27+ Empathy Map Examples
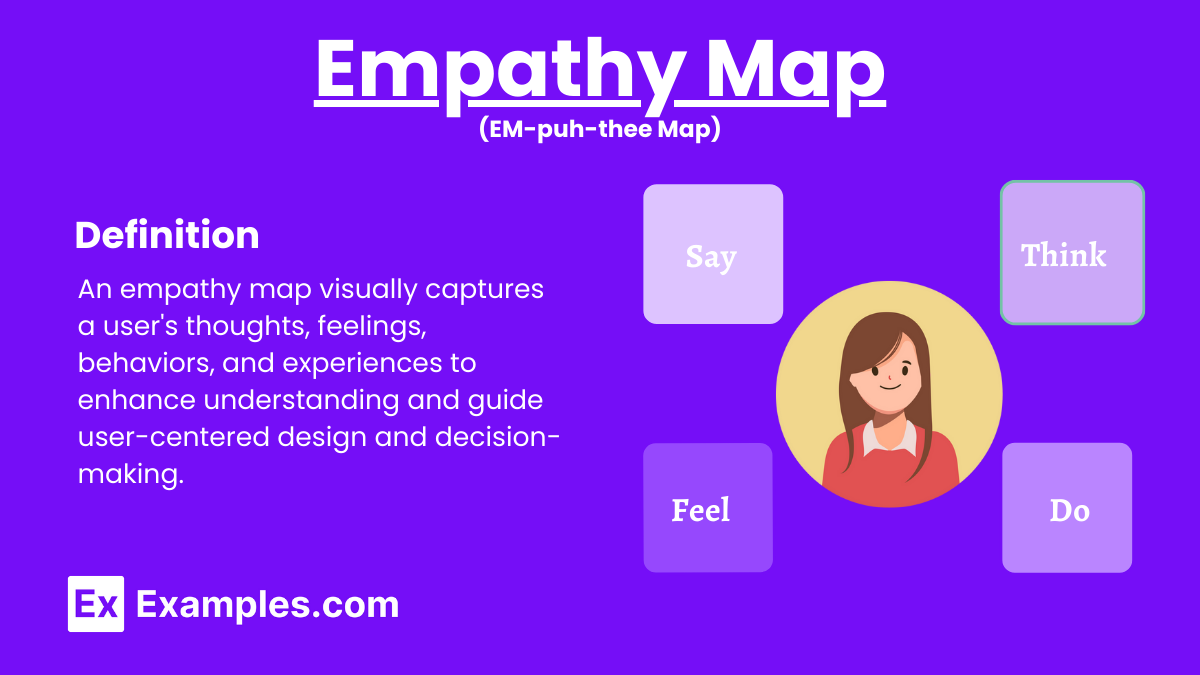
An Empathy Map is a collaborative tool used to gain deeper insight into customers’ self-concept, emotions, and behaviors. It helps in visualizing what customers say, think, feel, and do, allowing businesses to align their strategies with customer needs. By focusing on self-concept, teams can better understand how customers perceive themselves and their experiences. This enhances product development, marketing, and customer service, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
What is Empathy Map?
An Empathy Map is a collaborative tool that helps teams understand customers’ emotions, thoughts, and behaviors by visualizing what they say, think, feel, and do. It provides insights into customers’ self-concept, guiding better product development and customer-centric strategies.
Empathy Map Examples
- Product Development: Understanding user needs for a new app.
- Marketing Campaigns: Identifying customer pain points for targeted ads.
- Customer Service: Enhancing support based on common frustrations.
- UX Design: Improving website navigation based on user feedback.
- Healthcare: Understanding patient experiences to improve care.
- Education: Tailoring teaching methods to student needs.
- Retail: Enhancing in-store experience based on shopper behavior.
- Financial Services: Developing user-friendly banking apps.
- Nonprofits: Crafting messages that resonate with donors.
- Hospitality: Improving guest experiences in hotels.
- Automotive: Designing features that align with driver preferences.
- Tech Support: Addressing common technical issues reported by users.
- Government Services: Streamlining processes based on citizen feedback.
- E-commerce: Personalizing online shopping experiences.
- Travel: Enhancing travel booking experiences.
- Fitness: Creating user-centric workout programs.
- Entertainment: Developing content that resonates with viewers.
- Food and Beverage: Crafting menus that meet customer tastes and dietary needs.
Empathy Map Example For Students
- Course Feedback: Understanding students’ thoughts and intrusive thoughts about a particular course to improve its content and delivery..
- Study Habits: Identifying challenges and motivations behind students’ study habits to develop better study aids.
- Online Learning: Gaining insights into students’ experiences with online classes to enhance virtual learning environments.
- Class Participation: Understanding barriers to participation and engagement in class discussions.
- Exam Preparation: Identifying stress points and using critical thinking to develop effective strategies students use to prepare for exams.
- Time Management: Understanding how students balance academic, social, and personal responsibilities.
- Technology Use: Assessing how students use educational technology tools and platforms.
- Extracurricular Activities: Gaining insights into what drives students to participate in extracurricular activities and how it impacts their academic life.
- Peer Relationships: Understanding the dynamics of student interactions and support networks.
- Career Planning: Identifying students’ aspirations, concerns, and needs related to career planning and development.
Types
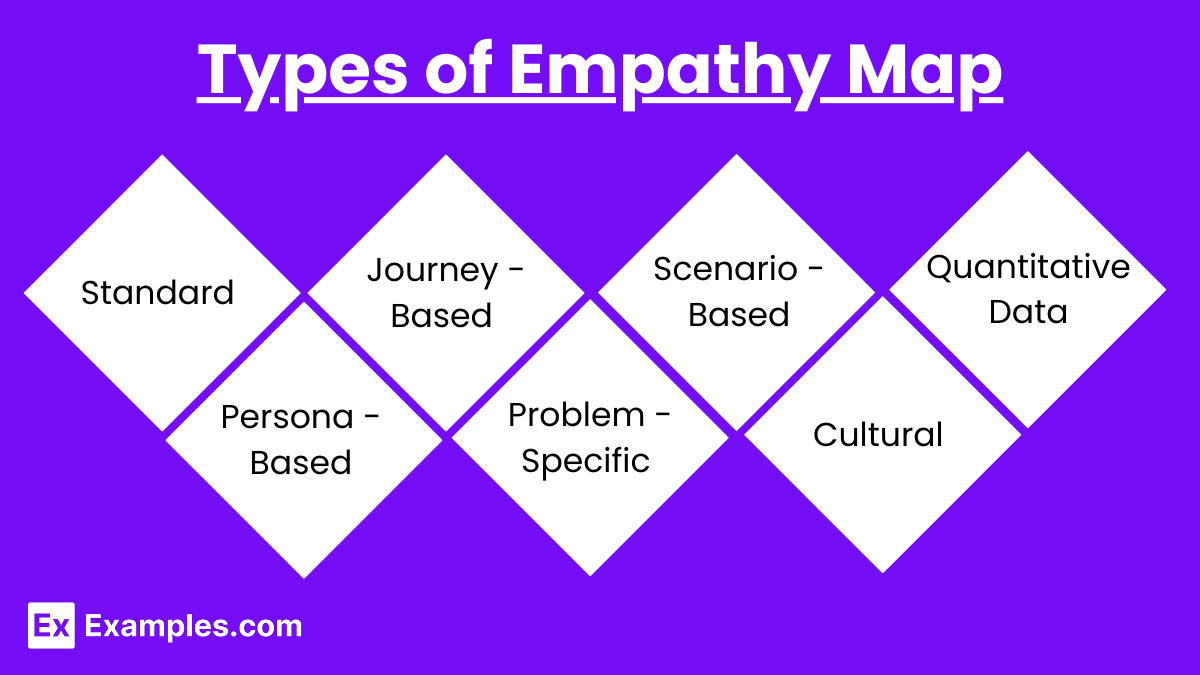
- Standard Empathy Map: Includes sections for what the user says, thinks, feels, and does, providing a holistic view of the user’s experience.
- Persona-Based Empathy Map: Tailored to specific user personas identified in research, focusing on their unique characteristics, behaviors, and needs.
- Journey-Based Empathy Map: Maps out the user’s emotional journey or experience over time, highlighting key touchpoints and emotions at each stage.
- Problem-Specific Empathy Map: Focuses on understanding a particular problem or challenge faced by users, emphasizing pain points and potential solutions.
- Scenario-Based Empathy Map: Created for specific scenarios or use cases, detailing how users interact with products or services in different contexts.
- Cultural Empathy Map: Acknowledges cultural influences, ensuring understanding of users’ values, norms, beliefs, and behaviors within the context of culture.
- Empathy Map with Quantitative Data: Integrates qualitative insights with quantitative data, such as metrics or analytics, for a more data-driven approach to empathy mapping.
Empathy Map Design Thinking
- Define the Purpose: Articulate the goal of the empathy map to ensure it stays focused and relevant to the design challenge, leveraging user skills and experiences.
- Identify the User: Select the specific user or persona based on demographics, behavior patterns, or needs relevant to the project.
- Gather Data: Collect qualitative data through interviews, surveys, observations, and user feedback to provide insights for the empathy map.
- Map the Insights: Divide the empathy map into sections for what the user says, thinks, feels, and does, then populate with data.
- Analyze the Map: Look for patterns, pain points, and opportunities in the data to better understand the user’s experiences and needs.
- Apply the Insights: Use the empathy map to inform design decisions, ensuring solutions align with user needs and improve their experience.
Why is empathy mapping important?
- Enhances Understanding: Provides a deeper insight into users’ emotions, thoughts, and behaviors, fostering a better understanding of their needs and experiences.
- Improves Communication: Serves as a visual tool that helps team members and stakeholders align on user insights and design objectives.
- Identifies Pain Points: Highlights users’ challenges and frustrations, guiding the design of solutions that effectively address these issues.
- Informs Design Decisions: Ensures that design choices are user-centered and enhanced by technical skills, leading to products and services that resonate with the target audience.
- Increases Empathy: Encourages teams to put themselves in the users’ shoes, promoting a culture of empathy and user-centric thinking.
- Supports Innovation: Reveals unmet needs and opportunities, inspiring innovative ideas and approaches to problem-solving.
Why Empathy Maps Matters for your bottom line?
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Understanding and addressing customer needs leads to higher satisfaction and loyalty, resulting in repeat business.
- Improved Product Design: Empathy-driven insights help create products that better meet user needs, reducing returns and increasing sales.
- Better Customer Service: Empathetic interactions with customers lead to positive experiences, fostering trust and long-term relationships.
- Increased Innovation: By understanding customers deeply, businesses can identify unmet needs and develop innovative solutions that drive market differentiation.
- Employee Engagement: Empathy within the workplace enhances morale, productivity, and performance, cultivating a supportive environment that retains talents and reduces turnover costs..
- Positive Brand Reputation: Companies that prioritize empathy are perceived more favorably, attracting more customers and enhancing brand loyalty.
What does an Empathy Map look like?
- Title and User Information: At the top, include the title “Empathy Map” and a brief description of the user or persona being mapped.
- Quadrants Setup: Divide the map into four main quadrants labeled “Says,” “Thinks,” “Does,” and “Feels.”
- Says Quadrant: Record direct quotes or statements from the user based on interviews or surveys.
- Thinks Quadrant: Capture the user’s thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes that may not be openly expressed.
- Does Quadrant: Note the user’s actions and behaviors observed or reported in relevant contexts.
- Feels Quadrant: Identify the user’s emotional state, capturing both positive and negative feelings.
Uses Of Empathy Maps
- Deepens User Understanding: Provides a comprehensive view of users’ emotions, thoughts, and behaviors, enhancing overall understanding.
- Improves Communication: Facilitates better communication among team members by offering a clear, visual representation of user insights.
- Highlights Pain Points: Identifies specific challenges and frustrations faced by users, guiding more effective problem-solving.
- Guides Design Decisions: Ensures design choices are aligned with users’ needs and preferences, leading to more user-friendly products.
- Fosters Empathy: Encourages teams to adopt a user-centric mindset, promoting empathy and deeper connection with users.
- Inspires Innovation: Uncovers unmet needs and opportunities, driving creative and innovative solutions.
Advantages of an Empathy Map
- Deeper User Understanding: Provides a comprehensive view of users’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, enhancing overall understanding.
- Improved Communication: Serves as a visual tool that helps team members and stakeholders align on user insights and design objectives.
- Identification of Pain Points: Highlights users’ challenges and frustrations, guiding the design of solutions that effectively address these issues.
- Informed Design Decisions: Ensures that design choices are user-centered, leading to products and services that resonate with the target audience.
- Enhanced Empathy: Encourages teams to put themselves in the users’ shoes, promoting a culture of empathy and user-centric thinking.
- Increased Innovation: Reveals unmet needs and opportunities, inspiring innovative ideas and approaches to problem-solving.
- Better Customer Experience: Leads to improved user experiences by addressing real user needs and desires more effectively.
- Faster Consensus: Helps teams quickly reach a shared understanding of user needs, accelerating the decision-making process.
How is an Empathy Map structured?
It typically consists of sections for what the user says, thinks, feels, and does.
What is the purpose of an Empathy Map?
It helps teams gain deeper insights into user needs and behaviors.
How do you create an Empathy Map?
By gathering qualitative data through interviews, observations, and feedback.
Who uses Empathy Maps?
They are used by product teams, designers, marketers, and researchers.
What insights can you gain from an Empathy Map?
Understanding user motivations, pain points, and desires.
Why are Empathy Maps useful?
They foster empathy and ensure user-centered design.
When should you use an Empathy Map?
During the early stages of product development or service design.
Are Empathy Maps only for customers?
No, they can also be used for understanding employees, stakeholders, or any target group.
How do Empathy Maps benefit organizations?
By improving product development, customer satisfaction, and innovation.