20+ Innovation Examples
Innovation is the process of turning creative ideas into practical solutions. It involves the introduction of new products, services, or methods that improve existing systems or create entirely new markets. Innovation drives progress, fuels economic growth, and enhances the quality of life. By embracing innovation, businesses can stay competitive, adapt to changing environments, and meet evolving customer needs. Whether through technological advancements, creative problem-solving, or new business models, innovation plays a crucial role in shaping the future. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of innovation, its importance, and how individuals and organizations can foster a culture of innovation.
What is Innovation?
Innovation Examples Across Various Industries
1. Healthcare: Telemedicine
Telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare by allowing patients to consult with doctors remotely using video calls. This innovation enhances accessibility and convenience for patients, especially in rural areas.
2. Finance: Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology provides a decentralized ledger for transactions, offering enhanced security and transparency. It has significant implications for banking, supply chain management, and beyond.
3. Automotive: Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles, such as those produced by Tesla, have transformed the automotive industry by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impact.
4. Retail: E-Commerce Platforms
Platforms like Amazon have reshaped retail by providing a convenient online shopping experience, extensive product range, and rapid delivery services.
5. Technology: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI advancements have enabled machines to learn and make decisions, impacting various sectors including healthcare, finance, and customer service through applications like chatbots and predictive analytics.
6. Agriculture: Precision Farming
Precision farming uses GPS and IoT devices to monitor and optimize crop yields, reducing waste and enhancing productivity.
7. Education: Online Learning Platforms
Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy offer accessible education to millions, allowing people to learn new skills from anywhere in the world.
8. Energy: Solar Power
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun, providing a renewable and sustainable energy source that reduces carbon footprints.
9. Manufacturing: 3D Printing
3D printing technology allows for the creation of complex structures and prototypes quickly and cost-effectively, revolutionizing product development and manufacturing processes.
10. Entertainment: Streaming Services
Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify have transformed how people consume media, providing on-demand access to a vast array of content.
11. Transportation: Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars, being developed by companies like Waymo, promise to enhance road safety and reduce traffic congestion.
12. Construction: Green Building Materials
Innovative materials like cross-laminated timber and recycled steel are used in construction to improve energy efficiency and sustainability.
13. Biotechnology: CRISPR Gene Editing
CRISPR technology allows for precise editing of DNA, offering potential cures for genetic disorders and advancements in agriculture.
14. Telecommunications: 5G Networks
5G technology offers faster data speeds and improved connectivity, paving the way for advancements in IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles.
15. Aerospace: Reusable Rockets
Companies like SpaceX have developed reusable rockets, significantly reducing the cost of space exploration and making it more sustainable.
16. Food Industry: Plant-Based Meat
Plant-based meat alternatives, such as those by Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, provide sustainable and ethical options for meat consumption.
17. Logistics: Drones for Delivery
Drones are being used for delivering packages, medical supplies, and even food, enhancing delivery speed and efficiency.
18. Water Management: Desalination Technology
Advanced desalination technology provides fresh water from seawater, addressing water scarcity in arid regions.
19. Fashion: Sustainable Textiles
The fashion industry is adopting sustainable textiles made from recycled materials or organic sources, reducing environmental impact.
20. Pharmaceuticals: Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors treatment to individual patients based on genetic profiles, improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
Process of Innovation
1. Idea Generation
- Brainstorming Sessions: Gather a diverse team to generate a wide range of ideas.
- Market Research: Identify gaps in the market by analyzing trends, customer needs, and competitors.
- Customer Feedback: Engage with customers to understand their pain points and desires.
- SWOT Analysis: Evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to generate relevant ideas.
2. Idea Screening
- Feasibility Study: Assess the technical, financial, and market feasibility of each idea.
- Prioritization: Rank ideas based on potential impact, alignment with business goals, and resource availability.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and challenges associated with each idea.
3. Concept Development and Testing
- Detailed Concept Description: Develop a detailed description and visual representation of the idea.
- Prototype Development: Create a prototype to visualize and test the concept.
- Customer Feedback: Present the prototype to a sample of potential customers to gather feedback.
- Refinement: Modify the concept based on feedback and test results.
4. Business Analysis
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Calculate the costs involved in developing and launching the product and compare them with the expected benefits.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate the target market size, growth potential, and competitive landscape.
- Financial Projections: Develop financial projections, including sales forecasts, profit margins, and break-even analysis.
5. Product Development
- Detailed Design: Develop detailed designs and specifications for the product.
- Production Plan: Create a plan for production, including sourcing materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct extensive testing to ensure the product meets quality and safety standards.
- Iteration: Make necessary adjustments based on test results and continue refining the product.
6. Market Testing
- Test Marketing: Launch the product in a limited market to gauge customer response.
- Marketing Strategy: Develop and implement a marketing strategy to promote the product.
- Sales Feedback: Collect feedback from the market test to understand customer acceptance and identify areas for improvement.
- Adjustment: Make final adjustments to the product and marketing strategy based on market test feedback.
7. Commercialization
- Launch Plan: Develop a comprehensive plan for the full-scale launch of the product.
- Distribution Channels: Establish distribution channels to ensure the product reaches the target market.
- Marketing Campaign: Implement a marketing campaign to create awareness and drive sales.
- Sales Strategy: Develop and execute a sales strategy to achieve revenue targets.
8. Post-Launch Review and Improvement
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor the product’s performance in the market using key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Customer Feedback: Continuously gather and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Implement changes and improvements based on feedback and performance data.
- Innovation Cycle: Repeat the innovation process to ensure continuous improvement and sustained competitive advantage.
Types of Innovation
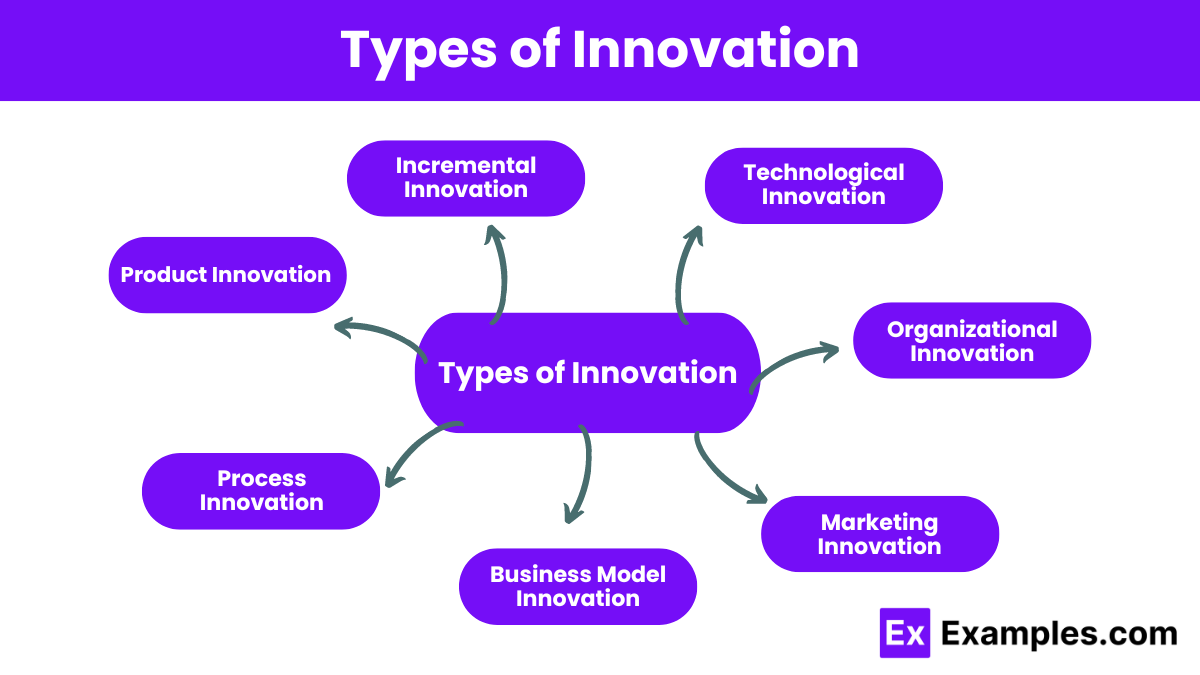
1. Product Innovation
Product innovation involves creating new products or improving existing ones to meet customer needs more effectively. This type of innovation focuses on enhancing product features, design, functionality, or performance.
Examples:
- Smartphones with advanced cameras and AI features
- Electric vehicles with improved battery life
2. Process Innovation
Process innovation refers to the implementation of new or significantly improved production or delivery methods. This type of innovation aims to increase efficiency, reduce costs, or improve quality.
Examples:
- Automation in manufacturing
- Lean production techniques
3. Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation involves changing the way a company creates, delivers, and captures value. This can include altering revenue streams, cost structures, or target markets.
Examples:
- Subscription-based services
- Freemium models in software
4. Marketing Innovation
Marketing innovation focuses on developing new marketing strategies, including changes in product design, packaging, promotion, or pricing. This type of innovation aims to better satisfy customer needs and increase market share.
Examples:
- Social media marketing campaigns
- Personalized advertising
5. Organizational Innovation
Organizational innovation involves the introduction of new organizational methods in business practices, workplace organization, or external relations. This type of innovation aims to improve a company’s performance and employee satisfaction.
Examples:
- Remote working policies
- Flat organizational structures
6. Technological Innovation
Technological innovation refers to the development and application of new technologies. This type of innovation can lead to the creation of new products, processes, or services.
Examples:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
7. Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves making small, continuous improvements to existing products, services, or processes. This type of innovation focuses on enhancing efficiency and maintaining competitiveness.
Examples:
- Regular software updates
- Minor design improvements in consumer electronics
8. Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation refers to innovations that create a new market and value network, eventually disrupting existing markets and displacing established products or services.
Examples:
- Streaming services replacing traditional cable TV
- Ride-sharing apps disrupting taxi services
9. Radical Innovation
Radical innovation involves breakthrough developments that result in substantial changes and can create entirely new industries. This type of innovation often requires significant investment and research.
Examples:
- The invention of the internet
- The development of CRISPR gene-editing technology
10. Open Innovation
Open innovation is the practice of businesses and organizations sourcing ideas and solutions from external sources, such as customers, partners, or research institutions, to drive innovation.
Examples:
- Crowdsourcing ideas from customers
- Collaborating with universities for research and development
Functions of Innovation
1. Driving Economic Growth
- Job Creation: Innovation leads to the development of new industries and sectors, creating jobs and opportunities.
- Increased Productivity: Innovative technologies and processes enhance productivity, enabling businesses to produce more with less.
- Market Expansion: New products and services open up new markets and increase consumer demand.
2. Enhancing Competitiveness
- Differentiation: Companies can distinguish themselves from competitors by offering unique products or services.
- Efficiency: Innovations in processes and technologies can streamline operations, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Customer Satisfaction: Innovative solutions can meet customer needs better and improve overall satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Solving Social and Environmental Issues
- Sustainability: Innovations in green technology help reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable practices.
- Healthcare: Medical innovations lead to better treatments, improved healthcare delivery, and longer life expectancy.
- Education: Technological advancements in education enhance learning experiences and accessibility.
4. Fostering Creativity and Learning
- Encouraging Experimentation: Innovation encourages a culture of experimentation and risk-taking, which can lead to breakthrough discoveries.
- Continuous Improvement: It promotes a mindset of continuous improvement, where individuals and organizations constantly seek better ways to do things.
- Knowledge Sharing: Innovation often involves collaboration and the sharing of knowledge, which can lead to collective progress.
5. Building Resilience
- Adaptability: Innovative organizations are better equipped to adapt to changes in the market or environment.
- Problem-Solving: Innovation provides tools and methods to solve complex problems effectively.
- Future-Proofing: By staying ahead of trends, innovative companies can anticipate and prepare for future challenges.
6. Improving Quality of Life
- Convenience: Innovations in technology and services make everyday life easier and more convenient.
- Safety: Advances in safety technology can protect people and property.
- Entertainment: Innovation in the entertainment industry provides new and engaging ways for people to enjoy their leisure time.
What Causes Innovation?
Innovation is the process of creating new ideas, products, or methods that bring significant improvements or changes to existing systems. Understanding the factors that drive innovation is crucial for fostering a culture of creativity and progress. Here are the key causes of innovation:
1. Necessity and Problem-Solving
- Necessity: Often termed as the mother of invention, necessity drives individuals and organizations to develop solutions to pressing problems.
- Problem-Solving: Identifying and addressing challenges or inefficiencies can lead to innovative ideas and technologies.
2. Technological Advancements
- New Technologies: The development of new technologies creates opportunities for innovation by providing new tools and methods.
- Digital Transformation: The rise of digital technologies has revolutionized industries, leading to innovative business models and practices.
3. Research and Development (R&D)
- Investment in R&D: Companies and governments that invest in R&D are more likely to develop new products and services.
- Scientific Discoveries: Breakthroughs in science often lead to technological innovations and new applications.
4. Market Demand and Competition
- Customer Needs: Understanding and responding to customer needs and preferences can drive innovation.
- Competitive Pressure: Competition encourages businesses to innovate to gain a competitive edge and maintain market relevance.
5. Creative and Diverse Workforce
- Diverse Perspectives: A diverse workforce brings different perspectives and ideas, fostering creativity and innovation.
- Encouraging Creativity: Creating an environment that encourages creativity and experimentation can lead to innovative solutions.
6. Economic and Policy Incentives
- Government Policies: Policies that support innovation, such as tax incentives and grants, can encourage investment in new ideas.
- Economic Environment: A stable and supportive economic environment can facilitate innovation by providing resources and reducing risks.
7. Collaboration and Networking
- Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between organizations, industries, and academic institutions can lead to the exchange of ideas and innovation.
- Networking: Building networks and partnerships can provide access to new knowledge and opportunities for innovation.
8. Cultural Factors
- Innovative Culture: Cultures that value and reward innovation are more likely to produce innovative individuals and organizations.
- Risk-Taking: A culture that supports risk-taking and tolerates failure can encourage experimentation and innovation.
9. Globalization
- Global Markets: Access to global markets provides opportunities for innovation by exposing businesses to new ideas and demands.
- International Collaboration: Collaborating with international partners can bring in new perspectives and technologies.
10. Education and Skill Development
- Educational Institutions: Universities and educational institutions play a crucial role in fostering innovation by providing knowledge and skills.
- Continuous Learning: Encouraging continuous learning and skill development can keep the workforce updated with the latest trends and technologies.
Innovation in Entrepreneurship
Innovation in entrepreneurship involves introducing new ideas, methods, or products to create value and drive business growth. It is a key factor in gaining a competitive edge and can encompass various aspects, including technological advancements, unique business models, or improved processes. Entrepreneurs leverage innovation to address market needs, solve problems, and enhance customer experiences. By fostering a culture of creativity and embracing change, businesses can adapt to evolving trends, seize opportunities, and sustain long-term success. Innovation in entrepreneurship is crucial for staying relevant and thriving in a dynamic, ever-changing market environment.
Innovation Journal
An innovation journal is a tool used by individuals or organizations to document creative ideas, track progress on innovation projects, and reflect on the process of developing new solutions. It serves as a repository for brainstorming, recording insights, and evaluating the effectiveness of different approaches. This journal can include sketches, notes, prototypes, and feedback, facilitating continuous improvement and fostering a culture of innovation. By regularly updating the journal, users can identify patterns, overcome obstacles, and ensure that valuable ideas are not lost, ultimately driving sustained innovation and growth.
Innovation in Business
Innovation in business refers to the process of creating and implementing new ideas, products, services, or processes to improve efficiency, drive growth, and gain a competitive edge. It involves leveraging creativity and strategic thinking to solve problems, meet customer needs, and adapt to market changes. This can include the development of new technologies, the introduction of novel business models, or the optimization of existing operations. Effective business innovation fosters a culture of continuous improvement and can significantly enhance a company’s value and market position.
Why Innovation is Important in Business
- Competitive Advantage: Innovation helps businesses stand out in a crowded market. By offering unique products or services, companies can attract more customers and differentiate themselves from competitors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Innovative solutions often address customer needs and preferences more effectively. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Innovation can streamline operations and reduce costs. By adopting new technologies and processes, businesses can improve efficiency and productivity.
- Growth and Expansion: Innovation drives business growth by opening up new markets and opportunities. It enables companies to expand their product lines and enter new industries.
- Adaptability: In a rapidly changing business environment, innovation helps companies adapt to market trends and economic shifts. It ensures that businesses remain relevant and can quickly respond to external changes.
- Profitability: By introducing new revenue streams and improving operational efficiencies, innovation can significantly boost a company’s profitability.
- Employee Engagement: A culture of innovation encourages employee creativity and engagement. It makes the workplace more dynamic and can attract top talent.
Goals and failures of innovation
Innovation aims to drive progress, solve problems, and create value by introducing new ideas, products, or processes. The goals of innovation often include improving efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, gaining a competitive edge, and fostering economic growth. However, innovation can also encounter failures, such as inadequate market demand, technological challenges, insufficient funding, or poor execution. These failures can result from a lack of understanding of market needs, overestimation of the technology’s potential, or misalignment with organizational capabilities. Despite these challenges, the pursuit of innovation remains crucial for long-term success and adaptability in a rapidly changing world.
Measuring Innovation
Measuring innovation is crucial for organizations to understand the effectiveness of their innovative efforts and to guide future innovations. There are various metrics and approaches used to assess innovation, each focusing on different aspects of the process.
Input Metrics
These metrics focus on the resources invested in innovation. They include:
- R&D Spending: This is a straightforward metric that measures the amount of money dedicated to research and development activities. It’s often expressed as a percentage of total revenue.
- Human Capital Investment: This includes the number of employees engaged in innovation activities and the training provided to enhance their skills.
Process Metrics
Process metrics assess the efficiency and effectiveness of the innovation processes within an organization:
- Time to Market: Measures the time it takes from the inception of an idea to its commercial release. A shorter time to market can indicate a more efficient innovation process.
- Innovation Pipeline Strength: Looks at the number of projects at various stages of development to assess the continuity and potential future impact of innovation.
Output Metrics
These metrics evaluate the outcomes of innovative activities:
- Number of Patents: This is a common metric for technological and scientific innovations, indicating the number of new inventions that have been legally protected.
- Revenue from New Products: Measures the percentage of total revenue that comes from products or services introduced within a specific timeframe (e.g., the last three or five years).
Outcome Metrics
Outcome metrics help gauge the broader impact of innovation on an organization:
- Market Share: Measures how much a new product or service contributes to increasing the company’s market share.
- Customer Satisfaction: Assesses how innovations have improved customer satisfaction and engagement.
Organizational and Cultural Metrics
These metrics look at the environment and capabilities that support innovation:
- Employee Engagement in Innovation: Measures how actively employees are participating in innovation, often assessed through surveys.
- Organizational Flexibility: Assesses the company’s ability to adapt and change direction quickly in response to innovative ideas or market changes.
Importance of Innovation?
Innovation is crucial for progress and growth in every sector of society. It drives economic development by creating new products, services, and industries, leading to job creation and increased competitiveness. In education, innovation enhances learning experiences and outcomes through advanced technologies and teaching methods. In healthcare, it improves patient care and treatment options with groundbreaking research and medical advancements. Socially, innovation addresses pressing challenges such as climate change and resource scarcity by providing sustainable solutions. Ultimately, innovation fosters a culture of continuous improvement, adaptability, and resilience, ensuring societies thrive in an ever-changing world.
What is innovation?
Innovation involves creating and implementing new ideas, products, or processes to improve efficiency, meet market demands, and drive growth.
Why is innovation important in business?
Innovation fosters competitive advantage, boosts productivity, and ensures long-term survival by adapting to market changes and technological advances.
How do companies measure innovation?
Companies measure innovation through inputs like R&D spending, outputs like patents, and outcomes like market share and customer satisfaction.
What are the types of innovation?
Innovation types include product, process, marketing, and organizational, each focusing on different aspects of business improvements.
What drives innovation in a company?
Key drivers include customer needs, technological advances, competitive pressure, and internal culture that encourages creativity.
How can innovation be fostered within an organization?
Promoting a culture of risk-taking, continuous learning, and supporting creative ideas with resources and incentives are effective strategies.
What are common barriers to innovation?
Barriers include lack of funding, resistance to change, inadequate resources, and poor alignment with business strategies.
Can innovation impact company culture?
Yes, successful innovation can lead to a more dynamic, flexible, and forward-thinking company culture.
What is open innovation?
Open innovation is a strategy where companies use external and internal ideas to accelerate development and enhance market offerings.
How does technology influence innovation?
Technology is a critical enabler of innovation, providing new tools, platforms, and methodologies to create and implement novel solutions.
20+ Innovation Examples
Innovation is the process of turning creative ideas into practical solutions. It involves the introduction of new products, services, or methods that improve existing systems or create entirely new markets. Innovation drives progress, fuels economic growth, and enhances the quality of life. By embracing innovation, businesses can stay competitive, adapt to changing environments, and meet evolving customer needs. Whether through technological advancements, creative problem-solving, or new business models, innovation plays a crucial role in shaping the future. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of innovation, its importance, and how individuals and organizations can foster a culture of innovation.
What is Innovation?
Innovation is the process of creating and implementing new ideas, products, services, or processes that bring significant improvements or changes. It involves the introduction of something new or making existing things better in a way that adds value. Innovation can occur in various fields such as technology, business, education, healthcare, and more.
Innovation Examples Across Various Industries
1. Healthcare: Telemedicine
Telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare by allowing patients to consult with doctors remotely using video calls. This innovation enhances accessibility and convenience for patients, especially in rural areas.
2. Finance: Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology provides a decentralized ledger for transactions, offering enhanced security and transparency. It has significant implications for banking, supply chain management, and beyond.
3. Automotive: Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles, such as those produced by Tesla, have transformed the automotive industry by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impact.
4. Retail: E-Commerce Platforms
Platforms like Amazon have reshaped retail by providing a convenient online shopping experience, extensive product range, and rapid delivery services.
5. Technology: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI advancements have enabled machines to learn and make decisions, impacting various sectors including healthcare, finance, and customer service through applications like chatbots and predictive analytics.
6. Agriculture: Precision Farming
Precision farming uses GPS and IoT devices to monitor and optimize crop yields, reducing waste and enhancing productivity.
7. Education: Online Learning Platforms
Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy offer accessible education to millions, allowing people to learn new skills from anywhere in the world.
8. Energy: Solar Power
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun, providing a renewable and sustainable energy source that reduces carbon footprints.
9. Manufacturing: 3D Printing
3D printing technology allows for the creation of complex structures and prototypes quickly and cost-effectively, revolutionizing product development and manufacturing processes.
10. Entertainment: Streaming Services
Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify have transformed how people consume media, providing on-demand access to a vast array of content.
11. Transportation: Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars, being developed by companies like Waymo, promise to enhance road safety and reduce traffic congestion.
12. Construction: Green Building Materials
Innovative materials like cross-laminated timber and recycled steel are used in construction to improve energy efficiency and sustainability.
13. Biotechnology: CRISPR Gene Editing
CRISPR technology allows for precise editing of DNA, offering potential cures for genetic disorders and advancements in agriculture.
14. Telecommunications: 5G Networks
5G technology offers faster data speeds and improved connectivity, paving the way for advancements in IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles.
15. Aerospace: Reusable Rockets
Companies like SpaceX have developed reusable rockets, significantly reducing the cost of space exploration and making it more sustainable.
16. Food Industry: Plant-Based Meat
Plant-based meat alternatives, such as those by Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, provide sustainable and ethical options for meat consumption.
17. Logistics: Drones for Delivery
Drones are being used for delivering packages, medical supplies, and even food, enhancing delivery speed and efficiency.
18. Water Management: Desalination Technology
Advanced desalination technology provides fresh water from seawater, addressing water scarcity in arid regions.
19. Fashion: Sustainable Textiles
The fashion industry is adopting sustainable textiles made from recycled materials or organic sources, reducing environmental impact.
20. Pharmaceuticals: Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors treatment to individual patients based on genetic profiles, improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
Process of Innovation
1. Idea Generation
Brainstorming Sessions: Gather a diverse team to generate a wide range of ideas.
Market Research: Identify gaps in the market by analyzing trends, customer needs, and competitors.
Customer Feedback: Engage with customers to understand their pain points and desires.
SWOT Analysis: Evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to generate relevant ideas.
2. Idea Screening
Feasibility Study: Assess the technical, financial, and market feasibility of each idea.
Prioritization: Rank ideas based on potential impact, alignment with business goals, and resource availability.
Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and challenges associated with each idea.
3. Concept Development and Testing
Detailed Concept Description: Develop a detailed description and visual representation of the idea.
Prototype Development: Create a prototype to visualize and test the concept.
Customer Feedback: Present the prototype to a sample of potential customers to gather feedback.
Refinement: Modify the concept based on feedback and test results.
4. Business Analysis
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Calculate the costs involved in developing and launching the product and compare them with the expected benefits.
Market Analysis: Evaluate the target market size, growth potential, and competitive landscape.
Financial Projections: Develop financial projections, including sales forecasts, profit margins, and break-even analysis.
5. Product Development
Detailed Design: Develop detailed designs and specifications for the product.
Production Plan: Create a plan for production, including sourcing materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control.
Testing and Validation: Conduct extensive testing to ensure the product meets quality and safety standards.
Iteration: Make necessary adjustments based on test results and continue refining the product.
6. Market Testing
Test Marketing: Launch the product in a limited market to gauge customer response.
Marketing Strategy: Develop and implement a marketing strategy to promote the product.
Sales Feedback: Collect feedback from the market test to understand customer acceptance and identify areas for improvement.
Adjustment: Make final adjustments to the product and marketing strategy based on market test feedback.
7. Commercialization
Launch Plan: Develop a comprehensive plan for the full-scale launch of the product.
Distribution Channels: Establish distribution channels to ensure the product reaches the target market.
Marketing Campaign: Implement a marketing campaign to create awareness and drive sales.
Sales Strategy: Develop and execute a sales strategy to achieve revenue targets.
8. Post-Launch Review and Improvement
Performance Monitoring: Monitor the product’s performance in the market using key performance indicators (KPIs).
Customer Feedback: Continuously gather and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement: Implement changes and improvements based on feedback and performance data.
Innovation Cycle: Repeat the innovation process to ensure continuous improvement and sustained competitive advantage.
Types of Innovation
1. Product Innovation
Product innovation involves creating new products or improving existing ones to meet customer needs more effectively. This type of innovation focuses on enhancing product features, design, functionality, or performance.
Examples:
Smartphones with advanced cameras and AI features
Electric vehicles with improved battery life
2. Process Innovation
Process innovation refers to the implementation of new or significantly improved production or delivery methods. This type of innovation aims to increase efficiency, reduce costs, or improve quality.
Examples:
Automation in manufacturing
Lean production techniques
3. Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation involves changing the way a company creates, delivers, and captures value. This can include altering revenue streams, cost structures, or target markets.
Examples:
Subscription-based services
Freemium models in software
4. Marketing Innovation
Marketing innovation focuses on developing new marketing strategies, including changes in product design, packaging, promotion, or pricing. This type of innovation aims to better satisfy customer needs and increase market share.
Examples:
Social media marketing campaigns
Personalized advertising
5. Organizational Innovation
Organizational innovation involves the introduction of new organizational methods in business practices, workplace organization, or external relations. This type of innovation aims to improve a company’s performance and employee satisfaction.
Examples:
Remote working policies
Flat organizational structures
6. Technological Innovation
Technological innovation refers to the development and application of new technologies. This type of innovation can lead to the creation of new products, processes, or services.
Examples:
Blockchain technology
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
7. Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves making small, continuous improvements to existing products, services, or processes. This type of innovation focuses on enhancing efficiency and maintaining competitiveness.
Examples:
Regular software updates
Minor design improvements in consumer electronics
8. Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation refers to innovations that create a new market and value network, eventually disrupting existing markets and displacing established products or services.
Examples:
Streaming services replacing traditional cable TV
Ride-sharing apps disrupting taxi services
9. Radical Innovation
Radical innovation involves breakthrough developments that result in substantial changes and can create entirely new industries. This type of innovation often requires significant investment and research.
Examples:
The invention of the internet
The development of CRISPR gene-editing technology
10. Open Innovation
Open innovation is the practice of businesses and organizations sourcing ideas and solutions from external sources, such as customers, partners, or research institutions, to drive innovation.
Examples:
Crowdsourcing ideas from customers
Collaborating with universities for research and development
Functions of Innovation
1. Driving Economic Growth
Job Creation: Innovation leads to the development of new industries and sectors, creating jobs and opportunities.
Increased Productivity: Innovative technologies and processes enhance productivity, enabling businesses to produce more with less.
Market Expansion: New products and services open up new markets and increase consumer demand.
2. Enhancing Competitiveness
Differentiation: Companies can distinguish themselves from competitors by offering unique products or services.
Efficiency: Innovations in processes and technologies can streamline operations, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Customer Satisfaction: Innovative solutions can meet customer needs better and improve overall satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Solving Social and Environmental Issues
Sustainability: Innovations in green technology help reduce environmental impact and promote sustainable practices.
Healthcare: Medical innovations lead to better treatments, improved healthcare delivery, and longer life expectancy.
Education: Technological advancements in education enhance learning experiences and accessibility.
4. Fostering Creativity and Learning
Encouraging Experimentation: Innovation encourages a culture of experimentation and risk-taking, which can lead to breakthrough discoveries.
Continuous Improvement: It promotes a mindset of continuous improvement, where individuals and organizations constantly seek better ways to do things.
Knowledge Sharing: Innovation often involves collaboration and the sharing of knowledge, which can lead to collective progress.
5. Building Resilience
Adaptability: Innovative organizations are better equipped to adapt to changes in the market or environment.
Problem-Solving: Innovation provides tools and methods to solve complex problems effectively.
Future-Proofing: By staying ahead of trends, innovative companies can anticipate and prepare for future challenges.
6. Improving Quality of Life
Convenience: Innovations in technology and services make everyday life easier and more convenient.
Safety: Advances in safety technology can protect people and property.
Entertainment: Innovation in the entertainment industry provides new and engaging ways for people to enjoy their leisure time.
What Causes Innovation?
Innovation is the process of creating new ideas, products, or methods that bring significant improvements or changes to existing systems. Understanding the factors that drive innovation is crucial for fostering a culture of creativity and progress. Here are the key causes of innovation:
1. Necessity and Problem-Solving
Necessity: Often termed as the mother of invention, necessity drives individuals and organizations to develop solutions to pressing problems.
Problem-Solving: Identifying and addressing challenges or inefficiencies can lead to innovative ideas and technologies.
2. Technological Advancements
New Technologies: The development of new technologies creates opportunities for innovation by providing new tools and methods.
Digital Transformation: The rise of digital technologies has revolutionized industries, leading to innovative business models and practices.
3. Research and Development (R&D)
Investment in R&D: Companies and governments that invest in R&D are more likely to develop new products and services.
Scientific Discoveries: Breakthroughs in science often lead to technological innovations and new applications.
4. Market Demand and Competition
Customer Needs: Understanding and responding to customer needs and preferences can drive innovation.
Competitive Pressure: Competition encourages businesses to innovate to gain a competitive edge and maintain market relevance.
5. Creative and Diverse Workforce
Diverse Perspectives: A diverse workforce brings different perspectives and ideas, fostering creativity and innovation.
Encouraging Creativity: Creating an environment that encourages creativity and experimentation can lead to innovative solutions.
6. Economic and Policy Incentives
Government Policies: Policies that support innovation, such as tax incentives and grants, can encourage investment in new ideas.
Economic Environment: A stable and supportive economic environment can facilitate innovation by providing resources and reducing risks.
7. Collaboration and Networking
Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between organizations, industries, and academic institutions can lead to the exchange of ideas and innovation.
Networking: Building networks and partnerships can provide access to new knowledge and opportunities for innovation.
8. Cultural Factors
Innovative Culture: Cultures that value and reward innovation are more likely to produce innovative individuals and organizations.
Risk-Taking: A culture that supports risk-taking and tolerates failure can encourage experimentation and innovation.
9. Globalization
Global Markets: Access to global markets provides opportunities for innovation by exposing businesses to new ideas and demands.
International Collaboration: Collaborating with international partners can bring in new perspectives and technologies.
10. Education and Skill Development
Educational Institutions: Universities and educational institutions play a crucial role in fostering innovation by providing knowledge and skills.
Continuous Learning: Encouraging continuous learning and skill development can keep the workforce updated with the latest trends and technologies.
Innovation in Entrepreneurship
Innovation in entrepreneurship involves introducing new ideas, methods, or products to create value and drive business growth. It is a key factor in gaining a competitive edge and can encompass various aspects, including technological advancements, unique business models, or improved processes. Entrepreneurs leverage innovation to address market needs, solve problems, and enhance customer experiences. By fostering a culture of creativity and embracing change, businesses can adapt to evolving trends, seize opportunities, and sustain long-term success. Innovation in entrepreneurship is crucial for staying relevant and thriving in a dynamic, ever-changing market environment.
Innovation Journal
An innovation journal is a tool used by individuals or organizations to document creative ideas, track progress on innovation projects, and reflect on the process of developing new solutions. It serves as a repository for brainstorming, recording insights, and evaluating the effectiveness of different approaches. This journal can include sketches, notes, prototypes, and feedback, facilitating continuous improvement and fostering a culture of innovation. By regularly updating the journal, users can identify patterns, overcome obstacles, and ensure that valuable ideas are not lost, ultimately driving sustained innovation and growth.
Innovation in Business
Innovation in business refers to the process of creating and implementing new ideas, products, services, or processes to improve efficiency, drive growth, and gain a competitive edge. It involves leveraging creativity and strategic thinking to solve problems, meet customer needs, and adapt to market changes. This can include the development of new technologies, the introduction of novel business models, or the optimization of existing operations. Effective business innovation fosters a culture of continuous improvement and can significantly enhance a company’s value and market position.
Why Innovation is Important in Business
Competitive Advantage: Innovation helps businesses stand out in a crowded market. By offering unique products or services, companies can attract more customers and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Customer Satisfaction: Innovative solutions often address customer needs and preferences more effectively. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Efficiency and Productivity: Innovation can streamline operations and reduce costs. By adopting new technologies and processes, businesses can improve efficiency and productivity.
Growth and Expansion: Innovation drives business growth by opening up new markets and opportunities. It enables companies to expand their product lines and enter new industries.
Adaptability: In a rapidly changing business environment, innovation helps companies adapt to market trends and economic shifts. It ensures that businesses remain relevant and can quickly respond to external changes.
Profitability: By introducing new revenue streams and improving operational efficiencies, innovation can significantly boost a company’s profitability.
Employee Engagement: A culture of innovation encourages employee creativity and engagement. It makes the workplace more dynamic and can attract top talent.
Goals and failures of innovation
Innovation aims to drive progress, solve problems, and create value by introducing new ideas, products, or processes. The goals of innovation often include improving efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, gaining a competitive edge, and fostering economic growth. However, innovation can also encounter failures, such as inadequate market demand, technological challenges, insufficient funding, or poor execution. These failures can result from a lack of understanding of market needs, overestimation of the technology’s potential, or misalignment with organizational capabilities. Despite these challenges, the pursuit of innovation remains crucial for long-term success and adaptability in a rapidly changing world.
Measuring Innovation
Measuring innovation is crucial for organizations to understand the effectiveness of their innovative efforts and to guide future innovations. There are various metrics and approaches used to assess innovation, each focusing on different aspects of the process.
Input Metrics
These metrics focus on the resources invested in innovation. They include:
R&D Spending: This is a straightforward metric that measures the amount of money dedicated to research and development activities. It’s often expressed as a percentage of total revenue.
Human Capital Investment: This includes the number of employees engaged in innovation activities and the training provided to enhance their skills.
Process Metrics
Process metrics assess the efficiency and effectiveness of the innovation processes within an organization:
Time to Market: Measures the time it takes from the inception of an idea to its commercial release. A shorter time to market can indicate a more efficient innovation process.
Innovation Pipeline Strength: Looks at the number of projects at various stages of development to assess the continuity and potential future impact of innovation.
Output Metrics
These metrics evaluate the outcomes of innovative activities:
Number of Patents: This is a common metric for technological and scientific innovations, indicating the number of new inventions that have been legally protected.
Revenue from New Products: Measures the percentage of total revenue that comes from products or services introduced within a specific timeframe (e.g., the last three or five years).
Outcome Metrics
Outcome metrics help gauge the broader impact of innovation on an organization:
Market Share: Measures how much a new product or service contributes to increasing the company’s market share.
Customer Satisfaction: Assesses how innovations have improved customer satisfaction and engagement.
Organizational and Cultural Metrics
These metrics look at the environment and capabilities that support innovation:
Employee Engagement in Innovation: Measures how actively employees are participating in innovation, often assessed through surveys.
Organizational Flexibility: Assesses the company’s ability to adapt and change direction quickly in response to innovative ideas or market changes.
Importance of Innovation?
Innovation is crucial for progress and growth in every sector of society. It drives economic development by creating new products, services, and industries, leading to job creation and increased competitiveness. In education, innovation enhances learning experiences and outcomes through advanced technologies and teaching methods. In healthcare, it improves patient care and treatment options with groundbreaking research and medical advancements. Socially, innovation addresses pressing challenges such as climate change and resource scarcity by providing sustainable solutions. Ultimately, innovation fosters a culture of continuous improvement, adaptability, and resilience, ensuring societies thrive in an ever-changing world.
What is innovation?
Innovation involves creating and implementing new ideas, products, or processes to improve efficiency, meet market demands, and drive growth.
Why is innovation important in business?
Innovation fosters competitive advantage, boosts productivity, and ensures long-term survival by adapting to market changes and technological advances.
How do companies measure innovation?
Companies measure innovation through inputs like R&D spending, outputs like patents, and outcomes like market share and customer satisfaction.
What are the types of innovation?
Innovation types include product, process, marketing, and organizational, each focusing on different aspects of business improvements.
What drives innovation in a company?
Key drivers include customer needs, technological advances, competitive pressure, and internal culture that encourages creativity.
How can innovation be fostered within an organization?
Promoting a culture of risk-taking, continuous learning, and supporting creative ideas with resources and incentives are effective strategies.
What are common barriers to innovation?
Barriers include lack of funding, resistance to change, inadequate resources, and poor alignment with business strategies.
Can innovation impact company culture?
Yes, successful innovation can lead to a more dynamic, flexible, and forward-thinking company culture.
What is open innovation?
Open innovation is a strategy where companies use external and internal ideas to accelerate development and enhance market offerings.
How does technology influence innovation?
Technology is a critical enabler of innovation, providing new tools, platforms, and methodologies to create and implement novel solutions.


