Information Examples
Information plays a crucial role in our daily lives, shaping our decisions and actions. It encompasses data, facts, knowledge, and news communicated or received. Accurate and reliable information helps individuals and organizations make informed choices. In today’s digital age, the accessibility and flow of information have transformed, impacting various aspects of society, including education, business, and personal interactions. Understanding the nature, sources, and impact of information empowers individuals to navigate the vast sea of data effectively and make sound decisions. This article delves into the significance of information, its types, sources, and the importance of information literacy in the modern world.
Definition
Information refers to data that has been processed and organized in a meaningful way. It includes facts, figures, and knowledge communicated or received about a particular subject. Information helps individuals understand concepts, make decisions, and solve problems. In essence, information is data that has been given context and relevance, making it useful for communication and decision-making.
Information Examples
For Students
- Information about the solar system helps students understand the planets, moons, and other celestial bodies.
- A math textbook provides information on solving algebraic equations.
- Information from a science experiment allows students to learn about chemical reactions.
- Historical documents provide information about significant events and figures in history.
- Information from research articles aids students in writing reports and essays.
Sentence
- The brochure contains information about the new community center programs.
- The doctor gave the patient important information about managing their condition.
- The librarian provided information on how to find specific books in the library.
- The tour guide shared fascinating information about the city’s landmarks.
- The website offers information on how to apply for scholarships.
In Computer
- A database stores information about customers, including names, addresses, and purchase history.
- A search engine retrieves information from the internet based on user queries.
- Information from a GPS device provides directions to a specified location.
- An email application organizes information such as messages, contacts, and schedules.
- A digital calendar stores and displays information about upcoming events and appointments.
In Real Life
- Traffic signs provide information about road rules and conditions.
- Nutrition labels on food packaging give information about the ingredients and nutritional value.
- News reports offer information about current events and issues.
- Instruction manuals provide information on how to assemble and use products.
- Public transportation schedules offer information on bus and train times and routes.
In Business
- Financial reports provide information about a company’s earnings, expenses, and profitability.
- Customer feedback gives businesses information about product satisfaction and areas for improvement.
- Market analysis reports offer information on industry trends and competitive landscape.
- Sales data provides information on the performance of different products and services.
- Employee performance reviews provide information on individual and team achievements and areas for growth.
Types of Information
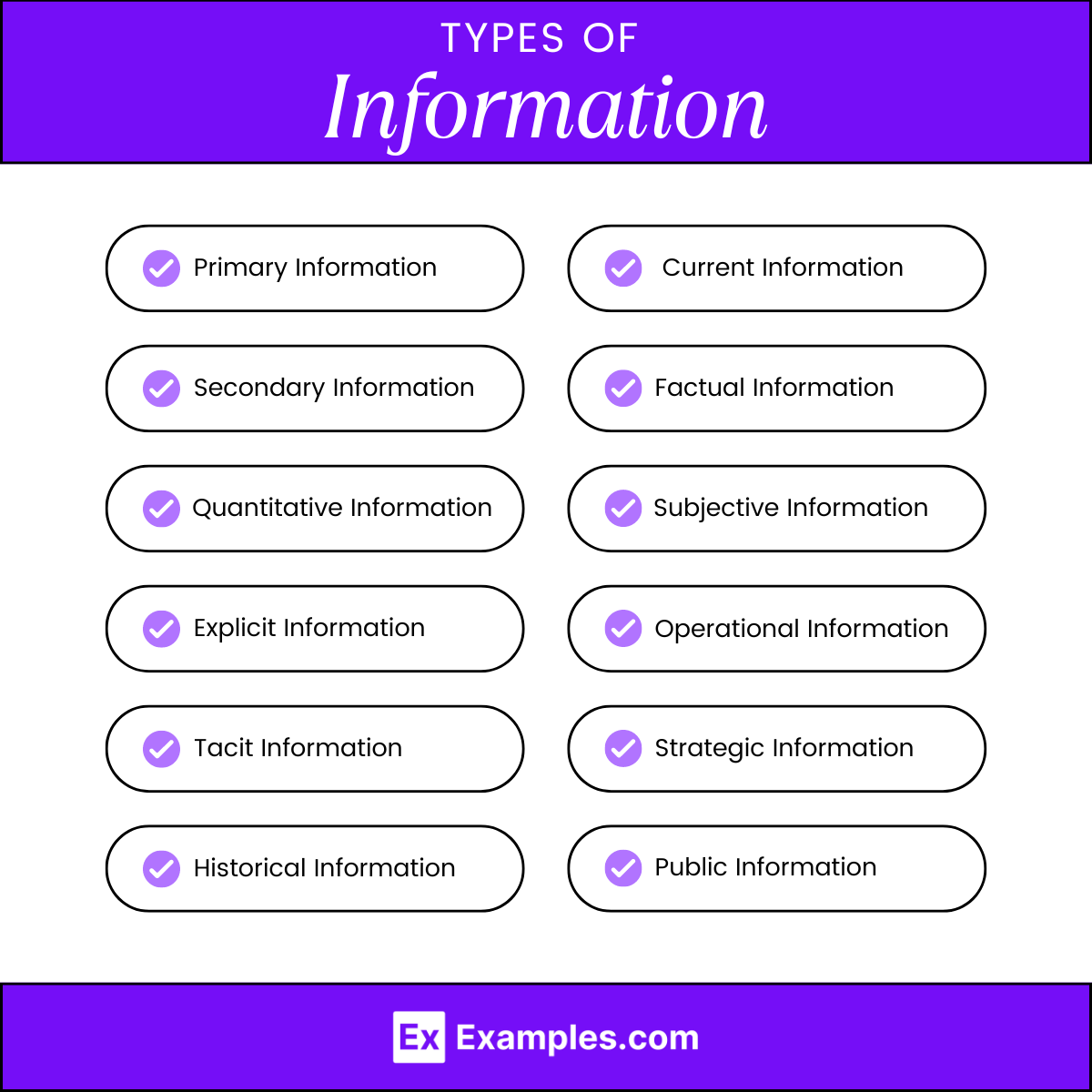
Information can be categorized in various ways based on its nature, source, and use. Here are several key types of information:
1. Primary Information
- Definition: Original data collected firsthand for a specific purpose.
- Examples:
- Survey responses
- Interviews
- Experiments
2. Secondary Information
- Definition: Information that has been collected, processed, and published by others.
- Examples:
- Research articles
- Books
- Reviews
3. Quantitative Information
- Definition: Numerical data that can be measured and quantified.
- Examples:
- Sales figures
- Statistics
- Financial reports
4. Qualitative Information
- Definition: Descriptive data that is not numerical.
- Examples:
- Interview transcripts
- Observational notes
- Personal narratives
5. Explicit Information
- Definition: Information that is clearly articulated and easily documented.
- Examples:
- Manuals
- Policies
- Textbooks
6. Tacit Information
- Definition: Knowledge gained through personal experience and context, often hard to formalize.
- Examples:
- Skills
- Intuition
- Expertise
7. Historical Information
- Definition: Data and records about past events.
- Examples:
- Archives
- Historical documents
- Chronologies
8. Current Information
- Definition: Up-to-date data relevant to present circumstances.
- Examples:
- News reports
- Market trends
- Current events
9. Factual Information
- Definition: Objective data that can be verified and proven.
- Examples:
- Scientific data
- Legal documents
- Statistical data
10. Subjective Information
- Definition: Data based on personal opinions, interpretations, feelings, or beliefs.
- Examples:
- Reviews
- Testimonials
- Editorials
11. Operational Information
- Definition: Information required for day-to-day operations.
- Examples:
- Schedules
- Workflow processes
- Production data
12. Strategic Information
- Definition: Information used for long-term planning and decision-making.
- Examples:
- Market analysis
- Business plans
- Competitive intelligence
13. Public Information
- Definition: Information that is accessible to the general public.
- Examples:
- Government publications
- News releases
- Public records
14. Confidential Information
- Definition: Sensitive data intended to be kept private and secure.
- Examples:
- Employee records
- Trade secrets
- Medical records
15. Digital Information
- Definition: Data stored and transmitted electronically.
- Examples:
- Emails
- Databases
- Social media content
16. Analog Information
- Definition: Data stored in a non-digital format.
- Examples:
- Vinyl records
- Printed books
- Photographs
17. Static Information
- Definition: Data that does not change over time.
- Examples:
- Historical facts
- Published research
- Archived records
18. Dynamic Information
- Definition: Data that is constantly changing.
- Examples:
- Stock prices
- Weather updates
- Social media trends
19. Internal Information
- Definition: Data generated within an organization.
- Examples:
- Internal reports
- Employee communications
- Financial statements
20. External Information
- Definition: Data obtained from sources outside an organization.
- Examples:
- Market research
- Industry news
- Customer feedback
How to Pronounce “Information”
Breakdown of the Word
Information is pronounced as: in-fer-MAY-shun
Phonetic Spelling
The phonetic spelling of “information” is: /ˌɪn.fərˈmeɪ.ʃən/
Syllable Breakdown
- In: /ɪn/
- for: /fər/
- ma: /meɪ/
- tion: /ʃən/
Pronunciation Steps
- In: Start with the short “i” sound as in “sit,” followed by “n.”
- for: Pronounce with a schwa sound /ər/, similar to the “er” in “teacher.”
- ma: Use a long “a” sound as in “say.”
- tion: End with a “shun” sound, where the “t” is silent, and the “ion” sounds like “shun.”
Information vs Data
Data refers to raw, unprocessed facts and figures without any context. It consists of numbers, text, symbols, or observations that alone do not provide any specific meaning. For example, individual temperature readings or survey responses are data points. On the other hand, information is data that has been processed, organized, and interpreted to provide context and meaning. It is used for decision-making and understanding. For instance, a weather report that analyzes temperature readings to predict weather conditions is information. While data serves as the input, information is the meaningful output derived from processing that data.
| Aspect | Data | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw facts and figures without context | Data that has been processed and given meaning |
| Example | 50, 75, 100 | Average score: 75% |
| Usage | Used as input for processing | Used for decision-making and understanding |
| Nature | Unorganized, unprocessed | Organized, processed |
| Dependency | Does not depend on information | Depends on data to be generated |
| Value | Low value in raw form | High value due to relevance and context |
| Purpose | To be processed or analyzed | To provide insight and context |
| Representation | Numbers, text, symbols | Summaries, reports, graphs |
| Context | Lacks context | Contextual and meaningful |
| Examples | Temperature readings, survey responses | Weather report, survey analysis |
Importance of Information
Information plays a crucial role in various aspects of life, from individual decision-making to the functioning of societies and organizations. Here are some key points highlighting its significance:
1. Decision Making
- Personal Decisions: Helps individuals make informed choices about health, finances, and lifestyle.
- Business Decisions: Enables companies to develop strategies, improve operations, and enhance customer satisfaction.
2. Education and Learning
- Knowledge Acquisition: Provides the basis for learning new concepts and skills.
- Research: Facilitates academic and scientific research by providing relevant data and references.
3. Communication
- Sharing Knowledge: Allows the exchange of ideas and information between people, fostering collaboration and innovation.
- Media and Journalism: Keeps the public informed about current events and important issues.
4. Technological Advancement
- Innovation: Drives technological progress by offering insights that lead to new inventions and improvements.
- Problem Solving: Provides the necessary data to tackle complex problems and develop solutions.
5. Economic Growth
- Market Analysis: Helps businesses understand market trends and consumer behavior.
- Efficiency: Improves productivity and efficiency in various sectors, leading to economic development.
6. Health and Medicine
- Medical Research: Contributes to the development of new treatments and cures.
- Public Health: Helps in tracking and controlling the spread of diseases, promoting better health practices.
7. Social Development
- Policy Making: Aids governments and organizations in creating policies that benefit society.
- Awareness: Raises awareness about social issues and encourages collective action.
Information in the Digital Age
In today’s digital era, the availability and accessibility of information have increased exponentially. The internet and digital technologies have transformed how information is created, shared, and consumed.
1. Big Data
- Analytics: Utilizes large datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and insights.
- Predictive Models: Helps in forecasting future events and behaviors.
2. Artificial Intelligence
- Automation: Automates processes and tasks, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Machine Learning: Enhances decision-making by learning from data and improving over time.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While information is incredibly valuable, it also presents challenges and ethical considerations:
1. Information Overload
- Cognitive Overload: The vast amount of information available can overwhelm individuals, making it difficult to discern what is relevant.
2. Misinformation and Fake News
- Credibility: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of information is crucial to avoid the spread of false information.
- Verification: Fact-checking and verification are essential to maintain the integrity of information.
3. Privacy and Security
- Data Protection: Safeguarding personal and sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Ethical Use: Ensuring information is used ethically and responsibly, respecting individuals’ privacy rights.
Sources of Information
Information sources are origins from which data, knowledge, or information is derived. These sources are crucial for research, learning, and decision-making processes. They can be categorized into primary, secondary, and tertiary sources, each serving a unique purpose in the information-gathering process.
Types of Information Sources
Primary Sources
Primary sources provide direct or firsthand evidence about an event, object, person, or work of art. They are created by witnesses or first recorders of these events at the time they occurred. Examples include:
- Historical Documents: Letters, diaries, speeches
- Research Data: Original research reports, lab notes
- Creative Works: Novels, paintings, music
- Artifacts: Tools, clothing, works of art from the time period
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources analyze, interpret, or summarize primary sources. They provide second-hand information and commentary from other researchers. Examples include:
- Books and Articles: Reviews, critical analyses, and biographies
- Documentaries: Films interpreting historical events or phenomena
- Essays and Critiques: Academic papers discussing original works or events
Tertiary Sources
Tertiary sources compile and synthesize information from primary and secondary sources. They are useful for providing a broad overview or for locating primary and secondary sources. Examples include:
- Encyclopedias: Comprehensive summaries of topics
- Databases: Collections of articles, books, and other research materials
- Indexes and Abstracts: Summaries of articles and books
Common Sources of Information
Libraries
Libraries are invaluable sources of information, offering access to books, academic journals, newspapers, and databases. Many libraries also provide digital resources and research assistance.
Academic Journals
Academic journals publish peer-reviewed articles written by experts in various fields. They are essential for accessing current research and developments in specific disciplines.
Online Databases
Databases such as JSTOR, PubMed, and Google Scholar provide access to a vast array of academic papers, articles, and other scholarly works.
Government Publications
Government agencies publish a wealth of information, including statistics, reports, and official documents. Websites like the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Archives are excellent resources.
Websites and Blogs
The internet hosts numerous websites and blogs that can be valuable sources of information. However, it’s important to evaluate the credibility of these sources, as anyone can publish content online.
News Outlets
Reputable news organizations provide up-to-date information on current events. Newspapers, magazines, and broadcast news are important sources for staying informed about the world.
Synonyms of Information
| Synonym | Definition |
|---|---|
| Data | Facts and statistics collected for reference or analysis |
| Knowledge | Awareness or familiarity gained by experience of a fact or situation |
| Details | Individual facts or pieces of information |
| Intelligence | Information of value for decision-making, especially in a strategic context |
| Facts | Information used as evidence or as part of a report or news article |
| Insight | The capacity to gain an accurate and deep understanding of something |
| News | Newly received or noteworthy information, especially about recent events |
| Report | An account given of a particular matter, especially in the form of an official document |
| Content | Information and experiences directed towards an end-user or audience |
| Data | Raw, unprocessed facts and figures |
| Message | Information sent from one person or group to another |
| Evidence | The available body of facts or information indicating whether a belief or proposition is true or valid |
Information Technology
Information Technology (IT) refers to the use of computers, software, networks, and other electronic systems to manage, store, process, and communicate information. IT is a crucial aspect of modern life, impacting nearly every sector from business and education to healthcare and entertainment.
Key Components of Information Technology
- Hardware
- Definition: The physical components of a computer system, such as the central processing unit (CPU), monitor, keyboard, and storage devices.
- Examples: Laptops, desktops, servers, and smartphones.
- Software
- Definition: Programs and applications that run on hardware and perform various tasks.
- Examples: Operating systems (Windows, macOS), productivity software (Microsoft Office, Google Workspace), and specialized applications (Adobe Photoshop, AutoCAD).
- Networks
- Definition: Systems that connect multiple computers and devices to share resources and information.
- Examples: Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), and the Internet.
- Data Management
- Definition: The process of storing, organizing, and maintaining data.
- Examples: Databases (MySQL, Oracle), data warehouses, and cloud storage services (Google Drive, Dropbox).
Importance of Information Technology
- Efficiency: IT streamlines processes, reduces manual labor, and increases productivity.
- Communication: Facilitates instant communication through email, messaging apps, and video conferencing.
- Data Management: Enables efficient storage, retrieval, and analysis of data, aiding in decision-making.
- Security: Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access through cybersecurity measures.
Applications of Information Technology
- Business
- Automation: IT automates routine tasks, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
- E-commerce: Online shopping platforms like Amazon and eBay.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Tools like Salesforce to manage customer interactions.
- Education
- E-learning: Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy offer online courses.
- Virtual Classrooms: Tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams facilitate remote learning.
- Research: Access to digital libraries and online databases.
- Healthcare
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Digital records of patient information.
- Telemedicine: Remote consultations via video conferencing.
- Medical Research: Data analysis for research and development of treatments.
- Entertainment
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and Spotify provide on-demand media.
- Video Games: Advanced graphics and immersive experiences through gaming consoles and PCs.
- Social Media: Connectivity and content sharing through Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Emerging Trends in Information Technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Definition: The simulation of human intelligence in machines.
- Applications: Chatbots, autonomous vehicles, and predictive analytics.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Definition: Network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data.
- Applications: Smart homes, wearable devices, and industrial automation.
- Blockchain
- Definition: A decentralized digital ledger technology.
- Applications: Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin), supply chain management, and secure voting systems.
- Cloud Computing
- Definition: Delivery of computing services over the Internet.
- Applications: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
What is information?
Information is processed data that is meaningful and useful for decision-making and understanding.
What are the types of information?
Types include factual, statistical, analytical, and descriptive information.
Why is information important?
Information is crucial for informed decision-making, problem-solving, and effective communication.
How does information differ from data?
Data are raw facts; information is data processed to be meaningful.
What are common sources of information?
Common sources include books, internet, reports, databases, and experts.
How is information used in businesses?
Businesses use information for strategic planning, market analysis, and operational efficiency.
What makes information reliable?
Reliable information is accurate, credible, timely, and verifiable.
How can information be protected?
Information can be protected through encryption, passwords, and secure storage.
What is the role of information in education?
Information is essential for learning, research, and academic development.
How is information technology related to information?
Information technology involves using computers and software to manage, store, and process information.