13+ Safety Culture Survey Examples to Download
Safety culture is something brought up in almost every organization intentional or not. From road safety signs in the streets to fun cartoon posters at the workplace, safety culture takes on many forms in many places. According to an article by Forbes creating a culture of safety is not about posters and catchy slogans but has to be a part of the organization’s DNA. What does this mean? It means having to come up with effective ways of promoting safety in a community and encouraging others to follow it. One way to bring that kind of attitude is to make use of a safety culture survey.
What is a Safety Culture Survey?
A safety culture survey is a tool used by the employers to collect feedback and learn what the employees think about the company’s safety culture. Safety culture refers to the beliefs and practices an organization follows to promote safety to the community. With this survey employers can determine if their safety culture is effective or needs improvement. Its contents are questions about the safety culture of the organization and several options are already given as answers. These answers are then measured by a scale that helps employers understand what the whole group thinks of as their safety culture.
A Culture of Safety Survey is a comprehensive tool designed to evaluate the attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors of employees regarding safety within an organization. This survey is pivotal in identifying strengths and areas for improvement in a company’s safety culture. It serves as a diagnostic instrument to measure the effectiveness of safety policies and practices, and it is essential for fostering a work environment where safety is a shared responsibility.
Key Elements of a Culture of Safety Survey:
- Employee Perception: The survey gauges how employees perceive the safety culture of their organization. This includes their confidence in reporting safety issues without fear of retribution.
- Safety Systems: It evaluates the effectiveness of the safety systems in place, including incident reporting mechanisms and safety training programs.
- Communication: The survey assesses the openness and effectiveness of communication regarding safety issues among staff and management.
- Learning and Development: It measures the organization’s commitment to learning from safety incidents and implementing improvements.
- Leadership Commitment: The survey examines the extent of leadership’s commitment to safety, which is crucial for a positive safety culture.
Importance of a Culture of Safety Survey:
- Identifies Strengths and Weaknesses: Organizations can pinpoint areas of success and those needing improvement, enabling targeted interventions.
- Promotes Employee Engagement: By involving staff in the survey process, it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards workplace safety.
- Improves Safety Outcomes: Insights from the survey can lead to enhanced safety practices, reducing the likelihood of accidents and errors.
- Supports Continuous Improvement: Regular surveys can track progress over time, ensuring continuous development of the safety culture.
Implementing the Survey for Optimal Impact:
- Anonymity: Ensuring responses are anonymous can encourage honesty and increase participation rates.
- Actionable Insights: The survey should be crafted to yield actionable insights, not just raw data.
- Leadership Involvement: Active participation from leadership can underscore the importance of the survey and drive engagement.
- Follow-up: Post-survey, it is crucial to communicate the findings and implement changes based on the feedback.
What is a Purpose of Safety Culture Survey?
Here is a Purpose of Safety Culture Survey:
The Purpose of a Safety Culture Survey:
Enhancing Awareness and Understanding:
A Safety Culture Survey primarily serves to enhance the organization’s awareness of its current safety culture. It provides a clear picture of how safety is perceived and practiced on a day-to-day basis by employees at all levels.
Identifying Safety Perceptions and Behaviors:
The survey identifies how employees perceive safety and their behaviors towards it. This includes understanding their willingness to report safety concerns and their belief in the efficacy of safety procedures.
Encouraging Open Communication:
By soliciting feedback, the survey encourages open communication about safety issues, which can often be sensitive or overlooked in the hustle of daily operations.
Establishing Benchmarks:
It helps in establishing benchmarks for safety performance. These benchmarks are critical for measuring progress and setting goals for safety improvement initiatives.
Driving Engagement and Ownership:
The drive of employee engagement survey by involving them in the process of safety evaluation. This sense of ownership can lead to more proactive safety behaviors.
Informing Safety Initiatives:
The insights gained from the survey inform the development and implementation of effective safety initiatives and training programs tailored to address specific issues identified.
Demonstrating Commitment to Safety:
The very act of conducting a job survey demonstrates the organization’s commitment to creating a safe working environment, which can boost morale and trust in the management.
Promoting a Proactive Safety Culture:
Ultimately, the purpose of a Safety Culture Survey is to promote a proactive safety culture where safety is not just a priority but a core value integrated into every aspect of the organization’s operations.
What is an Example of Good Safety Culture?
Best Examples of Safety Culture Survey:
Here is a Best Examples of Safety Culture Survey:
Comprehensive Safety Culture Assessment:
This type of survey encompasses a wide range of factors including leadership commitment to safety, employee involvement, safety communication, and response to incidents. It provides a holistic view of the organization’s safety culture.
Targeted Departmental Safety Surveys:
These surveys are tailored to specific departments within an organization, recognizing that safety challenges can vary greatly between different areas of operation. They allow for a more focused approach to addressing safety concerns.
Safety Climate Surveys:
A safety climate survey is a snapshot of the organization’s safety culture at a point in time. It assesses employee attitudes and perceptions about safety, often focusing on the psychological aspects of the safety culture.
Safety Perception Surveys:
These social surveys are designed to gauge how employees perceive safety and their beliefs about the organization’s safety policies and procedures. They can reveal discrepancies between the intended and actual impact of safety programs.
Safety Behavior Surveys:
Behavior-based safety surveys focus on the actions and behaviors of employees regarding safety in the workplace assessment. They help in identifying unsafe practices and developing strategies to promote safe behaviors.
Leadership Safety Culture Surveys:
Focused on the leadership team, these surveys assess how leaders’ actions and decisions impact the overall safety culture. They can highlight the need for leadership training in safety principles.
Safety Systems Effectiveness Surveys:
These surveys evaluate the effectiveness of the safety systems in place, such as incident reporting tools and safety training programs, providing insights into areas that may require technological or procedural enhancements.
Incident Follow-up Surveys:
Post-incident surveys gather feedback on how safety incidents are managed and investigated. They can provide valuable information on the effectiveness of incident response and the learning culture of the organization.
New Initiative Feedback Surveys:
When new safety policies or initiatives are introduced, these customer surveys measure their reception and effectiveness, ensuring that the changes are working as intended and are embraced by employees.
Continuous Improvement Safety Surveys:
Regularly conducted, these food surveys track changes in the safety culture over time, helping organizations to measure the impact of their continuous improvement efforts in safety.
Each of these surveys can be a powerful tool in building and maintaining a robust safety culture. The best choice depends on the organization’s specific needs, goals, and the particular aspects of safety culture they wish to explore and enhance.
13+ Safety Culture Survey Examples in PDF | DOC
1. Transport and Logistics Safety Culture Assessment Survey

2. Safety Culture Survey Template
3. Food Safety Culture Questionnaire Example
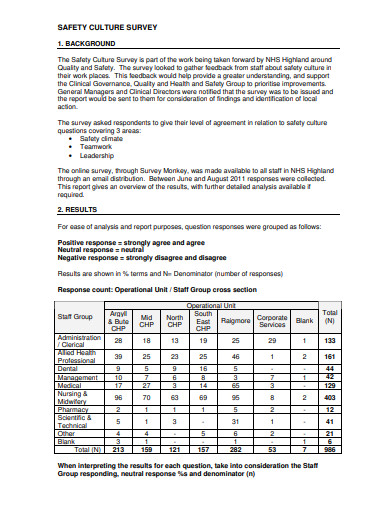
4. Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture
5. Sample Safety Culture Survey
6. Simple Safety Culture Survey
How to Conduct a Safety Culture Survey?
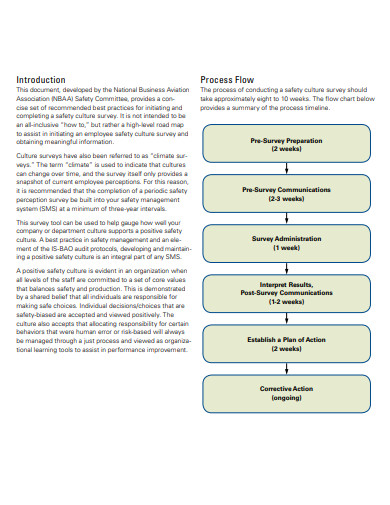
Introduction
A safety culture survey is a critical tool for assessing the attitudes, perceptions, and values of employees towards workplace safety. This survey provides insights into how safety is viewed within the organization and identifies areas that require improvement. Conducting an effective safety culture survey involves several key steps to ensure the data collected is reliable and actionable.
Step 1: Define the Objectives
Before launching a survey, clearly define what you aim to achieve. Are you looking to assess the overall safety climate, identify specific safety issues, or evaluate the effectiveness of current safety programs? Having clear objectives will guide the development of your survey questions and the analysis of the data.
Step 2: Develop the Survey
Create a survey that reflects your objectives. Ensure questions are clear, concise, and relevant to your workforce. Include a mix of question types, such as multiple-choice, Likert scale, and open-ended questions, to gather both quantitative and qualitative data.
Step 3: Ensure Anonymity and Confidentiality
To get honest and candid responses, it’s crucial to ensure that survey responses are anonymous and confidential. Communicate this to your employees to increase participation rates and the reliability of the data collected.
Step 4: Administer the Survey
Decide on the method of distribution that best suits your organization, whether it be online, paper-based, or a combination of both. Ensure that all employees have access to the survey and understand its importance. Set a reasonable deadline for completion and send reminders to maximize response rates.
Step 5: Analyze the Data
Once the survey is completed, analyze the data to identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern. Look for gaps between management and employee perceptions of safety and areas where safety practices can be improved.
Step 6: Communicate the Findings
Share the results with your employees and involve them in discussions about the findings. Transparency is key to maintaining trust and demonstrates a commitment to improving workplace safety.
Step 7: Develop Action Plans
Based on the survey results, develop action plans to address the identified issues. Assign responsibilities and set timelines to ensure that improvements are made.
Step 8: Follow Up
After implementing changes, follow up to assess their effectiveness. This can be done through informal feedback, follow-up surveys, or other assessment tools.
Conclusion
A safety culture survey is a powerful tool for enhancing workplace safety. By following these steps, organizations can gain valuable insights into their safety culture and make informed decisions to foster a safer work environment.
7. Safety Culture Self-Assessment Survey
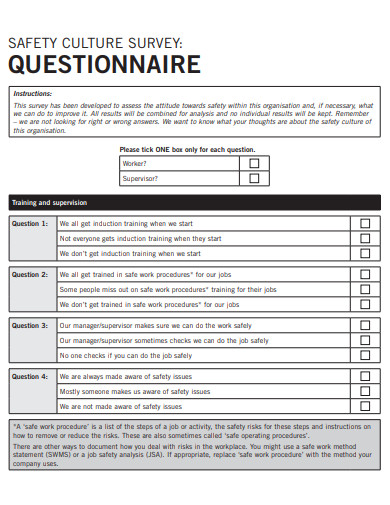
8. Health and Safety Culture Questionnaire for Employee
9. Workplace Safety Culture Survey Example
10. Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture Example
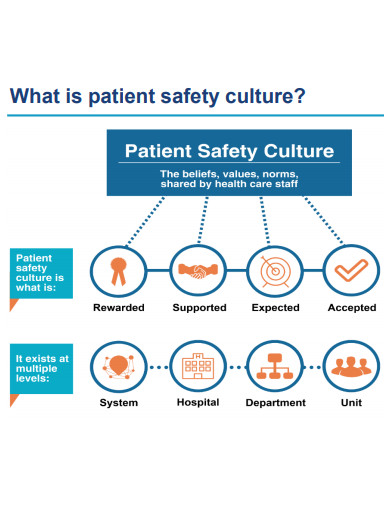
11. Patient Safety Culture Survey Format
12. Sample Employee Safety Culture Survey Example
13. Driving Safety Culture Survey Examples
14. Nursing Home Safety Culture Survey
How to Measure Safety Culture?
Here is a Measures for Safety Culture:
Understanding Safety Culture:
Safety culture is the collection of beliefs, perceptions, and values that employees share in relation to safety within an organization. It’s a crucial aspect of an organization’s overall safety management system and can significantly influence workplace safety and health performance.
Key Metrics for Assessing Safety Culture:
Safety Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Employee Perception Surveys: These surveys assess employees‘ attitudes and perceptions towards safety, including their belief in the importance of safety and their willingness to report unsafe conditions.
- Safety Climate Tools: Short, focused surveys that provide a snapshot of the organization’s current safety culture.
Safety Audits and Inspections:
- Compliance Audits: Regular audits to ensure that safety practices comply with legal and internal standards.
- Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) Observations: Observations of employees’ behavior to identify safe and at-risk actions.
Incident Metrics:
- Near-Miss Reporting: Tracking and analyzing near-miss incidents can provide insights into potential future risks.
- Incident Rates: Monitoring the frequency and severity of workplace incidents and accidents.
Training and Development:
- Training Completion Rates: The percentage of employees who have completed mandatory safety training.
- Competency Assessments: Evaluations of employees’ understanding and application of safety procedures.
Leadership Engagement:
- Management Participation: The extent to which management is involved in safety training, meetings, and initiatives.
- Safety Meetings: Regular meetings that focus on safety-related topics, including discussions on improvements and sharing safety metrics.
Communication Effectiveness:
- Feedback Mechanisms: Systems in place for employees to report safety concerns and receive feedback.
- Safety Messaging: Analysis of the frequency and effectiveness of safety communications.
Employee Engagement:
- Participation in Safety Programs: Employee involvement in safety committees, training sessions, and safety improvement initiatives.
- Safety Suggestions: The number and quality of safety suggestions submitted by employees.
Implementing the Measurement Process
- Set Clear Objectives: Define what you want to measure and why.
- Use a Combination of Tools: Employ both qualitative and quantitative methods to get a comprehensive view.
- Benchmark and Set Targets: Compare your results with industry standards and set improvement targets.
- Regular Review and Action: Use the findings to inform safety strategies and action plans.
- Feedback Loop: Ensure there is a process for communicating results back to employees and involving them in action planning.
How to Create a Safety Culture Survey?
To come up with effective cultural practices in safety you will need to have an effective tool to gather all the information you need. With a cultural safety survey, you can gather enough data to come up with a framework to create an organization safety culture in any community. If you need some tips continue reading this article for ideas on how to get started.
1. Specify Your Questions
When making a safety culture survey you have to make your questions relevant to your audience. So be specific with your questions when you are doing the write-up. For example suppose you are creating a safety culture survey for a construction company then tailor your questions for the employees. Instead of placing the question ‘I feel safe in this working environment,’ you can write ‘I feel safe in the building site.’ That is more effective because it will give you a more specific answer. Writing vague and general questions is going to make it challenging for you later on when you are analyzing all the data you have collected.
2. Use a Reliable Scale
To make it easy for you to organize, and understand the answers you have gathered for your survey, make use of a response scale. They are presented as optional answers to the questions in the survey. Two common types of scales used in surveys are called dichotomous and rating scales. Dichotomous scales are typically represented as ‘yes or no’ and ‘agree or disagree’ answers in a survey. Rating scales are represented as ‘on the scale of 1 to 10’ kind of answers. Choose these to give your audience a convenient way to answer and easy time for you to analyze the data.
3. Provide Space for Feedback
Do not limit your safety culture survey with optional answers. Perhaps there is more people want to say regarding the safety culture of a community. With that in mind add some space where your audience can give any feedback, or suggestions that they have. For example, if you are making a survey for a hospital you can place a question like, ‘What else do you think can make the hospital a safe and healthy environment?’ and provide space for them to write it down. Doing this can lead to new ideas and strategies for you to work on the safety culture of an organization.
4. Keep It Organized
When you are doing the write-up for your safety culture survey keep it short and concise. Refrain from making your survey a lot wordy and get to the point with your questions. When you are drafting your survey take a look at the questions and try to organize them in a way that they feel connected. This can help your audience feel a sense of progression when they are answering the survey because putting two different questions can be off-putting at times.
Difference Between Safety Culture Survey and Safety Culture Questionnaire?
A Safety Culture Survey and a Safety Culture Questionnaire both serve as tools to assess the safety culture of an organization. However, they can be differentiated based on their structure, application, and depth of analysis.
Here’s a comparative table outlining the differences:
| Aspect | Safety Culture Survey | Safety Culture Questionnaire |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To measure and quantify the overall safety culture within an organization. | To gather specific information about attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors related to safety. |
| Structure | Often uses a mix of quantitative (Likert scales) and some open-ended qualitative questions. | Primarily consists of a structured set of questions that may be close-ended or open-ended. |
| Analysis | Designed for a more in-depth statistical analysis, which can involve benchmarking against industry standards. | Analysis may be less complex, focusing on straightforward responses that provide direct insights. |
| Scope | Broad, aiming to capture a comprehensive picture of the safety culture across various dimensions. | Can be narrow, targeting specific areas or issues within the safety culture. |
| Respondents | Usually administered to a wide range of employees across different levels of the organization. | May be targeted to specific groups or individuals, depending on the focus area. |
| Frequency | Conducted at regular intervals (e.g., annually) to track changes and improvements over time. | May be used more frequently as part of routine assessments or following specific incidents or training sessions. |
| Result Interpretation | Results are typically used to inform strategic decisions and develop long-term safety initiatives. | Results can prompt immediate actions or serve as a diagnostic tool to identify specific problems. |
| Question Type | Questions are often more general to allow for a broad understanding of the safety culture. | Questions are more targeted to elicit information about particular aspects of safety culture. |
| Feedback | Results may provide a feedback loop for ongoing improvement and organizational learning about safety. | May provide immediate feedback on specific interventions or the effectiveness of recent policy changes. |
| Development | Surveys are often developed with the help of safety culture experts and may be validated through research. | Questionnaires may be developed internally and can be more flexible to specific organizational needs. |
Both tools are crucial for developing a strong safety culture in the workplace. Surveys might be used as a more formal, periodic assessment tool, while questionnaires can function as a quick check on particular areas of interest or concern within the organization’s safety culture.
FAQs
How do you promote a safety culture in the workplace?
You can promote safety culture by providing training to your employees. Run sessions with them on what to practice to create a culture of safety. Another way to do this is leading by example. Initiating practices that promote safety culture will encourage the employees to do the same.
What does a strong safety culture look like?
A strong safety culture is characterized by proactive safety behaviors, open communication, and a shared commitment to safety at all organizational levels. It prioritizes continuous learning from incidents, values employee input, and integrates safety into every aspect of operations, with leadership actively fostering and exemplifying these principles.
How to create a strong and positive safety culture?
Encouraging communication is one way to promote it. You can let your team members voice out what they think will make them feel safe in the organization. Encourage them to give feedback for whatever initiatives you take to promote safety as well. That way you can make it both strong and positive.
What does a culture of safety include?
A culture of safety includes a collective and ongoing commitment to safety, open communication about risks, non-punitive reporting of errors, continuous education and training, effective safety systems, and leadership that prioritizes and models safe practices. It’s an environment where safety is everyone’s responsibility and is embedded in every activity.
What is effective safety culture?
An effective safety culture is where safety is a core value, deeply embedded in every level of an organization. It’s marked by proactive risk management, open communication, trust, and a blame-free environment where all employees are empowered and encouraged to speak up and contribute to safety practices.
How do you test a safety culture in the workplace?
One way to test the safety culture of a company is to collect data through the use of a survey. You can also conduct group, and individual interviews to collect feedback right out of the employees themselves. Then with this information, you can see whether the current safety culture is effective or needs improvement.
What makes a safety culture different from a safety climate?
A safety culture takes building up and maintenance over a long period. Meanwhile, safety climate refers to what is being seen in a particular moment. Basically safety climates are what helps build up the safety culture.
How do you build a safety culture at work?
To build a safety culture at work, engage all employees in safety training, establish clear safety protocols, encourage open dialogue about risks, and ensure leadership models safe behavior. Foster an environment where reporting hazards is valued and rewarded, and continuously review and improve safety practices based on feedback and incidents.
With a well written safety culture survey we can determine if current safety practices and beliefs are effective or not. We will be able to identify behaviors and beliefs that need to continue or change. That way we can reduce the risk of danger to our community and focus on other important things instead. A safety environment promotes productivity and positive growth after all.