21+ Contemporary Art Examples
Contemporary art refers to the artwork produced in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, reflecting current cultural, social, and political themes. This dynamic and diverse art form often challenges traditional boundaries and explores new media and techniques. Artist bios are essential in contemporary art, providing insights into the creators’ backgrounds, inspirations, and influences. Renowned contemporary artists like Ai Weiwei and Yayoi Kusama use their unique perspectives to engage and provoke thought in global audiences.
What is Contemporary Art?
Contemporary art refers to the artwork created in the present time, typically from the late 20th century to now. It encompasses diverse styles and mediums, reflecting current issues, ideas, and innovations in society, culture, and technology.
Contemporary Art Examples
- Ai Weiwei’s “Sunflower Seeds”
- Yayoi Kusama’s “Infinity Mirrored Room”
- Banksy’s “Girl with Balloon”
- Damien Hirst’s “The Physical Impossibility of Death in the Mind of Someone Living”
- Jean-Michel Basquiat’s “Untitled” (1981)
- Takashi Murakami’s “727”
- Cindy Sherman’s “Untitled Film Stills”
- Marina Abramović’s “The Artist is Present”
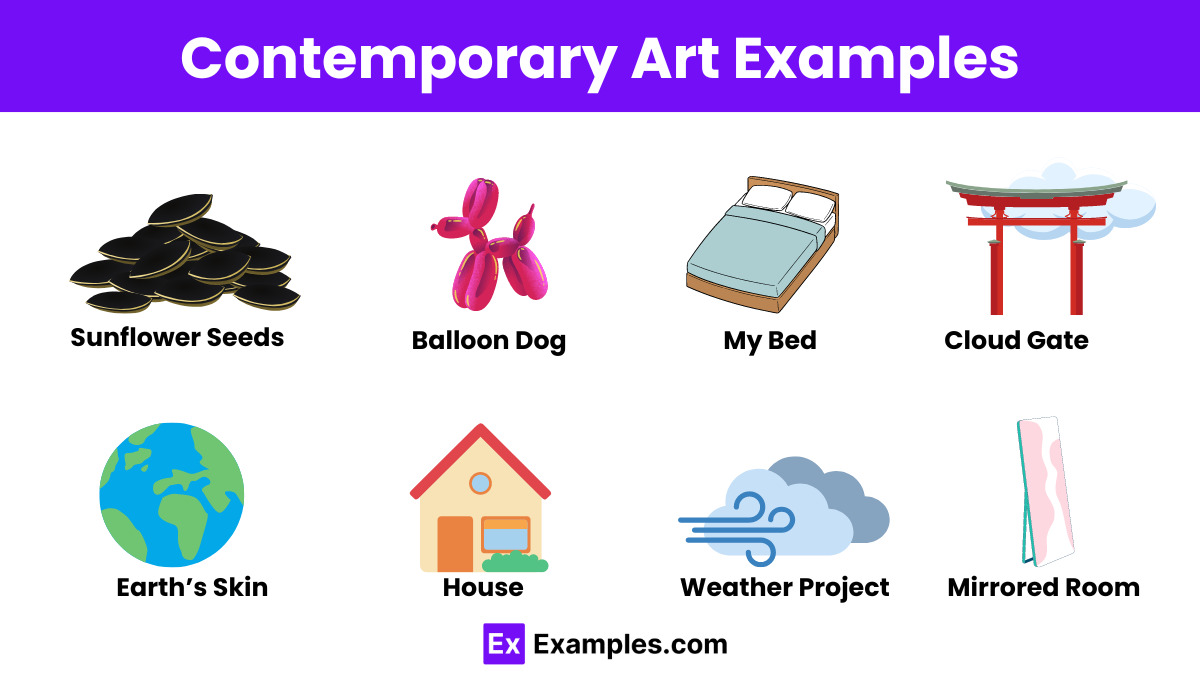
- Jeff Koons’ “Balloon Dog”
- Tracey Emin’s “My Bed”
- Kara Walker’s “A Subtlety”
- Olafur Eliasson’s “The Weather Project”
- Kehinde Wiley’s “Portrait of Barack Obama”
- Anish Kapoor’s “Cloud Gate”
- El Anatsui’s “Earth’s Skin”
- Jenny Holzer’s “Truisms”
- Richard Serra’s “Tilted Arc”
- Rachel Whiteread’s “House”
- Damien Hirst’s “For the Love of God”
- David Hockney’s “A Bigger Splash”
- Barbara Kruger’s “Untitled” (Your Body is a Battleground)
- Louise Bourgeois’s “Maman”
Types of Contemporary Art
- Abstract Art – Non-representational art that uses shapes, colors, and forms to achieve its effect.
- Conceptual Art – Art where the idea or concept behind the work is more important than the finished art object.
- Minimalism – Art characterized by simplicity and the use of minimal elements, often geometric shapes.
- Pop Art – Art that draws on popular culture and mass media, often using bright colors and commercial techniques.
- Street Art – Art created in public spaces, often with a rebellious or socially critical message.
- Digital Art – Art created using digital technology, including computer graphics and virtual reality.
- Installation Art – Three-dimensional works designed to transform a viewer’s perception of a space.
- Performance Art – Art where the artist’s actions are the medium, often involving live performances.
- Photorealism – Art that aims to depict real life with high accuracy, resembling photographs.
- Environmental Art – Art that addresses ecological issues or is created in harmony with the environment.
- Video Art – Art that relies on moving images and video technology as its primary medium.
Contemporary Art Characteristics
- Diversity of Mediums – Contemporary art employs a wide range of mediums, from traditional painting and sculpture to digital, performance art, and even narrative poetry.
- Conceptual Focus – Emphasis on ideas and concepts rather than aesthetics alone, often challenging traditional boundaries.
- Global Perspective – Reflects diverse cultural, social, and political issues from around the world, embracing multiculturalism.
- Innovation and Experimentation – Artists frequently experiment with new techniques and materials, pushing the boundaries of what art can be.
- Interdisciplinary Approach – Often incorporates elements from various disciplines such as literature, science, and technology.
- Audience Engagement – Many works are interactive, inviting viewer participation and engagement.
- Social Commentary – Contemporary art often addresses contemporary issues such as politics, identity, and the environment, weaving these themes into a compelling narrative format that provides a critical perspective.
- Pluralism – There is no single style or movement; instead, contemporary art encompasses a wide array of styles and approaches.
- Temporal Relevance – Reflects current trends, events, and societal changes, making it highly relevant to its time.
- Use of Technology – Integrates digital tools and platforms, including virtual reality and social media, into the creation and dissemination of art.
Contemporary Art Time Period
The contemporary art time period began in the late 20th century and continues to the present day. This era is characterized by a departure from modernism, embracing a wide range of styles and practices. Abstractionism, which focuses on non-representational forms and emphasizes shapes, colors, and lines, remains a significant influence. Contemporary art reflects current cultural, social, and political issues, showcasing a diversity of mediums and innovative approaches that challenge traditional boundaries and engage global audiences.
Famous Contemporary Art

- “Sunflower Seeds” by Ai Weiwei – An installation of millions of hand-painted porcelain sunflower seeds.
- “Infinity Mirrored Room” by Yayoi Kusama – An immersive room with mirrors and LED lights creating an infinite reflection effect.
- “Girl with Balloon” by Banksy – A stenciled image of a girl letting go of a heart-shaped balloon.
- “The Physical Impossibility of Death in the Mind of Someone Living” by Damien Hirst – A preserved shark in a tank of formaldehyde.
- “Untitled” (1981) by Jean-Michel Basquiat – A vibrant, expressive painting blending text, symbols, and abstract forms.
- “727” by Takashi Murakami – A colorful, anime-inspired painting featuring the artist’s iconic characters and motifs.
- “Untitled Film Stills” by Cindy Sherman – A series of black-and-white photographs depicting the artist in various roles and scenarios.
- “The Artist is Present” by Marina Abramović – A performance piece where Abramović sat silently across from visitors, inviting them to share a moment of presence.
- “Balloon Dog” by Jeff Koons – A large, shiny sculpture resembling a balloon animal.
- “My Bed” by Tracey Emin – An installation featuring the artist’s unmade bed surrounded by personal items.
How to Visit a Contemporary Art Museum?
- Research the Museum – Before visiting, research the contemporary art museum’s exhibits, artists, and events online using primary sources. Look for visitor reviews and find out if there are any special exhibitions or guided tours available.
- Plan Your Visit – Decide on the best time to visit, considering the museum’s hours and any peak visiting times. Some museums may offer discounted or free admission on certain days.
- Purchase Tickets – Buy your tickets in advance if possible. Many contemporary art museums offer online ticket purchasing, which can save you time and sometimes money.
- Explore the Exhibits – Upon arrival, pick up a map or guide. Start with the main exhibits and then move on to special or temporary exhibitions. Take your time to appreciate the diverse styles, mediums, and concepts.
- Engage with the Art – Read the descriptions and artist bios provided for each piece. Take notes, photos (if allowed), and think about the themes and messages. Many museums also have interactive exhibits that encourage participation.
- Visit the Museum Shop and Cafe – Before leaving, visit the museum shop to find books, prints, and souvenirs related to contemporary art. Relax at the cafe to reflect on your experience and perhaps discuss it with fellow visitors.
The next era of contemporary art
- Digital and Virtual Art – As technology advances, digital visual arts such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI) will become more prevalent. Artists will explore new ways to create immersive experiences and interactive works that engage viewers in novel ways.
- Environmental and Sustainable Art – With growing awareness of climate change and environmental issues, artists will increasingly focus on creating works that address sustainability. This includes using recycled materials, creating eco-friendly installations, and highlighting ecological concerns through their art.
- Global and Inclusive Perspectives – The next era will continue to embrace diversity, with more artists from various cultural backgrounds and underrepresented communities gaining recognition. This will lead to a richer tapestry of voices and stories in the art world.
- Social and Political Engagement – Art will remain a powerful tool for social and political commentary. Contemporary artists will tackle pressing issues such as inequality, human rights, and global conflicts, using their work to provoke thought and inspire change.
- Collaborative and Interdisciplinary Projects – Artists will increasingly collaborate with professionals from other fields such as science, technology, and humanities. These interdisciplinary projects will push the boundaries of what art can be and explore new ways of thinking and creating.
- New Art Market Dynamics – The art market will continue to evolve with the rise of digital platforms and online galleries. NFTs (non-fungible tokens) and blockchain technology will play a significant role in how art is bought, sold, and owned, leading to new economic models for artists.
- Emphasis on Experience and Participation – The future of contemporary art will focus more on the experience and participation of the audience. Interactive installations, performance art, and experiential exhibits will become more common, inviting viewers to be part of the art-making process.
- This new era of contemporary art will reflect the rapidly changing world, incorporating technology, addressing global issues, and celebrating diverse voices, ultimately leading to a more inclusive and innovative artistic landscape.
Modern Art vs. Contemporary Art
| Aspect | Modern Art | Contemporary Art |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Late 19th century to mid-20th century | Late 20th century to present |
| Key Movements | Impressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Fauvism | Conceptual Art, Digital Art, Installation Art, Street Art |
| Main Characteristics | Emphasis on abstraction and experimentation | Emphasis on diversity, innovation, and global perspectives |
| Artists | Pablo Picasso, Vincent van Gogh, Salvador Dalí | Ai Weiwei, Yayoi Kusama, Banksy |
| Mediums Used | Traditional mediums like painting, sculpture | Diverse mediums including digital, performance, and multimedia |
| Themes | Exploring new perspectives, breaking away from tradition | Reflecting current cultural, social, and political issues |
| Audience Engagement | Primarily visual and interpretative | Often interactive and participatory |
| Technology | Limited to available tools of the time | Integrates advanced technologies like VR, AR, and AI |
| Art Market | Traditional galleries and auctions | Includes online platforms and NFTs |
| Global Influence | Western-centric | Global and inclusive |
Who are some famous contemporary artists?
Famous contemporary artists include Ai Weiwei, Yayoi Kusama, and Banksy.
What mediums are used in contemporary art?
Contemporary art uses diverse mediums, including digital, performance, installation, and traditional forms.
How does contemporary art differ from modern art?
Contemporary art focuses on current issues and diverse perspectives, while modern art emphasizes abstraction and experimentation.
What themes are common in contemporary art?
Common themes include social and political issues, identity, and cultural diversity.
Where can I see contemporary art?
Contemporary art can be seen in museums, galleries, public spaces, and online platforms.
What is the role of technology in contemporary art?
Technology plays a significant role, with artists using digital tools, VR, AR, and AI in their work.
What is conceptual art?
Conceptual art is a movement where the idea or concept behind the work is more important than the finished object.
How does contemporary art engage the audience?
Contemporary art often includes interactive and participatory elements to engage the audience.
What is performance art?
Performance art is a form where the artist’s actions are the medium, often involving live performances.
What is installation art?
Installation art consists of large-scale, three-dimensional works designed to transform a viewer’s perception of a space.