Preparing for the CMT Exam requires a comprehensive understanding of “Sentiment Measures from External Data,” a critical aspect of technical analysis. This area focuses on an analyst’s ability to assess sentiment data derived from external sources, interpret shifts in investor behavior, and evaluate the broader market environment. Mastering these skills enables analysts to gauge external influences on market sentiment, anticipate potential market trends, and make informed strategic decisions, which is crucial for achieving success on the CMT Exam.
Learning Objectives
In studying “Sentiment Measures from External Data” for the CMT, you should learn to understand the impact of sentiment indicators that derive from external data sources. These indicators reflect broader market psychology and investor mood. Familiarize yourself with commonly referenced external sentiment metrics, such as news sentiment scores, social media sentiment analysis, and macroeconomic sentiment indices. Recognize how heightened sentiment extremes can reveal potential market inflection points, signaling conditions of overconfidence or caution that may indicate market reversals.
Introduction to Sentiment Measures from External Data
Sentiment measures from external data are valuable tools for understanding market psychology and anticipating shifts in market trends. These measures include data from news, social media, economic surveys, and investor sentiment indices, which together provide insights into public opinion and investor mood. By analyzing these external data sources, analysts and traders can enhance their understanding of market sentiment, aiding in more accurate predictions and adaptive trading strategies. Incorporating sentiment from external data enriches traditional analysis, offering a broader, real-time perspective on market dynamics.
Key Sentiment Indicators from External Data
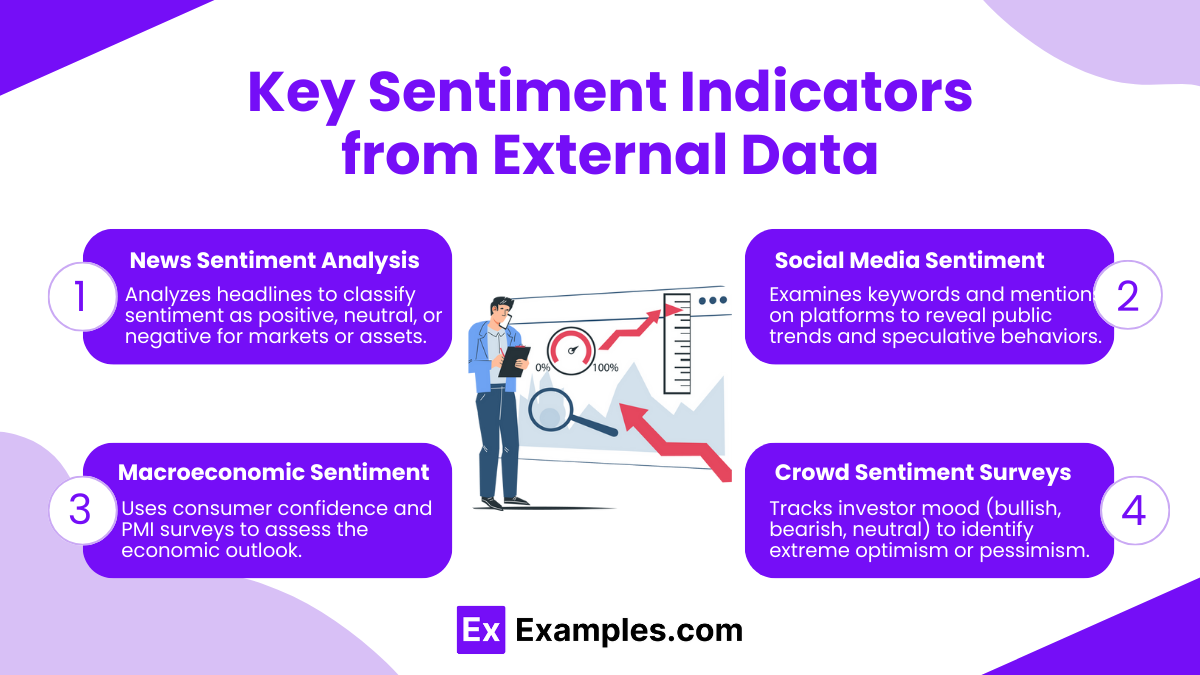
- News Sentiment Analysis: Algorithms analyze news headlines and articles to determine whether sentiment around a specific market or asset is positive, neutral, or negative. Tools like sentiment analysis in Bloomberg and other financial platforms assign scores to news items, helping analysts gauge the overall sentiment direction.
- Social Media Sentiment: Platforms such as Twitter, Reddit, and specialized finance forums can reveal retail investor sentiment and trends. Social media sentiment analysis assesses keywords, hashtags, and mentions to reveal public sentiment and highlight potential “herd mentality” or speculative bubbles.
- Macroeconomic Sentiment: These include indicators like consumer confidence surveys, purchasing manager indices (PMIs), and economic sentiment surveys (e.g., University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment). These measures indicate the economic outlook from a broad base, providing context for shifts in market sentiment.
- Crowd Sentiment Surveys: Investor sentiment surveys, such as the AAII (American Association of Individual Investors) Sentiment Survey, measure the percentage of investors who are bullish, bearish, or neutral. This data can be used to gauge the mood of individual investors and detect extreme optimism or pessimism.
Importance of Sentiment Measures from External Data
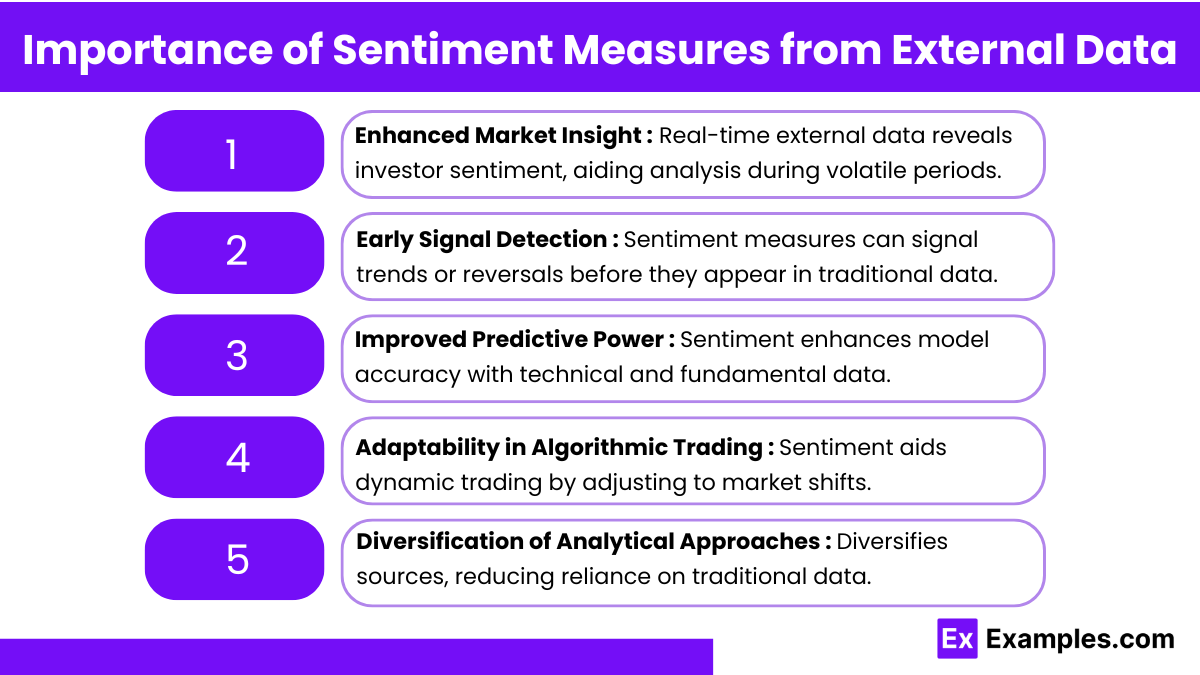
1. Enhanced Market Insight
External data sources, such as news, social media, and public sentiment, provide real-time insights into market psychology and investor behavior. This can help analysts understand prevailing sentiment, especially during volatile periods.
2. Early Signal Detection
Sentiment measures can act as early indicators of market shifts, allowing analysts to detect trends or reversals ahead of time. For example, spikes in social media sentiment around a stock can signal upcoming price action before it’s reflected in traditional data.
3. Improved Predictive Power
Incorporating sentiment analysis into models improves the predictive accuracy of price movements. Sentiment data often complements fundamental and technical indicators, enhancing the robustness of investment models.
4. Adaptability in Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading strategies leverage sentiment measures to optimize entry and exit points. Sentiment data can provide a dynamic edge, allowing algorithms to adapt to changing market conditions more effectively than relying solely on historical price data.
5. Diversification of Analytical Approaches
By incorporating external sentiment data, analysts diversify their information sources, reducing reliance on traditional data. This approach minimizes blind spots in market analysis, offering a broader view and enabling better-informed decision-making.
Examples
Example 1. Financial Market Analysis
Investors and analysts often use sentiment measures from external news sources, social media, and industry reports to gauge public perception of specific stocks or sectors. For instance, a sudden surge in positive sentiment around technology stocks on social media platforms like Twitter and financial forums can signal potential buying interest, encouraging traders to adjust their portfolios accordingly. This sentiment-based approach helps investors make more informed decisions by adding a layer of public perception data to traditional metrics.
Example 2. Brand Reputation Management
Companies use external sentiment data to understand public opinions about their brand, products, or competitors. By analyzing reviews, news mentions, and customer discussions on various platforms, brands can quickly detect negative trends or customer dissatisfaction. This information allows them to address issues proactively, manage brand reputation more effectively, and improve customer relations by responding directly to feedback seen in the data.
Example 3. Policy-Making and Public Opinion
Governments and public organizations leverage sentiment measures from news reports, social media posts, and other public opinion sources to gauge the reaction of citizens to new policies or current events. For example, if sentiment analysis shows a negative response to a new policy on social media, policymakers may reconsider certain aspects to improve public reception. This approach ensures that decisions align more closely with public sentiment, potentially increasing support and compliance.
Example 4. Product Development and Marketing
Businesses utilize sentiment analysis from social platforms and review sites to gain insights into consumer preferences and needs. By tracking sentiment around specific product features or competitor offerings, companies can refine their products and marketing strategies. For example, if external data shows positive sentiment towards eco-friendly packaging, a company may prioritize sustainable packaging in future product lines to align with consumer preferences and boost brand loyalty.
Example 5. Crisis Management and Risk Assessment
During crises, such as product recalls or market downturns, companies and investors monitor sentiment from media sources and public comments to assess the potential impact. Real-time sentiment tracking allows them to respond quickly to negative press or customer backlash, helping mitigate reputational damage. For instance, during a market crisis, investors can use sentiment data to identify signs of recovery or further decline, aiding in timely decision-making that minimizes losses.
Practice Questions
Question 1
Which of the following external data sources is commonly used in sentiment analysis for financial markets?
A) Company balance sheets
B) Social media platforms
C) Federal Reserve interest rate announcements
D) Internal trading data
Answer: B) Social media platforms
Explanation:
Social media platforms, like Twitter and Reddit, are valuable sources of external sentiment data because they capture real-time public opinion and reactions to financial news. These platforms are widely used in sentiment analysis because they offer insights into how investors feel about market trends, individual stocks, or economic events. Unlike internal trading data or structured financial statements (such as balance sheets), social media provides unstructured data that can be processed through sentiment analysis techniques to gauge investor mood and potential market movement.
Question 2
What is the primary purpose of using sentiment analysis on external news sources in market analysis?
A) To predict long-term stock price trends
B) To assess a company’s financial performance
C) To gauge short-term market reactions and investor mood
D) To analyze economic indicators
Answer: C) To gauge short-term market reactions and investor mood
Explanation:
Sentiment analysis on external news sources, such as online news articles, financial news websites, and even press releases, helps analysts and traders understand the immediate emotional reaction and mood of investors. This can be critical for short-term trading strategies, as markets can react quickly to news, whether it’s positive, negative, or neutral. Unlike economic indicators or traditional performance analysis, which often provide more long-term perspectives, sentiment analysis of news aims to capture quick shifts in investor behavior that might influence market prices.
Question 3
Sentiment scores are typically quantified on a scale. What does a high positive sentiment score usually indicate about market behavior?
A) Investors are likely to engage in a selling trend
B) The market may experience increased volatility
C) Investors generally have a bullish outlook
D) The company’s stock is undervalued
Answer: C) Investors generally have a bullish outlook
Explanation:
A high positive sentiment score reflects an optimistic mood among investors, often indicating a bullish outlook where investors are inclined toward buying rather than selling. This score is derived by analyzing words, phrases, and language used in external data sources, such as news headlines and social media posts. Positive sentiment can signal confidence in the market or in a particular asset, potentially leading to upward price movement. While high sentiment can correlate with volatility, it does not specifically indicate it; rather, it represents a general trend in investor sentiment.