200+ Occupation Examples
An occupation is a person’s regular work or profession. It provides income and defines a role in society. Occupations range from skilled trades like carpentry and plumbing to professional roles such as doctors, lawyers, and teachers. Each occupation requires specific skills, education, and training. Understanding various occupations helps individuals make informed career choices, enhances economic productivity, and fosters a sense of purpose and identity. This article explores different types of occupations, the importance of career planning, and the impact of job satisfaction and Job Risk Assessment on overall well-being. Dive in to learn more about the diverse world of work and how to navigate it effectively.
Definition of Occupation
Occupation Examples

- Teacher: Educates students in various subjects at different educational levels.
- Doctor: Diagnoses and treats illnesses, prescribes medication, and provides healthcare advice.
- Nurse: Provides patient care, administers medication, and assists doctors.
- Dentist: Treats oral health issues, including teeth, gums, and mouth diseases.
- Pharmacist: Dispenses medication, advises on drug interactions, and counsels patients.
- Lawyer: Represents clients in legal matters, provides legal advice, and prepares legal documents.
- Engineer: Designs, develops, and tests new products, structures, and systems.
- Architect: Designs buildings and other structures, ensuring they are safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
- Accountant: Manages financial records, prepares taxes, and advises on financial matters.
- Financial Analyst: Analyzes financial data to guide investment decisions and business strategies.
- Software Developer: Creates, tests, and maintains software applications and systems.
- Graphic Designer: Creates visual content for print and digital media using design software.
- Web Developer: Builds and maintains websites and web applications.
- Data Scientist: Analyzes complex data to extract insights and help inform business decisions.
- Chef: Prepares meals in restaurants or other food establishments, often creating new recipes.
- Baker: Bakes bread, cakes, and pastries, often working in bakeries or restaurants.
- Waiter/Waitress: Serves food and drinks to customers in a restaurant.
- Bartender: Mixes and serves drinks at bars, restaurants, or events.
- Electrician: Installs and repairs electrical systems in homes, businesses, and factories.
- Plumber: Installs and repairs pipes and fixtures for water, gas, and sewage systems.
- Carpenter: Builds, installs, and repairs structures made of wood and other materials.
- Mechanic: Repairs and maintains vehicles and machinery.
- Construction Worker: Performs various tasks on construction sites, such as building, loading, and demolition.
- Police Officer: Enforces laws, maintains public order, and protects citizens.
- Firefighter: Extinguishes fires, rescues people, and provides emergency medical services.
- Paramedic: Provides emergency medical care and transportation to patients.
- Pilot: Operates aircraft to transport passengers or cargo.
- Flight Attendant: Ensures passenger safety and comfort on flights.
- Taxi Driver: Transports passengers to their destinations in a taxi or ride-share vehicle.
- Bus Driver: Drives buses to transport passengers on scheduled routes.
- Train Conductor: Oversees the operation of passenger or freight trains.
- Real Estate Agent: Assists clients in buying, selling, and renting properties.
- Property Manager: Manages rental properties, handling tenant relations and maintenance.
- Journalist: Investigates, writes, and reports news stories for media outlets.
- Photographer: Captures images for various purposes, including commercial, artistic, and personal use.
- Videographer: Records and edits video footage for various media productions.
- Editor: Reviews and revises content for publications, ensuring accuracy and clarity.
- Author: Writes books, articles, or other literary works.
- Librarian: Manages library resources, assists patrons, and organizes information.
- Scientist: Conducts research and experiments to advance knowledge in various fields.
- Researcher: Investigates specific topics to gather data and draw conclusions.
- Biologist: Studies living organisms and their interactions with the environment.
- Chemist: Analyzes substances and chemical reactions to develop new products or knowledge.
- Physicist: Studies the properties and interactions of matter and energy.
- Psychologist: Studies mental processes and behavior, providing therapy and counseling.
- Therapist: Provides mental health treatment to individuals or groups.
- Social Worker: Supports individuals and families in overcoming challenges and improving their well-being.
- Veterinarian: Provides medical care to animals, including diagnosis, treatment, and surgery.
- Farmer: Grows crops and raises animals for food production.
- Fisherman: Catches fish and other aquatic animals for commercial or recreational purposes.
- Retail Salesperson: Sells products to customers in a retail setting.
- Cashier: Handles transactions at points of sale, processing payments and providing receipts.
- Customer Service Representative: Assists customers with inquiries, complaints, and support.
- Marketing Manager: Develops and implements marketing strategies to promote products or services.
- Public Relations Specialist: Manages the public image and communication strategies of organizations or individuals.
- Human Resources Manager: Oversees hiring, training, and employee relations within an organization.
- Event Planner: Organizes and coordinates events, such as weddings, conferences, and parties.
- Hotel Manager: Manages hotel operations, ensuring guest satisfaction and efficient functioning.
- Travel Agent: Plans and arranges travel itineraries and bookings for clients.
- Personal Trainer: Provides fitness training and advice to clients, often in a gym or private setting.
- Fitness Instructor: Leads group exercise classes, such as yoga, aerobics, or Pilates.
- Yoga Teacher: Instructs students in yoga practices, promoting physical and mental well-being.
- Musician: Performs, composes, and records music.
- Actor/Actress: Performs in films, television, theater, or other productions.
- Dancer: Performs dance routines for entertainment or artistic expression.
How to Pronounce “Occupation”
The word “occupation” can be broken down into syllables to help with pronunciation. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Break it into syllables: oc-cu-pa-tion
- Pronounce each syllable:
- Oc: Say “ok” as in “sock” but without the “s”.
- Cu: Say “kyoo” like the letter “Q”.
- Pa: Say “pay”.
- Tion: Say “shun”.
- Combine the syllables:
- “Ok-kyoo-pay-shun”
How to Answer “What is your occupation?”
- Be Specific: Clearly state your job title and provide a brief description of your role.
- Highlight Key Responsibilities: Mention your main duties and responsibilities to give a fuller picture of your occupation.
- Use Simple Language: Avoid jargon or technical terms that might be unfamiliar to the listener.
- Relate to the Listener: Tailor your answer to the context and the person asking the question.
How to Answer in Different Contexts
In a Casual Setting:
- “I teach English to high school students. It’s rewarding to help them improve their language skills and appreciate literature.”
In a Professional Setting:
- “I am a high school English teacher, responsible for designing curriculum, delivering engaging lessons, and evaluating student performance to ensure academic growth.”
Example Answers
For a Teacher:
- “I am an English teacher. I teach language arts to high school students, focusing on improving their reading, writing, and critical thinking skills.”
For a Software Developer:
- “I am a software developer. I design and create software applications, focusing on improving user experiences and solving technical problems.”
For a Marketing Manager:
- “I am a marketing manager. I develop and implement marketing strategies to promote products and services, aiming to increase brand awareness and drive sales.”
For a Nurse:
- “I am a nurse. I provide medical care and support to patients, working closely with doctors to ensure the best possible treatment outcomes.”
Types of Occupation
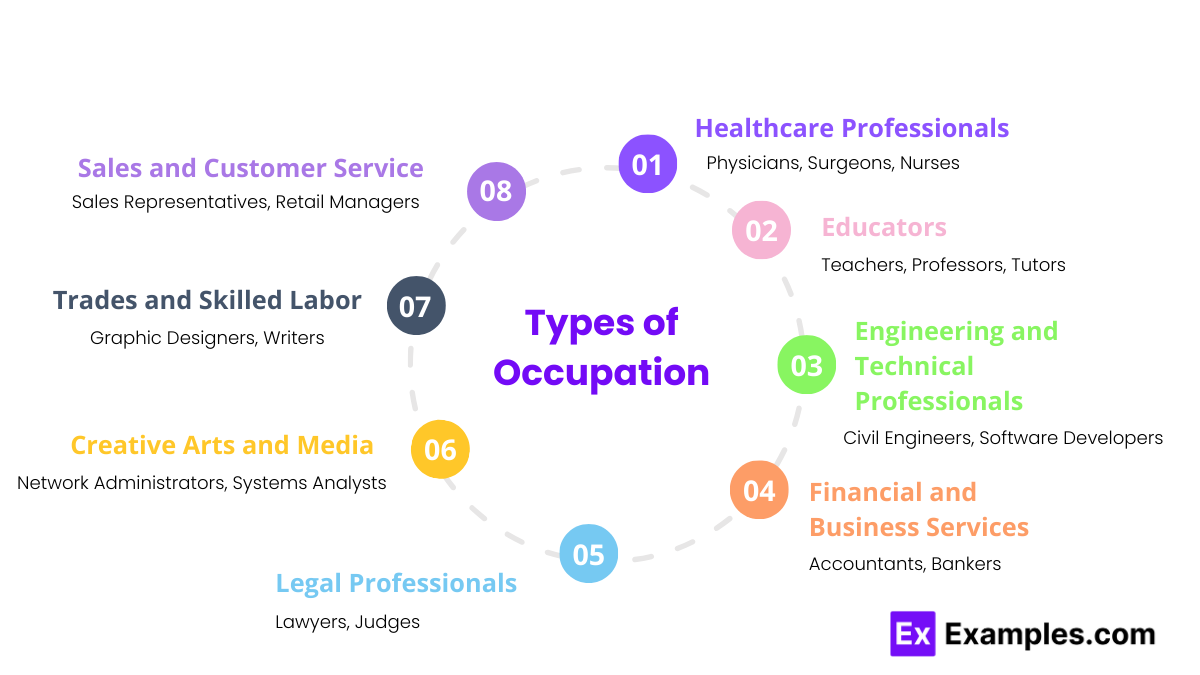
Occupations encompass a wide range of activities and roles within society. Here are ten common types of occupations, each playing a crucial role in the functioning and development of communities.
1. Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals include doctors, nurses, and therapists who provide medical care to patients. Their roles are vital in diagnosing, treating, and preventing illnesses.
Examples:
- Physicians
- Surgeons
- Nurses
- Pharmacists
- Physical Therapists
2. Educators
Educators impart knowledge and skills to students at various levels, from primary education to higher education. They play a significant role in shaping future generations.
Examples:
- Teachers
- Professors
- Tutors
- School Administrators
- Counselors
3. Engineering and Technical Professionals
These professionals apply scientific and mathematical principles to solve technical problems. Their work ranges from designing infrastructure to developing software.
Examples:
- Civil Engineers
- Software Developers
- Mechanical Engineers
- Electrical Engineers
- Architects
4. Financial and Business Services
Professionals in this field manage money, provide financial advice, and help businesses operate efficiently. Their expertise ensures the economic stability of organizations and individuals.
Examples:
- Accountants
- Financial Analysts
- Bankers
- Business Consultants
- Marketing Managers
5. Legal Professionals
Legal professionals interpret and apply the law. They represent clients, draft legal documents, and ensure justice is served.
Examples:
- Lawyers
- Judges
- Paralegals
- Legal Assistants
- Notaries
6. Information Technology (IT) Specialists
IT specialists manage and support computer systems and networks. They are essential in maintaining the digital infrastructure of businesses and organizations.
Examples:
- Network Administrators
- IT Support Specialists
- Cybersecurity Analysts
- Systems Analysts
- Database Administrators
7. Creative Arts and Media
Professionals in this field produce creative content, including visual art, music, literature, and film. They contribute to cultural and entertainment industries.
Examples:
- Graphic Designers
- Writers
- Musicians
- Film Directors
- Journalists
8. Trades and Skilled Labor
Tradespeople and skilled laborers perform specialized tasks that require manual skills and technical knowledge. They are essential in construction, manufacturing, and maintenance.
Examples:
- Electricians
- Plumbers
- Carpenters
- Welders
- Mechanics
9. Sales and Customer Service
These professionals engage with customers to sell products and services, and ensure customer satisfaction. Their roles are crucial in maintaining business-client relationships.
Examples:
- Sales Representatives
- Customer Service Agents
- Retail Managers
- Real Estate Agents
- Call Center Operators
10. Public Services
Public service professionals work in government and non-profit organizations to provide essential services to the community. Their work supports public safety, welfare, and infrastructure.
Examples:
- Police Officers
- Firefighters
- Social Workers
- Public Health Officials
Occupations List
- Urban Planner: Designs and plans urban spaces, ensuring efficient use of land and resources.
- Zoologist: Studies animal behavior, physiology, and classification.
- Astrophysicist: Studies the physical properties of celestial bodies.
- Archaeologist: Studies human history through excavation and analysis of artifacts.
- Oceanographer: Studies the ocean and its processes, including marine life and ecosystems.
- Meteorologist: Studies weather patterns and forecasts weather conditions.
- Geologist: Studies the Earth’s physical structure and substances.
- Paleontologist: Studies fossils to understand the history of life on Earth.
- Anthropologist: Studies human societies, cultures, and their development.
- Sociologist: Studies social behavior and society’s development, structure, and functioning.
- Economist: Analyzes economic data to understand and forecast economic trends.
- Statistician: Analyzes data to solve problems in various fields.
- Actuary: Analyzes financial risks using mathematics and statistics.
- Mathematician: Conducts research to develop and understand mathematical principles.
- Linguist: Studies language and its structure, evolution, and use.
- Translator: Converts written material from one language to another.
- Interpreter: Converts spoken language in real-time from one language to another.
- Ethnographer: Studies cultures and people through fieldwork and observation.
- Curator: Manages collections of artwork, artifacts, or other items in museums and galleries.
- Archivist: Preserves and organizes historical documents and records.
- Conservator: Restores and preserves artifacts and artworks.
- Art Historian: Studies the history and development of visual arts.
- Art Critic: Analyzes and evaluates works of art.
- Fashion Designer: Creates clothing, accessories, and footwear.
- Costume Designer: Designs costumes for theater, film, and television productions.
- Interior Designer: Plans and designs interior spaces for functionality and aesthetics.
- Set Designer: Designs sets for theater, film, and television productions.
- Lighting Designer: Plans and implements lighting for performances and events.
- Sound Engineer: Manages sound production for recordings and live events.
- Producer: Oversees the production of films, television shows, and other media.
- Director: Oversees the creative aspects of a film, television show, or theater production.
- Screenwriter: Writes scripts for films, television shows, and other media.
- Animator: Creates animations for films, television, and video games.
- Voice Actor: Provides voices for animated characters and other a productions.
- Stunt Performer: Performs dangerous actions in films and television.
- Choreographer: Creates and arranges dance sequences.
- Model: Poses for photoshoots, advertisements, and fashion shows.
- Magician: Performs magic tricks and illusions for entertainment.
- Comedian: Performs stand-up comedy routines.
- Radio Host: Hosts radio shows, playing music and discussing various topics.
- Podcast Host: Produces and hosts podcast episodes on various topics.
- News Anchor: Presents news stories on television or radio.
- TV Presenter: Hosts television shows and segments.
- Sports Commentator: Provides live commentary and analysis of sports events.
- Sports Coach: Trains and guides athletes and sports teams.
- Personal Shopper: Assists clients with selecting and purchasing clothing and other items.
- Sommelier: Expert in wine, advising on selections and pairings.
- Barista: Prepares and serves coffee and other beverages in cafes.
- Chocolatier: Creates and sells chocolate confections.
- Florist: Arranges and sells flowers and floral arrangements.
- Landscaper: Designs and maintains outdoor spaces and gardens.
- Horticulturist: Studies and cultivates plants for gardening and agriculture.
- Forester: Manages and conserves forested areas.
- Environmental Scientist: Studies and develops solutions to environmental problems.
- Ecologist: Studies ecosystems and the relationships between organisms and their environment.
- Wildlife Biologist: Studies wildlife and their habitats.
- Agricultural Scientist: Researches ways to improve agricultural practices and crop production.
- Food Scientist: Studies food processing, safety, and nutrition.
- Nutritionist: Advises on diet and nutrition for health and wellness.
- Dietitian: Provides medical nutrition therapy and dietary advice.
- Occupational Therapist: Helps patients develop, recover, and improve skills needed for daily living.
- Speech Therapist: Diagnoses and treats speech and communication disorders.
- Audiologist: Diagnoses and treats hearing and balance disorders.
- Optometrist: Provides eye care, including vision tests and prescribing glasses.
- Orthodontist: Specializes in correcting teeth and jaw alignment.
- Surgeon: Performs surgical procedures to treat injuries and diseases.
- Anesthesiologist: Administers anesthesia and manages pain during surgeries.
- Radiologist: Interprets medical images to diagnose diseases.
- Pathologist: Studies tissues, cells, and organs to diagnose diseases.
- Cardiologist: Specializes in diagnosing and treating heart conditions.
- Oncologist: Diagnoses and treats cancer.
- Neurologist: Treats disorders of the nervous system.
- Endocrinologist: Treats hormone-related disorders.
- Dermatologist: Treats skin conditions.
- Pediatrician: Provides medical care for children.
- Geriatrician: Provides medical care for elderly patients.
- Psychiatrist: Diagnoses and treats mental health disorders.
- Counselor: Provides guidance and support for personal and psychological issues.
- Marriage and Family Therapist: Provides therapy to individuals, couples, and families.
- Substance Abuse Counselor: Supports individuals in overcoming addiction.
- Rehabilitation Counselor: Assists individuals with disabilities in achieving personal and vocational goals.
- Forensic Scientist: Analyzes physical evidence for criminal investigations.
- Criminal Investigator: Conducts investigations to solve crimes.
- Probation Officer: Supervises offenders on probation to ensure compliance with court orders.
- Correctional Officer: Oversees individuals in correctional facilities.
- Security Guard: Protects property and individuals by maintaining security.
- Private Investigator: Conducts investigations for private clients.
- Bailiff: Maintains order in courtrooms and enforces court orders.
- Judge: Presides over legal proceedings and makes decisions based on the law.
- Paralegal: Assists lawyers with legal research and document preparation.
- Legal Secretary: Provides administrative support to lawyers and law firms.
- Court Reporter: Transcribes spoken or recorded speech during legal proceedings.
- Mediator: Facilitates negotiations and conflict resolution between parties.
- Urban Farmer: Grows crops and raises animals in urban areas.
- Beekeeper: Manages bee colonies to produce honey and other products.
- Rancher: Raises livestock for meat, dairy, and other products.
- Fisheries Biologist: Studies fish populations and aquatic ecosystems.
- Aquaculturist: Cultivates fish and other aquatic organisms for commercial purposes.
- Game Warden: Enforces laws related to wildlife and natural resources.
Key Aspects of Occupation
1. Roles and Responsibilities
Each occupation comes with specific roles and responsibilities that define what is expected of the individual. These roles can vary widely based on the nature of the occupation and the context in which it is performed. For example, a teacher’s responsibilities include preparing lessons, grading papers, and providing support to students.
2. Skills and Competencies
Occupations require various skills and competencies, which can be technical, interpersonal, or cognitive. These skills are often developed through education, training, and experience. For instance, a software developer needs programming skills, while a nurse needs medical knowledge and patient care skills.
3. Work Environment
The environment in which an occupation is performed can significantly impact job satisfaction and performance. Work environments can be physical spaces like offices, factories, and homes, or virtual spaces for remote jobs. Factors such as ergonomics, noise levels, and workplace culture also play a crucial role.
4. Economic and Social Impact
Occupations have a substantial impact on both the economy and society. Employment provides financial stability for individuals and families, contributes to economic growth, and supports public services through taxes. Additionally, volunteer work and caregiving roles have significant social value, enhancing community well-being.
5. Work-Life Balance
Balancing occupational responsibilities with personal life is essential for maintaining overall well-being. Effective time management, flexible working hours, and supportive work policies help individuals achieve a healthy work-life balance, reducing stress and improving quality of life.
6. Career Development
Career development involves the ongoing process of managing one’s occupational journey through lifelong learning, skill enhancement, and career planning. It includes exploring new opportunities, setting career goals, and adapting to changes in the job market.
7. Occupational Health and Safety
Ensuring a safe and healthy work environment is crucial for preventing injuries and illnesses. Occupational health and safety regulations and practices help protect workers from hazards and promote a culture of safety in the workplace.
8. Job Satisfaction and Motivation
Job satisfaction and motivation are key determinants of occupational success and personal fulfillment. Factors influencing job satisfaction include recognition, job security, work-life balance, and opportunities for growth. Motivated employees are more productive, engaged, and committed to their roles.
9. Cultural and Societal Influences
Cultural and societal norms influence perceptions of various occupations and shape individuals’ career choices. Societal values, economic conditions, and cultural beliefs all play a role in determining which occupations are respected, desired, or considered essential.
The difference between occupations, jobs, careers and professions
| Aspect | Occupation | Job | Career | Profession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A broad category of work that involves similar tasks and responsibilities. | A specific position of employment within an occupation or company. | The progression of related jobs over a person’s lifetime. | A vocation that requires specialized education and training. |
| Examples | Teaching, Engineering, Healthcare | High school teacher at ABC High School, Software Engineer at XYZ Inc. | A teacher moving from high school to university level. | Doctor, Lawyer, Architect |
| Focus | General area of work | Specific tasks and responsibilities | Long-term professional development and growth | Ethical standards, expertise, and a commitment to service |
| Time Frame | Long-term or lifetime | Short-term or until the contract ends | Spans over a lifetime with various roles and experiences | Long-term commitment and continuous professional development |
| Training Required | Varies, generally formal education or training needed | On-the-job training, specific to the position | Continuous learning and skill development | Extensive formal education, certification, and licensure |
| Scope | Broad and includes various jobs | Narrow, specific to the role | Comprehensive, includes multiple jobs within an occupation | Specialized, focused on a particular field |
| Goal | To be employed in a field of interest | To perform specific tasks for compensation | To achieve professional growth and fulfillment | To provide specialized services adhering to high standards |
| Stability | Moderate to high, as it includes various jobs | Varies, can be temporary or permanent | High, as it encompasses the entire professional life | High, due to the necessity of continuous education and adherence to standards |
| Commitment Level | Varies, but generally lower than a career or profession | Low to medium, depending on the nature of the job | High, due to long-term goals and aspirations | Very high, due to the dedication to maintaining standards and expertise |
Importance of Occupation
Economic Stability
Occupations are fundamental in providing individuals with a source of income, ensuring economic stability for themselves and their families.
Social Identity
Occupations often define social status and identity, contributing to how individuals perceive themselves and how they are perceived by others.
Skill Development
Occupations allow individuals to develop and refine skills, contributing to personal and professional growth.
Community Contribution
Through their work, individuals contribute to the community and society, providing necessary services and products.
Personal Fulfillment
Many people find personal satisfaction and fulfillment in their occupations, contributing to overall well-being and mental health.
Economic Growth
A diverse range of occupations supports economic growth by driving innovation, productivity, and competitiveness.
Social Mobility
Occupations provide opportunities for upward social mobility, allowing individuals to improve their socioeconomic status through education and career advancement.
Social Structure
Occupations help in maintaining social structures by defining roles and responsibilities within society.
Public Services
Occupations in fields such as healthcare, education, and public safety are essential for the well-being and functioning of society.
Cultural Significance
Occupations often carry cultural significance, influencing traditions, norms, and values within a community.
The Impact of Occupation on overall well-being
Occupation significantly influences overall well-being by shaping daily experiences, financial stability, and personal identity. A fulfilling job can enhance mental health, provide a sense of purpose, and foster social connections, all of which contribute to emotional well-being. Financial security gained through stable employment reduces stress and supports physical health by enabling access to quality healthcare and a healthy lifestyle. Conversely, job dissatisfaction, unemployment, or stressful work environments can lead to chronic stress, anxiety, and physical health issues. Therefore, the nature of one’s occupation plays a crucial role in determining overall life satisfaction and health outcomes.
Synonyms for “Occupation”
| Synonym | Synonym |
|---|---|
| Job | Profession |
| Career | Vocation |
| Employment | Work |
| Trade | Line of work |
| Field | Position |
| Role | Calling |
| Pursuit | Business |
What is an occupation?
An occupation is a person’s regular work or profession, typically performed for payment, such as teaching, engineering, or nursing.
Why is occupation important?
Occupation provides financial stability, personal fulfillment, and contributes to societal development through various roles and responsibilities.
How do you choose an occupation?
Consider your interests, skills, values, job market trends, and educational background when choosing an occupation.
What are some examples of occupations?
Examples include doctor, teacher, engineer, lawyer, artist, and software developer.
How can you advance in your occupation?
Advance through continuous learning, networking, gaining experience, and improving skills relevant to your field.
What is the difference between occupation and career?
Occupation refers to a specific job, while a career is the progression of related jobs and experiences over time.
How does education impact occupation?
Education provides the necessary knowledge and skills, opening up more opportunities and higher-paying occupations.
What is occupational health and safety?
Occupational health and safety involves practices to ensure a safe and healthy work environment, preventing injuries and illnesses.
How can you balance occupation and personal life?
Balance by setting boundaries, managing time effectively, and prioritizing self-care and personal activities.
What are the future trends in occupations?
Future trends include remote work, automation, and the rise of technology-driven jobs in fields like AI, cybersecurity, and renewable energy.
200+ Occupation Examples
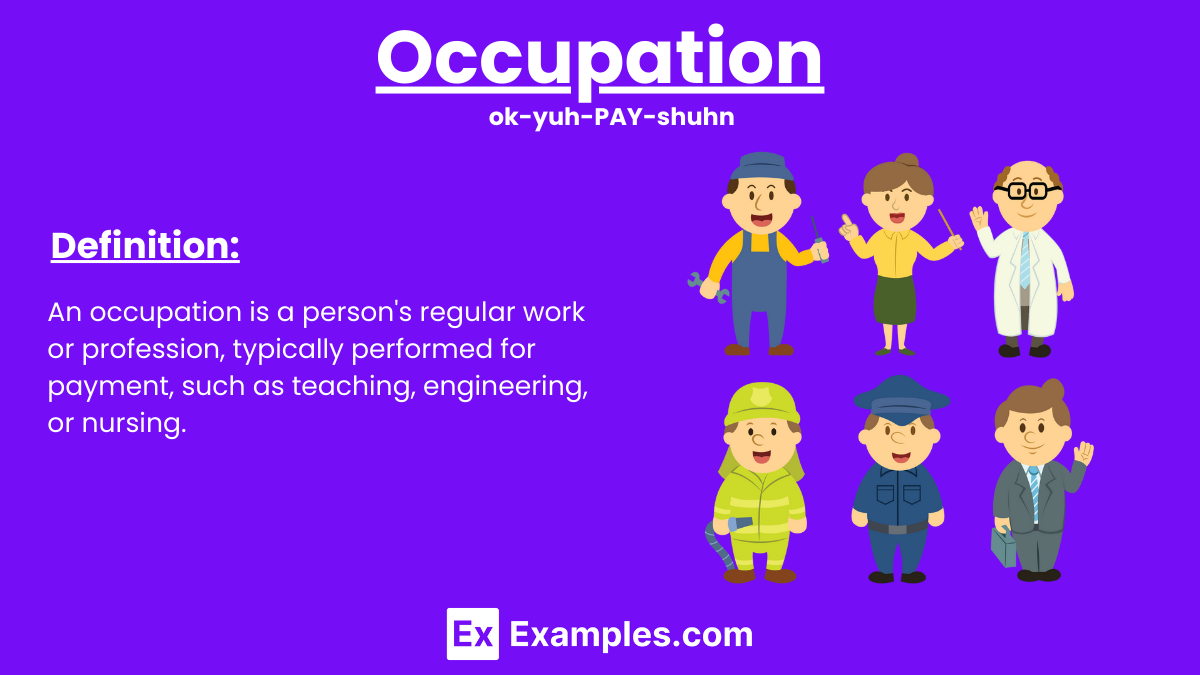
An occupation is a person’s regular work or profession. It provides income and defines a role in society. Occupations range from skilled trades like carpentry and plumbing to professional roles such as doctors, lawyers, and teachers. Each occupation requires specific skills, education, and training. Understanding various occupations helps individuals make informed career choices, enhances economic productivity, and fosters a sense of purpose and identity. This article explores different types of occupations, the importance of career planning, and the impact of job satisfaction and Job Risk Assessment on overall well-being. Dive in to learn more about the diverse world of work and how to navigate it effectively.
Definition of Occupation
Occupation refers to the regular activity or profession that a person engages in, typically to earn a living. It encompasses various types of work, roles, Carrier or duties performed by an individual. Occupations can range from manual labor and skilled trades to professional careers and managerial positions.
Occupation Examples
Teacher: Educates students in various subjects at different educational levels.
Doctor: Diagnoses and treats illnesses, prescribes medication, and provides healthcare advice.
Nurse: Provides patient care, administers medication, and assists doctors.
Dentist: Treats oral health issues, including teeth, gums, and mouth diseases.
Pharmacist: Dispenses medication, advises on drug interactions, and counsels patients.
Lawyer: Represents clients in legal matters, provides legal advice, and prepares legal documents.
Engineer: Designs, develops, and tests new products, structures, and systems.
Architect: Designs buildings and other structures, ensuring they are safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
Accountant: Manages financial records, prepares taxes, and advises on financial matters.
Financial Analyst: Analyzes financial data to guide investment decisions and business strategies.
Software Developer: Creates, tests, and maintains software applications and systems.
Graphic Designer: Creates visual content for print and digital media using design software.
Web Developer: Builds and maintains websites and web applications.
Data Scientist: Analyzes complex data to extract insights and help inform business decisions.
Chef: Prepares meals in restaurants or other food establishments, often creating new recipes.
Baker: Bakes bread, cakes, and pastries, often working in bakeries or restaurants.
Waiter/Waitress: Serves food and drinks to customers in a restaurant.
Bartender: Mixes and serves drinks at bars, restaurants, or events.
Electrician: Installs and repairs electrical systems in homes, businesses, and factories.
Plumber: Installs and repairs pipes and fixtures for water, gas, and sewage systems.
Carpenter: Builds, installs, and repairs structures made of wood and other materials.
Mechanic: Repairs and maintains vehicles and machinery.
Construction Worker: Performs various tasks on construction sites, such as building, loading, and demolition.
Police Officer: Enforces laws, maintains public order, and protects citizens.
Firefighter: Extinguishes fires, rescues people, and provides emergency medical services.
Paramedic: Provides emergency medical care and transportation to patients.
Pilot: Operates aircraft to transport passengers or cargo.
Flight Attendant: Ensures passenger safety and comfort on flights.
Taxi Driver: Transports passengers to their destinations in a taxi or ride-share vehicle.
Bus Driver: Drives buses to transport passengers on scheduled routes.
Train Conductor: Oversees the operation of passenger or freight trains.
Real Estate Agent: Assists clients in buying, selling, and renting properties.
Property Manager: Manages rental properties, handling tenant relations and maintenance.
Journalist: Investigates, writes, and reports news stories for media outlets.
Photographer: Captures images for various purposes, including commercial, artistic, and personal use.
Videographer: Records and edits video footage for various media productions.
Editor: Reviews and revises content for publications, ensuring accuracy and clarity.
Author: Writes books, articles, or other literary works.
Librarian: Manages library resources, assists patrons, and organizes information.
Scientist: Conducts research and experiments to advance knowledge in various fields.
Researcher: Investigates specific topics to gather data and draw conclusions.
Biologist: Studies living organisms and their interactions with the environment.
Chemist: Analyzes substances and chemical reactions to develop new products or knowledge.
Physicist: Studies the properties and interactions of matter and energy.
Psychologist: Studies mental processes and behavior, providing therapy and counseling.
Therapist: Provides mental health treatment to individuals or groups.
Social Worker: Supports individuals and families in overcoming challenges and improving their well-being.
Veterinarian: Provides medical care to animals, including diagnosis, treatment, and surgery.
Farmer: Grows crops and raises animals for food production.
Fisherman: Catches fish and other aquatic animals for commercial or recreational purposes.
Retail Salesperson: Sells products to customers in a retail setting.
Cashier: Handles transactions at points of sale, processing payments and providing receipts.
Customer Service Representative: Assists customers with inquiries, complaints, and support.
Marketing Manager: Develops and implements marketing strategies to promote products or services.
Public Relations Specialist: Manages the public image and communication strategies of organizations or individuals.
Human Resources Manager: Oversees hiring, training, and employee relations within an organization.
Event Planner: Organizes and coordinates events, such as weddings, conferences, and parties.
Hotel Manager: Manages hotel operations, ensuring guest satisfaction and efficient functioning.
Travel Agent: Plans and arranges travel itineraries and bookings for clients.
Personal Trainer: Provides fitness training and advice to clients, often in a gym or private setting.
Fitness Instructor: Leads group exercise classes, such as yoga, aerobics, or Pilates.
Yoga Teacher: Instructs students in yoga practices, promoting physical and mental well-being.
Musician: Performs, composes, and records music.
Actor/Actress: Performs in films, television, theater, or other productions.
Dancer: Performs dance routines for entertainment or artistic expression.
How to Pronounce “Occupation”
The word “occupation” can be broken down into syllables to help with pronunciation. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Break it into syllables: oc-cu-pa-tion
Pronounce each syllable:
Oc: Say “ok” as in “sock” but without the “s”.
Cu: Say “kyoo” like the letter “Q”.
Pa: Say “pay”.
Tion: Say “shun”.
Combine the syllables:
“Ok-kyoo-pay-shun”
How to Answer “What is your occupation?”
Be Specific: Clearly state your job title and provide a brief description of your role.
Highlight Key Responsibilities: Mention your main duties and responsibilities to give a fuller picture of your occupation.
Use Simple Language: Avoid jargon or technical terms that might be unfamiliar to the listener.
Relate to the Listener: Tailor your answer to the context and the person asking the question.
How to Answer in Different Contexts
In a Casual Setting:
“I teach English to high school students. It’s rewarding to help them improve their language skills and appreciate literature.”
In a Professional Setting:
“I am a high school English teacher, responsible for designing curriculum, delivering engaging lessons, and evaluating student performance to ensure academic growth.”
Example Answers
For a Teacher:
“I am an English teacher. I teach language arts to high school students, focusing on improving their reading, writing, and critical thinking skills.”
For a Software Developer:
“I am a software developer. I design and create software applications, focusing on improving user experiences and solving technical problems.”
For a Marketing Manager:
“I am a marketing manager. I develop and implement marketing strategies to promote products and services, aiming to increase brand awareness and drive sales.”
For a Nurse:
“I am a nurse. I provide medical care and support to patients, working closely with doctors to ensure the best possible treatment outcomes.”
Types of Occupation
Occupations encompass a wide range of activities and roles within society. Here are ten common types of occupations, each playing a crucial role in the functioning and development of communities.
1. Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals include doctors, nurses, and therapists who provide medical care to patients. Their roles are vital in diagnosing, treating, and preventing illnesses.
Examples:
Physicians
Surgeons
Nurses
Pharmacists
Physical Therapists
2. Educators
Educators impart knowledge and skills to students at various levels, from primary education to higher education. They play a significant role in shaping future generations.
Examples:
Teachers
Professors
Tutors
School Administrators
Counselors
3. Engineering and Technical Professionals
These professionals apply scientific and mathematical principles to solve technical problems. Their work ranges from designing infrastructure to developing software.
Examples:
Civil Engineers
Software Developers
Mechanical Engineers
Electrical Engineers
Architects
4. Financial and Business Services
Professionals in this field manage money, provide financial advice, and help businesses operate efficiently. Their expertise ensures the economic stability of organizations and individuals.
Examples:
Accountants
Financial Analysts
Bankers
Business Consultants
Marketing Managers
5. Legal Professionals
Legal professionals interpret and apply the law. They represent clients, draft legal documents, and ensure justice is served.
Examples:
Lawyers
Judges
Paralegals
Legal Assistants
Notaries
6. Information Technology (IT) Specialists
IT specialists manage and support computer systems and networks. They are essential in maintaining the digital infrastructure of businesses and organizations.
Examples:
Network Administrators
IT Support Specialists
Cybersecurity Analysts
Systems Analysts
Database Administrators
7. Creative Arts and Media
Professionals in this field produce creative content, including visual art, music, literature, and film. They contribute to cultural and entertainment industries.
Examples:
Graphic Designers
Writers
Musicians
Film Directors
Journalists
8. Trades and Skilled Labor
Tradespeople and skilled laborers perform specialized tasks that require manual skills and technical knowledge. They are essential in construction, manufacturing, and maintenance.
Examples:
Electricians
Plumbers
Carpenters
Welders
Mechanics
9. Sales and Customer Service
These professionals engage with customers to sell products and services, and ensure customer satisfaction. Their roles are crucial in maintaining business-client relationships.
Examples:
Sales Representatives
Customer Service Agents
Retail Managers
Real Estate Agents
Call Center Operators
10. Public Services
Public service professionals work in government and non-profit organizations to provide essential services to the community. Their work supports public safety, welfare, and infrastructure.
Examples:
Police Officers
Firefighters
Social Workers
Public Health Officials
Occupations List
Urban Planner: Designs and plans urban spaces, ensuring efficient use of land and resources.
Zoologist: Studies animal behavior, physiology, and classification.
Astrophysicist: Studies the physical properties of celestial bodies.
Archaeologist: Studies human history through excavation and analysis of artifacts.
Oceanographer: Studies the ocean and its processes, including marine life and ecosystems.
Meteorologist: Studies weather patterns and forecasts weather conditions.
Geologist: Studies the Earth’s physical structure and substances.
Paleontologist: Studies fossils to understand the history of life on Earth.
Anthropologist: Studies human societies, cultures, and their development.
Sociologist: Studies social behavior and society’s development, structure, and functioning.
Economist: Analyzes economic data to understand and forecast economic trends.
Statistician: Analyzes data to solve problems in various fields.
Actuary: Analyzes financial risks using mathematics and statistics.
Mathematician: Conducts research to develop and understand mathematical principles.
Linguist: Studies language and its structure, evolution, and use.
Translator: Converts written material from one language to another.
Interpreter: Converts spoken language in real-time from one language to another.
Ethnographer: Studies cultures and people through fieldwork and observation.
Curator: Manages collections of artwork, artifacts, or other items in museums and galleries.
Archivist: Preserves and organizes historical documents and records.
Conservator: Restores and preserves artifacts and artworks.
Art Historian: Studies the history and development of visual arts.
Art Critic: Analyzes and evaluates works of art.
Fashion Designer: Creates clothing, accessories, and footwear.
Costume Designer: Designs costumes for theater, film, and television productions.
Interior Designer: Plans and designs interior spaces for functionality and aesthetics.
Set Designer: Designs sets for theater, film, and television productions.
Lighting Designer: Plans and implements lighting for performances and events.
Sound Engineer: Manages sound production for recordings and live events.
Producer: Oversees the production of films, television shows, and other media.
Director: Oversees the creative aspects of a film, television show, or theater production.
Screenwriter: Writes scripts for films, television shows, and other media.
Animator: Creates animations for films, television, and video games.
Voice Actor: Provides voices for animated characters and other a productions.
Stunt Performer: Performs dangerous actions in films and television.
Choreographer: Creates and arranges dance sequences.
Model: Poses for photoshoots, advertisements, and fashion shows.
Magician: Performs magic tricks and illusions for entertainment.
Comedian: Performs stand-up comedy routines.
Radio Host: Hosts radio shows, playing music and discussing various topics.
Podcast Host: Produces and hosts podcast episodes on various topics.
News Anchor: Presents news stories on television or radio.
TV Presenter: Hosts television shows and segments.
Sports Commentator: Provides live commentary and analysis of sports events.
Sports Coach: Trains and guides athletes and sports teams.
Personal Shopper: Assists clients with selecting and purchasing clothing and other items.
Sommelier: Expert in wine, advising on selections and pairings.
Barista: Prepares and serves coffee and other beverages in cafes.
Chocolatier: Creates and sells chocolate confections.
Florist: Arranges and sells flowers and floral arrangements.
Landscaper: Designs and maintains outdoor spaces and gardens.
Horticulturist: Studies and cultivates plants for gardening and agriculture.
Forester: Manages and conserves forested areas.
Environmental Scientist: Studies and develops solutions to environmental problems.
Ecologist: Studies ecosystems and the relationships between organisms and their environment.
Wildlife Biologist: Studies wildlife and their habitats.
Agricultural Scientist: Researches ways to improve agricultural practices and crop production.
Food Scientist: Studies food processing, safety, and nutrition.
Nutritionist: Advises on diet and nutrition for health and wellness.
Dietitian: Provides medical nutrition therapy and dietary advice.
Occupational Therapist: Helps patients develop, recover, and improve skills needed for daily living.
Speech Therapist: Diagnoses and treats speech and communication disorders.
Audiologist: Diagnoses and treats hearing and balance disorders.
Optometrist: Provides eye care, including vision tests and prescribing glasses.
Orthodontist: Specializes in correcting teeth and jaw alignment.
Surgeon: Performs surgical procedures to treat injuries and diseases.
Anesthesiologist: Administers anesthesia and manages pain during surgeries.
Radiologist: Interprets medical images to diagnose diseases.
Pathologist: Studies tissues, cells, and organs to diagnose diseases.
Cardiologist: Specializes in diagnosing and treating heart conditions.
Oncologist: Diagnoses and treats cancer.
Neurologist: Treats disorders of the nervous system.
Endocrinologist: Treats hormone-related disorders.
Dermatologist: Treats skin conditions.
Pediatrician: Provides medical care for children.
Geriatrician: Provides medical care for elderly patients.
Psychiatrist: Diagnoses and treats mental health disorders.
Counselor: Provides guidance and support for personal and psychological issues.
Marriage and Family Therapist: Provides therapy to individuals, couples, and families.
Substance Abuse Counselor: Supports individuals in overcoming addiction.
Rehabilitation Counselor: Assists individuals with disabilities in achieving personal and vocational goals.
Forensic Scientist: Analyzes physical evidence for criminal investigations.
Criminal Investigator: Conducts investigations to solve crimes.
Probation Officer: Supervises offenders on probation to ensure compliance with court orders.
Correctional Officer: Oversees individuals in correctional facilities.
Security Guard: Protects property and individuals by maintaining security.
Private Investigator: Conducts investigations for private clients.
Bailiff: Maintains order in courtrooms and enforces court orders.
Judge: Presides over legal proceedings and makes decisions based on the law.
Paralegal: Assists lawyers with legal research and document preparation.
Legal Secretary: Provides administrative support to lawyers and law firms.
Court Reporter: Transcribes spoken or recorded speech during legal proceedings.
Mediator: Facilitates negotiations and conflict resolution between parties.
Urban Farmer: Grows crops and raises animals in urban areas.
Beekeeper: Manages bee colonies to produce honey and other products.
Rancher: Raises livestock for meat, dairy, and other products.
Fisheries Biologist: Studies fish populations and aquatic ecosystems.
Aquaculturist: Cultivates fish and other aquatic organisms for commercial purposes.
Game Warden: Enforces laws related to wildlife and natural resources.
Key Aspects of Occupation
1. Roles and Responsibilities
Each occupation comes with specific roles and responsibilities that define what is expected of the individual. These roles can vary widely based on the nature of the occupation and the context in which it is performed. For example, a teacher’s responsibilities include preparing lessons, grading papers, and providing support to students.
2. Skills and Competencies
Occupations require various skills and competencies, which can be technical, interpersonal, or cognitive. These skills are often developed through education, training, and experience. For instance, a software developer needs programming skills, while a nurse needs medical knowledge and patient care skills.
3. Work Environment
The environment in which an occupation is performed can significantly impact job satisfaction and performance. Work environments can be physical spaces like offices, factories, and homes, or virtual spaces for remote jobs. Factors such as ergonomics, noise levels, and workplace culture also play a crucial role.
4. Economic and Social Impact
Occupations have a substantial impact on both the economy and society. Employment provides financial stability for individuals and families, contributes to economic growth, and supports public services through taxes. Additionally, volunteer work and caregiving roles have significant social value, enhancing community well-being.
5. Work-Life Balance
Balancing occupational responsibilities with personal life is essential for maintaining overall well-being. Effective time management, flexible working hours, and supportive work policies help individuals achieve a healthy work-life balance, reducing stress and improving quality of life.
6. Career Development
Career development involves the ongoing process of managing one’s occupational journey through lifelong learning, skill enhancement, and career planning. It includes exploring new opportunities, setting career goals, and adapting to changes in the job market.
7. Occupational Health and Safety
Ensuring a safe and healthy work environment is crucial for preventing injuries and illnesses. Occupational health and safety regulations and practices help protect workers from hazards and promote a culture of safety in the workplace.
8. Job Satisfaction and Motivation
Job satisfaction and motivation are key determinants of occupational success and personal fulfillment. Factors influencing job satisfaction include recognition, job security, work-life balance, and opportunities for growth. Motivated employees are more productive, engaged, and committed to their roles.
9. Cultural and Societal Influences
Cultural and societal norms influence perceptions of various occupations and shape individuals’ career choices. Societal values, economic conditions, and cultural beliefs all play a role in determining which occupations are respected, desired, or considered essential.
The difference between occupations, jobs, careers and professions
Aspect | Occupation | Job | Career | Profession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Definition | A broad category of work that involves similar tasks and responsibilities. | A specific position of employment within an occupation or company. | The progression of related jobs over a person’s lifetime. | A vocation that requires specialized education and training. |
Examples | Teaching, Engineering, Healthcare | High school teacher at ABC High School, Software Engineer at XYZ Inc. | A teacher moving from high school to university level. | Doctor, Lawyer, Architect |
Focus | General area of work | Specific tasks and responsibilities | Long-term professional development and growth | Ethical standards, expertise, and a commitment to service |
Time Frame | Long-term or lifetime | Short-term or until the contract ends | Spans over a lifetime with various roles and experiences | Long-term commitment and continuous professional development |
Training Required | Varies, generally formal education or training needed | On-the-job training, specific to the position | Continuous learning and skill development | Extensive formal education, certification, and licensure |
Scope | Broad and includes various jobs | Narrow, specific to the role | Comprehensive, includes multiple jobs within an occupation | Specialized, focused on a particular field |
Goal | To be employed in a field of interest | To perform specific tasks for compensation | To achieve professional growth and fulfillment | To provide specialized services adhering to high standards |
Stability | Moderate to high, as it includes various jobs | Varies, can be temporary or permanent | High, as it encompasses the entire professional life | High, due to the necessity of continuous education and adherence to standards |
Commitment Level | Varies, but generally lower than a career or profession | Low to medium, depending on the nature of the job | High, due to long-term goals and aspirations | Very high, due to the dedication to maintaining standards and expertise |
Importance of Occupation
Economic Stability
Occupations are fundamental in providing individuals with a source of income, ensuring economic stability for themselves and their families.
Social Identity
Occupations often define social status and identity, contributing to how individuals perceive themselves and how they are perceived by others.
Skill Development
Occupations allow individuals to develop and refine skills, contributing to personal and professional growth.
Community Contribution
Through their work, individuals contribute to the community and society, providing necessary services and products.
Personal Fulfillment
Many people find personal satisfaction and fulfillment in their occupations, contributing to overall well-being and mental health.
Economic Growth
A diverse range of occupations supports economic growth by driving innovation, productivity, and competitiveness.
Social Mobility
Occupations provide opportunities for upward social mobility, allowing individuals to improve their socioeconomic status through education and career advancement.
Social Structure
Occupations help in maintaining social structures by defining roles and responsibilities within society.
Public Services
Occupations in fields such as healthcare, education, and public safety are essential for the well-being and functioning of society.
Cultural Significance
Occupations often carry cultural significance, influencing traditions, norms, and values within a community.
The Impact of Occupation on overall well-being
Occupation significantly influences overall well-being by shaping daily experiences, financial stability, and personal identity. A fulfilling job can enhance mental health, provide a sense of purpose, and foster social connections, all of which contribute to emotional well-being. Financial security gained through stable employment reduces stress and supports physical health by enabling access to quality healthcare and a healthy lifestyle. Conversely, job dissatisfaction, unemployment, or stressful work environments can lead to chronic stress, anxiety, and physical health issues. Therefore, the nature of one’s occupation plays a crucial role in determining overall life satisfaction and health outcomes.
Synonyms for “Occupation”
Synonym | Synonym |
|---|---|
Job | Profession |
Career | Vocation |
Employment | Work |
Trade | Line of work |
Field | Position |
Role | Calling |
Pursuit | Business |
What is an occupation?
An occupation is a person’s regular work or profession, typically performed for payment, such as teaching, engineering, or nursing.
Why is occupation important?
Occupation provides financial stability, personal fulfillment, and contributes to societal development through various roles and responsibilities.
How do you choose an occupation?
Consider your interests, skills, values, job market trends, and educational background when choosing an occupation.
What are some examples of occupations?
Examples include doctor, teacher, engineer, lawyer, artist, and software developer.
How can you advance in your occupation?
Advance through continuous learning, networking, gaining experience, and improving skills relevant to your field.
What is the difference between occupation and career?
Occupation refers to a specific job, while a career is the progression of related jobs and experiences over time.
How does education impact occupation?
Education provides the necessary knowledge and skills, opening up more opportunities and higher-paying occupations.
What is occupational health and safety?
Occupational health and safety involves practices to ensure a safe and healthy work environment, preventing injuries and illnesses.
How can you balance occupation and personal life?
Balance by setting boundaries, managing time effectively, and prioritizing self-care and personal activities.
What are the future trends in occupations?
Future trends include remote work, automation, and the rise of technology-driven jobs in fields like AI, cybersecurity, and renewable energy.


