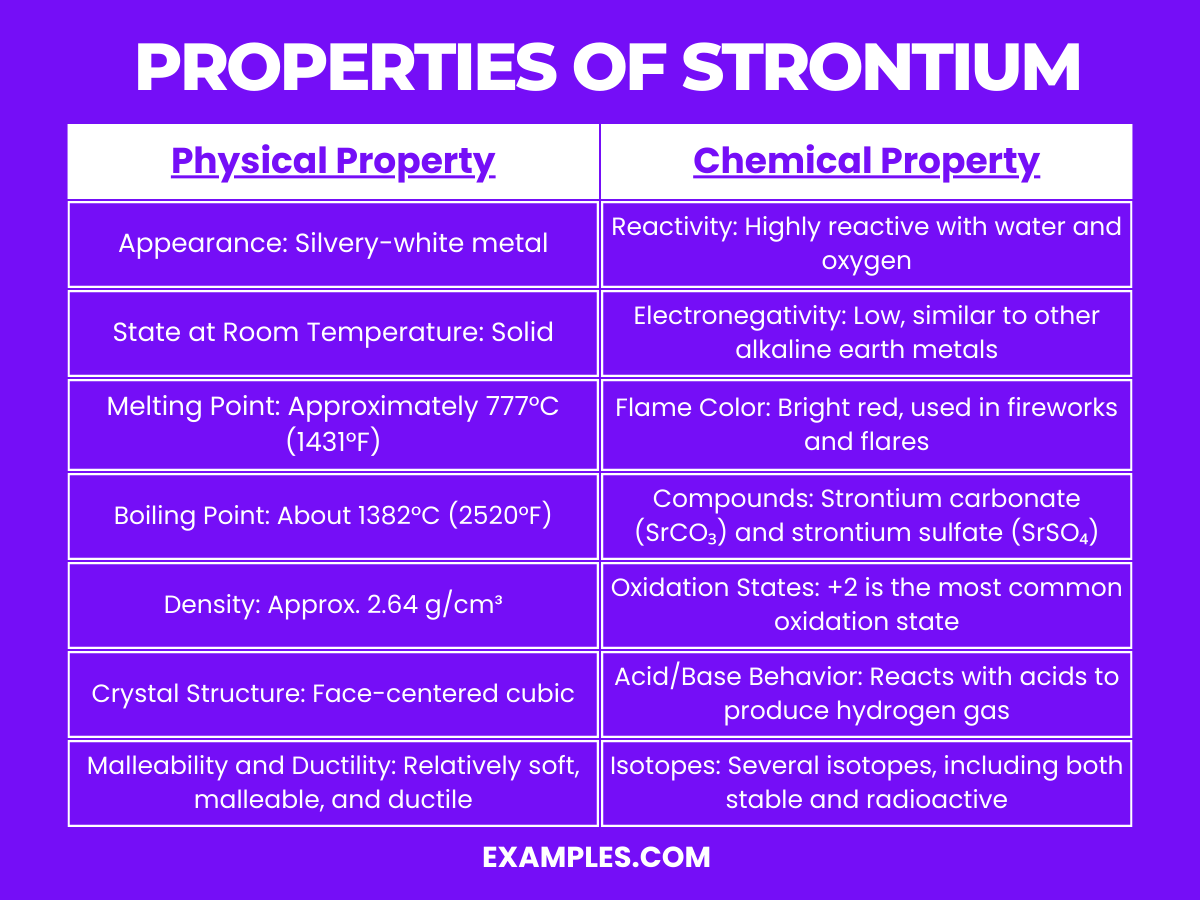
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Soft, silvery metal that tarnishes in air |
| Melting Point | 777°C |
| Boiling Point | 1382°C |
| Density | 2.64 g/cm³ |
| State at Room Temp. | Solid |
| Malleability | Highly malleable and ductile |
| Conductivity | Good electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Crystal Structure | Face-centered cubic (FCC) |
Strontium is a reactive element, particularly known for its reactivity with water and air:
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 777°C (1431°F) |
| Boiling Point | 1382°C (2520°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35.4 W/(m·K) |
| Specific Heat | 0.300 J/(g·K) |
| Heat of Vaporization | 137.4 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Fusion | 9.2 kJ/mol |
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Phase at STP | Solid |
| Density | 2.64 g/cm³ |
| Young’s Modulus | 15.7 GPa |
| Tensile Strength | 15-20 MPa |
| Mohs Hardness | 1.5 |
| Elastic Modulus | 15.7 GPa |
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Susceptibility | Paramagnetic |
| Electrical Conductivity | 7.4 MS/m |
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 38 |
| Atomic Mass | 87.62 u |
| Neutron Cross Section | 1.28 barns (for ^88Sr) |
| Isotopes | Natural strontium is a mix of ^84Sr, ^86Sr, ^87Sr, and ^88Sr |
| Radioactivity | ^90Sr is a notable radioactive isotope with a half-life of 28.8 years, resulting from nuclear fallout |
| Isotope | Description |
|---|---|
| Strontium-84 | Rare and radioactive, used for scientific research. |
| Strontium-86 | Stable isotope, used in geological studies. |
| Strontium-87 | Stable isotope, plays a crucial role in radiometric dating. |
| Strontium-88 | Most abundant and stable isotope, comprising about 83% of natural strontium. |
| Strontium-89 | Radioactive, used in medicine for treating bone cancer. |
| Strontium-90 | Radioactive, a byproduct of nuclear fission with environmental and health implications. |
The production of strontium predominantly involves the processing of the minerals celestite (strontium sulfate, SrSO₄) and strontianite (strontium carbonate, SrCO₃). Here’s a detailed overview of the process:
Strontium’s health effects largely depend on its forms – natural, stable isotopes versus radioactive ones:
It’s important to distinguish between the health impacts of natural strontium, which can be beneficial, and radioactive strontium, which poses significant health risks.
The environmental impact of strontium varies depending on its form:
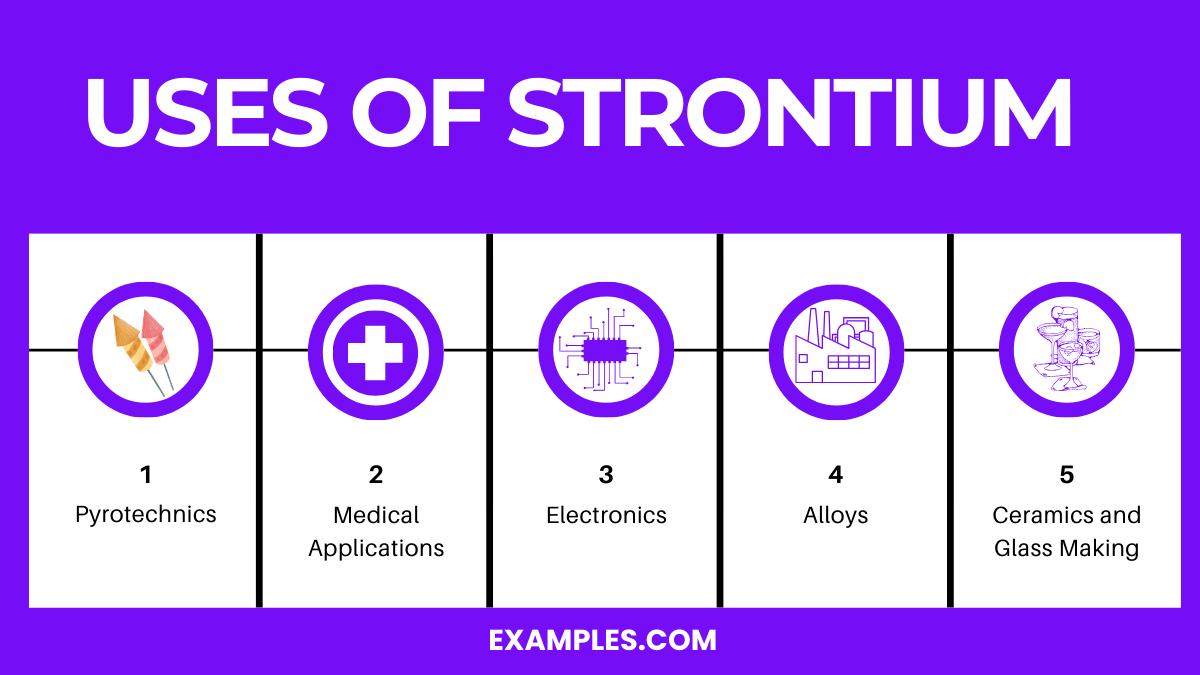
Strontium is used in pyrotechnics, ceramics, medical treatments for bone diseases, alloys in manufacturing, and in the electronics industry.
Natural strontium is not harmful and can benefit bone health. However, radioactive strontium, like strontium-90, is hazardous and can cause serious health issues.
Radioactive strontium is hazardous as it mimics calcium, accumulating in bones and potentially causing bone cancer and leukemia.
Strontium’s role in bone health and osteoporosis treatment is significant. Its similarity to calcium allows it to strengthen bone density. However, understanding its use and potential risks is essential for safe and effective application in health and industry.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
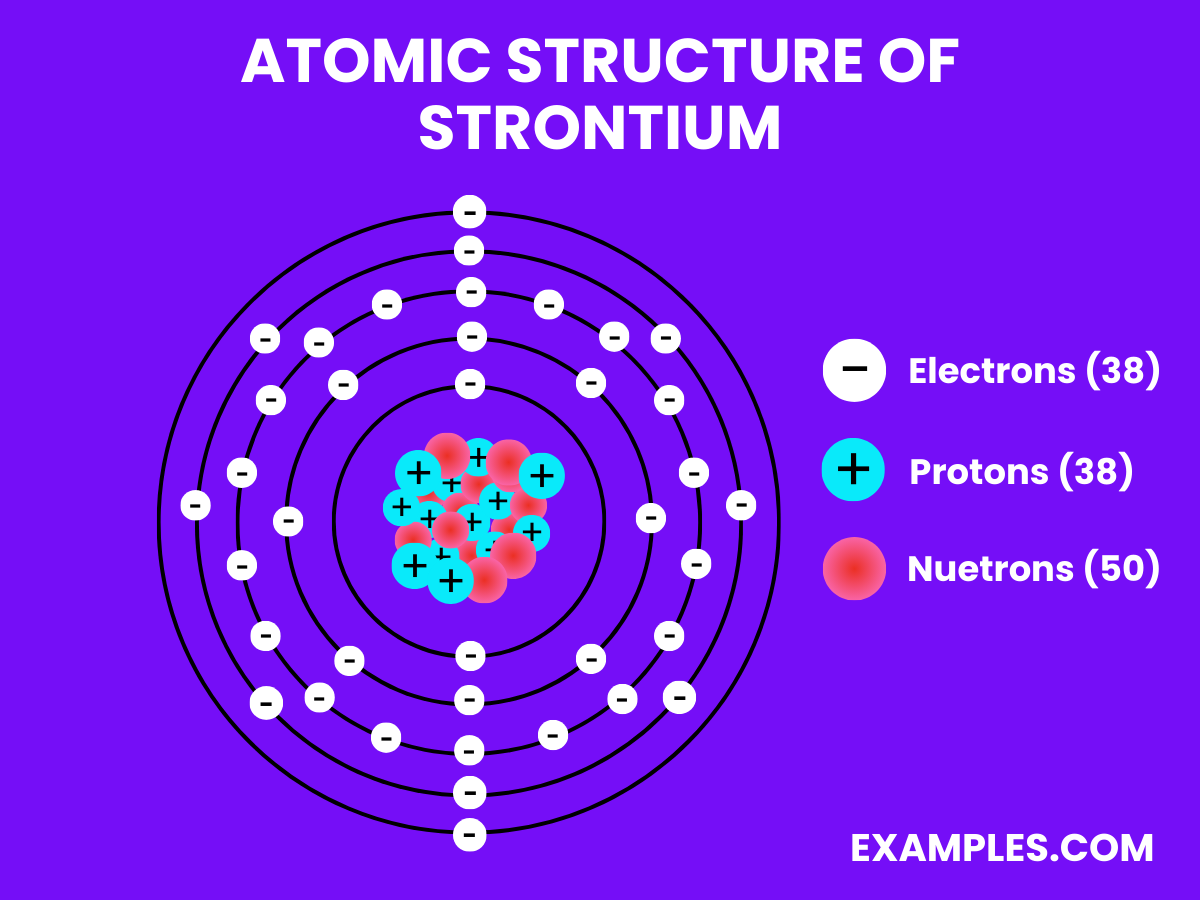
Electrons
Neutrons
Protons
What is the atomic number of Strontium?
36
38
40
42
What is the chemical symbol for Strontium?
St
Sr
Sn
Sm
Strontium belongs to which group in the periodic table?
Group 1
Group 2
Group 13
Group 14
What is the most common oxidation state of Strontium?
+1
+2
+3
+4
What is the atomic mass of Strontium?
87.62 u
88.91 u
89.87 u
90.98 u
Which of the following is a common use of Strontium compounds?
Fireworks
Fertilizers
Plastics
Textiles
What is the natural state of Strontium at room temperature?
Gas
Liquid
Solid
Plasma
Which mineral is a primary source of Strontium?
Bauxite
Celestine
Galena
Hematite
What is the color of Strontium flame in a flame test?
Green
Blue
Red
Yellow
Which isotope of Strontium is commonly used in medical applications?
Strontium-86
Strontium-88
Strontium-89
Strontium-90
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

