Preparing for the CMA Exam requires a thorough understanding of internal controls, an essential component of organizational governance and risk management. Mastering internal control frameworks, including risk assessment, control activities, and monitoring mechanisms, is crucial for ensuring reliability in financial reporting and safeguarding company assets. This knowledge forms the foundation for achieving accuracy and compliance in financial processes, a critical area for CMA success.
Learning Objective
In studying “Internal Controls” for the CMA Exam, you should gain a comprehensive understanding of the processes that safeguard assets, ensure the accuracy of financial information, and promote operational efficiency. Learn to evaluate key control activities, such as segregation of duties, authorization, documentation, and reconciliation. Understand the principles behind risk assessment, control environment, and monitoring to manage and mitigate potential risks effectively. Additionally, examine how internal controls support compliance with laws and regulations, contribute to accurate financial reporting, and enhance decision-making. Apply this knowledge to interpret scenarios involving internal control systems and assess their effectiveness in real-world applications.
1. Definition and Purpose of Internal Controls
Internal controls are policies, procedures, and practices implemented by a company to safeguard its assets, ensure accurate and reliable financial reporting, promote operational efficiency, and enforce adherence to established policies. These controls are crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial information and managing risk.
2. Objectives of Internal Controls

Internal controls serve to:
- Safeguard Assets: Prevent unauthorized access and fraud.
- Ensure Reliability of Financial Reporting: Improve accuracy in financial records.
- Enhance Operational Efficiency: Promote effective resource utilization.
- Compliance with Laws and Regulations: Ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
3. Components of Internal Control (COSO Framework)
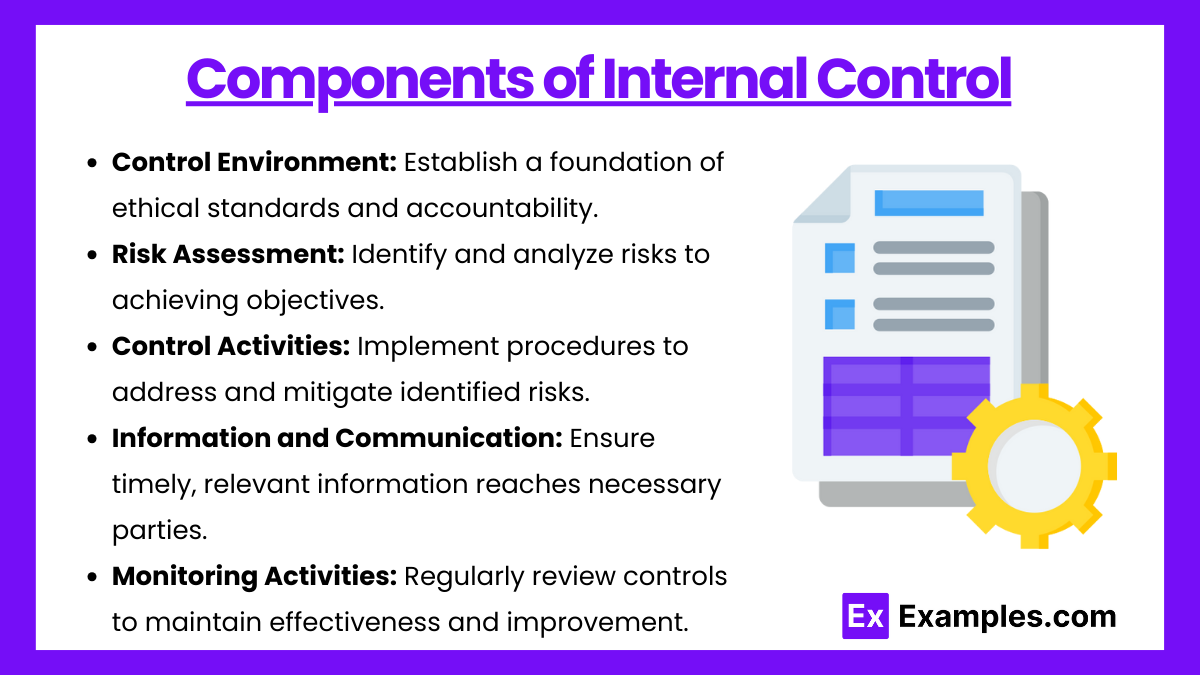
The COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations) framework, a widely used guideline, defines five core components of internal control:
- Control Environment: The foundation for all internal controls, emphasizing ethical values, management philosophy, and organizational structure.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and analyzing risks that could hinder achieving organizational objectives.
- Control Activities: Policies and procedures that help mitigate risks. These include authorization, verification, and reconciliation processes.
- Information and Communication: Ensuring timely, relevant information flows across all levels of the organization.
- Monitoring: Regular evaluation of control effectiveness, including audits and management reviews.
4. Types of Internal Controls

- Preventive Controls: Designed to prevent errors or irregularities, such as access restrictions and segregation of duties.
- Detective Controls: Identify errors or issues that have occurred, like reconciliations, audits, and variance analyses.
- Corrective Controls: Correct identified issues and prevent recurrence, such as error reporting and policy updates.
- Compensating Controls: Used when it’s impractical to implement standard controls, often to offset risks associated with control limitations.
Examples
Example 1: Importance of Segregation of Duties
- Segregation of Duties (SoD): This internal control ensures that no single individual has control over all aspects of a financial transaction, reducing the risk of error or fraud.
- Application of SoD: For instance, the person who authorizes payments should not be the same person who processes them, helping safeguard assets and ensure accountability.
Example 2: Implementing Access Controls
- Access Control Mechanisms: Restricting access to systems and data to authorized personnel only, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Application of Access Controls: Only specific employees can access critical financial data, limiting unauthorized changes and enhancing accuracy in financial reporting.
Example 3: Conducting Internal Audits
- Purpose of Internal Audits: Regular internal audits help verify compliance with policies and procedures, identify areas of improvement, and detect potential issues.
- Audit Effectiveness: By auditing financial processes, organizations can ensure internal controls function as intended and correct any deficiencies, bolstering stakeholder confidence.
Example 4: Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- KPI Monitoring: Key performance indicators are tracked to assess the effectiveness of internal controls, such as error rates in financial transactions or compliance breaches.
- Performance Assessment: Monitoring KPIs allows organizations to identify trends and respond proactively to any control weaknesses, ensuring ongoing risk management.
Example 5: Documentation of Policies and Procedures
- Importance of Documented Procedures: Documenting processes and internal controls provides clear guidelines for employees, promoting consistency and adherence to protocols.
- Documentation Benefits: Detailed documentation enables smoother training, faster issue resolution, and ensures regulatory compliance, contributing to organizational transparency.
Practice Questions
Question 1:
Which internal control principle helps prevent fraud by ensuring that no one individual controls an entire transaction?
A) Access Controls
B) Internal Audits
C) Segregation of Duties
D) Documentation of Policies
Answer: C) Segregation of Duties
Explanation: Segregation of Duties prevents fraud and errors by dividing responsibilities among multiple individuals, reducing the likelihood that errors or fraudulent actions go undetected.
Question 2:
What is the main purpose of implementing access controls within an organization?
A) To streamline financial reporting
B) To reduce the need for internal audits
C) To limit system and data access to authorized individuals
D) To document policies and procedures
Answer: C) To limit system and data access to authorized individuals
Explanation: Access controls restrict data access to authorized personnel, protecting data integrity and reducing risks associated with unauthorized data alterations.
Question 3:
Which activity best demonstrates effective monitoring of internal controls in a company?
A) Increasing the frequency of financial audits
B) Reviewing and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs)
C) Simplifying documentation procedures
D) Restricting access to accounting data
Answer: B) Reviewing and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs)
Explanation: Monitoring KPIs enables management to assess control effectiveness continuously, identifying potential issues proactively and ensuring robust risk management.


