Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) transforms the world with its advanced capabilities. AI mimics human intelligence through machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics. It powers everyday applications like virtual assistants, recommendation systems, and autonomous vehicles. Businesses use AI to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. AI also revolutionizes healthcare, education, finance, and more, offering new solutions to complex problems. Understanding AI’s impact and potential is crucial as it continues to evolve and shape our future.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think and learn like humans. These intelligent systems can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. AI encompasses various subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, and computer vision. It aims to create systems that can perform complex tasks autonomously, improve over time through experience, and adapt to new situations. AI continues to evolve, influencing various industries and transforming the way we live and work.
Artificial Intelligence Examples
In Daily Life
- Voice Assistants: AI-powered assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant help with tasks, answer questions, and control smart home devices.
- Personalized Recommendations: Streaming services (Netflix, Spotify) and e-commerce platforms (Amazon) use AI to recommend content and products based on user behavior.
- Navigation Apps: AI in apps like Google Maps and Waze provides real-time traffic updates and route optimization.
- Smart Home Devices: AI controls smart thermostats, lighting, and security systems, learning user preferences and habits.
- Social Media: AI algorithms curate news feeds, suggest friends, and target advertisements on platforms like Facebook and Instagram.
- Email Filtering: AI helps filter spam and categorize emails in services like Gmail.
- Online Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants on websites provide instant support and answer queries.
In Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: AI analyzes X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect diseases like cancer and fractures.
- Predictive Analytics: AI predicts patient outcomes, hospital readmissions, and disease outbreaks.
- Personalized Medicine: AI helps tailor treatments to individual patients based on genetic information and other data.
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI chatbots and apps provide medical advice, reminders for medication, and health tracking.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates the discovery of new drugs by analyzing biological data and predicting how different compounds will behave.
- Robotic Surgery: AI-powered robots assist in surgeries, increasing precision and reducing recovery time.
- Remote Monitoring: AI systems monitor patients’ health data in real-time, alerting healthcare providers to any critical changes.
In Business
- Customer Service: AI chatbots handle customer inquiries, providing 24/7 support and improving response times.
- Fraud Detection: AI detects fraudulent transactions and activities in real-time.
- Data Analytics: AI analyzes large datasets to uncover insights, trends, and business opportunities.
- Marketing: AI personalizes marketing campaigns and content to target specific audiences more effectively.
- Supply Chain Management: AI optimizes logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting.
- HR and Recruitment: AI screens resumes, schedules interviews, and even conducts initial interviews.
- Financial Analysis: AI assists in financial forecasting, risk management, and investment strategies.
In Robots
- Industrial Robots: AI robots perform tasks like assembly, welding, and packaging in manufacturing.
- Service Robots: AI robots provide services in hospitality, retail, and customer service environments.
- Healthcare Robots: AI robots assist in surgeries, rehabilitation, and patient care.
- Delivery Robots: AI-powered drones and robots deliver packages and food.
- Companion Robots: AI robots provide companionship and assistance to the elderly and disabled.
- Exploration Robots: AI robots explore hazardous environments, such as deep-sea and space missions.
- Educational Robots: AI robots are used in classrooms to assist with teaching and engage students in learning.
In Ethical Dilemmas
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI must make split-second decisions in potential accident scenarios, raising questions about prioritizing human lives.
- Surveillance: AI surveillance systems balance security benefits with privacy concerns.
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inherit biases from training data, leading to unfair outcomes in areas like hiring and lending.
- Job Displacement: AI automation impacts employment, necessitating discussions on job displacement and retraining.
- Decision Making: AI decision-making in healthcare and law enforcement raises ethical concerns about transparency and accountability.
- Data Privacy: AI’s reliance on large datasets brings up issues of consent and data security.
- Autonomous Weapons: The development of AI-powered weapons poses significant ethical and moral questions.
In Applications
- Natural Language Processing: AI is used in applications like translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbots.
- Image and Speech Recognition: AI applications include facial recognition, voice assistants, and security systems.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI predicts equipment failures in industries like manufacturing and aviation.
- Energy Management: AI optimizes energy consumption in smart grids and buildings.
- Agriculture: AI applications in precision farming, crop monitoring, and pest detection.
- Healthcare: AI applications in diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient monitoring.
- Finance: AI applications in trading, fraud detection, and customer service.
In Companies
- Google: Uses AI for search algorithms, Google Assistant, and self-driving cars.
- Amazon: Uses AI for product recommendations, Alexa, and warehouse automation.
- Apple: Uses AI for Siri, facial recognition, and personalized services.
- Microsoft: Uses AI for Cortana, Azure AI services, and Office 365 features.
- IBM: Uses AI for Watson, healthcare analytics, and business intelligence.
- Facebook: Uses AI for content curation, ad targeting, and facial recognition.
- Tesla: Uses AI for autonomous driving and vehicle safety features.
In Education
- Personalized Learning: AI tailors educational content and pacing to individual student needs.
- Automated Grading: AI systems grade assignments and provide feedback.
- Tutoring Systems: AI-powered tutors help students with specific subjects and concepts.
- Learning Analytics: AI analyzes student data to identify learning patterns and areas needing improvement.
- Course Recommendations: AI recommends courses and learning paths based on students’ interests and performance.
- Language Learning: AI applications assist in learning new languages through interactive exercises.
- Virtual Classrooms: AI enhances virtual learning environments with interactive and adaptive content.
For Students
- Study Assistants: AI apps help students with organizing study schedules and managing time.
- Homework Help: AI platforms provide step-by-step solutions and explanations for homework problems.
- Language Translation: AI translation tools help students understand and learn foreign languages.
- Research Tools: AI-powered tools assist students in finding and organizing research materials.
- Career Guidance: AI platforms provide insights into potential career paths based on students’ skills and interests.
- Mental Health Support: AI apps offer mental health resources and support for students.
- Interactive Learning: AI-based educational games and simulations make learning engaging and fun.
In Agriculture
- Precision Farming: AI analyzes soil and crop data to optimize planting and harvesting schedules.
- Pest Detection: AI identifies pest infestations early, enabling targeted interventions.
- Crop Monitoring: AI drones and sensors monitor crop health and growth.
- Yield Prediction: AI models predict crop yields based on weather and soil data.
- Automated Irrigation: AI systems manage irrigation based on real-time data, conserving water.
- Soil Health Analysis: AI analyzes soil samples to recommend nutrient management practices.
- Robotic Harvesting: AI-powered robots assist in harvesting crops efficiently.
In Games
- Non-Player Characters (NPCs): AI controls NPC behavior, making them more realistic and challenging.
- Procedural Content Generation: AI generates game levels, maps, and scenarios dynamically.
- Game Balancing: AI analyzes gameplay data to adjust difficulty levels and balance game mechanics.
- Player Behavior Analysis: AI studies player behavior to enhance game design and player experience.
- Virtual Reality (VR): AI enhances VR experiences by creating more immersive and responsive environments.
- Adaptive Learning: AI adapts game content and challenges based on players’ skills and progress.
- Cheat Detection: AI detects and prevents cheating in online games, ensuring fair play.
How Artificial Intelligence Works
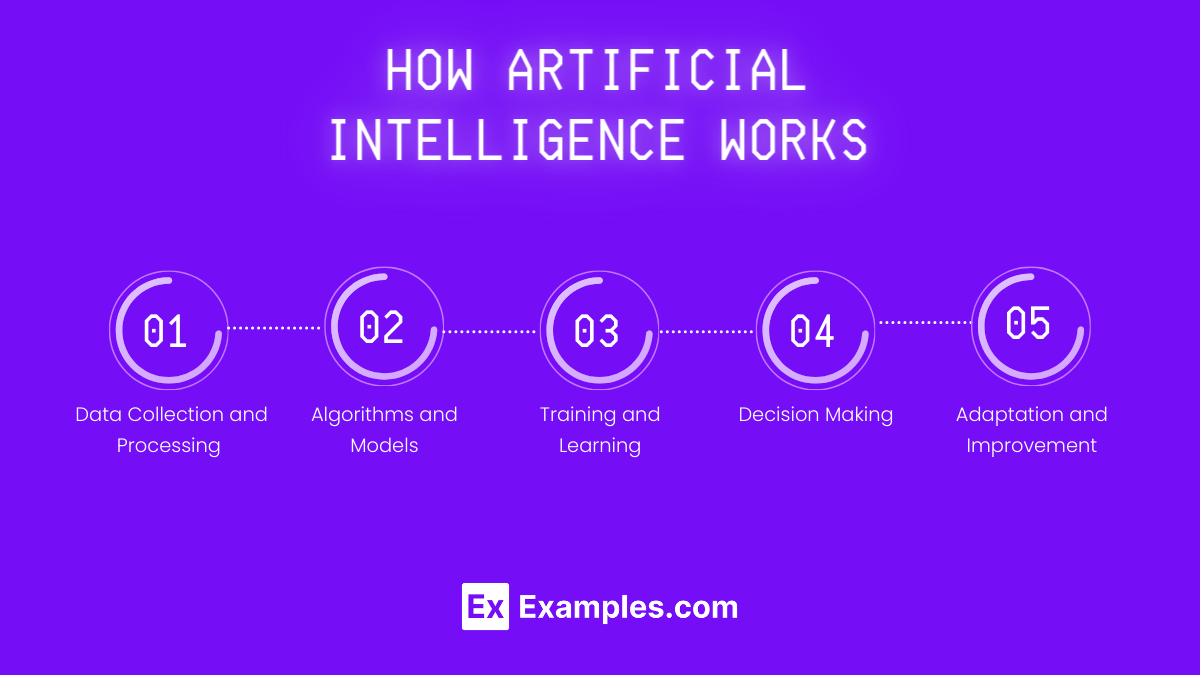
Artificial Intelligence (AI) works through a combination of algorithms, data processing, and machine learning techniques. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
1. Data Collection and Processing
- Data Gathering: AI systems collect vast amounts of data from various sources, such as sensors, databases, and online platforms.
- Data Processing: The system cleans and organizes this data to make it suitable for analysis.
2. Algorithms and Models
- Algorithms: AI uses algorithms to process data and identify patterns. These are sets of rules that guide the system on how to solve problems or perform tasks.
- Machine Learning Models: These models learn from data to make predictions or decisions. Common models include neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines.
3. Training and Learning
- Supervised Learning: The system learns from labeled data, where it receives input-output pairs and learns to map inputs to the correct outputs.
- Unsupervised Learning: The system learns from unlabeled data, identifying patterns and relationships without predefined outputs.
- Reinforcement Learning: The system learns by interacting with its environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
4. Decision Making
- Inference: After training, the AI system uses its learned models to make predictions or decisions based on new data.
- Reasoning: Some AI systems incorporate logic and reasoning to make complex decisions, mimicking human thought processes.
5. Adaptation and Improvement
- Continuous Learning: AI systems continuously update their knowledge base with new data, improving their accuracy and efficiency over time.
- Feedback Loops: Systems use feedback from their performance to refine their algorithms and models.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
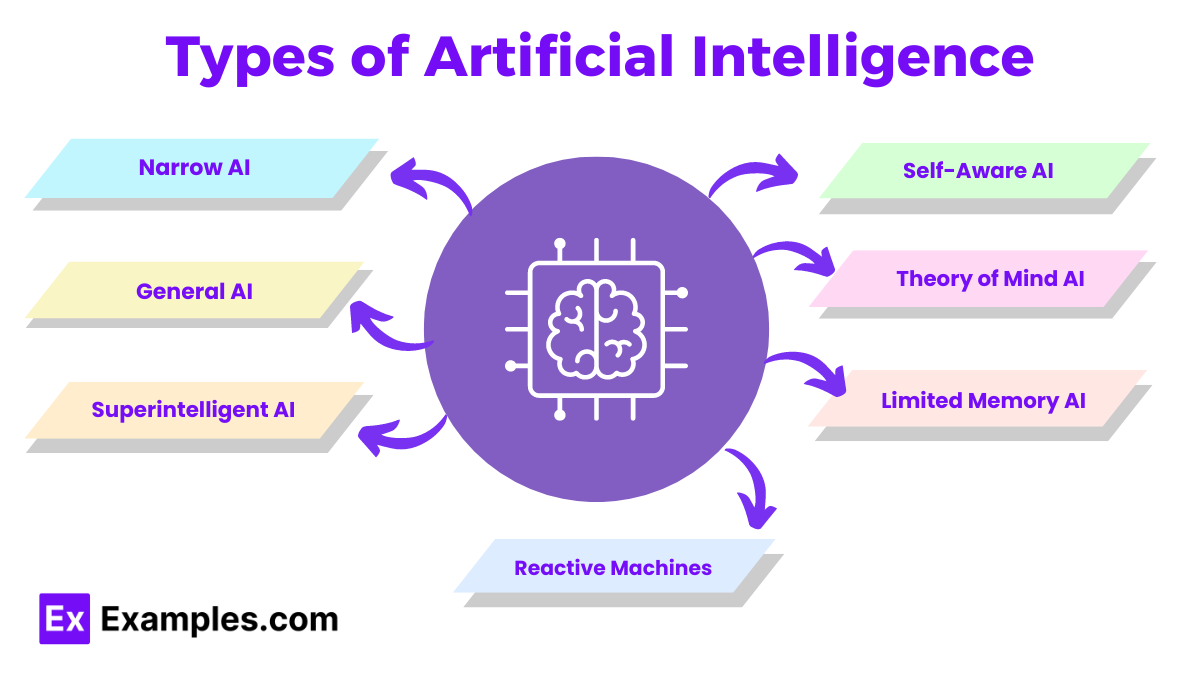
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving field that has revolutionized various industries. Understanding the different types of AI can help in grasping its potential and limitations. AI can be categorized into several types based on its capabilities and functionalities.
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Definition: Narrow AI refers to AI systems that are designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. They operate under a limited set of constraints and cannot perform beyond their programming.
Examples:
- Voice Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
- Recommendation Systems: Netflix and Amazon recommendations.
- Image Recognition Systems: Facial recognition on smartphones.
2. General AI (Strong AI)
Definition: General AI is a theoretical form of AI that possesses the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, similar to human intelligence. It can autonomously solve problems without human intervention.
Examples: Currently, there are no true examples of General AI as it remains a concept under research and development.
3. Superintelligent AI
Definition: Superintelligent AI refers to AI that surpasses human intelligence and capabilities in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making. It is considered a potential future development in AI technology.
Examples: Superintelligent AI is hypothetical and does not exist yet. It is a subject of speculation and ethical discussions.
4. Reactive Machines
Definition: Reactive machines are the most basic type of AI that can only react to specific stimuli or situations. They do not have memory or the ability to learn from past experiences.
Examples:
- IBM’s Deep Blue: A chess-playing computer that defeated world champion Garry Kasparov.
- Google’s AlphaGo: An AI system designed to play the board game Go.
5. Limited Memory AI
Definition: Limited memory AI systems can use past experiences or data to make decisions. They have a limited memory that allows them to learn and improve over time.
Examples:
- Self-Driving Cars: Use sensors and data to navigate and make driving decisions.
- Chatbots: Can remember previous interactions to provide better responses.
6. Theory of Mind AI
Definition: Theory of Mind AI aims to understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions. This type of AI is still in the experimental stage and seeks to interact more naturally and intuitively with humans.
Examples: Current AI systems are progressing towards Theory of Mind but are not fully developed yet.
7. Self-Aware AI
Definition: Self-aware AI represents the most advanced form of AI, which possesses self-consciousness and awareness. It understands its own existence and can think, learn, and make decisions independently.
Examples: Self-aware AI remains a theoretical concept and does not exist in reality as of now.
Table of AI Types and Characteristics
| Type of AI | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Narrow AI | AI designed for specific tasks. | Siri, Alexa, Netflix recommendations |
| General AI | AI with human-like intelligence across a wide range of tasks. | Currently hypothetical |
| Superintelligent AI | AI surpassing human intelligence in all aspects. | Hypothetical |
| Reactive Machines | Basic AI reacting to specific stimuli. | IBM’s Deep Blue, Google’s AlphaGo |
| Limited Memory AI | AI with the ability to learn from past experiences. | Self-driving cars, chatbots |
| Theory of Mind AI | AI aiming to understand human emotions and beliefs. | Experimental stage |
| Self-Aware AI | AI with self-consciousness and independent thinking. | Theoretical concept |
Techniques of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses various techniques and methodologies to create intelligent systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These techniques can be broadly categorized based on the specific capabilities and applications of AI.
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Definition: Machine Learning is a subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. ML algorithms improve their performance as they are exposed to more data over time.
Key Techniques:
- Supervised Learning: Algorithms learn from labeled data to make predictions. Examples include classification and regression.
- Unsupervised Learning: Algorithms identify patterns and relationships in unlabeled data. Examples include clustering and dimensionality reduction.
- Reinforcement Learning: Algorithms learn through trial and error by receiving rewards or penalties. This technique is often used in robotics and game playing.
2. Neural Networks
Definition: Neural Networks are computational models inspired by the human brain’s structure. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process input data to produce output.
Key Techniques:
- Feedforward Neural Networks: The simplest type of neural network where data flows in one direction from input to output.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Specialized for processing grid-like data such as images. They are widely used in image and video recognition.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Designed for sequential data, such as time series or natural language. They have loops allowing information to persist.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Definition: NLP involves the interaction between computers and human language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Key Techniques:
- Tokenization: Breaking text into words or phrases.
- Sentiment Analysis: Determining the sentiment expressed in text.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying and classifying entities in text, such as names of people or places.
- Machine Translation: Translating text from one language to another.
4. Expert Systems
Definition: Expert Systems mimic the decision-making abilities of a human expert. They use a knowledge base and inference rules to solve specific problems.
Key Techniques:
- Rule-Based Systems: Use predefined rules to make decisions.
- Fuzzy Logic: Deals with reasoning that is approximate rather than fixed and exact. It is useful for handling uncertainty and imprecision.
5. Robotics
Definition: Robotics involves the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. AI techniques enable robots to perform tasks autonomously.
Key Techniques:
- Path Planning: Determining an optimal path for a robot to follow.
- Object Recognition: Identifying objects in the environment.
- Motion Control: Controlling the movements of the robot.
6. Computer Vision
Definition: Computer Vision enables machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world.
Key Techniques:
- Image Classification: Categorizing images into predefined classes.
- Object Detection: Identifying and locating objects within an image.
- Image Segmentation: Partitioning an image into multiple segments to simplify analysis.
- Facial Recognition: Identifying and verifying individuals based on their facial features.
7. Genetic Algorithms
Definition: Genetic Algorithms are search heuristics inspired by the process of natural selection. They are used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems.
Key Techniques:
- Selection: Choosing the best individuals from a population.
- Crossover: Combining two parent solutions to produce offspring.
- Mutation: Introducing random changes to individuals to maintain diversity.
Table of AI Techniques and Applications
| Technique | Definition | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Algorithms learning from data to make predictions. | Spam detection, recommendation systems |
| Neural Networks | Models inspired by the human brain’s structure. | Image recognition, natural language processing |
| Natural Language Processing | Interaction between computers and human language. | Chatbots, machine translation |
| Expert Systems | Mimicking human expert decision-making. | Medical diagnosis, financial planning |
| Robotics | Design and use of robots. | Autonomous vehicles, industrial automation |
| Computer Vision | Interpreting visual information. | Surveillance, augmented reality |
| Genetic Algorithms | Search heuristics inspired by natural selection. | Optimization problems, machine learning |
Deep learning vs. machine learning
| Aspect | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data. | Subset of machine learning using neural networks with many layers. |
| Data Dependency | Performs well with less data. | Requires large amounts of data to perform effectively. |
| Feature Engineering | Requires manual feature extraction. | Automatically extracts features from raw data. |
| Complexity | Simpler models like decision trees, SVMs, and linear regression. | Complex models with multiple layers (neural networks). |
| Training Time | Faster training with simpler algorithms. | Longer training times due to complex architectures. |
| Hardware Requirements | Can run on conventional CPUs. | Often requires GPUs for efficient processing. |
| Interpretability | Easier to interpret and understand the decision-making process. | Often considered a “black box” with less interpretability. |
| Applications | Fraud detection, recommendation systems, predictive maintenance. | Image and speech recognition, natural language processing, autonomous vehicles. |
Is artificial intelligence smarter than humans?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not inherently smarter than humans; it excels in specific tasks through data processing and pattern recognition. AI can outperform humans in areas like calculations, data analysis, and repetitive tasks due to its speed and accuracy. However, it lacks general intelligence, creativity, emotional understanding, and common sense, which are inherent to humans. AI enhances human capabilities but does not replace the breadth and depth of human intelligence.
What is the main idea of artificial intelligence?
The main idea of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is to create machines that can simulate human intelligence, performing tasks that typically require human cognitive functions. This includes learning from experience, understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, and making decisions. AI aims to enhance efficiency and solve complex problems across various fields by automating processes and providing intelligent solutions.
What was the first artificial intelligence?
The first artificial intelligence program, known as the Logic Theorist, was developed in 1955 by Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon. This pioneering AI program aimed to mimic human problem-solving skills and was capable of proving mathematical theorems. The Logic Theorist is often regarded as the first significant milestone in AI research, laying the groundwork for future developments in the field.
History
Early Foundations
1940s-1950s: The Beginnings
- Alan Turing and the Turing Test: In 1950, British mathematician and logician Alan Turing published a paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” which proposed the idea of a machine being able to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. This concept later became known as the Turing Test.
- Cybernetics: During the 1940s and 1950s, the field of cybernetics emerged, focusing on the study of regulatory systems, feedback, and control in animals and machines. Key figures include Norbert Wiener and John von Neumann.
The Birth of AI
1956: The Dartmouth Conference
- This conference is often considered the birth of AI as a field. Organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, it brought together researchers to discuss the potential of creating machines that can “think.” The term “artificial intelligence” was coined during this event.
The Rise and Fall
1950s-1970s: Early Optimism and Challenges
- Early Programs: Researchers developed early AI programs like the Logic Theorist and the General Problem Solver (GPS), which could solve mathematical problems and prove theorems.
- Perceptrons: Frank Rosenblatt developed the perceptron, an early neural network model, in the late 1950s. However, Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert later demonstrated its limitations, leading to reduced funding and interest in neural networks.
- AI Winter: The 1970s saw a decline in AI research funding and interest, known as the “AI winter,” due to unmet expectations and the limitations of early AI systems.
Renewed Interest and Progress
1980s-1990s: Expert Systems and Machine Learning
- Expert Systems: AI research experienced a resurgence with the development of expert systems, which used knowledge-based rules to solve complex problems in specific domains (e.g., MYCIN for medical diagnosis).
- Backpropagation: The backpropagation algorithm, rediscovered in the mid-1980s, revived interest in neural networks by providing a method for training multi-layer networks, leading to significant improvements in machine learning.
Modern AI
2000s-Present: Deep Learning and Big Data
- Big Data: The explosion of data and advances in computing power have fueled the development of AI. Machine learning, particularly deep learning, has become central to AI research and applications.
- Deep Learning: Techniques such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have achieved breakthroughs in image recognition, natural language processing, and other fields.
- AI in Everyday Life: AI technologies like virtual assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa), recommendation systems, and autonomous vehicles have become part of everyday life.
Key AI Milestones
- 1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeats world chess champion Garry Kasparov.
- 2011: IBM’s Watson wins the quiz show Jeopardy! against human champions.
- 2016: DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeats Go champion Lee Sedol, showcasing the power of deep learning and reinforcement learning.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
As AI continues to advance, ethical and societal implications have become increasingly important. Issues such as bias in AI systems, privacy concerns, and the impact of automation on jobs are being actively addressed by researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders.
The Future of AI
The future of AI holds exciting possibilities, including advancements in general AI, more sophisticated human-AI collaboration, and AI applications in areas like healthcare, education, and climate change. However, it also requires careful consideration of ethical, legal, and societal challenges to ensure AI benefits humanity as a whole.
Applications
AI has a wide range of applications across various industries and sectors. Here are some key areas where AI is making a significant impact:
Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: AI algorithms help in analyzing medical images (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans) to detect diseases such as cancer, tumors, and other abnormalities.
- Personalized Medicine: AI can analyze a patient’s genetic information, lifestyle, and medical history to recommend personalized treatment plans.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates the process of drug discovery by predicting how different drugs will interact with biological targets.
Finance
- Fraud Detection: AI systems can identify unusual patterns and flag potentially fraudulent transactions.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI algorithms analyze market data and execute trades at high speeds, optimizing investment strategies.
- Risk Management: AI helps in assessing and managing financial risks by analyzing large datasets.
Transportation
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI powers self-driving cars, enabling them to navigate and make decisions in real-time.
- Traffic Management: AI systems optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion by analyzing traffic patterns and controlling traffic signals.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI predicts when vehicles and machinery need maintenance, preventing breakdowns and reducing costs.
Retail
- Customer Personalization: AI analyzes customer data to provide personalized recommendations and improve the shopping experience.
- Inventory Management: AI optimizes inventory levels by predicting demand and managing stock efficiently.
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots assist customers with inquiries, improving customer service and support.
Manufacturing
- Quality Control: AI systems inspect products for defects and ensure high-quality standards in manufacturing processes.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI improves supply chain efficiency by predicting demand, optimizing inventory, and managing logistics.
- Robotics: AI-driven robots perform complex tasks, enhancing productivity and safety in manufacturing environments.
Education
- Personalized Learning: AI tailors educational content to individual students’ needs and learning styles.
- Automated Grading: AI systems grade assignments and exams, providing immediate feedback to students.
- Virtual Tutors: AI-powered virtual tutors assist students with their studies, offering help and explanations on various subjects.
Agriculture
- Precision Farming: AI analyzes data from sensors and drones to optimize crop yields and manage resources efficiently.
- Disease Detection: AI systems detect plant diseases early, allowing for timely intervention and reducing crop loss.
- Automated Harvesting: AI-driven machines automate the harvesting process, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Entertainment
- Content Recommendation: AI algorithms recommend movies, music, and other content based on user preferences.
- Game Development: AI enhances video game experiences by creating realistic characters and adaptive gameplay.
- Content Creation: AI generates creative content such as music, art, and writing, expanding the possibilities in the entertainment industry.
Customer Service
- Virtual Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants handle customer queries and perform tasks, improving efficiency.
- Sentiment Analysis: AI analyzes customer feedback and sentiment to improve products and services.
- Automated Support: AI systems provide 24/7 customer support through chatbots and automated response systems.
Energy
- Smart Grids: AI optimizes the distribution and consumption of electricity, improving the efficiency of power grids.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI predicts when equipment in energy infrastructure needs maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
- Energy Management: AI systems manage and optimize energy use in buildings and industrial processes.
These are just a few examples of how AI is transforming various industries. As AI technology continues to advance, its applications are expected to expand even further, driving innovation and improving efficiency across all sectors.
Cons of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers many benefits, but it also presents several potential disadvantages and challenges:
- Job Displacement:
- Automation and AI-driven technologies can replace human jobs, particularly in manufacturing, customer service, and data analysis. This can lead to significant job losses and economic disruption.
- Bias and Discrimination:
- AI systems can perpetuate and even exacerbate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair and discriminatory outcomes, especially in areas like hiring, law enforcement, and lending.
- Privacy Concerns:
- AI technologies, particularly those used in surveillance and data analysis, can infringe on individual privacy. The extensive data collection required for AI to function effectively can lead to concerns over data misuse and unauthorized access.
- Security Risks:
- AI systems can be vulnerable to hacking and cyber-attacks, which could lead to significant security breaches. Additionally, AI can be used maliciously, such as in creating deepfakes or autonomous weapons.
- Ethical Issues:
- The deployment of AI raises various ethical questions, including the moral implications of using AI in decision-making processes, the potential for loss of human agency, and the impact on human rights.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Many AI systems, particularly those using deep learning, operate as “black boxes” where it is difficult to understand how they arrive at specific decisions. This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust and difficulty in accountability.
- Dependence and Over-reliance:
- Society’s increasing reliance on AI for critical tasks can lead to a loss of human skills and knowledge. Over-reliance on AI systems might also result in catastrophic failures if the technology malfunctions or is misused.
- Cost and Resources:
- Developing, implementing, and maintaining AI systems can be costly and resource-intensive. Smaller businesses and developing countries may find it challenging to compete with larger organizations that can afford advanced AI technologies.
- Social and Economic Inequality:
- The benefits of AI might not be evenly distributed, potentially widening the gap between rich and poor. Those with access to AI technologies can gain significant advantages over those without.
- Impact on Mental Health:
- The pervasive use of AI, particularly in social media and digital communication, can impact mental health by contributing to issues like addiction, anxiety, and social isolation.
- Environmental Impact:
- Training large AI models requires significant computational power, which can lead to substantial energy consumption and environmental impact, contributing to carbon emissions and electronic waste.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI is the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think, learn, and solve problems.
How does AI work?
AI uses algorithms and data to perform tasks by mimicking human cognition through machine learning and deep learning.
What are the types of AI?
Types include narrow AI (specific tasks), general AI (human-like intelligence), and superintelligent AI (surpasses human intelligence).
What are the benefits of AI?
AI enhances efficiency, automates tasks, improves decision-making, and enables innovations in various fields.
What are the risks of AI?
Risks include job displacement, privacy issues, bias, security threats, and ethical concerns.
How is AI used in everyday life?
AI is used in virtual assistants, recommendation systems, autonomous vehicles, and smart home devices.
What industries benefit from AI?
AI benefits healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and transportation by improving processes and outcomes.
Can AI replace human jobs?
AI can automate certain tasks, potentially replacing some jobs, but also creating new opportunities.
What is machine learning?
Machine learning is a subset of AI where systems learn from data to improve performance over time.
How is AI regulated?
AI is regulated through policies, standards, and guidelines to ensure ethical use and mitigate risks.