30+ Advocacy Examples
Advocacy involves actively supporting, defending, or arguing for a cause, policy, or group. It empowers individuals and communities to influence decision-making processes and bring about positive change. Advocacy can take many forms, including public speaking, writing letters, organizing campaigns, and lobbying policymakers. Whether you champion social justice, environmental protection, or educational reforms, advocacy plays a crucial role in promoting and achieving meaningful progress. Understanding the principles and methods of effective advocacy equips you with the tools to create a significant impact on the issues that matter most to you.
What is Advocacy?
Advocacy refers to the act of actively supporting, promoting, or arguing for a particular cause, policy, or group. It involves various activities aimed at influencing public opinion, policymakers, and decision-making processes to bring about social, political, or environmental change. Advocacy can be practiced by individuals, organizations, or communities and often includes actions.
Advocacy Examples
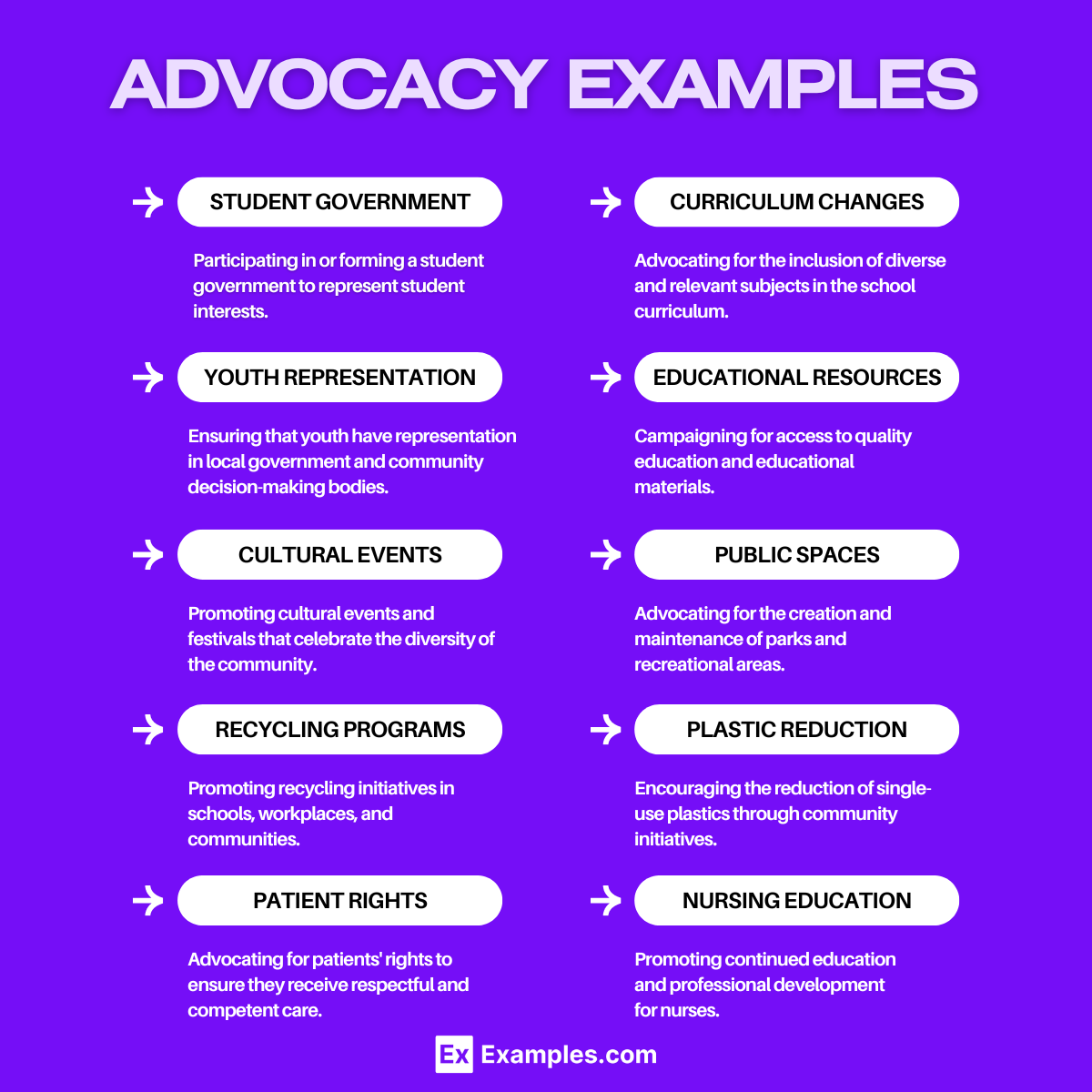
For Students
- Petitioning for Better School Facilities: Organizing a petition to improve the quality of school buildings and resources.
- Anti-Bullying Campaigns: Creating awareness and prevention programs to combat bullying in schools.
- Student Government: Participating in or forming a student government to represent student interests.
- Curriculum Changes: Advocating for the inclusion of diverse and relevant subjects in the school curriculum.
- Mental Health Support: Promoting mental health resources and counseling services in schools.
- Scholarship Programs: Campaigning for more scholarships and financial aid for students.
- Safe Spaces: Establishing safe spaces for students to express themselves and find support.
For Youth
- Youth Empowerment Programs: Creating programs that empower young people to develop leadership skills.
- Employment Opportunities: Advocating for job training and employment opportunities for youth.
- Substance Abuse Prevention: Organizing initiatives to educate youth about the dangers of substance abuse.
- Youth Representation: Ensuring that youth have representation in local government and community decision-making bodies.
- Educational Resources: Campaigning for access to quality education and educational materials.
- Mentorship Programs: Establishing mentorship programs to guide and support young people.
- Youth Centers: Promoting the development of community youth centers that offer recreational and educational activities.
In Community
- Neighborhood Watch Programs: Organizing community watch groups to enhance neighborhood safety.
- Community Gardens: Advocating for the creation of community gardens to promote local food production and community bonding.
- Local Policy Changes: Engaging with local government to address community-specific issues such as housing, transportation, and public safety.
- Cultural Events: Promoting cultural events and festivals that celebrate the diversity of the community.
- Access to Healthcare: Campaigning for accessible healthcare services within the community.
- Environmental Cleanup: Organizing community cleanups to improve the local environment.
- Public Spaces: Advocating for the creation and maintenance of parks and recreational areas.
For the Environment
- Recycling Programs: Promoting recycling initiatives in schools, workplaces, and communities.
- Renewable Energy: Advocating for the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
- Wildlife Conservation: Supporting efforts to protect endangered species and their habitats.
- Climate Change Awareness: Organizing events and campaigns to raise awareness about climate change.
- Plastic Reduction: Encouraging the reduction of single-use plastics through community initiatives.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture and business practices.
- Environmental Legislation: Lobbying for stronger environmental protection laws and regulations.
In Nursing
- Patient Rights: Advocating for patients’ rights to ensure they receive respectful and competent care.
- Workplace Safety: Campaigning for safer working conditions for nurses and healthcare staff.
- Nursing Education: Promoting continued education and professional development for nurses.
- Staffing Levels: Advocating for adequate nurse-to-patient ratios to ensure quality care.
- Mental Health Support: Supporting mental health resources for nurses to address burnout and stress.
- Policy Changes: Engaging in policy advocacy to influence healthcare legislation that impacts nursing practice.
- Community Health Initiatives: Participating in public health campaigns to improve community health outcomes.
For Health
- Access to Healthcare: Campaigning for universal healthcare access for all individuals.
- Preventive Health Programs: Promoting preventive health measures such as vaccinations and screenings.
- Mental Health Awareness: Raising awareness and reducing stigma around mental health issues.
- Nutrition and Exercise: Advocating for programs that promote healthy eating and physical activity.
- Health Education: Providing education on various health topics to communities and schools.
- Chronic Disease Management: Supporting initiatives that help individuals manage chronic illnesses effectively.
- Substance Abuse Treatment: Advocating for accessible and effective treatment programs for substance abuse.
Personal Advocacy
- Self-Advocacy: Speaking up for oneself to ensure personal needs and rights are met.
- Family Advocacy: Advocating for the rights and needs of family members, such as elderly parents or children.
- Workplace Advocacy: Addressing workplace issues such as discrimination, harassment, or unfair treatment.
- Healthcare Advocacy: Ensuring that oneself or a loved one receives appropriate medical care and treatment.
- Legal Advocacy: Seeking legal assistance or representing oneself in legal matters to protect personal rights.
- Consumer Rights: Advocating for fair treatment and transparency from businesses and service providers.
- Community Involvement: Participating in local advocacy groups or committees to address community concerns.
Types of Advocacy
Advocacy plays a crucial role in bringing about social change, promoting justice, and supporting those in need. Understanding the different types of advocacy can help individuals and organizations choose the most effective strategies for their causes. Below are the primary types of advocacy:
Individual Advocacy
Individual advocacy involves supporting and representing a single person, ensuring their rights are respected and their needs are met. This type of advocacy is often used for vulnerable individuals who may not be able to advocate for themselves.
Examples:
- Helping a student with disabilities obtain necessary educational accommodations.
- Assisting an elderly person in navigating healthcare services.
Group Advocacy
Group advocacy focuses on representing the interests and needs of a specific group of people who share common issues or concerns. This type of advocacy is often carried out by non-profit organizations and community groups.
Examples:
- Advocating for better working conditions for farmworkers.
- Campaigning for the rights of the LGBTQ+ community.
Systemic Advocacy
Systemic advocacy aims to bring about changes in policies, laws, and systems to benefit a large group of people or society as a whole. This type of advocacy often involves lobbying, policy analysis, and working with lawmakers.
Examples:
- Lobbying for reforms in the criminal justice system.
- Campaigning for environmental protection laws.
Legal Advocacy
Legal advocacy involves using the legal system to advance a cause, protect rights, or seek justice. This can include providing legal representation, filing lawsuits, or engaging in other legal actions.
Examples:
- Representing clients in civil rights cases.
- Filing class-action lawsuits against corporations for harmful practices.
Self-Advocacy
Self-advocacy is when individuals advocate for their own rights and needs. This type of advocacy empowers people to speak up for themselves and take control of their own lives.
Examples:
- A person with a disability requesting reasonable accommodations at work.
- A student advocating for their educational needs and preferences.
Peer Advocacy
Peer advocacy involves individuals who have shared similar experiences supporting and advocating for one another. This type of advocacy is often seen in support groups and peer mentoring programs.
Examples:
- People in recovery from addiction supporting each other.
- Students with similar academic challenges helping one another navigate school systems.
Professional Advocacy
Professional advocacy is conducted by trained professionals, such as social workers, counselors, or advocacy organizations. These advocates use their expertise to support individuals and groups in need.
Examples:
- Social workers helping families access social services.
- Non-profit organizations advocating for policy changes.
Health Advocacy
Health advocacy focuses on promoting patients’ health and ensuring access to healthcare. Health advocates work to improve health outcomes and navigate the healthcare system.
Examples:
- Advocating for patients’ rights in medical settings.
- Campaigning for affordable healthcare policies.
Media Advocacy
Media advocacy uses media platforms to raise awareness, shape public opinion, and influence policy decisions. This type of advocacy leverages the power of media to bring attention to specific issues.
Examples:
- Using social media campaigns to raise awareness about climate change.
- Working with journalists to highlight social injustices.
Advocacy Methods
Lobbying
Lobbying involves directly engaging with policymakers to influence their decisions. This method includes meeting with legislators, providing them with information, and persuading them to support specific legislation.
Public Campaigns
Public campaigns raise awareness and mobilize public support. These campaigns use various media channels, including social media, to disseminate information and encourage public participation.
Grassroots Advocacy
Grassroots advocacy encourages ordinary people to take action. This method involves organizing local communities, hosting events, and empowering individuals to contact their representatives.
Coalition Building
Forming coalitions with other organizations and groups can amplify the advocacy effort. Working together with allies can strengthen the influence and resources available for the cause.
Policy Research and Analysis
Conducting research and analyzing policies help advocates present informed arguments. Providing evidence-based data can support the advocacy position and persuade decision-makers.
Media Engagement
Engaging with the media is crucial for spreading the advocacy message. Writing op-eds, issuing press releases, and participating in interviews can help reach a broader audience.
Public Speaking and Presentations
Public speaking at events, conferences, and meetings allows advocates to share their message directly with an audience. This method is effective in educating and inspiring others to join the cause.
Petitions and Letter Writing Campaigns
Petitions and letter-writing campaigns mobilize public support by gathering signatures or sending letters to decision-makers. These actions demonstrate the level of public backing for a cause.
Legal Action
Taking legal action can challenge or defend laws and policies in court. Legal advocacy often involves filing lawsuits, submitting amicus briefs, and participating in hearings.
Educational Workshops and Training
Organizing workshops and training sessions educate people about the issue and how they can contribute. This method builds capacity and empowers individuals to advocate effectively.
Direct Action
Direct action includes protests, sit-ins, and demonstrations. These actions draw public attention to the issue and put pressure on decision-makers to act.
Storytelling and Personal Testimonials
Sharing personal stories and testimonials humanizes the issue and makes it more relatable. This method can be powerful in connecting with the audience emotionally.
Social Media Advocacy
Using social media platforms to spread the advocacy message allows for quick and widespread dissemination. Social media campaigns can engage a large audience and create viral support for the cause.
Engaging Influencers and Celebrities
Partnering with influencers and celebrities can amplify the advocacy message. Their reach and influence can attract more attention to the cause.
Mobilizing Volunteers
Recruiting and organizing volunteers can help execute advocacy activities. Volunteers can participate in events, spread the message, and engage in various advocacy efforts.
Engaging with Local Governments
Working with local governments can address issues at the community level. Advocates can influence local policies and practices that directly impact their cause.
Using Digital Tools and Technology
Leveraging digital tools, such as online petitions, email campaigns, and advocacy platforms, can enhance the efficiency and reach of advocacy efforts.
How to Pronounce “Advocacy”
Advocacy is pronounced as ˈad-və-kə-sē. Here is a breakdown:
- ad as in “advertise”
- və as in “sofa”
- kə as in “comply”
- sē as in “see”
Synonyms for Advocacy
| Synonym | Description |
|---|---|
| Support | Giving assistance or backing to a cause or policy. |
| Promotion | Actively encouraging or publicizing a cause or idea. |
| Championing | Defending or supporting a cause vigorously. |
| Endorsement | Official approval or recommendation of a cause. |
| Backing | Support or help for a cause or policy. |
| Defense | Protection or justification of a cause or policy. |
| Lobbying | Attempting to influence decisions of policymakers. |
| Sponsorship | Supporting a cause, often financially. |
| Advancement | Promoting the progress or development of a cause. |
Why Advocacy Is Important
Advocacy plays a crucial role in society, offering numerous benefits and driving positive change. Here are key reasons why advocacy is essential:
1. Amplifies Voices
Advocacy ensures that the voices of individuals or groups, especially those marginalized or underrepresented, are heard. This amplification can lead to greater awareness and attention to issues that might otherwise be ignored.
2. Promotes Social Change
Through advocacy, systemic changes can be initiated and sustained. Advocates work to alter policies, practices, and attitudes, leading to significant social transformation and improved conditions for many.
3. Protects Rights
Advocacy is vital in protecting the rights of individuals and communities. It helps to safeguard against injustices and discrimination, ensuring that everyone has access to their fundamental rights and freedoms.
4. Informs and Educates
Advocacy involves raising awareness and educating the public about specific issues. This education can lead to a more informed society, where individuals understand and support necessary changes.
5. Influences Policy
Advocates often work to influence legislation and policy-making. By presenting well-researched information and persuasive arguments, they can shape laws and regulations that benefit society.
6. Empowers Individuals
Advocacy empowers people by giving them the tools and confidence to stand up for themselves and others. This empowerment leads to a more active and engaged citizenry.
7. Fosters Community Engagement
Advocacy encourages community involvement and collaboration. It brings people together to work towards common goals, strengthening community bonds and fostering a sense of collective responsibility.
8. Drives Accountability
By holding individuals, organizations, and governments accountable, advocacy ensures transparency and integrity. This accountability helps to maintain trust and credibility within society.
9. Addresses Inequality
Advocacy tackles various forms of inequality by addressing disparities in areas such as education, healthcare, employment, and justice. It aims to create a more equitable and just society for all.
10. Supports Mental Health
For individuals and communities facing challenges, advocacy can provide a sense of support and solidarity. Knowing that someone is fighting for their rights and needs can have a positive impact on mental health and well-being.
Advocacy Skills
Advocacy skills refer to the abilities and techniques used to persuade and influence others to support a particular cause or policy. These skills encompass communication, negotiation, research, and strategic planning.
Key Components of Advocacy Skills
1. Communication Skills
Effective communication is at the heart of advocacy. This includes:
- Public Speaking: Articulating your message clearly and confidently to an audience.
- Writing: Crafting persuasive letters, articles, and social media posts.
- Active Listening: Understanding others’ perspectives and responding thoughtfully.
2. Research Skills
Thorough research underpins successful advocacy. This involves:
- Gathering Evidence: Collecting data and facts to support your position.
- Analyzing Information: Interpreting data to make a compelling case.
- Staying Informed: Keeping up-to-date with current events and policy changes.
3. Negotiation Skills
Negotiation is essential for reaching agreements and compromises. Key aspects include:
- Building Relationships: Establishing trust and rapport with stakeholders.
- Finding Common Ground: Identifying areas of agreement to facilitate cooperation.
- Problem-Solving: Developing creative solutions to address conflicts.
4. Strategic Planning
Advocacy requires a well-thought-out plan. This includes:
- Setting Goals: Defining clear, achievable objectives.
- Developing Strategies: Creating a roadmap to reach your goals.
- Monitoring Progress: Evaluating the effectiveness of your advocacy efforts and adjusting as needed.
5. Campaigning Skills
Running effective advocacy campaigns involves:
- Mobilizing Support: Engaging and motivating people to join your cause.
- Media Engagement: Using media outlets to amplify your message.
- Event Planning: Organizing events, rallies, and meetings to garner attention.
6. Legal Knowledge
Understanding legal frameworks and rights is critical for advocacy. This involves:
- Knowing the Law: Familiarizing yourself with relevant laws and regulations.
- Legal Writing: Preparing legal documents and submissions.
- Advocacy in Court: Representing clients or causes in legal settings.
How to Develop Advocacy Skills
To develop advocacy skills, consider the following steps:
- Education: Take courses or attend workshops on communication, law, and public policy.
- Practice: Gain experience through volunteering, internships, or working with advocacy organizations.
- Mentorship: Seek guidance from experienced advocates or mentors.
- Networking: Connect with other advocates, organizations, and policymakers.
- Reflection: Continuously evaluate and refine your advocacy techniques.
Advocacy in mental health
Advocacy in mental health involves promoting policies, practices, and services that improve mental health care and support individuals with mental health conditions. It includes raising public awareness about mental health issues, reducing stigma, and ensuring access to quality mental health services. Advocates work to influence legislation, support funding for mental health programs, and create inclusive environments that prioritize mental well-being. By engaging with policymakers, the media, and communities, mental health advocates aim to foster understanding, provide education, and empower individuals to seek help and support. Their efforts contribute to a more compassionate and responsive mental health care system.
Advocacy Nursing
Advocacy nursing involves representing and supporting patients’ rights and well-being within the healthcare system. Nurses in this role actively listen to patients’ concerns, ensure they understand their medical conditions and treatment options, and work to protect their interests in healthcare decisions. Advocacy nurses also address systemic issues, promoting policies that improve patient care and access to services. This crucial aspect of nursing fosters trust and empowers patients, ensuring they receive holistic and personalized care. By bridging the gap between patients and healthcare providers, advocacy nurses enhance the overall quality of the healthcare experience.
How to Set Your Advocacy
Self-identification and actualization are one of the most difficult things a person can do, as some may not be even able to achieve them. One of the best ways to do this is to learn and identify the advocacies you want to promote and support.
1.) Write Down Your Core Values
Begin by writing down your core values to help you narrow down the various causes you may or may not support. You will need to write down your core values on note-taking software or an accessible sheet of paper.
2.) Research Various Causes
You must then research various causes that are aligned with your written down core values. These causes can be various statements lifted from organizations or even sentiments for a specific type of change or support.
3.) List Out Causes that Resonate With You
After you have researched the causes, you must list out any of these causes that will resonate with your core values. Listing them all out will help you narrow down the sentiments you want to set as your advocacy.
4.) Select One or More Advocacies to Integrate into Your Life
You must then select one or more advocacies you want to integrate into your everyday life and internal reasoning. This will help you learn more about yourself and will even help you search for people with similar interests and values.
What are Advocacy Issues?
Advocacy issues refer to problems or concerns that individuals or groups actively work to address through public campaigns, education, and policy changes. These issues span a wide range of social, economic, and political topics, aiming to bring about positive change and improve the lives of affected populations.
Common Advocacy Issues
- Human Rights
- Definition: The basic rights and freedoms that belong to every person in the world.
- Examples:
- Campaigning against human trafficking
- Advocating for freedom of speech and religion
- Fighting for the rights of marginalized communities
- Environmental Protection
- Definition: Efforts to preserve natural resources and protect the planet from harmful human activities.
- Examples:
- Promoting renewable energy sources
- Campaigning against deforestation
- Advocating for policies to combat climate change
- Education Reform
- Definition: Efforts to improve the quality and accessibility of education for all individuals.
- Examples:
- Campaigning for equitable funding for schools
- Advocating for inclusive education policies
- Promoting early childhood education programs
- Health Care Access
- Definition: Efforts to ensure all individuals have access to affordable and quality health care services.
- Examples:
- Campaigning for universal health coverage
- Advocating for mental health services
- Promoting preventive health care measures
- Social Justice
- Definition: Efforts to create a fair and just society by addressing inequalities and discrimination.
- Examples:
- Fighting for gender equality
- Advocating for racial justice
- Campaigning for LGBTQ+ rights
What is advocacy?
Advocacy is the act of supporting or arguing for a cause, policy, or individual’s rights, aiming to influence decisions within political, economic, and social systems.
Why is advocacy important?
Advocacy ensures that voices of marginalized or underrepresented groups are heard, promoting social justice, policy change, and improved access to resources and opportunities.
What are the types of advocacy?
Types of advocacy include self-advocacy, individual advocacy, systems advocacy, and legislative advocacy, each focusing on different levels of influence and support.
How does advocacy work?
Advocacy works through actions such as raising awareness, lobbying, public speaking, and collaborating with stakeholders to create positive changes in policies and practices.
Who can be an advocate?
Anyone can be an advocate, including individuals, professionals, organizations, and community groups, by actively supporting and speaking up for causes they believe in.
What skills are needed for effective advocacy?
Effective advocacy requires strong communication, critical thinking, problem-solving, negotiation, and interpersonal skills, along with a deep understanding of the relevant issues and policies.
What is patient advocacy in healthcare?
Patient advocacy involves supporting patients’ rights and needs within the healthcare system, ensuring they receive appropriate care, informed consent, and respect throughout their medical journey.
How can one get involved in advocacy?
Get involved in advocacy by joining advocacy groups, participating in campaigns, volunteering, contacting legislators, and using social media to raise awareness about important issues.
What challenges do advocates face?
Advocates face challenges such as resistance to change, limited resources, legal and political obstacles, and potential backlash or opposition from those benefiting from the status quo.
How can advocacy create social change?
Advocacy creates social change by raising awareness, shaping public opinion, influencing policy decisions, and mobilizing communities to address systemic issues and injustices.



