9+ Generic Bill of Lading Examples to Download
A lot of business transactions such as in a sales-purchase transaction that we encounter today involve shipping the goods or items from the seller to the buyer because the buyer is either far from the location of the seller or the buyer cannot carry the purchased goods from the store to their house or designated location. Hence, a shipper or carrier is important for these transactions so that the goods will be transferred from the seller’s store to the buyer’s premises. However, when the goods are being entrusted by the seller to the carrier, the seller must ensure that the carrier will exercise proper care for the goods to be shipped. This requires the carrier to issue a type of document that contains important information with regard to the shipped goods such as the details for the item, the quantity, information regarding the seller as well as the buyer and other information relevant to the delivery of the goods. This document is called bill of lading, which will be discussed further in the succeeding sections.
To give you examples and templates of bill of lading, you may refer to the next section of this article. Further related documents can also be found through these links:
Comprehensive Bill of Lading Example
Minimalist Bill of Lading Example
Non-negotiable Straight Bill of Lading Example
Definition of a Bill of Lading
A bill of lading is a legal document that is issued by a carrier or its agent to the shipper that details the type, quantity, and destination of the goods to be shipped. It also serves as a contract of carriage of goods and as a shipment receipt when the carrier delivers the goods at the predetermined destination. It must accompany the goods being shipped no matter what type of transportation is used for the shipment or delivery. It must be signed by an authorized representative from the carrier, shipper, as well as receiver.
It serves as a proof of ownership of the shipment or cargo. It can be issued either in a negotiable or non-negotiable form. For non-negotiable bill of lading, it functions as is, while for those that are issued in a negotiable form, it is commonly used in letter of credit transactions and may be bought, sold, traded, or used as security or collateral for borrowing money.
Three Main Functions
A bill of lading, as one of the three crucial documents used in international trade, ensures that the carriers receive payment and the recipients receive the merchandise. It has three main functions which are as follows:
- A conclusive receipt – it is an acknowledgment that the goods have been loaded to the carrier completely and is ready for shipment.
- An evidence – it serves as an evidence of the terms of the contract of carriage.
- A document of title – it also serves as a document of title to the goods which is subject to the nemo dat quod non habet rule or simply “nemo dat” rule which means “no one gives what he doesn’t have” and state that the purchase of a possession from someone who has no ownership right to it also denies the purchaser any ownership title.
Original Bill of Lading Example
Overland Bill of Lading Example
Simple Bill of Lading Example
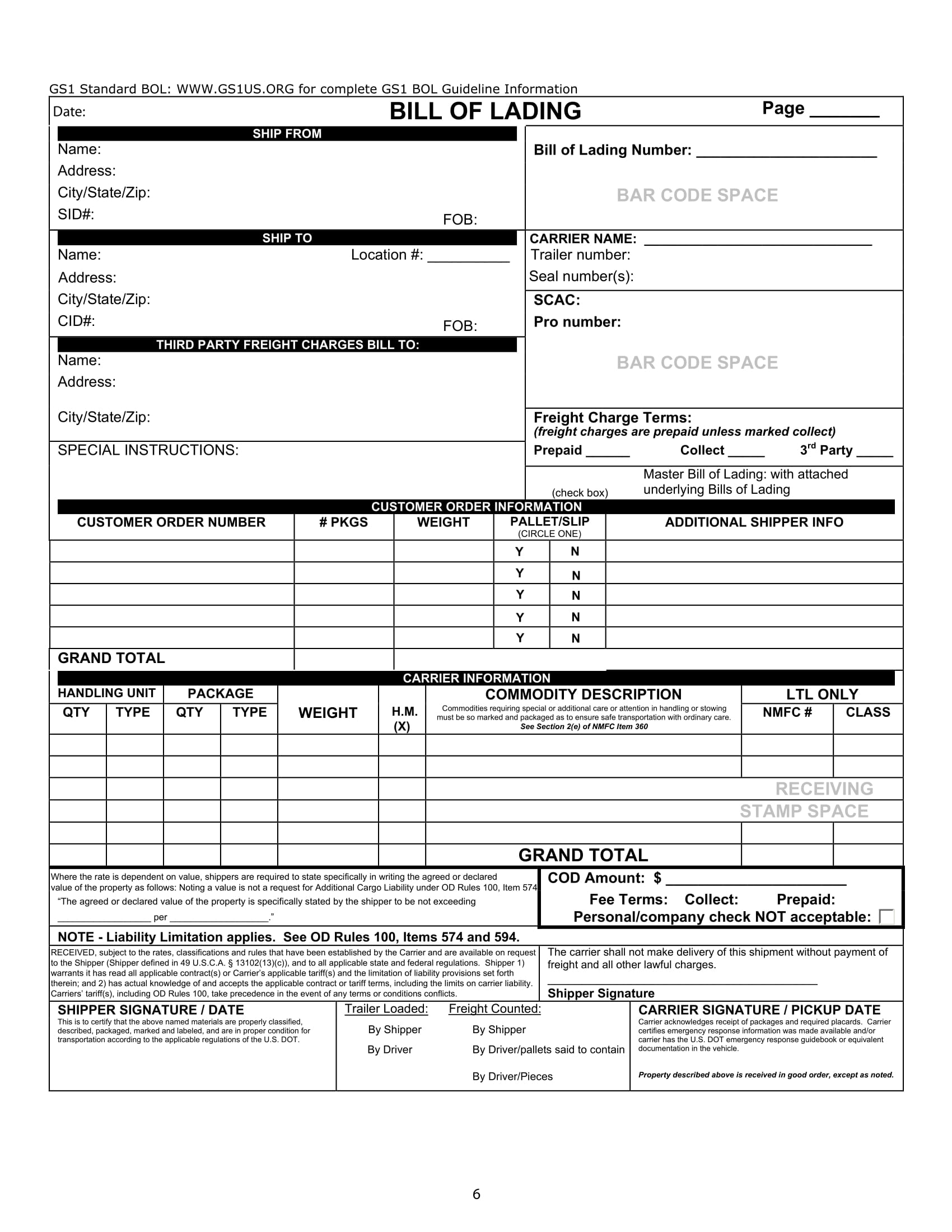
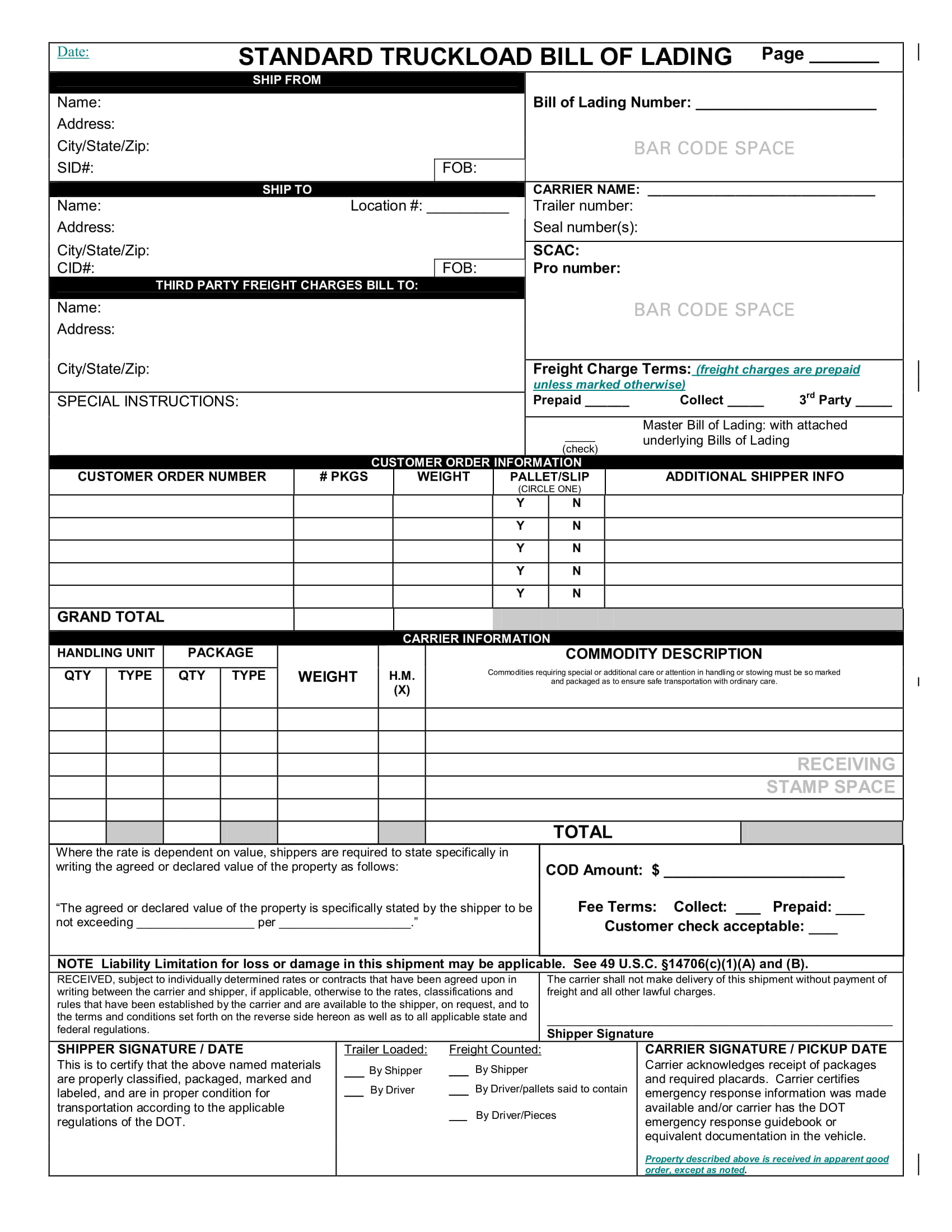
Standard Truckload Bill of Lading Example
Information Contained in a Bill of Lading
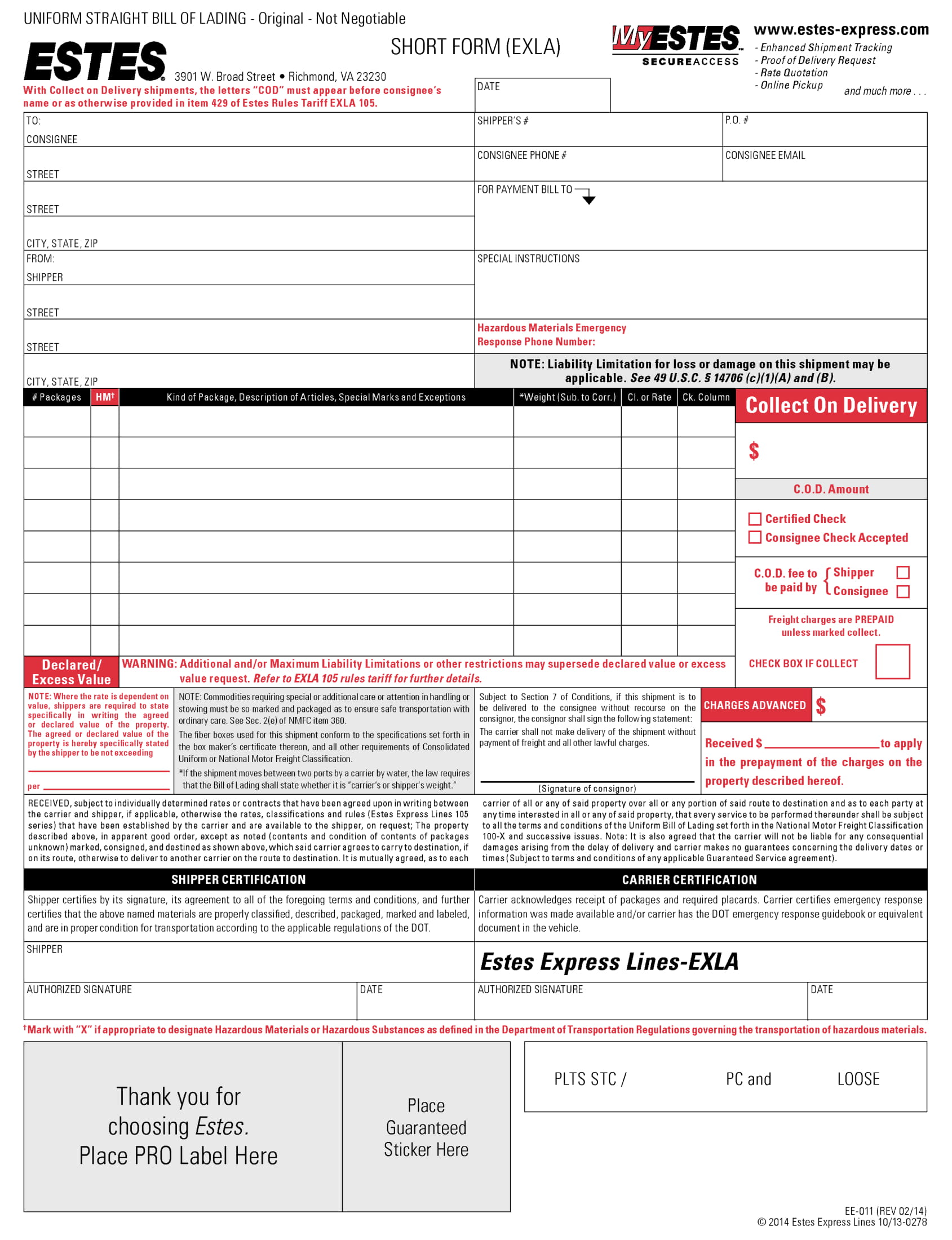
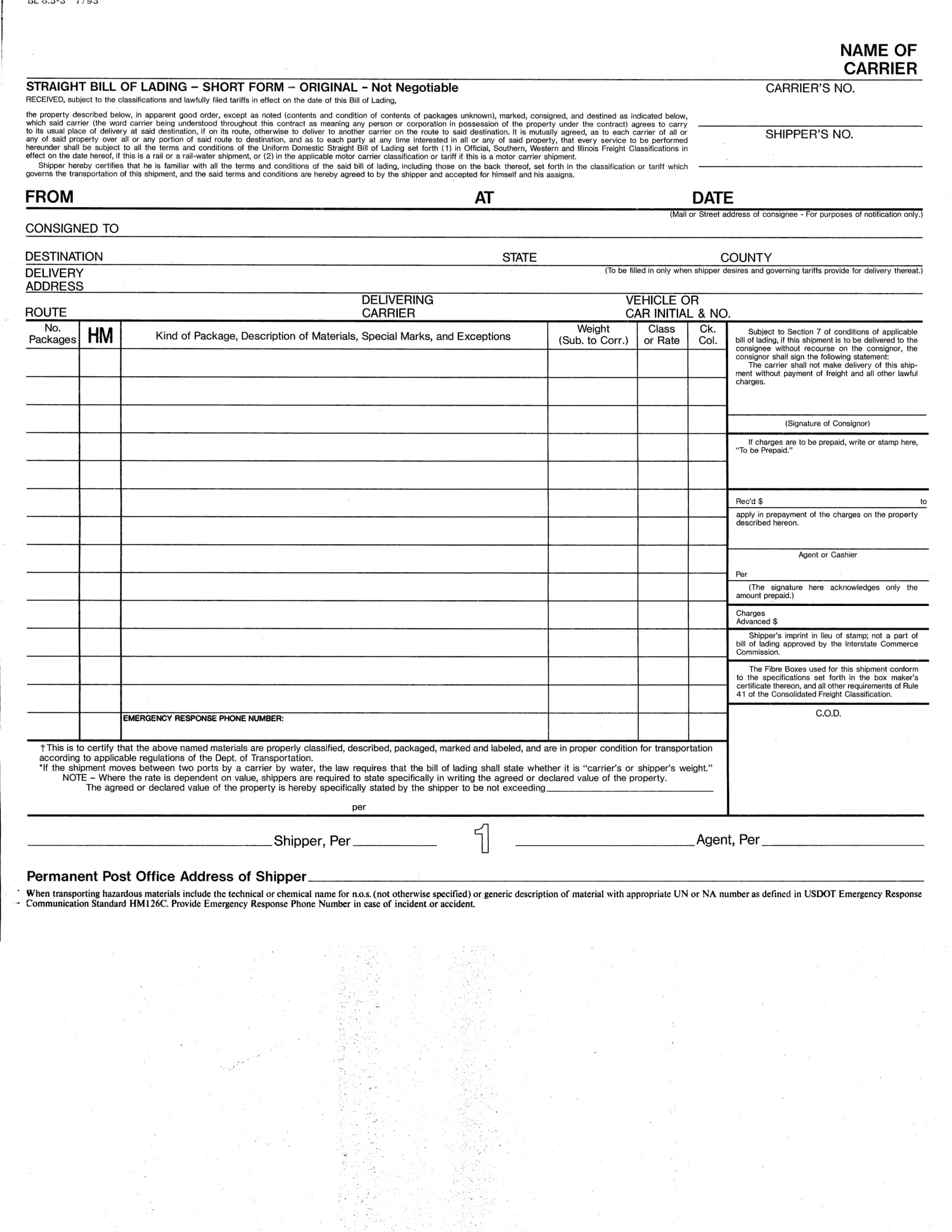
At this point, we already know that a bill of lading can serve as a contract of carriage of goods and, at the same time, a shipment receipt. Hence, in creating a bill of lading, you must ensure that you will not fail to include the important information to be placed in a bill of lading. You must check if your bill of lading contains the following:
- Consignor’s name – also called the sender’s name or shipper’s name; this information is important so that the receiver can trace the sender in case he or she has some unfinished business with the sender.
- Consignee’s name – also called the buyer’s name, the receiver’s name, or the recipient’s name. This is also important so that the carrier can easily identify who they are going to send the goods to.
- Name of the port of departure – this information is important so that the consignor or the shipper as well as the recipient can track the point of origin of the shipment.
- Name of the port of destination – again, this is important for the consignor and the recipient to keep track of the shipment as well as to confirm if the point of destination is correct.
- Name of the vessel – name of the vessel is an important detail so that the cargo will be carried by the correct vessel and to trace the said vessel.
- Date of departure – the bill of lading must contain the date of departure for the parties involved to be aware of the shipment date and for the carrier to ship the cargo on time.
- Date of arrival – similar to the date of departure, it must also contain the date of arrival although this date is a tentative one. This is for the parties to know that the shipment has already arrived.
- List of goods – the goods in the shipment or cargo must be itemized in the list of goods being transported along with their number of packages and the kind of packages. This is to ensure completeness of the items being delivered.
- Marks and number on packages – the individual packages contained in the shipment must be marked or numbered for identification.
- Weight or volume of the cargo – the weight of the cargo must also be determined for this will affect the cost of delivery and it gives information to the handlers of the cargo to have an extra care toward the shipment.
- Packaging type – the packaging type must also be noted whether the shipment is contained in cartons, crates, pallets, and drums when shipping.
- NMFC freight class – this might give an impact to the cost of your shipment. This can be broken down into 18 classes based on weight, dimensions, density, storage capability, ease of handling, value, and liability.
- Freight rate or amount – the amount of the freight or delivery must also be included in the bill of lading. This amount is to be paid by the buyer, in case of freight collect, or by the seller, in case of freight prepaid.
- Special instructions – this is a kind of note or instructions for the carrier that are not extra service requests like liftgate or delivery notification.
- Department of Transportation hazardous material designation – if the shipment contains hazardous items, it must be clearly cited. Special rules and requirements apply when shipping this kind of shipment.
Common Types of Bills of Lading by Transportation Mode
Shipping can be categorized whether you are shipping your goods by sea, air, truck, or rail. The common types of bill of lading by mode of transportation are as follows:
Ocean Transportation
An ocean bill of lading is issued when goods are transported by ship. The freight to or from the USA is regulated by the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC). The subtypes of ocean bills of lading are the following:
- Straight bill of lading. This bill of lading is a non-negotiable and is addressed directly to the buyer. The carrier will issue three original bills of lading, one of which must be endorsed by the consignee and presented in order to obtain the cargo at destination. This bill of lading is typically issued if the buyer still owes payment for all or part of the goods.
- Order bill of lading. This is also a negotiable type of bill of lading that is addressed “to order” instead of being consigned to the buyer. The carrier will turn over the shipment to the one presenting the bill of lading, as long as it has an endorsement. It is assumed that the holder of the order bill of lading is the owner of the goods being shipped.
- Electronic “telex” release: This eliminates the need for an original bill of lading to be presented at the destination, and instead, the shipper endorses an original bill of lading and submits it to the carrier or carrier’s agent at the origin who will then notify the agent at the destination that the goods may be released without the hard copy bill of lading present. Traditionally, it was done by telex, hence the name electronic telex release. Again this is typically issued if the buyer still owes for all or part of the goods.
- Express bill of lading: This is a non-negotiable document, and the carrier agrees to only release the goods to the named consignee or notify party. No original bills of lading are issued. This is typically issued if the importer paid for the goods before shipping or has credit with the supplier.
Air Transportation or Air Waybills
These are non-negotiable and issued when goods are transported by air. It is immediately handed over to the consignee or their customs broker for customs clearance and final delivery. They serve as a contract of carriage, a cargo receipt, and a delivery instructions.
Land Transportation Waybill
This is a short form contract of carriage for overland shipments that refer only vaguely to terms and conditions in the carrier’s tariff. It is non-negotiable and is never consigned “to order.”
Uniform Bill of Lading
This is issued for overland shipments and is subject to uniform terms and conditions with widely adopted transportation tariffs or contract carriage agreements that may be consigned “to order.”
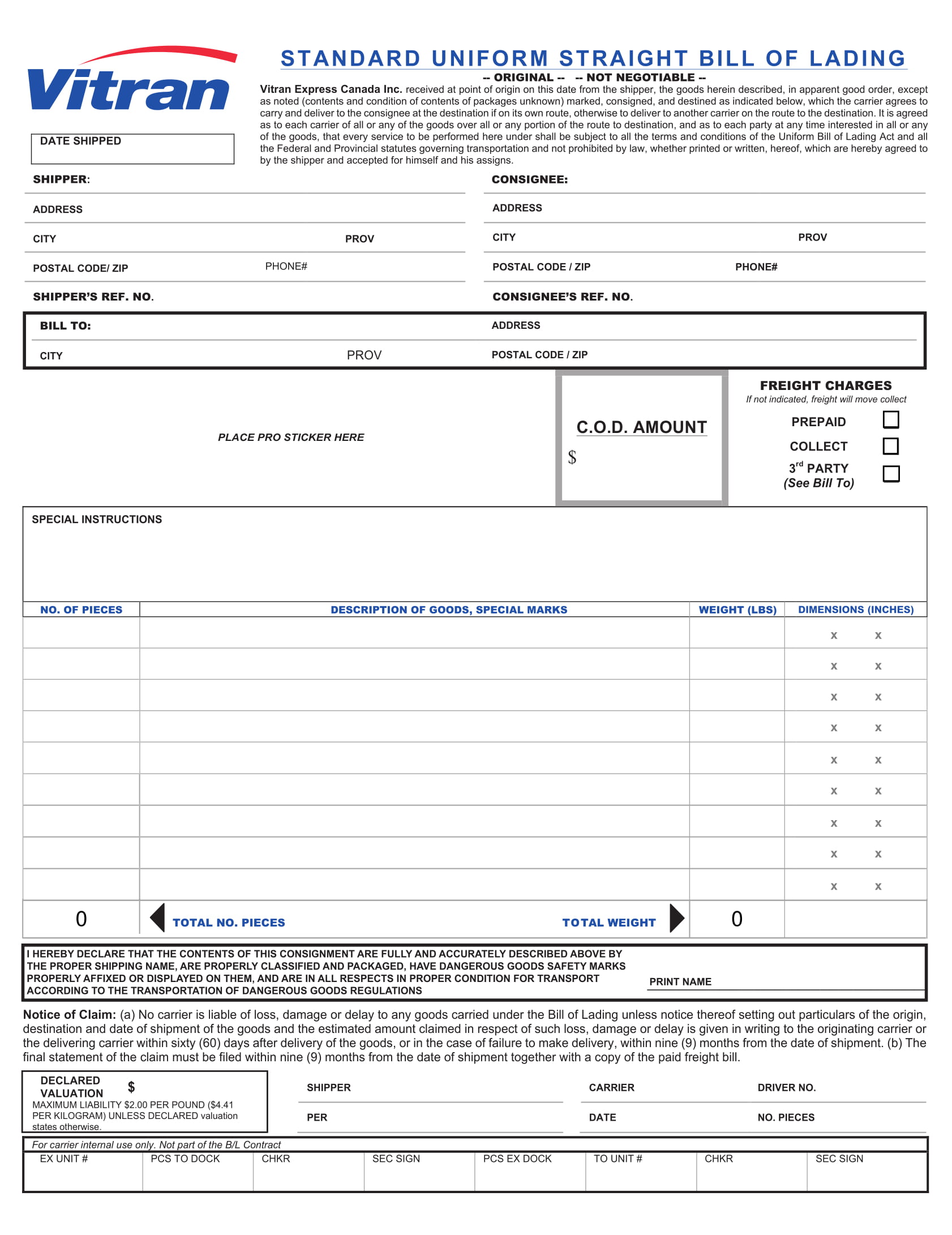
Standard Uniform Straight Bill of Lading Example
Straight Bill of Lading Example
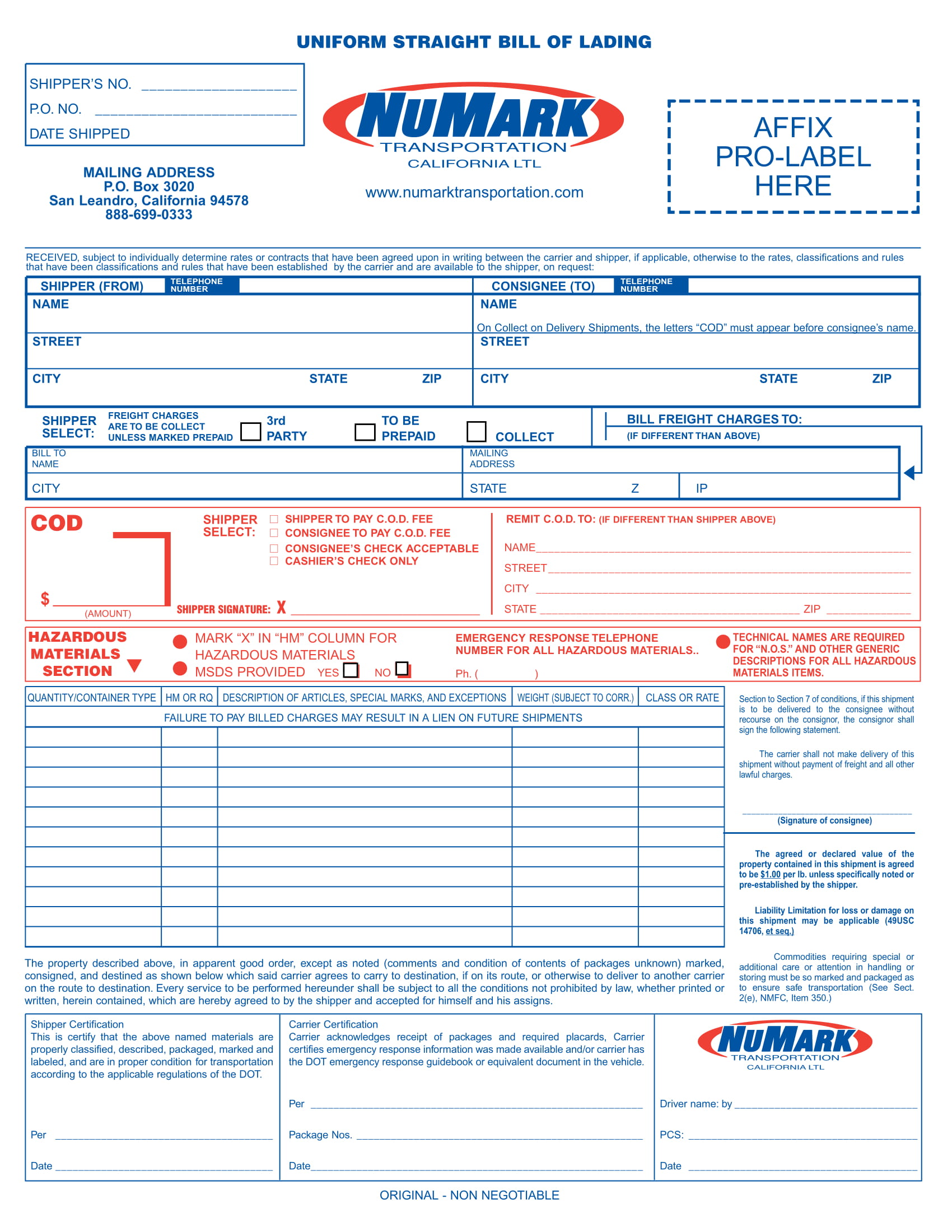
Uniform Straight Bill of Lading Example
Quick Recap
A bill of lading is a legal document or a contract of carriage of goods as well as a shipment receipt that contains important information with regard to the cargo or shipment such as the type, quantity, and destination of the goods to be shipped. It functions as a conclusive receipt, an evidence of contract, and a document of title. It contains information such as the consignor’s and consignee’s name, names of the port of departure and destination, name of the vessel, date of departure, date of arrival, list of goods, marks and number on packages, weight or volume of the cargo, packaging type, NMFC freight class, freight rate or amount, special instructions, and Department of Transportation hazardous material designation.
The common types of bill of lading by transportation mode are as follows: ocean transportation which consists of straight bill of lading, order bill of lading, electronic “telex” release, and express bill of lading; air transportation, land transportation waybill, uniform bill of lading, and hand tag.
If you are not sure on how to start creating your own bill of lading, don’t forget to check out the examples and templates of bill of lading presented in the above section.