10+ Exchange Traded Fund Examples to Download
Exchange-traded funds refer to the investment funds that are a collection of securities like stocks. It helps to track the underlying index such as stock index and bond index. ETF contains different investments like stocks, commodities, and bonds and sometimes a mixture of all the entities that it retains. The main reason for its attraction to the investors is that it offers low costs, tax-efficient, and stock-like features.
What are the Different Types of ETFs?
There are various types of ETFs and each is better for different performances and works. Investors use each type based on their requirements and need of the trade. The mentioned points define exchange-traded fund vs mutual fund.
- Bond ETFs: This bond might include governmental regulations or government bonds, corporate, state or local bonds. That is why many times this is also called municipal bonds. These bonds are seen to thrive in economic recessions due to investors withdrawing their capital from the stock markets and putting into bonds.
- Index ETFs: ETFs, most of the time, are index funds that represent or replicates the performance of a specific index. The index is always based on reading the stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies. An index fund tries to track the performance of index holding contents or a representative sample in its portfolio index.
- Commodity ETFs: The funds that are invested in commodities like crude oil or gas or gold are commodity ETFs.
- Currency ETFs: Funds used in forex trading or for tradings of foreign exchange or in foreign currencies.
- Industry ETFs- The funds used or are to be invested in a particular industry that you have taken track of before investments, such industries can be technology, banking or other giant gas or oil industries.
- Inverse ETFs- This sort of fund tries to earn from shorting stocks. Shorting refers to the selling, a decline in value and buying the stock again but now at a lower price.
How Mutual Funds is Different from Exchange-traded Funds?
- Mutual fund refers to the invested capital of different individuals whose money is pooled and invested in diversified securities. Whereas exchange-traded funds are the index funds that track the index and also listed and traded in the financial market.
- Holdings are disclosed in mutual funds quarterly whereas in ETFs there is daily holding disclosure.
- Trading or buying and selling shares in mutual funds proceeded from the fund house. Opposite to it, trading in ETFs is a process between the investors at the secondary market.
- Funds are traded on the NAV in the mutual funds. Contrary to it ETFs are traded on quoted price.
- Mutual funds taxes are higher and ETFs are more tax-efficient.
- A mutual fund doesn’t pay any brokerage charge bur ETFs does pay.
- ETFs cannot be traded or sold in a fraction but mutual funds can be issued in a fraction.
- Managers are appointed to manage the functioning of the mutual funds. But in ETFs passive management is used to handle the specific index they deal with.
10+ Exchange Traded Fund Examples
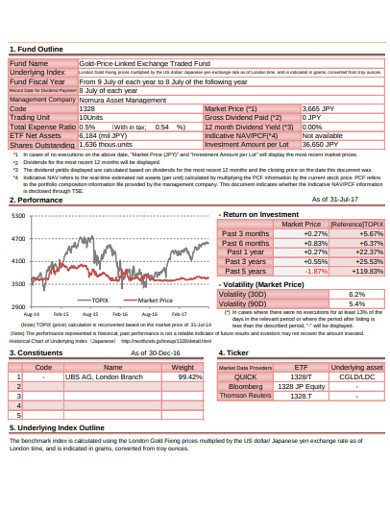
1. Sample Exchange Traded Fund Example
If you are tired of investing in the mutual funds then exchange-traded funds is the best option market for you to try new trade. This traded index fund opposes the techniques and features that mutual fund does and offers passive management of the stocks. You can get more ideas on the trading tool by having a look at this example. The example template defines various aspects of the ETF process and frames it precisely. So have a look at it and define your prepare your ETF plan today!
2. Product Exchange-Traded Fund Example
If you are hoping to make capital funding on different stocks but don’t want to choose mutual funding option try ETFs once. You can also refer to the mentioned example template here to understand and plan your ETF. Because the structure the template follows can help you to gain the knowledge of the ETF processing and ideas to prepare the plan to strategize it properly. So, check the template out today and if it can communicate properly grab it today!