Information systems and data management are essential components of modern business operations, enabling the collection, processing, and storage of data for decision-making and financial reporting. Effective data management ensures data accuracy, consistency, and compliance with regulatory standards. Information systems, such as ERP and database management systems (DBMS), streamline business processes and support operational efficiency. As technology evolves, professionals must understand IT controls, data governance, cybersecurity, and emerging technologies to manage risks.
Learning Objectives
In studying "Information Systems and Data Management" for the CPA Exam, you should understand the role of information systems in supporting business operations, decision-making, and financial reporting. Learn the principles of data governance, data security, and database management systems (DBMS) to ensure data accuracy and compliance. Evaluate the importance of IT general and application controls, such as access controls and backup procedures, in safeguarding financial information. Explore how technologies like ERP systems, cloud computing, and big data analytics enhance business processes. Apply your understanding to identify risks, assess IT controls, and interpret scenarios related to information systems in CPA practice questions.
1. Role of Information Systems in Organizations
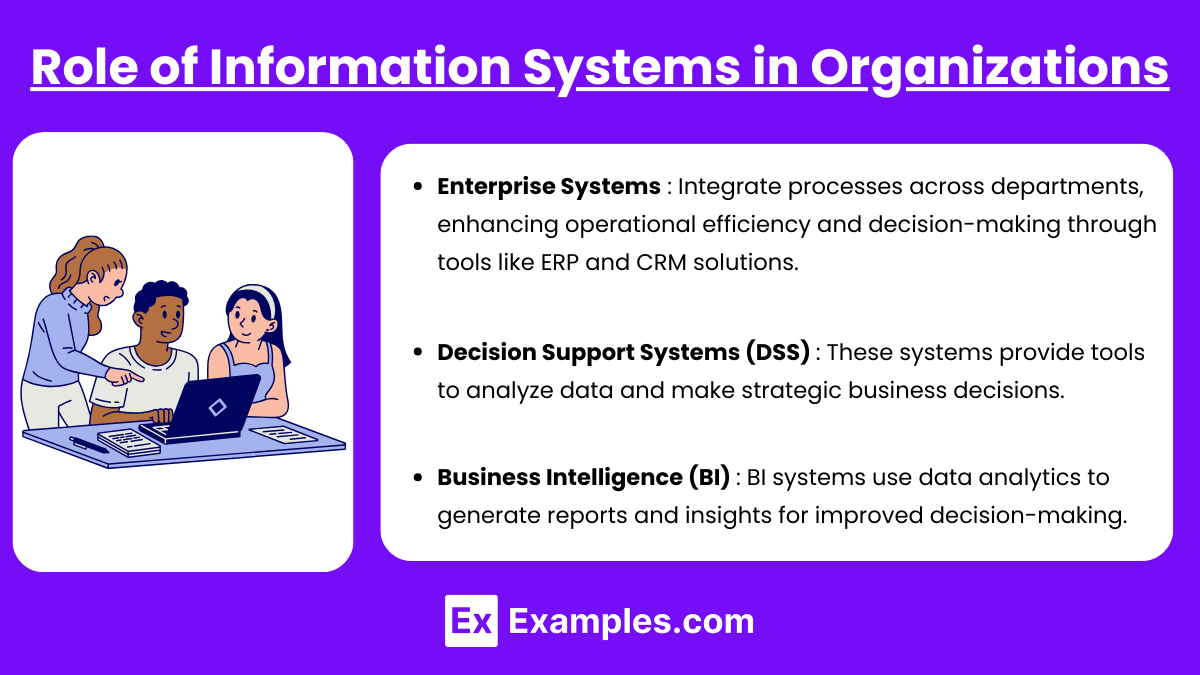
Enterprise Systems: Information systems support operational efficiency and decision-making by integrating processes across departments, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Decision Support Systems (DSS): These systems provide tools to analyze data and make strategic business decisions.
Business Intelligence (BI): BI systems use data analytics to generate reports and insights for improved decision-making.
2. Components of Information Systems
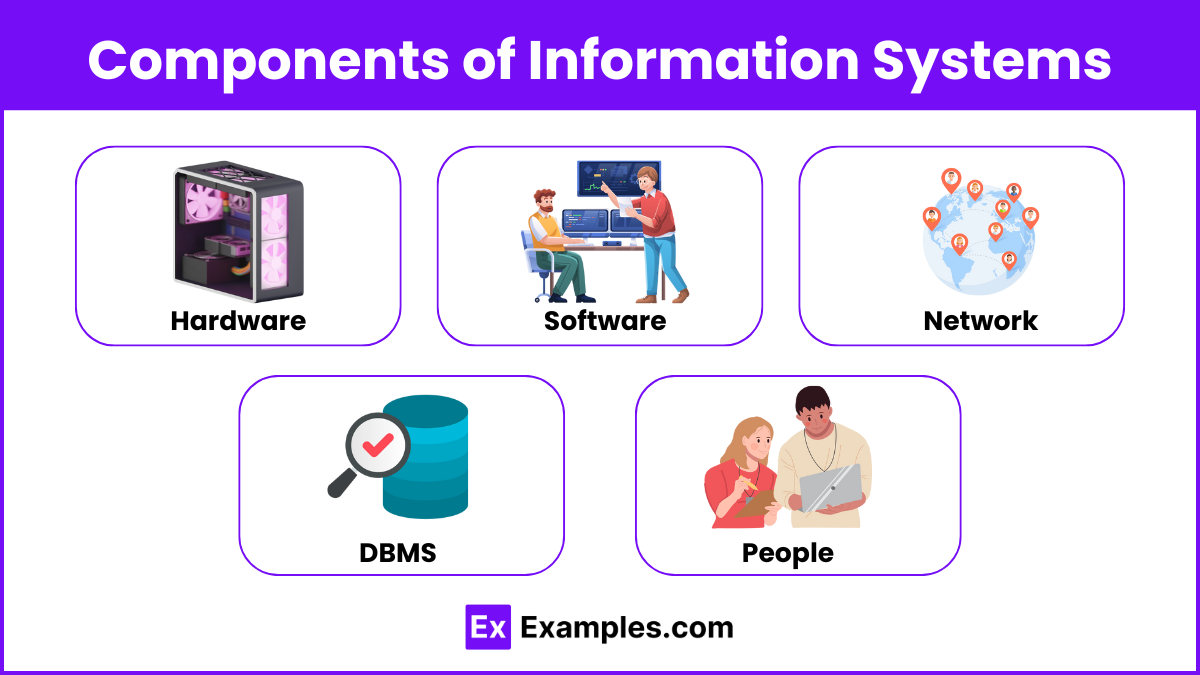
Hardware: Physical devices like computers, servers, networking equipment, and storage devices.
Software: Application programs and operating systems essential for business operations.
Network: Includes Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), and the internet, facilitating communication.
Database Management Systems (DBMS): Systems used to store, manage, and retrieve data efficiently.
People: Users of information systems, including management, IT professionals, and end-users.
3. Data Management
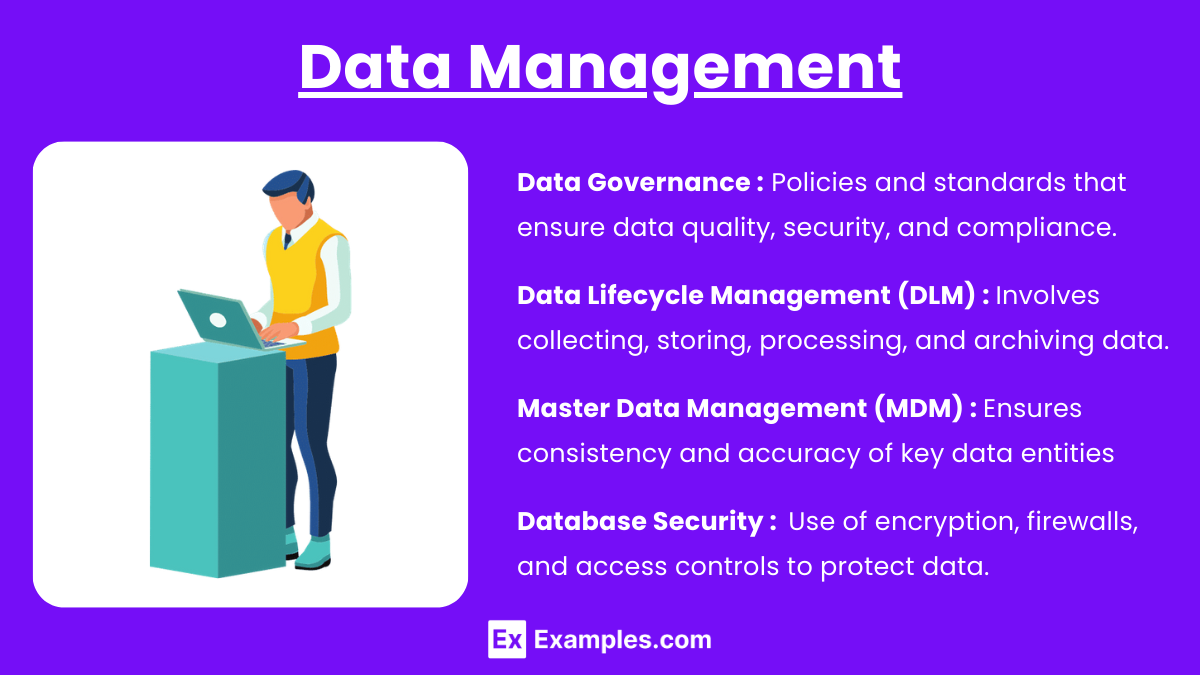
Data Governance: Policies and standards that ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM): Involves collecting, storing, processing, and archiving data.
Master Data Management (MDM): Ensures consistency and accuracy of key data entities (like customers and products) across systems.
Database Security: Use of encryption, firewalls, and access controls to protect data.
4. Systems Development and Life Cycle Management (SDLC)
Planning: Understanding business needs and defining the project scope.
Analysis: Assessing requirements and documenting processes.
Design: Creating system architecture and interface designs.
Implementation: Building, testing, and deploying the system.
Maintenance: Ongoing monitoring and updates to ensure system performance.
5. Data Analytics and Big Data
Data Analytics: Techniques like descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics to derive insights from data.
Big Data: Managing large, complex datasets from diverse sources, often requiring special tools like Hadoop or Spark.
Data Visualization: Presenting data in meaningful ways using charts, graphs, and dashboards (e.g., Tableau, Power BI).
6. IT Controls and Risk Management

General IT Controls: Policies to ensure the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of systems and data (e.g., access controls, backup procedures).
Application Controls: Automated checks embedded within systems to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and validity (e.g., input validation, error reports).
Risk Assessment: Identifying and managing risks associated with the use of information systems.
Cybersecurity: Protecting information assets from threats through the use of firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems.
Examples
Example 1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems integrate core business processes across departments such as finance, human resources, procurement, and inventory management. By providing a unified platform, ERP systems ensure real-time data availability, improve workflow efficiency, and reduce redundancy. A CPA candidate must understand how ERP systems impact financial reporting, internal control structures, and operational performance.
Example 2. Data Governance and Quality Management
Data governance involves policies, procedures, and controls that maintain the quality, integrity, and security of data across an organization. A CPA must recognize how poor data quality can lead to financial errors or compliance issues and how effective data governance frameworks support regulatory reporting. Tools like master data management (MDM) ensure consistent use of key data across multiple systems, such as customer and product databases.
Example 3. IT General and Application Controls
CPAs need to assess IT controls, including general controls (access management, change management, backups) and application controls (input validation, reconciliation reports). For example, in an accounting information system (AIS), automated controls might prevent duplicate invoices from being processed. Understanding the distinction between these control types helps auditors identify weaknesses in IT environments.
Example 4. Big Data Analytics in Financial Auditing
The use of big data tools has transformed auditing by enabling advanced analytics on large datasets. For instance, continuous auditing involves monitoring transactions in real-time to detect anomalies and fraud patterns. A CPA should be familiar with how technologies like data visualization tools (e.g., Power BI) and predictive analytics enhance decision-making and financial statement analysis.
Example 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management Frameworks
CPAs must understand the importance of cybersecurity in protecting sensitive financial data. This includes knowledge of frameworks such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and how organizations manage cybersecurity risks. For example, firms may implement multi-factor authentication and encryption to safeguard client financial information. A CPA should also assess how effective cybersecurity practices impact internal controls and compliance.
Practice Questions
Question 1
Which of the following best describes the primary function of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system?
A. Automates payroll processing and employee benefits management.
B. Facilitates the real-time integration of data across various departments.
C. Provides data analytics specifically for customer relationship management (CRM).
D. Stores and archives historical financial statements for regulatory compliance.
Answer: B. Facilitates the real-time integration of data across various departments.
Explanation: ERP systems are designed to integrate the core processes of an organization, such as accounting, procurement, human resources, and inventory, in real time. This integration improves data flow across different departments, eliminating redundancies and ensuring consistency. Option A refers only to payroll, which is a small component of ERP. Option C relates to CRM systems, not ERP. Option D is incorrect because ERP systems focus on real-time operations, not just storing historical data.
Question 2
What is the primary purpose of data governance in an organization?
A. To ensure that data is accessible to all employees at all times.
B. To maintain data consistency, security, and compliance with regulations.
C. To integrate multiple databases into one centralized repository.
D. To manage the development lifecycle of software applications.
Answer: B. To maintain data consistency, security, and compliance with regulations.
Explanation: Data governance ensures that data within an organization is accurate, consistent, secure, and compliant with regulatory standards. It involves policies, processes, and controls for data management, supporting effective decision-making and reducing risks. Option A is incorrect because access to data should be controlled based on roles and responsibilities. Option C describes database integration, which is a part of data management, not governance. Option D refers to software development, which is unrelated to data governance.
Question 3
Which of the following IT general controls is most critical to ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial reports?
A. System access control policies.
B. Backup and disaster recovery procedures.
C. Application input validation controls.
D. User training programs.
Answer: A. System access control policies.
Explanation: System access control policies are essential for protecting financial data from unauthorized access, which is critical for the integrity and reliability of financial reports. Proper access controls ensure that only authorized individuals can modify or view financial data. Option B is important but more relevant to business continuity than financial report accuracy. Option C relates to application controls, which are important but specific to data entry. Option D, while beneficial, is not directly related to financial data accuracy or IT controls.