What is the chemical formula for sulfuric acid?
HCl
HNO₃
H₂SO₄
H₂CO₃

Sulfuric acid is a powerful substance that plays a big role in the world of chemistry. It’s a covalent compound, which means it’s made up of atoms that share electrons to stick together. This clear, colorless liquid is known for its unique ability to react with other substances, making it super important in making lots of things we use every day.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | H₂SO₄ |
| Hill formula | H₂O₄S |
| Name | Sulfuric acid |
| Alternate names | Anhydrous sulfuric acid, Dihydrogen sulfate, Oil of vitriol, Sulphuric acid |
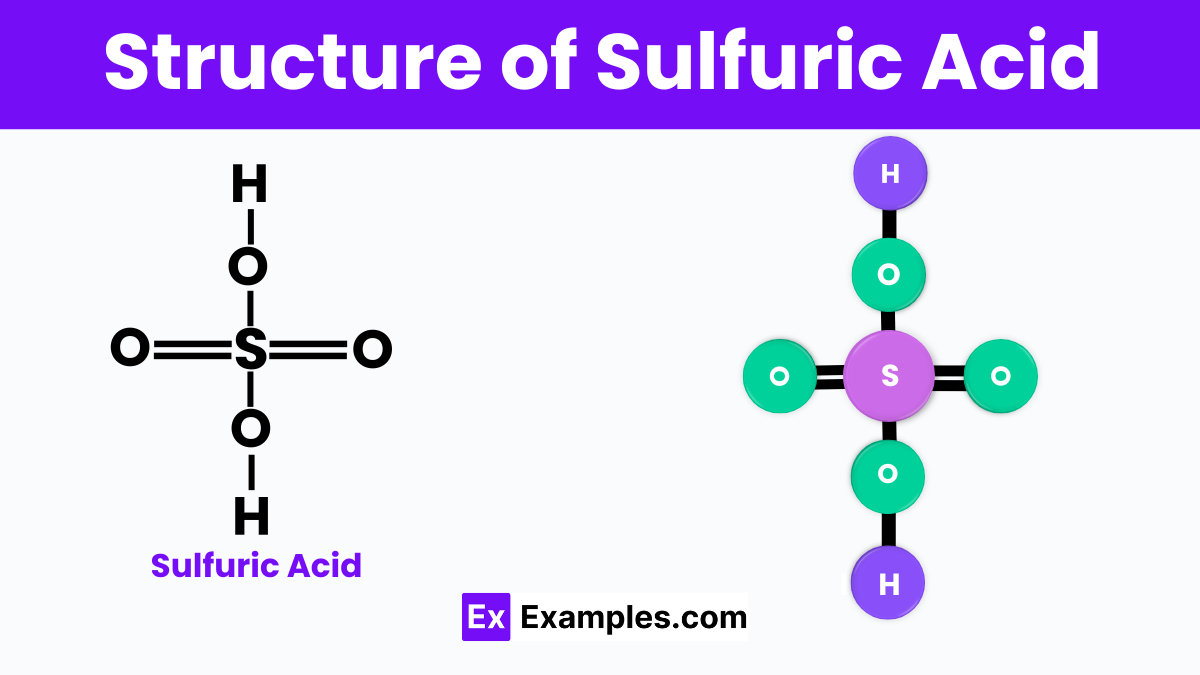
Sulfuric acid is a chemical compound with a complex and interesting structure. It has the chemical formula H₂SO₄. This means it is made up of two hydrogen atoms (H), one sulfur atom (S), and four oxygen atoms (O). The structure of sulfuric acid can be thought of as a central sulfur atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. Two of these oxygen atoms are double-bonded to the sulfur atom, and the other two are single-bonded but also attached to hydrogen atoms.This arrangement makes sulfuric acid a very strong acid. It’s able to donate two protons (the hydrogen atoms) when it reacts with other substances. This ability to give away protons easily makes it a very important and widely used chemical in many industries. Its structure is key to its reactivity and usefulness in making a wide variety of products.
Sulfuric acid is made using a method called the Contact Process. This process involves a few key steps. First, sulfur (S) is burned in air to create sulfur dioxide (SO₂). This is represented by the equation:
Next, the sulfur dioxide is mixed with more oxygen (O₂) in the presence of a catalyst, typically vanadium(V) oxide (V₂O₅). This helps convert the sulfur dioxide into sulfur trioxide (SO₃), shown by the equation:
Once sulfur trioxide is formed, it’s not directly combined with water to make sulfuric acid because that reaction is too violent. Instead, the sulfur trioxide is first absorbed into a pre-existing concentration of sulfuric acid. This forms oleum (H₂S₂O₇), which is then carefully diluted with water to form sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄). The final step can be represented by the equation:
This careful process allows for the production of highly concentrated sulfuric acid, which is essential for many industrial applications.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless, oily liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Molecular Weight | 98.079 g/mol |
| Density | 1.84 g/cm³ at 20°C |
| Melting Point | 10°C (50°F) |
| Boiling Point | 337°C (639°F) |
| Solubility in Water | Completely soluble, releases heat upon mixing |
| pH | Highly acidic (pH < 1 for concentrated solutions) |
| Viscosity | High, varies with concentration |
| Conductivity | Good conductor of electricity due to ionization in water |
Sulfuric acid is a very strong acid. It can donate two protons (H⁺ ions) in reactions. This makes it very reactive with bases and capable of causing burns.
It has the ability to absorb water from the air. This property makes it useful for drying out substances.
Sulfuric acid can remove water from other compounds. For example, when it reacts with sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁), it removes water, leaving a black mass of carbon and releasing water vapour.
Equation: C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ + H₂SO₄ → 12C + 11H₂O + Heat
Mixing sulfuric acid with water releases a lot of heat. This reaction should be done carefully by adding acid to water, not the other way around, to avoid splashing of the hot acid.
In concentrated form, sulfuric acid can act as a powerful oxidizing agent. It can take electrons from other substances, leading to oxidation. This property allows it to react with metals, non-metals, and carbon compounds, often producing sulfur dioxide (SO₂) or sulfates.
Sulfuric acid reacts with most metals, producing hydrogen gas and metal sulfate. For example, zinc reacts with sulfuric acid to produce zinc sulfate and hydrogen gas.
It reacts with bases (like sodium hydroxide) to form water and a salt. This reaction with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces water and sodium sulfate.
Equation: 2NaOH → Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS registry number | 7664-93-9 |
| Beilstein number | 2037554 |
| PubChem compound ID | 1118 |
| PubChem substance ID | 24859176 |
| SMILES identifier | OS(=O)(=O)O |
| InChI identifier | InChI=1/H2O4S/c1-5(2,3)4/h(H2,1,2,3,4)/f/h1-2H |
| MDL number | MFCD00064589 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA health rating | 3 |
| NFPA fire rating | 0 |
| NFPA reactivity rating | 2 |
| NFPA hazards | Water reactive |
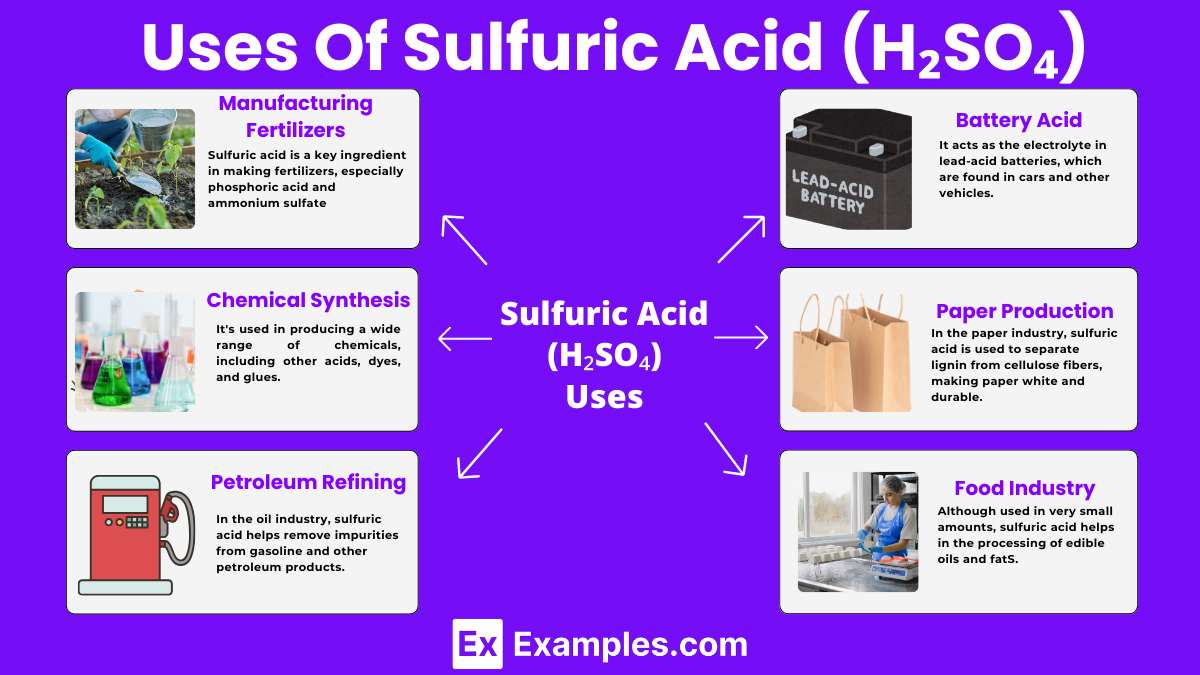
Sulfuric acid is a key ingredient in making fertilizers, especially phosphoric acid and ammonium sulfate. These fertilizers help plants grow by providing them essential nutrients.
It’s used in producing a wide range of chemicals, including other acids, dyes, and glues. This process involves reactions where sulfuric acid helps create new compounds.
In the oil industry, sulfuric acid helps remove impurities from gasoline and other petroleum products. This refining process ensures the fuel is clean and efficient.
Sulfuric acid is used to clean metals before they are coated or plated with other metals. It removes rust and prepares the surface for further treatment.
It acts as the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, which are found in cars and other vehicles. The acid allows electricity to flow between the battery’s plates.
Sulfuric acid is used in water treatment plants to adjust the pH levels of water, making it safe for drinking and use in industrial processes.
In the paper industry, sulfuric acid is used to separate lignin from cellulose fibers, making paper white and durable.
It plays a role in manufacturing various medicines, acting as a catalyst in the production processes of drugs and antibiotics.
Although used in very small amounts, sulfuric acid helps in the processing of edible oils and fats. It also acts as a preservative in some food products.
Adding water to sulfuric acid can cause violent reactions, emitting heat and potentially leading to splashes or explosions. Always add acid to water instead.
Sulfuric acid burns skin upon contact, causing severe chemical burns, tissue damage, and possible scarring. Immediate rinsing with water is crucial for affected areas.
Sulfuric acid has a strong, pungent odor resembling burnt matches, due to the release of sulfur oxides when exposed to air, indicating its corrosive nature.
Contact with sulfuric acid results in chemical burns, skin irritation, and potential tissue damage. Immediate and thorough washing with water is necessary to mitigate injuries.

Sulfuric acid is a powerful substance that plays a big role in the world of chemistry. It’s a covalent compound, which means it’s made up of atoms that share electrons to stick together. This clear, colorless liquid is known for its unique ability to react with other substances, making it super important in making lots of things we use every day.
Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that’s used in lots of different ways, from making batteries to cleaning metals. Its formula is H₂SO₄, which means it has two hydrogen atoms, one sulfur atom, and four oxygen atoms all bonded together. This makes it a powerful chemical that can react with many other substances, making it super important in various industries. It’s also known for being really good at dissolving things, which is why it’s used so much in chemistry and manufacturing.
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Formula | H₂SO₄ |
Hill formula | H₂O₄S |
Name | Sulfuric acid |
Alternate names | Anhydrous sulfuric acid, Dihydrogen sulfate, Oil of vitriol, Sulphuric acid |

Sulfuric acid is a chemical compound with a complex and interesting structure. It has the chemical formula H₂SO₄. This means it is made up of two hydrogen atoms (H), one sulfur atom (S), and four oxygen atoms (O). The structure of sulfuric acid can be thought of as a central sulfur atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. Two of these oxygen atoms are double-bonded to the sulfur atom, and the other two are single-bonded but also attached to hydrogen atoms.This arrangement makes sulfuric acid a very strong acid. It’s able to donate two protons (the hydrogen atoms) when it reacts with other substances. This ability to give away protons easily makes it a very important and widely used chemical in many industries. Its structure is key to its reactivity and usefulness in making a wide variety of products.
Sulfuric acid is made using a method called the Contact Process. This process involves a few key steps. First, sulfur (S) is burned in air to create sulfur dioxide (SO₂). This is represented by the equation:
2S + O₂ → SO₂.
Next, the sulfur dioxide is mixed with more oxygen (O₂) in the presence of a catalyst, typically vanadium(V) oxide (V₂O₅). This helps convert the sulfur dioxide into sulfur trioxide (SO₃), shown by the equation:
2SO₂ + O₂ → 2SO₃ (in the presence of V₂O₅)
Once sulfur trioxide is formed, it’s not directly combined with water to make sulfuric acid because that reaction is too violent. Instead, the sulfur trioxide is first absorbed into a pre-existing concentration of sulfuric acid. This forms oleum (H₂S₂O₇), which is then carefully diluted with water to form sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄). The final step can be represented by the equation:
H₂S₂O₇ + H₂O → 2H₂SO₄
This careful process allows for the production of highly concentrated sulfuric acid, which is essential for many industrial applications.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Appearance | Colorless, oily liquid |
Odor | Odorless |
Molecular Weight | 98.079 g/mol |
Density | 1.84 g/cm³ at 20°C |
Melting Point | 10°C (50°F) |
Boiling Point | 337°C (639°F) |
Solubility in Water | Completely soluble, releases heat upon mixing |
pH | Highly acidic (pH < 1 for concentrated solutions) |
Viscosity | High, varies with concentration |
Conductivity | Good conductor of electricity due to ionization in water |
Sulfuric acid is a very strong acid. It can donate two protons (H⁺ ions) in reactions. This makes it very reactive with bases and capable of causing burns.
It has the ability to absorb water from the air. This property makes it useful for drying out substances.
Sulfuric acid can remove water from other compounds. For example, when it reacts with sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁), it removes water, leaving a black mass of carbon and releasing water vapour.
Equation: C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ + H₂SO₄ → 12C + 11H₂O + Heat
Mixing sulfuric acid with water releases a lot of heat. This reaction should be done carefully by adding acid to water, not the other way around, to avoid splashing of the hot acid.
In concentrated form, sulfuric acid can act as a powerful oxidizing agent. It can take electrons from other substances, leading to oxidation. This property allows it to react with metals, non-metals, and carbon compounds, often producing sulfur dioxide (SO₂) or sulfates.
Sulfuric acid reacts with most metals, producing hydrogen gas and metal sulfate. For example, zinc reacts with sulfuric acid to produce zinc sulfate and hydrogen gas.
It reacts with bases (like sodium hydroxide) to form water and a salt. This reaction with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces water and sodium sulfate.
Equation: 2NaOH → Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
Property | Value |
|---|---|
CAS registry number | 7664-93-9 |
Beilstein number | 2037554 |
PubChem compound ID | 1118 |
PubChem substance ID | 24859176 |
SMILES identifier | OS(=O)(=O)O |
InChI identifier | InChI=1/H2O4S/c1-5(2,3)4/h(H2,1,2,3,4)/f/h1-2H |
MDL number | MFCD00064589 |
Property | Value |
|---|---|
NFPA health rating | 3 |
NFPA fire rating | 0 |
NFPA reactivity rating | 2 |
NFPA hazards | Water reactive |

Sulfuric acid is a key ingredient in making fertilizers, especially phosphoric acid and ammonium sulfate. These fertilizers help plants grow by providing them essential nutrients.
It’s used in producing a wide range of chemicals, including other acids, dyes, and glues. This process involves reactions where sulfuric acid helps create new compounds.
In the oil industry, sulfuric acid helps remove impurities from gasoline and other petroleum products. This refining process ensures the fuel is clean and efficient.
Sulfuric acid is used to clean metals before they are coated or plated with other metals. It removes rust and prepares the surface for further treatment.
It acts as the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, which are found in cars and other vehicles. The acid allows electricity to flow between the battery’s plates.
Sulfuric acid is used in water treatment plants to adjust the pH levels of water, making it safe for drinking and use in industrial processes.
In the paper industry, sulfuric acid is used to separate lignin from cellulose fibers, making paper white and durable.
It plays a role in manufacturing various medicines, acting as a catalyst in the production processes of drugs and antibiotics.
Although used in very small amounts, sulfuric acid helps in the processing of edible oils and fats. It also acts as a preservative in some food products.
Fertilizer Production: Sulfuric acid is crucial in manufacturing fertilizers, which enhance soil nutrition and boost crop yields significantly.
Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a fundamental ingredient in the synthesis of various chemicals, facilitating the production of dyes, pigments, and many other industrial compounds.
Metal Processing: The acid’s ability to clean metal surfaces ensures better adhesion of coatings, improving the longevity and quality of metal products.
Battery Efficiency: As the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, sulfuric acid is essential for the storage and provision of electrical energy, particularly in vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
Water Treatment: By adjusting pH levels, sulfuric acid plays a pivotal role in water purification processes, making water safe for consumption and use in industries.
Pollution Control: It aids in removing harmful substances from industrial emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
Petroleum Refining: The acid helps refine petroleum products, ensuring cleaner burning fuels and reducing emissions from vehicles.
Paper Production: Its use in the paper industry leads to higher quality paper by removing impurities and enhancing the brightness and strength of the paper.
Drug Manufacturing: Sulfuric acid is used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce various medicines, helping in the fight against diseases and infections.
Food Processing: Though used in minimal quantities, it assists in the processing and preservation of certain food products, maintaining their quality and safety.
Health Hazards: Causes severe skin burns, eye damage, respiratory issues, and digestive tract harm upon contact or inhalation.
Environmental Impact: Can lead to water and soil pollution, contributing to ecosystem damage and soil infertility.
Material Corrosion: Corrodes metals and building materials, posing infrastructure risks.
Safety Risks: Improper handling and storage can result in accidents and exposure.
Adding water to sulfuric acid can cause violent reactions, emitting heat and potentially leading to splashes or explosions. Always add acid to water instead.
Sulfuric acid burns skin upon contact, causing severe chemical burns, tissue damage, and possible scarring. Immediate rinsing with water is crucial for affected areas.
Sulfuric acid has a strong, pungent odor resembling burnt matches, due to the release of sulfur oxides when exposed to air, indicating its corrosive nature.
Contact with sulfuric acid results in chemical burns, skin irritation, and potential tissue damage. Immediate and thorough washing with water is necessary to mitigate injuries.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula for sulfuric acid?
HCl
HNO₃
H₂SO₄
H₂CO₃
Sulfuric acid is commonly used in which of the following industries?
Food and beverage
Pharmaceuticals
Petroleum refining
Textile manufacturing
What is the primary use of sulfuric acid in batteries?
To neutralize pH
To act as an electrolyte
To create a buffer solution
To prevent corrosion
Sulfuric acid is considered what type of acid?
Strong acid
Weak acid
Neutral acid
Organic acid
What safety precaution is essential when handling sulfuric acid?
Wearing rubber gloves
Using a plastic container
Working in a well-ventilated area
Mixing with water first
Sulfuric acid reacts with metals to produce which gas?
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Carbon dioxide
What is the appearance of concentrated sulfuric acid?
Yellow liquid
Colorless liquid
Red solid
Blue gas
How does sulfuric acid affect the pH of a solution?
Raises the pH
Lowers the pH
Has no effect on pH
Neutralizes the pH
In the laboratory, what is one common use of sulfuric acid?
To neutralize bases
To synthesize esters
To precipitate proteins
To dissolve salts
Sulfuric acid is a by-product in the production of which chemical?
Ammonia
Chlorine
Nitric acid
Hydrogen peroxide
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

