Boundaries are limits that define where one thing ends and another begins. They can be physical, emotional, social, or conceptual and play a crucial role in literature, history, and personal interactions. Understanding boundaries helps you analyze characters, themes, and conflicts, which is essential for tackling reading comprehension questions on the Digital SAT effectively.
Learning Objectives
In studying “Boundaries” for the Digital SAT, you should learn to understand how to identify boundaries in reading passages, including shifts in tone, perspective, or topic. Analyze how authors structure their arguments or narratives, and recognize transitions that signal changes in ideas or focus. Evaluate how these boundaries influence the meaning and coherence of the text, helping you to better comprehend complex passages. Additionally, develop skills in identifying context clues that indicate boundaries and use this understanding to answer related reading comprehension questions effectively.
Understanding Boundaries: A Guide for the Digital SAT
Boundaries in the context of the SAT can refer to the limits within relationships, personal space, time management, and communication. The term can also extend to ideas in literature and social sciences, such as moral or ethical boundaries, or physical and geographical boundaries. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying the concept of boundaries, which will help you answer questions effectively on the Digital SAT.
Boundaries
Boundaries are limits or borders that define the scope of something. They can be physical, emotional, or conceptual, helping to distinguish where one thing ends and another begins. In personal and social contexts, boundaries help individuals protect their personal space, emotions, and time. In literary contexts, boundaries can be thematic, like those that separate good and evil or freedom and oppression.
Types of Boundaries
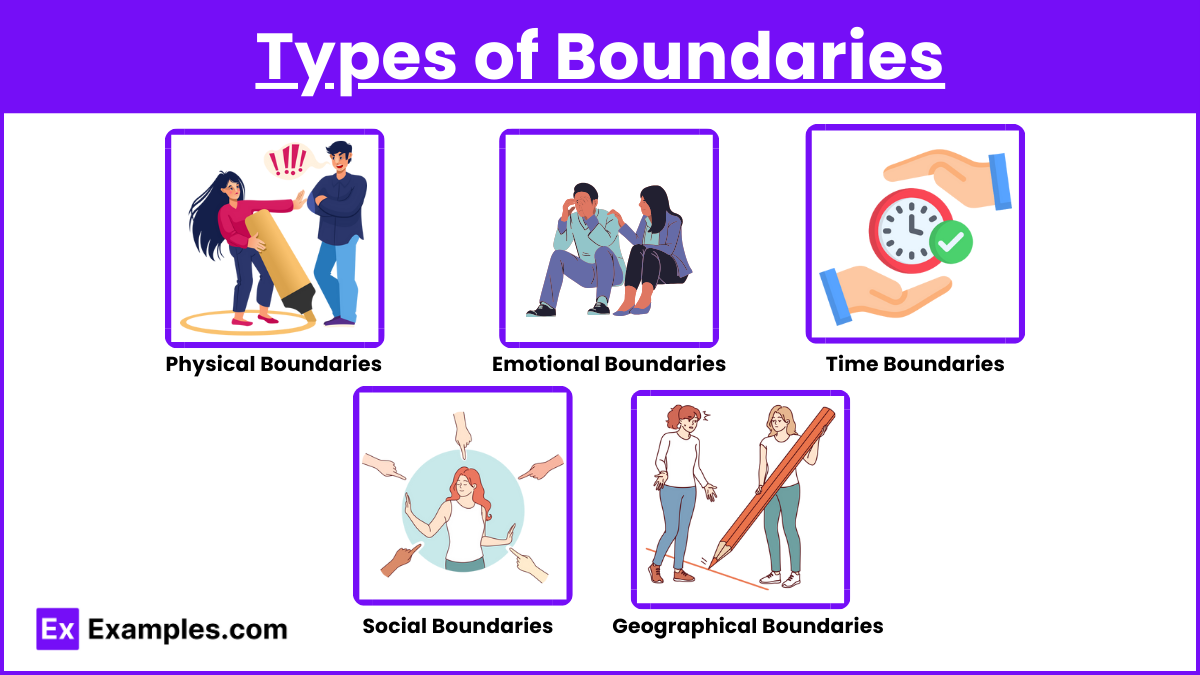
1. Physical Boundaries
Physical boundaries define personal space and physical limits between individuals.
- Examples: Standing a certain distance away from someone in conversation, respecting someone’s personal belongings, or choosing not to touch someone without permission.
2. Emotional Boundaries
Emotional boundaries protect your feelings and emotional well-being. They help define how you respond to others and express your own emotions.
- Examples: Saying “no” when you feel uncomfortable, not oversharing personal details, or choosing not to engage in gossip.
3. Time Boundaries
Time boundaries refer to the limits you set regarding how you spend your time.
- Examples: Scheduling specific times for study and rest, setting aside time for family and friends, or avoiding excessive work outside of dedicated hours.
4. Social Boundaries
Social boundaries involve cultural, moral, or ethical lines that society or individuals should not cross.
- Examples: Norms around privacy, respecting other cultures, and adhering to ethical standards in communication.
5. Geographical Boundaries
Geographical boundaries are the physical demarcations between countries, states, and cities.
- Examples: Borders between countries, such as the United States and Canada, or natural boundaries like rivers and mountains.
Boundaries in Literature and Reading Passages
Understanding boundaries is essential for reading comprehension questions. Here are some ways boundaries might appear in literary passages:
- Character Boundaries: Characters often face internal and external boundaries, like personal fears or societal restrictions.
- Theme Boundaries: Themes may explore the crossing or breaking of boundaries, such as the pursuit of forbidden knowledge or breaking social norms.
- Setting Boundaries: Boundaries in the setting can help develop the plot, like a locked door or a forbidden forest, symbolizing confinement or exploration.
Boundaries in Social Sciences and History Passages

The SAT often includes passages that require analysis of social or historical contexts. Boundaries can be relevant here as well:
- Political Boundaries: Discussions about the formation of nations, treaties, and conflicts often involve geographical and political boundaries.
- Ethical Boundaries: These are often explored in social sciences to discuss moral implications of decisions, policies, or cultural practices.
- Cultural Boundaries: Understanding how cultures establish their norms and values helps in analyzing texts focused on cultural interactions and clashes.
Examples
Example 1: Personal Space in Relationships
A person may establish a boundary by maintaining physical space, such as choosing to stand a few feet away during conversations. This boundary helps them feel comfortable and respected in social interactions.
Example 2: Time Management in Work-Life Balance
Setting aside specific hours for work and personal time is a common boundary. For example, someone might choose not to respond to work emails after 6 PM, preserving time for relaxation and family.
Example 3: Cultural Differences in Social Norms
In one culture, it may be customary to greet with a kiss on the cheek, while in another, a handshake is preferred. These cultural boundaries highlight differences in traditions and respectful behavior between societies.
Example 4: Geographical Borders Between Countries
The boundary between the United States and Canada is a physical and political border that defines the territories and governments of each country. Such boundaries impact immigration, trade, and international relations.
Example 5: Emotional Boundaries in Friendships
Someone might decide not to share certain personal details with a friend to protect their feelings. This emotional boundary helps them manage privacy and maintain emotional security in the relationship.
Practice Questions
Question 1:
Geographical boundaries are most often used to define:
A. Emotional responses to certain situations.
B. The lines between different countries or states.
C. Ethical decisions in difficult situations.
D. Privacy settings on social media accounts.
Answer: B. The lines between different countries or states.
Explanation: Geographical boundaries are physical divisions that define the limits of territories, such as countries or states. These boundaries are often marked by borders or natural features like rivers and mountains.
Question 2:
Which option illustrates an emotional boundary?
A. Saying “no” to avoid overwhelming responsibilities.
B. Avoiding eye contact in a conversation.
C. Setting aside time for exercise each morning.
D. Respecting another person’s cultural traditions.
Answer: A. Saying “no” to avoid overwhelming responsibilities.
Explanation: An emotional boundary involves protecting your emotional well-being. Saying “no” to tasks that could lead to stress or burnout is a way of maintaining an emotional boundary.
Question 3:
Which of the following best represents a cultural boundary?
a) A country’s physical border
b) Standing a certain distance from others
c) Different greetings in various countries (e.g., handshakes vs. bows)
d) Setting limits on work hours
Answer: c) Different greetings in various countries (e.g., handshakes vs. bows)
Explanation:
Cultural boundaries define differences in norms and practices between cultures, like how greetings vary from one country to another. Physical borders refer to geographical boundaries, while standing distance is about physical boundaries. Work hours relate to time boundaries, not cultural ones.