60+ Health Disparities Examples
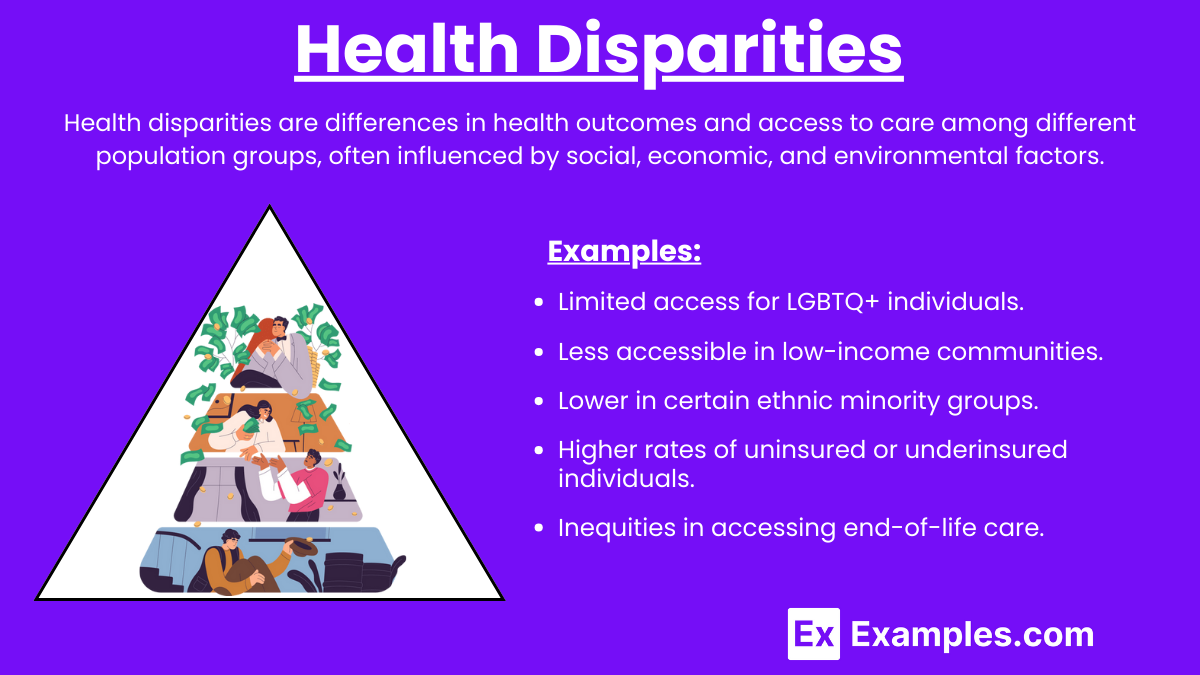
Health disparities are differences in health outcomes and access to healthcare among various population groups, often influenced by socioeconomic factors.
What Are Health Disparities?
Health disparities are differences in health outcomes among different populations, often due to socioeconomic factors. A Disparity Impact Statement highlights these inequities, while a Health Thesis Statement addresses their causes and solutions. Effective Health Communication is essential to mitigate these disparities.
Examples of Health Disparities
- Access to Healthcare: Rural areas often have fewer healthcare facilities compared to urban areas.
- Infant Mortality Rates: Higher in African American communities than in white communities.
- Life Expectancy: Shorter in low-income populations compared to higher-income groups.
- Chronic Diseases: Higher rates of diabetes in Hispanic and Native American populations.
- Mental Health Services: Limited access for LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Cancer Screening: Lower rates of breast cancer screening in uninsured women.
- Obesity: Higher prevalence in low-income neighborhoods.
- Vaccination Rates: Lower in certain ethnic minority groups.
- Heart Disease: Higher rates in African American men compared to white men.
- Substance Abuse Treatment: Less accessible in low-income communities.
Examples of Health Disparities in Rural Areas
- Limited Healthcare Facilities: Fewer hospitals and clinics compared to urban areas.
- Access to Specialists: Less availability of specialized medical care.
- Emergency Services: Longer response times for emergency medical services.
- Chronic Disease Management: Higher rates of unmanaged chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.Mental Health Services: Scarcity of mental health professionals and facilities.
- Preventive Care: Lower rates of screenings and vaccinations.
- Health Education: Limited access to health education and resources.
- Transportation: Difficulties in accessing healthcare due to long distances and lack of public transportation.
- Health Insurance: Higher rates of uninsured or underinsured individuals.
- Substance Abuse: Increased rates of substance abuse with fewer treatment options.
Examples of Health Disparities in the Elderly
- Medication Management: Difficulty in accessing and affording necessary medications.
- Mobility Issues: Limited access to physical therapy and mobility aids.
- Nutrition: Higher risk of malnutrition due to financial constraints or limited availability of healthy food.
- Social Isolation: Increased risk of loneliness and mental health issues.
- Chronic Pain: Less effective pain management and treatment options.
- Dental Care: Limited access to dental services and higher rates of untreated dental issues.
- Vision and Hearing Care: Reduced access to eye and hearing examinations and corrective devices.
- In-Home Care: Limited availability of affordable in-home health care services.
- Palliative and Hospice Care: Inequities in accessing end-of-life care.
- Technology Access: Challenges in using telehealth services due to lack of familiarity with technology.
Examples of Health Disparities in Minority
- Language Barriers: Difficulty accessing healthcare due to lack of language services.
- Cultural Competence: Healthcare providers may lack understanding of cultural differences affecting treatment.
- Maternal Health: Higher rates of complications and mortality in pregnancy among African American and Native American women.
- HIV/AIDS: Disproportionately higher infection rates in minority populations.
- Asthma: Higher prevalence and severity in African American and Hispanic children.
- Mental Health Stigma: Greater stigma around mental health issues, leading to underutilization of mental health services.
- Environmental Health: Greater exposure to pollution and environmental hazards in minority communities.
- Hypertension: Higher rates and poorer management in African American and Latino populations.
- Diabetes: Increased prevalence and complications in Hispanic, African American, and Native American groups.
- Access to Healthy Food: Limited availability of fresh, affordable food in predominantly minority neighborhoods.
Examples of Health Disparities in Global
- Access to Clean Water: Many developing countries struggle with access to safe drinking water.
- Vaccination Rates: Lower vaccination rates in low-income countries, leading to preventable diseases.
- Maternal Mortality: Higher maternal mortality rates in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
- Malnutrition: Widespread malnutrition in parts of Africa and Asia.
- Infectious Diseases: Higher prevalence of diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS in developing countries.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Poor healthcare infrastructure in rural and low-income regions.
- Chronic Diseases: Rising rates of diabetes and heart disease in low- and middle-income countries.
- Child Mortality: Higher child mortality rates in poorer nations.
- Mental Health Services: Limited access to mental health care in many parts of the world.
- Health Education: Lack of health education and preventive care awareness in many global regions.
Potential Solutions for Health Disparities
1. Increase Access to Healthcare
- Expand Health Insurance Coverage: Ensure that everyone has access to affordable health insurance.
- Mobile Clinics: Use mobile clinics to reach remote and underserved areas.
- Telehealth Services: Promote the use of telehealth to provide healthcare services to people in rural and underserved areas.
2. Improve Health Education
- Community Health Programs: Implement health education programs in communities to raise awareness about preventive care and healthy lifestyles.
- School Health Education: Include comprehensive health education in school curriculums to teach children about nutrition, exercise, and disease prevention.
3. Address Social Determinants of Health
- Improve Housing: Ensure safe and affordable housing for all.
- Increase Income Support: Provide financial support to low-income families to reduce economic stress.
- Access to Healthy Foods: Promote access to affordable and nutritious foods in all communities.
4. Enhance Cultural Competence in Healthcare
- Cultural Training: Provide cultural competence training for healthcare providers to improve communication and trust with patients from diverse backgrounds.
- Diverse Healthcare Workforce: Increase diversity in the healthcare workforce to better reflect and understand the communities they serve.
5. Strengthen Community Partnerships
- Community Involvement: Engage community leaders and organizations in health planning and decision-making.
- Local Health Initiatives: Support local health initiatives that address specific community needs.
6. Implement Policy Changes
- Health Equity Policies: Advocate for policies that promote health equity and reduce disparities.
- Funding for Disparity Reduction Programs: Secure funding for programs specifically designed to address health disparities.
7. Improve Data Collection and Research
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Collect detailed data on health outcomes across different population groups to identify and address disparities.
- Research on Health Disparities: Fund research focused on understanding and finding solutions for health disparities.
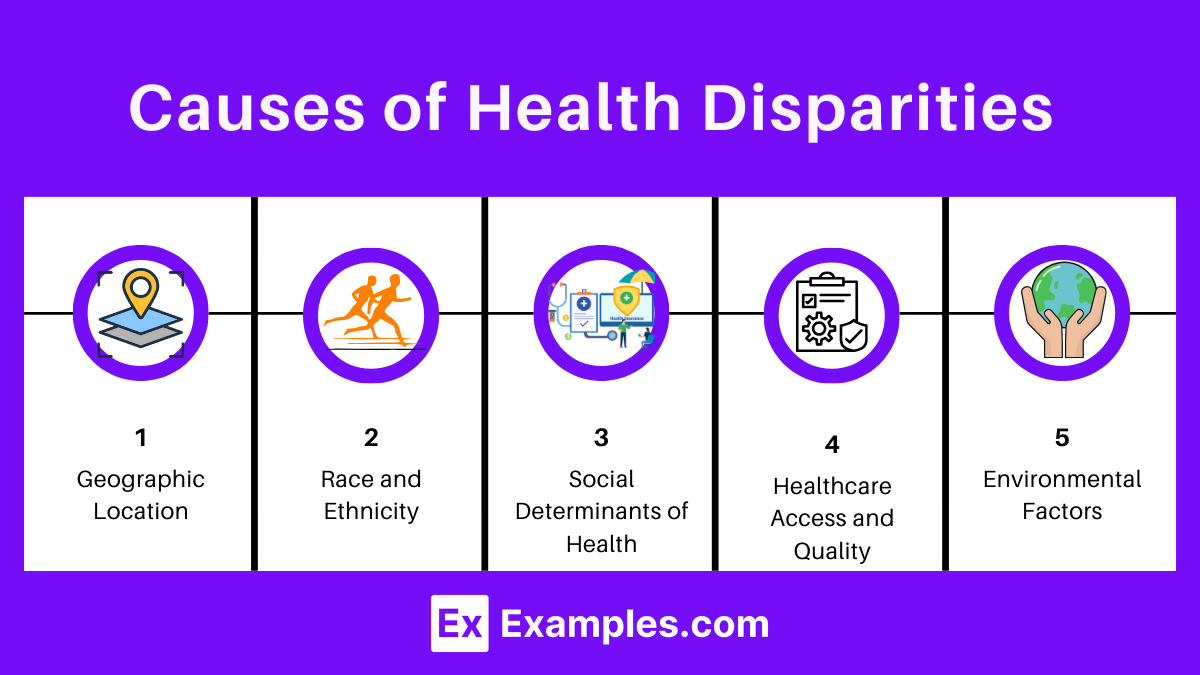
Causes of Health Disparities
1. Socioeconomic Status
- Income: Lower-income individuals often have limited access to healthcare services and healthy lifestyle choices.
- Education: Limited educational opportunities can lead to a lack of health knowledge and poor health behaviors.
- Employment: Unemployment or jobs without health benefits can restrict access to healthcare and preventive services.
2. Geographic Location
- Rural Areas: People living in rural areas may face barriers such as fewer healthcare facilities, longer travel distances to access care, and limited healthcare professionals.
- Urban Areas: In some urban areas, especially underserved neighborhoods, there can be a lack of healthcare resources and higher exposure to environmental health risks.
3. Race and Ethnicity
- Discrimination: Systemic racism and discrimination can lead to unequal treatment in healthcare settings.
- Cultural Barriers: Language differences and cultural beliefs can hinder effective communication and access to care.
- Genetic Factors: Some health conditions may be more prevalent in certain racial or ethnic groups due to genetic predispositions.
4. Social Determinants of Health
- Housing: Poor housing conditions, such as overcrowding and exposure to pollutants, can negatively impact health.
- Food Security: Lack of access to affordable, nutritious food can lead to poor health outcomes.
- Education and Literacy: Lower levels of education and health literacy can result in a lack of understanding of health information and how to navigate the healthcare system.
5. Healthcare Access and Quality
- Insurance Coverage: Lack of health insurance or underinsurance can limit access to necessary medical care.
- Healthcare Facilities: Inequitable distribution of healthcare facilities can create access issues for certain populations.
- Provider Availability: Shortages of healthcare providers, particularly in underserved areas, can lead to delays in receiving care.
6. Behavioral Factors
- Health Behaviors: Differences in lifestyle choices, such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, can contribute to health disparities.
- Stress: Chronic stress, often more prevalent in disadvantaged communities, can have significant negative health effects.
7. Environmental Factors
- Exposure to Pollutants: Communities located near industrial areas or with poor environmental regulations may face higher exposure to harmful pollutants.
- Climate and Weather: Extreme weather conditions and climate-related events can disproportionately affect vulnerable populations.
8. Genetics and Biology
- Inherited Conditions: Certain genetic conditions can be more common in specific population groups.
- Biological Differences: Biological factors, such as age and sex, can influence health outcomes and susceptibility to diseases.
Types of Health Disparities
1. Racial and Ethnic Disparities
- Differences in health outcomes and healthcare access among racial and ethnic groups.
- Examples: Higher rates of diabetes in African Americans, higher rates of asthma in Hispanic communities.
2. Socioeconomic Disparities
- Differences in health based on income, education, and occupation.
- Examples: Low-income individuals having higher rates of chronic diseases, less access to preventive care for those with lower educational attainment.
3. Geographic Disparities
- Differences in health outcomes based on where people live.
- Examples: Rural areas having less access to hospitals and specialists, urban areas with high pollution affecting respiratory health.
4. Gender Disparities
- Differences in health outcomes between men and women.
- Examples: Women having higher rates of certain cancers (like breast cancer), men having higher rates of heart disease.
5. Age Disparities
- Differences in health based on age groups.
- Examples: Older adults experiencing more chronic conditions, children having higher rates of certain infectious diseases.
6. Disability Disparities
- Differences in health outcomes between those with and without disabilities.
- Examples: People with disabilities facing higher rates of obesity and depression.
7. LGBTQ+ Disparities
- Differences in health outcomes among LGBTQ+ individuals compared to the general population.
- Examples: Higher rates of mental health issues and HIV/AIDS in LGBTQ+ communities.
8. Insurance Status Disparities
- Differences in health outcomes based on whether individuals have health insurance.
- Examples: Uninsured individuals having less access to preventive services and higher mortality rates.
Health Disparities Synonym
- Health inequalities
- Health inequities
- Health differences
- Health gaps
- Health imbalances
- Health divides
- Health discrepancies
Health Disparities vs Health Inequities
| Aspect | Health Disparities | Health Inequities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Differences in health outcomes among different population groups. | Unjust and avoidable differences in health outcomes among groups. |
| Focus | Broad differences, can be measured. | Ethical and fairness aspects of health differences. |
| Examples | Higher rates of diabetes in one ethnic group compared to another. | Lack of access to healthcare in low-income communities. |
| Causes | Can be due to genetics, behavior, environment, etc. | Rooted in social, economic, and environmental disadvantages. |
| Implications | Identifies where differences exist. | Highlights the need for systemic change to address unfairness. |
| Interventions | Targeted health programs, increased access to healthcare. | Policy changes, addressing social determinants of health. |
| Measurement | Statistical analysis of health data. | Examination of policies, practices, and social factors. |
Reasons for Health Disparities
- Economic Status: People with less money often have limited access to healthcare, healthy food, and safe housing.
- Education: Lower education levels are linked to poorer health outcomes because education influences job opportunities and health knowledge.
- Healthcare Access: Not having nearby healthcare facilities, insurance, or culturally competent care can prevent people from receiving proper health services.
- Neighborhood and Physical Environment: Living in areas with pollution, unsafe housing, and lack of parks or grocery stores can lead to health problems.
- Racial and Ethnic Background: Discrimination and systemic racism can lead to worse health outcomes for certain racial and ethnic groups.
- Gender: Health risks can vary between genders due to biological differences, social roles, and unequal power relations.
- Language Barriers: Non-native speakers may struggle to get good healthcare if they can’t communicate effectively with providers.
Addressing Health Disparities
- Improve Access to Healthcare: Make healthcare more available and affordable for everyone. This can include more clinics in underserved areas and better health insurance options.
- Educate the Community: Teach people about healthy habits and preventive care. Schools and community centers can offer classes on nutrition, exercise, and managing chronic diseases.
- Promote Fair Employment: Support policies that provide good jobs and fair pay to everyone. Healthy work environments and fair wages can greatly improve a person’s health.
- Enhance Local Environments: Make neighborhoods safer and more livable. This can involve cleaning up pollution, creating parks, and ensuring that everyone has access to healthy food.
- Support Research and Data Collection: Study health disparities and understand their causes. This can help tailor solutions to the specific needs of different communities.
- Cultural Competence in Healthcare: Train healthcare providers to understand and respect cultural differences. This helps in providing care that meets the unique needs of each patient.
- Advocate for Policy Changes: Support laws and policies that aim to reduce inequalities. This includes efforts to reduce poverty, discrimination, and improve education.
Maternal Health Disparities
1. Racial and Ethnic Disparities
- African American Women: Higher rates of maternal mortality and complications during pregnancy.
- Hispanic Women: Higher rates of gestational diabetes and lower access to prenatal care.
2. Socioeconomic Disparities
- Low-Income Women: Less access to quality prenatal and postnatal care, higher risk of complications.
- Uninsured Women: Limited access to necessary healthcare services during pregnancy.
3. Geographic Disparities
- Rural Areas: Fewer healthcare facilities and specialists, longer travel times to receive care.
- Urban Underserved Areas: Limited access to quality maternity care and higher stress environments.
4. Age Disparities
- Teen Mothers: Higher risk of complications and lower access to prenatal care.
- Older Mothers: Increased risk of complications such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
5. Access to Healthcare
- Lack of Providers: Shortage of obstetricians and midwives in some areas.
- Insurance Issues: High costs and lack of coverage can limit access to care.
6. Behavioral Factors
- Health Behaviors: Smoking, alcohol use, and poor nutrition can negatively impact maternal health.
- Mental Health: Stress and mental health issues can lead to poor pregnancy outcomes.
Tips for Health Disparities
- Increase Access to Care: Ensure everyone can access affordable, quality healthcare.
- Promote Health Education: Educate communities about preventive care and healthy lifestyles.
- Support Community Programs: Fund local health initiatives targeting underserved populations.
- Enhance Cultural Competence: Train healthcare providers in cultural awareness and sensitivity.
- Expand Insurance Coverage: Advocate for policies that provide comprehensive health insurance for all.
- Improve Data Collection: Collect and use data to identify and address disparities.
- Engage Local Leaders: Involve community leaders in health planning and decision-making.
What causes health disparities?
Health disparities are caused by factors such as socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, geographic location, and access to healthcare.
Who is affected by health disparities?
Health disparities affect racial and ethnic minorities, low-income individuals, rural residents, and other underserved groups.
How can health disparities be reduced?
Health disparities can be reduced by increasing access to healthcare, improving health education, addressing social determinants of health, and implementing equitable policies.
What role does education play in health disparities?
Education impacts health disparities by influencing health knowledge, behaviors, and access to resources for better health outcomes.
How does socioeconomic status affect health disparities?
Lower socioeconomic status often leads to limited access to healthcare, nutritious food, and safe living conditions, contributing to poorer health outcomes.
What are social determinants of health?
Social determinants of health include factors like income, education, employment, housing, and access to healthcare that influence health outcomes.
Can health disparities be completely eliminated?
While it may be challenging to completely eliminate health disparities, significant improvements can be made through targeted interventions and policy changes.
How does geographic location affect health disparities?
Geographic location impacts health disparities by limiting access to healthcare services, especially in rural and underserved urban areas.
What strategies can healthcare providers use to address health disparities?
Healthcare providers can use cultural competence training, provide language services, and engage with community leaders to address health disparities.
How does policy influence health disparities?
Policy influences health disparities by shaping access to healthcare, funding for health programs, and addressing social determinants of health.
60+ Health Disparities Examples
Health disparities are differences in health outcomes and access to healthcare among various population groups, often influenced by socioeconomic factors.
What Are Health Disparities?
Health disparities are differences in health outcomes among different populations, often due to socioeconomic factors. A Disparity Impact Statement highlights these inequities, while a Health Thesis Statement addresses their causes and solutions. Effective Health Communication is essential to mitigate these disparities.
Examples of Health Disparities
Access to Healthcare: Rural areas often have fewer healthcare facilities compared to urban areas.
Infant Mortality Rates: Higher in African American communities than in white communities.
Life Expectancy: Shorter in low-income populations compared to higher-income groups.
Chronic Diseases: Higher rates of diabetes in Hispanic and Native American populations.
Mental Health Services: Limited access for LGBTQ+ individuals.
Cancer Screening: Lower rates of breast cancer screening in uninsured women.
Obesity: Higher prevalence in low-income neighborhoods.
Vaccination Rates: Lower in certain ethnic minority groups.
Heart Disease: Higher rates in African American men compared to white men.
Substance Abuse Treatment: Less accessible in low-income communities.
Examples of Health Disparities in Rural Areas
Limited Healthcare Facilities: Fewer hospitals and clinics compared to urban areas.
Access to Specialists: Less availability of specialized medical care.
Emergency Services: Longer response times for emergency medical services.
Chronic Disease Management: Higher rates of unmanaged chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.Mental Health Services: Scarcity of mental health professionals and facilities.
Preventive Care: Lower rates of screenings and vaccinations.
Health Education: Limited access to health education and resources.
Transportation: Difficulties in accessing healthcare due to long distances and lack of public transportation.
Health Insurance: Higher rates of uninsured or underinsured individuals.
Substance Abuse: Increased rates of substance abuse with fewer treatment options.
Examples of Health Disparities in the Elderly
Medication Management: Difficulty in accessing and affording necessary medications.
Mobility Issues: Limited access to physical therapy and mobility aids.
Nutrition: Higher risk of malnutrition due to financial constraints or limited availability of healthy food.
Social Isolation: Increased risk of loneliness and mental health issues.
Chronic Pain: Less effective pain management and treatment options.
Dental Care: Limited access to dental services and higher rates of untreated dental issues.
Vision and Hearing Care: Reduced access to eye and hearing examinations and corrective devices.
In-Home Care: Limited availability of affordable in-home health care services.
Palliative and Hospice Care: Inequities in accessing end-of-life care.
Technology Access: Challenges in using telehealth services due to lack of familiarity with technology.
Examples of Health Disparities in Minority
Language Barriers: Difficulty accessing healthcare due to lack of language services.
Cultural Competence: Healthcare providers may lack understanding of cultural differences affecting treatment.
Maternal Health: Higher rates of complications and mortality in pregnancy among African American and Native American women.
HIV/AIDS: Disproportionately higher infection rates in minority populations.
Asthma: Higher prevalence and severity in African American and Hispanic children.
Mental Health Stigma: Greater stigma around mental health issues, leading to underutilization of mental health services.
Environmental Health: Greater exposure to pollution and environmental hazards in minority communities.
Hypertension: Higher rates and poorer management in African American and Latino populations.
Diabetes: Increased prevalence and complications in Hispanic, African American, and Native American groups.
Access to Healthy Food: Limited availability of fresh, affordable food in predominantly minority neighborhoods.
Examples of Health Disparities in Global
Access to Clean Water: Many developing countries struggle with access to safe drinking water.
Vaccination Rates: Lower vaccination rates in low-income countries, leading to preventable diseases.
Maternal Mortality: Higher maternal mortality rates in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
Malnutrition: Widespread malnutrition in parts of Africa and Asia.
Infectious Diseases: Higher prevalence of diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS in developing countries.
Healthcare Infrastructure: Poor healthcare infrastructure in rural and low-income regions.
Chronic Diseases: Rising rates of diabetes and heart disease in low- and middle-income countries.
Child Mortality: Higher child mortality rates in poorer nations.
Mental Health Services: Limited access to mental health care in many parts of the world.
Health Education: Lack of health education and preventive care awareness in many global regions.
Potential Solutions for Health Disparities
1. Increase Access to Healthcare
Expand Health Insurance Coverage: Ensure that everyone has access to affordable health insurance.
Mobile Clinics: Use mobile clinics to reach remote and underserved areas.
Telehealth Services: Promote the use of telehealth to provide healthcare services to people in rural and underserved areas.
2. Improve Health Education
Community Health Programs: Implement health education programs in communities to raise awareness about preventive care and healthy lifestyles.
School Health Education: Include comprehensive health education in school curriculums to teach children about nutrition, exercise, and disease prevention.
3. Address Social Determinants of Health
Improve Housing: Ensure safe and affordable housing for all.
Increase Income Support: Provide financial support to low-income families to reduce economic stress.
Access to Healthy Foods: Promote access to affordable and nutritious foods in all communities.
4. Enhance Cultural Competence in Healthcare
Cultural Training: Provide cultural competence training for healthcare providers to improve communication and trust with patients from diverse backgrounds.
Diverse Healthcare Workforce: Increase diversity in the healthcare workforce to better reflect and understand the communities they serve.
5. Strengthen Community Partnerships
Community Involvement: Engage community leaders and organizations in health planning and decision-making.
Local Health Initiatives: Support local health initiatives that address specific community needs.
6. Implement Policy Changes
Health Equity Policies: Advocate for policies that promote health equity and reduce disparities.
Funding for Disparity Reduction Programs: Secure funding for programs specifically designed to address health disparities.
7. Improve Data Collection and Research
Comprehensive Data Collection: Collect detailed data on health outcomes across different population groups to identify and address disparities.
Research on Health Disparities: Fund research focused on understanding and finding solutions for health disparities.
Causes of Health Disparities
1. Socioeconomic Status
Income: Lower-income individuals often have limited access to healthcare services and healthy lifestyle choices.
Education: Limited educational opportunities can lead to a lack of health knowledge and poor health behaviors.
Employment: Unemployment or jobs without health benefits can restrict access to healthcare and preventive services.
2. Geographic Location
Rural Areas: People living in rural areas may face barriers such as fewer healthcare facilities, longer travel distances to access care, and limited healthcare professionals.
Urban Areas: In some urban areas, especially underserved neighborhoods, there can be a lack of healthcare resources and higher exposure to environmental health risks.
3. Race and Ethnicity
Discrimination: Systemic racism and discrimination can lead to unequal treatment in healthcare settings.
Cultural Barriers: Language differences and cultural beliefs can hinder effective communication and access to care.
Genetic Factors: Some health conditions may be more prevalent in certain racial or ethnic groups due to genetic predispositions.
4. Social Determinants of Health
Housing: Poor housing conditions, such as overcrowding and exposure to pollutants, can negatively impact health.
Food Security: Lack of access to affordable, nutritious food can lead to poor health outcomes.
Education and Literacy: Lower levels of education and health literacy can result in a lack of understanding of health information and how to navigate the healthcare system.
5. Healthcare Access and Quality
Insurance Coverage: Lack of health insurance or underinsurance can limit access to necessary medical care.
Healthcare Facilities: Inequitable distribution of healthcare facilities can create access issues for certain populations.
Provider Availability: Shortages of healthcare providers, particularly in underserved areas, can lead to delays in receiving care.
6. Behavioral Factors
Health Behaviors: Differences in lifestyle choices, such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, can contribute to health disparities.
Stress: Chronic stress, often more prevalent in disadvantaged communities, can have significant negative health effects.
7. Environmental Factors
Exposure to Pollutants: Communities located near industrial areas or with poor environmental regulations may face higher exposure to harmful pollutants.
Climate and Weather: Extreme weather conditions and climate-related events can disproportionately affect vulnerable populations.
8. Genetics and Biology
Inherited Conditions: Certain genetic conditions can be more common in specific population groups.
Biological Differences: Biological factors, such as age and sex, can influence health outcomes and susceptibility to diseases.
Types of Health Disparities
1. Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Differences in health outcomes and healthcare access among racial and ethnic groups.
Examples: Higher rates of diabetes in African Americans, higher rates of asthma in Hispanic communities.
2. Socioeconomic Disparities
Differences in health based on income, education, and occupation.
Examples: Low-income individuals having higher rates of chronic diseases, less access to preventive care for those with lower educational attainment.
3. Geographic Disparities
Differences in health outcomes based on where people live.
Examples: Rural areas having less access to hospitals and specialists, urban areas with high pollution affecting respiratory health.
4. Gender Disparities
Differences in health outcomes between men and women.
Examples: Women having higher rates of certain cancers (like breast cancer), men having higher rates of heart disease.
5. Age Disparities
Differences in health based on age groups.
Examples: Older adults experiencing more chronic conditions, children having higher rates of certain infectious diseases.
6. Disability Disparities
Differences in health outcomes between those with and without disabilities.
Examples: People with disabilities facing higher rates of obesity and depression.
7. LGBTQ+ Disparities
Differences in health outcomes among LGBTQ+ individuals compared to the general population.
Examples: Higher rates of mental health issues and HIV/AIDS in LGBTQ+ communities.
8. Insurance Status Disparities
Differences in health outcomes based on whether individuals have health insurance.
Examples: Uninsured individuals having less access to preventive services and higher mortality rates.
Health Disparities Synonym
Health inequalities
Health inequities
Health differences
Health gaps
Health imbalances
Health divides
Health discrepancies
Health Disparities vs Health Inequities
Aspect | Health Disparities | Health Inequities |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Differences in health outcomes among different population groups. | Unjust and avoidable differences in health outcomes among groups. |
Focus | Broad differences, can be measured. | Ethical and fairness aspects of health differences. |
Examples | Higher rates of diabetes in one ethnic group compared to another. | Lack of access to healthcare in low-income communities. |
Causes | Can be due to genetics, behavior, environment, etc. | Rooted in social, economic, and environmental disadvantages. |
Implications | Identifies where differences exist. | Highlights the need for systemic change to address unfairness. |
Interventions | Targeted health programs, increased access to healthcare. | Policy changes, addressing social determinants of health. |
Measurement | Statistical analysis of health data. | Examination of policies, practices, and social factors. |
Reasons for Health Disparities
Economic Status: People with less money often have limited access to healthcare, healthy food, and safe housing.
Education: Lower education levels are linked to poorer health outcomes because education influences job opportunities and health knowledge.
Healthcare Access: Not having nearby healthcare facilities, insurance, or culturally competent care can prevent people from receiving proper health services.
Neighborhood and Physical Environment: Living in areas with pollution, unsafe housing, and lack of parks or grocery stores can lead to health problems.
Racial and Ethnic Background: Discrimination and systemic racism can lead to worse health outcomes for certain racial and ethnic groups.
Gender: Health risks can vary between genders due to biological differences, social roles, and unequal power relations.
Language Barriers: Non-native speakers may struggle to get good healthcare if they can’t communicate effectively with providers.
Addressing Health Disparities
Improve Access to Healthcare: Make healthcare more available and affordable for everyone. This can include more clinics in underserved areas and better health insurance options.
Educate the Community: Teach people about healthy habits and preventive care. Schools and community centers can offer classes on nutrition, exercise, and managing chronic diseases.
Promote Fair Employment: Support policies that provide good jobs and fair pay to everyone. Healthy work environments and fair wages can greatly improve a person’s health.
Enhance Local Environments: Make neighborhoods safer and more livable. This can involve cleaning up pollution, creating parks, and ensuring that everyone has access to healthy food.
Support Research and Data Collection: Study health disparities and understand their causes. This can help tailor solutions to the specific needs of different communities.
Cultural Competence in Healthcare: Train healthcare providers to understand and respect cultural differences. This helps in providing care that meets the unique needs of each patient.
Advocate for Policy Changes: Support laws and policies that aim to reduce inequalities. This includes efforts to reduce poverty, discrimination, and improve education.
Maternal Health Disparities
1. Racial and Ethnic Disparities
African American Women: Higher rates of maternal mortality and complications during pregnancy.
Hispanic Women: Higher rates of gestational diabetes and lower access to prenatal care.
2. Socioeconomic Disparities
Low-Income Women: Less access to quality prenatal and postnatal care, higher risk of complications.
Uninsured Women: Limited access to necessary healthcare services during pregnancy.
3. Geographic Disparities
Rural Areas: Fewer healthcare facilities and specialists, longer travel times to receive care.
Urban Underserved Areas: Limited access to quality maternity care and higher stress environments.
4. Age Disparities
Teen Mothers: Higher risk of complications and lower access to prenatal care.
Older Mothers: Increased risk of complications such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
5. Access to Healthcare
Lack of Providers: Shortage of obstetricians and midwives in some areas.
Insurance Issues: High costs and lack of coverage can limit access to care.
6. Behavioral Factors
Health Behaviors: Smoking, alcohol use, and poor nutrition can negatively impact maternal health.
Mental Health: Stress and mental health issues can lead to poor pregnancy outcomes.
Tips for Health Disparities
Increase Access to Care: Ensure everyone can access affordable, quality healthcare.
Promote Health Education: Educate communities about preventive care and healthy lifestyles.
Support Community Programs: Fund local health initiatives targeting underserved populations.
Enhance Cultural Competence: Train healthcare providers in cultural awareness and sensitivity.
Expand Insurance Coverage: Advocate for policies that provide comprehensive health insurance for all.
Improve Data Collection: Collect and use data to identify and address disparities.
Engage Local Leaders: Involve community leaders in health planning and decision-making.
What causes health disparities?
Health disparities are caused by factors such as socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, geographic location, and access to healthcare.
Who is affected by health disparities?
Health disparities affect racial and ethnic minorities, low-income individuals, rural residents, and other underserved groups.
How can health disparities be reduced?
Health disparities can be reduced by increasing access to healthcare, improving health education, addressing social determinants of health, and implementing equitable policies.
What role does education play in health disparities?
Education impacts health disparities by influencing health knowledge, behaviors, and access to resources for better health outcomes.
How does socioeconomic status affect health disparities?
Lower socioeconomic status often leads to limited access to healthcare, nutritious food, and safe living conditions, contributing to poorer health outcomes.
What are social determinants of health?
Social determinants of health include factors like income, education, employment, housing, and access to healthcare that influence health outcomes.
Can health disparities be completely eliminated?
While it may be challenging to completely eliminate health disparities, significant improvements can be made through targeted interventions and policy changes.
How does geographic location affect health disparities?
Geographic location impacts health disparities by limiting access to healthcare services, especially in rural and underserved urban areas.
What strategies can healthcare providers use to address health disparities?
Healthcare providers can use cultural competence training, provide language services, and engage with community leaders to address health disparities.
How does policy influence health disparities?
Policy influences health disparities by shaping access to healthcare, funding for health programs, and addressing social determinants of health.


