35+ Active Listening Examples
Active listening is a communication technique where the listener fully concentrates, understands, responds, and remembers what is being said. It involves giving full attention and providing feedback to the speaker.
What Is Active Listening?
Active Listening communication skills that enhances interactions by ensuring full engagement and understanding between parties. By practicing active listening in communication skills, individuals can build stronger connections, demonstrate empathy, and provide thoughtful responses. This technique is particularly vital in Active Listening in Assertive Communication, where clear and respectful exchanges are crucial significantly bolster strong communication skills, leading to more meaningful and productive conversations.
Examples for Active Listening
- Nodding: Show you are listening by nodding occasionally.
- Eye Contact: Maintain eye contact with the speaker.
- Summarizing: Repeat back what the speaker said in your own words.
- Asking Questions: Ask relevant questions to clarify points.
- Paraphrasing: Restate the speaker’s message to show understanding.
- Minimal Encouragers: Use small verbal comments like “I see,” “Go on,” or “Interesting.”
- Body Language: Use open body language, such as facing the speaker and leaning slightly forward.
- Avoid Interrupting: Let the speaker finish before you respond.
- Reflecting Feelings: Acknowledge the speaker’s emotions, e.g., “You seem upset about this.”
- Providing Feedback: Give appropriate feedback that reflects understanding, e.g., “I understand you’re feeling frustrated with this situation.”
Examples of Active Listening in the Workplace
- Taking Notes: Jot down key points during meetings.
- Confirming Deadlines: Repeat deadlines back to ensure clarity.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Use facial expressions to show engagement.
- Clarifying Instructions: Ask for additional details when tasks are unclear.
- Offering Solutions: Suggest ideas based on what you’ve heard.
- Following Up: Send a follow-up email summarizing the discussion.
- Allowing Pauses: Give colleagues time to think before they respond.
- Acknowledging Contributions: Thank team members for their input.
- Staying Focused: Eliminate distractions during conversations.
- Encouraging Sharing: Invite quieter colleagues to share their thoughts.
Examples of Active Listening for Students
- Nod: Show you understand by nodding.
- Ask Questions: Seek clarification when confused.
- Summarize: Briefly restate what the teacher said.
- Stay Quiet: Avoid talking when someone else is speaking.
- Eye Contact: Look at the teacher or speaker.
- Take Notes: Write down important points.
- Lean Forward: Show interest by leaning slightly forward.
- Paraphrase: Repeat what classmates say in your own words.
- React Appropriately: Smile or show concern as needed.
- Follow Instructions: Do what the teacher asks promptly.
Examples of Active Listening Sentences
- “I see, go on.”
- “Can you explain that part again?”
- “So, you’re saying…”
- “That must have been difficult for you.”
- “What happened next?”
- “I understand how you feel.”
- “It sounds like you’re upset.”
- “Can you give me an example?”
- “I appreciate your point of view.”
- “Let me make sure I got that right.”
Examples of Active listening in Childcare
- Get on Their Level: Kneel down to make eye contact.
- Use Simple Encouragements: Say “I’m listening” or “Tell me more.
- “Repeat Their Words: Mirror what the child says.
- Show Patience: Wait for them to finish speaking.
- Use Positive Body Language: Smile and nod.
- Clarify by Asking: “Did you mean…?”
- Acknowledge Feelings: “You seem happy/sad/angry”.
- Summarize Stories: “So, you played with blocks today”.
- Engage with Questions: “What happened next?”
- Avoid Distractions: Put away your phone while they talk.
Examples of Active Listening in Communication
- Maintain Eye Contact: Look at the speaker to show attention.
- Nod Affirmatively: Nod your head to indicate understanding.
- Paraphrase: Restate what the speaker said in your own words.
- Ask Clarifying Questions: “Can you explain that further?”
- Reflect Feelings: “It sounds like you’re feeling…”
- Use Minimal Encouragers: “I see,” “Uh-huh,” “Go on.”
- Avoid Interrupting: Let the speaker finish before responding.
- Summarize Key Points: “So, your main concern is…”
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive comments based on what was said.
- Eliminate Distractions: Focus fully on the speaker, avoiding phone or other interruptions.
Examples of Active Listening in the Classroom
- Lean Forward: Show interest by leaning slightly towards the speaker.
- Repeat Questions: When a classmate asks a question, repeat it for clarity.
- Respond to Non-Verbal Cues: Notice and respond to the teacher’s body language.
- Use Verbal Prompts: Say “Yes,” “I understand,” or “That makes sense.”
- Participate Actively: Engage in discussions by adding relevant points.
- Ask Follow-Up Questions: Inquire further about the topic being discussed.
- Provide Examples: Share examples that relate to what was discussed.
- Group Work Listening: Listen carefully to peers during group activities.
- Restate Instructions: Repeat classroom instructions to ensure understanding.
- Give Non-Verbal Feedback: Use facial expressions to show comprehension or confusion.
Types of Active Listening
- Reflective Listening: Paraphrasing and restating what the speaker says.
- Empathetic Listening: Understanding and sharing the speaker’s feelings.
- Critical Listening: Analyzing and evaluating the speaker’s message.
- Informational Listening: Focusing on understanding and retaining information.
- Comprehensive Listening: Combining multiple listening types for full understanding.
- Appreciative Listening: Enjoying and valuing the speaker’s message.
6 Active Listening Techniques
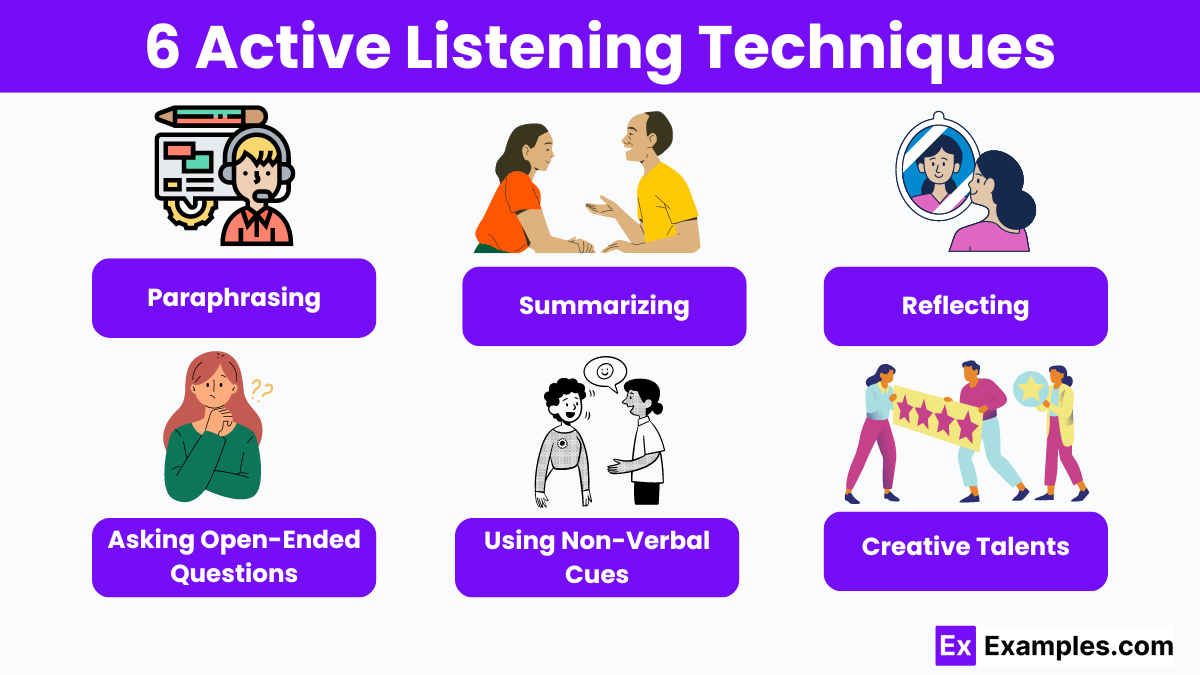
- Paraphrasing: Restate what the speaker has said in your own words to show understanding and verify accuracy.
- Summarizing: Condense the main points of the conversation to confirm understanding and keep track of important details.
- Reflecting: Mirror the speaker’s emotions by acknowledging their feelings, e.g., “You seem excited about this.”
- Asking Open-Ended Questions: Encourage the speaker to elaborate by asking questions that require more than a yes or no answer, e.g., “Can you tell me more about that?”
- Using Non-Verbal Cues: Show attentiveness through body language such as nodding, maintaining eye contact, and leaning forward.
- Giving Feedback: Provide thoughtful and relevant responses that show you are actively engaged in the conversation, e.g., “I appreciate your perspective on this issue.”
The Benefits of Active Listening
- Improves Understanding: Helps grasp the speaker’s message clearly.
- Builds Trust: Strengthens relationships through genuine attention.
- Enhances Communication: Promotes clear and effective exchanges.
- Reduces Misunderstandings: Clarifies points, minimizing confusion.
- Encourages Empathy: Shows you care about others’ feelings and perspectives.
- Boosts Problem-Solving: Facilitates better solutions through thorough comprehension.
Differences Between Active Listening and Passive Listening
| Aspect | Active Listening | Passive Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Fully engaged and attentive | Minimal engagement |
| Response | Provides feedback and responses | Little to no response |
| Understanding | Seeks to understand the speaker’s message | May not fully understand the speaker’s message |
| Interaction | Interactive and participative | Non-interactive |
| Focus | Focused on the speaker | Easily distracted |
| Body Language | Uses positive body language (nodding, eye contact) | Passive body language (no significant gestures) |
| Feedback | Offers constructive feedback and clarifications | Provides limited or no feedback |
| Empathy | Demonstrates empathy and understanding | Lacks demonstration of empathy |
| Purpose | Aims to build a deeper connection and understanding | Primarily hears the message without seeking deeper meaning |
| Effectiveness | Leads to effective communication and stronger relationships | Can lead to misunderstandings and weaker relationships |
Top Tips for Active Listening
- Stay Focused: Pay full attention to the speaker without getting distracted.
- Avoid Interrupting: Let the speaker finish before you respond.
- Show Interest: Use facial expressions and body language to show engagement.
- Be Patient: Allow the speaker time to express their thoughts completely.
- Avoid Judging: Listen without forming immediate opinions or judgments.
- Reflect Back: Mirror the speaker’s message and emotions to show understanding.
- Take Notes: Write down key points for better retention and response.
- Clarify Doubts: Ask questions if something is unclear.
- Encourage Speaker: Use encouraging words and gestures to prompt the speaker to continue.
- Respond Appropriately: Provide thoughtful and relevant feedback based on what was said.
Why is active listening important?
Active listening improves understanding, builds trust, enhances communication, reduces misunderstandings, and shows empathy.
How can I improve my active listening skills?
Practice techniques such as paraphrasing, summarizing, reflecting, asking open-ended questions, using non-verbal cues, and giving feedback.
What are common barriers to active listening?
Common barriers include distractions, interrupting, forming judgments, and not giving full attention.
How does active listening benefit relationships?
Active listening strengthens relationships by building trust, showing respect, and fostering better communication.
What is the difference between active and passive listening?
Active listening involves full engagement and response, while passive listening involves hearing without full attention or interaction.
Can active listening be practiced in group settings?
Yes, active listening can be practiced in group settings by focusing on each speaker, avoiding interruptions, and providing feedback.
How does active listening enhance problem-solving?
By fully understanding the issue through active listening, you can identify better solutions and make more informed decisions.
What role does body language play in active listening?
Body language, such as maintaining eye contact, nodding, and leaning forward, shows attentiveness and encourages the speaker.
How can I practice active listening in a noisy environment?
Find a quieter spot if possible, focus intently on the speaker, and use verbal cues to show understanding despite the noise.
How does active listening improve empathy?
By fully understanding and acknowledging the speaker’s feelings, active listening fosters a deeper sense of empathy.
35+ Active Listening Examples

Active listening is a communication technique where the listener fully concentrates, understands, responds, and remembers what is being said. It involves giving full attention and providing feedback to the speaker.
What Is Active Listening?
Active Listening communication skills that enhances interactions by ensuring full engagement and understanding between parties. By practicing active listening in communication skills, individuals can build stronger connections, demonstrate empathy, and provide thoughtful responses. This technique is particularly vital in Active Listening in Assertive Communication, where clear and respectful exchanges are crucial significantly bolster strong communication skills, leading to more meaningful and productive conversations.
Examples for Active Listening
Nodding: Show you are listening by nodding occasionally.
Eye Contact: Maintain eye contact with the speaker.
Summarizing: Repeat back what the speaker said in your own words.
Asking Questions: Ask relevant questions to clarify points.
Paraphrasing: Restate the speaker’s message to show understanding.
Minimal Encouragers: Use small verbal comments like “I see,” “Go on,” or “Interesting.”
Body Language: Use open body language, such as facing the speaker and leaning slightly forward.
Avoid Interrupting: Let the speaker finish before you respond.
Reflecting Feelings: Acknowledge the speaker’s emotions, e.g., “You seem upset about this.”
Providing Feedback: Give appropriate feedback that reflects understanding, e.g., “I understand you’re feeling frustrated with this situation.”
Examples of Active Listening in the Workplace
Taking Notes: Jot down key points during meetings.
Confirming Deadlines: Repeat deadlines back to ensure clarity.
Non-Verbal Cues: Use facial expressions to show engagement.
Clarifying Instructions: Ask for additional details when tasks are unclear.
Offering Solutions: Suggest ideas based on what you’ve heard.
Following Up: Send a follow-up email summarizing the discussion.
Allowing Pauses: Give colleagues time to think before they respond.
Acknowledging Contributions: Thank team members for their input.
Staying Focused: Eliminate distractions during conversations.
Encouraging Sharing: Invite quieter colleagues to share their thoughts.
Examples of Active Listening for Students
Nod: Show you understand by nodding.
Ask Questions: Seek clarification when confused.
Summarize: Briefly restate what the teacher said.
Stay Quiet: Avoid talking when someone else is speaking.
Eye Contact: Look at the teacher or speaker.
Take Notes: Write down important points.
Lean Forward: Show interest by leaning slightly forward.
Paraphrase: Repeat what classmates say in your own words.
React Appropriately: Smile or show concern as needed.
Follow Instructions: Do what the teacher asks promptly.
Examples of Active Listening Sentences
“I see, go on.”
“Can you explain that part again?”
“So, you’re saying…”
“That must have been difficult for you.”
“What happened next?”
“I understand how you feel.”
“It sounds like you’re upset.”
“Can you give me an example?”
“I appreciate your point of view.”
“Let me make sure I got that right.”
Examples of Active listening in Childcare
Get on Their Level: Kneel down to make eye contact.
Use Simple Encouragements: Say “I’m listening” or “Tell me more.
“Repeat Their Words: Mirror what the child says.
Show Patience: Wait for them to finish speaking.
Use Positive Body Language: Smile and nod.
Clarify by Asking: “Did you mean…?”
Acknowledge Feelings: “You seem happy/sad/angry”.
Summarize Stories: “So, you played with blocks today”.
Engage with Questions: “What happened next?”
Avoid Distractions: Put away your phone while they talk.
Examples of Active Listening in Communication
Maintain Eye Contact: Look at the speaker to show attention.
Nod Affirmatively: Nod your head to indicate understanding.
Paraphrase: Restate what the speaker said in your own words.
Ask Clarifying Questions: “Can you explain that further?”
Reflect Feelings: “It sounds like you’re feeling…”
Use Minimal Encouragers: “I see,” “Uh-huh,” “Go on.”
Avoid Interrupting: Let the speaker finish before responding.
Summarize Key Points: “So, your main concern is…”
Provide Feedback: Offer constructive comments based on what was said.
Eliminate Distractions: Focus fully on the speaker, avoiding phone or other interruptions.
Examples of Active Listening in the Classroom
Lean Forward: Show interest by leaning slightly towards the speaker.
Repeat Questions: When a classmate asks a question, repeat it for clarity.
Respond to Non-Verbal Cues: Notice and respond to the teacher’s body language.
Use Verbal Prompts: Say “Yes,” “I understand,” or “That makes sense.”
Participate Actively: Engage in discussions by adding relevant points.
Ask Follow-Up Questions: Inquire further about the topic being discussed.
Provide Examples: Share examples that relate to what was discussed.
Group Work Listening: Listen carefully to peers during group activities.
Restate Instructions: Repeat classroom instructions to ensure understanding.
Give Non-Verbal Feedback: Use facial expressions to show comprehension or confusion.
Types of Active Listening
Reflective Listening: Paraphrasing and restating what the speaker says.
Empathetic Listening: Understanding and sharing the speaker’s feelings.
Critical Listening: Analyzing and evaluating the speaker’s message.
Informational Listening: Focusing on understanding and retaining information.
Comprehensive Listening: Combining multiple listening types for full understanding.
Appreciative Listening: Enjoying and valuing the speaker’s message.
6 Active Listening Techniques
Paraphrasing: Restate what the speaker has said in your own words to show understanding and verify accuracy.
Summarizing: Condense the main points of the conversation to confirm understanding and keep track of important details.
Reflecting: Mirror the speaker’s emotions by acknowledging their feelings, e.g., “You seem excited about this.”
Asking Open-Ended Questions: Encourage the speaker to elaborate by asking questions that require more than a yes or no answer, e.g., “Can you tell me more about that?”
Using Non-Verbal Cues: Show attentiveness through body language such as nodding, maintaining eye contact, and leaning forward.
Giving Feedback: Provide thoughtful and relevant responses that show you are actively engaged in the conversation, e.g., “I appreciate your perspective on this issue.”
The Benefits of Active Listening
Improves Understanding: Helps grasp the speaker’s message clearly.
Builds Trust: Strengthens relationships through genuine attention.
Enhances Communication: Promotes clear and effective exchanges.
Reduces Misunderstandings: Clarifies points, minimizing confusion.
Encourages Empathy: Shows you care about others’ feelings and perspectives.
Boosts Problem-Solving: Facilitates better solutions through thorough comprehension.
Differences Between Active Listening and Passive Listening
Aspect | Active Listening | Passive Listening |
|---|---|---|
Engagement | Fully engaged and attentive | Minimal engagement |
Response | Provides feedback and responses | Little to no response |
Understanding | Seeks to understand the speaker’s message | May not fully understand the speaker’s message |
Interaction | Interactive and participative | Non-interactive |
Focus | Focused on the speaker | Easily distracted |
Body Language | Uses positive body language (nodding, eye contact) | Passive body language (no significant gestures) |
Feedback | Offers constructive feedback and clarifications | Provides limited or no feedback |
Empathy | Demonstrates empathy and understanding | Lacks demonstration of empathy |
Purpose | Aims to build a deeper connection and understanding | Primarily hears the message without seeking deeper meaning |
Effectiveness | Leads to effective communication and stronger relationships | Can lead to misunderstandings and weaker relationships |
Top Tips for Active Listening
Stay Focused: Pay full attention to the speaker without getting distracted.
Avoid Interrupting: Let the speaker finish before you respond.
Show Interest: Use facial expressions and body language to show engagement.
Be Patient: Allow the speaker time to express their thoughts completely.
Avoid Judging: Listen without forming immediate opinions or judgments.
Reflect Back: Mirror the speaker’s message and emotions to show understanding.
Take Notes: Write down key points for better retention and response.
Clarify Doubts: Ask questions if something is unclear.
Encourage Speaker: Use encouraging words and gestures to prompt the speaker to continue.
Respond Appropriately: Provide thoughtful and relevant feedback based on what was said.
Why is active listening important?
Active listening improves understanding, builds trust, enhances communication, reduces misunderstandings, and shows empathy.
How can I improve my active listening skills?
Practice techniques such as paraphrasing, summarizing, reflecting, asking open-ended questions, using non-verbal cues, and giving feedback.
What are common barriers to active listening?
Common barriers include distractions, interrupting, forming judgments, and not giving full attention.
How does active listening benefit relationships?
Active listening strengthens relationships by building trust, showing respect, and fostering better communication.
What is the difference between active and passive listening?
Active listening involves full engagement and response, while passive listening involves hearing without full attention or interaction.
Can active listening be practiced in group settings?
Yes, active listening can be practiced in group settings by focusing on each speaker, avoiding interruptions, and providing feedback.
How does active listening enhance problem-solving?
By fully understanding the issue through active listening, you can identify better solutions and make more informed decisions.
What role does body language play in active listening?
Body language, such as maintaining eye contact, nodding, and leaning forward, shows attentiveness and encourages the speaker.
How can I practice active listening in a noisy environment?
Find a quieter spot if possible, focus intently on the speaker, and use verbal cues to show understanding despite the noise.
How does active listening improve empathy?
By fully understanding and acknowledging the speaker’s feelings, active listening fosters a deeper sense of empathy.


