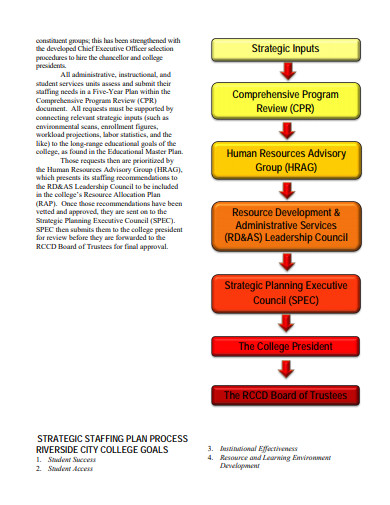
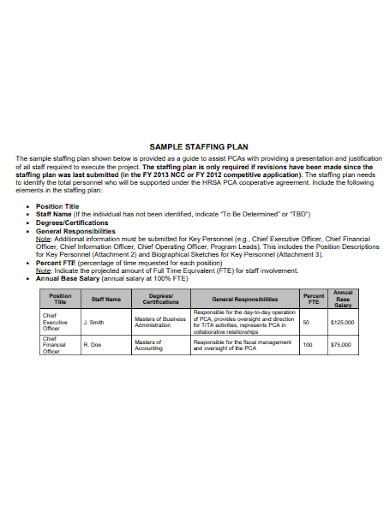
10+ Staffing Plan Examples to Download
Most professionals started as an employee at the lowest organizational level of a company. As time passed by, they climbed the ladder and put themselves in a more secure spot. For those who don’t know, the satisfactory results of such careers are products of a business strategic process called workforce planning. Such a practice is under an HR action plan, project, or proposal that deals with a certain company’s staffing needs through its various staffing strategies. It is very much applicable to all lines of business, especially on manufacturing, healthcare, and call center. If you lack a few staff for a particular department of your company, then don’t waste time and develop a staffing plan right away!
10+ Staffing Plan Examples
1. Restaurant Staffing Plan

2. Staffing Compensation Plan

3. Staffing or Recruiting Plan

4. Recruitment or Staffing Agency Business Plan

5. Human Resources Staffing Plan
6. Nonprofit Staffing Plan
7. Emergency Staffing Plan
8. Staffing Plan Checklist
9. Nurse Staffing Plan
10. Clinic Staffing Plan
11. Project Staffing Plan
What Is a Staffing Plan?
A staffing plan is a systematic scheming of activities and strategies that are relevant to onboarding or employee promotion. According to Wonolo, a job posting site, such a plan has to identify two crucial things – the accurate number of available job positions and the right professionals to fill the posts. For a company to determine these things, a well-ordered collaboration between its HR department and other departments concerned must take place. The plan may fall under a project action plan, employee action plan, or corrective action plan.
Common Staffing Problems and Their Workarounds
Every aspect of a business has its complications, and staffing is never an exception. Below are the three common staffing problems, along with their effective workarounds.
1. Employee Turnover – Employees come and go for various reasons, some of them are personal, and some of them are employer-related. Whatever the reason is, the solution to such a problem is communication. Through it, you can identify the main cause of the recent turnovers in your company. The results of your HR survey or job satisfaction survey will make way for agreements that may avoid the likeliness of turnover.
2. Overstaffing – There will be times when your company takes more people than it could handle. As a consequence, some employees will become uncertain of the functionalities of their positions, increasing the chances of turnovers. Not only that, but your company also wastes ample financial resources for unnecessary staff. The right solution to this problem is to reform your structure. You can start by conducting a job safety analysis, employee assessment, and company analysis.
3. Understaffing – Companies, sometimes, fall short in terms of workforce. This problem dramatically affects the overall performance of businesses, especially in regards to profitability and sustainability. To resolve this kind of problem, you have to get a recruitment or temp agency. Just by signing their recruitment agency contracts, you can have as many talents as you want.
How To Organize a Staffing Plan
To successfully organize your company’s staffing plan, you have to set your priorities straight on what must be done. Fortunately, we have our outline ready below. Before that, you may want to check out these HR Guidelines That Help You Manage Your People.
1. Identify Goals
Always start your plans by identifying your corporate goals. By doing so, give yourself a direction on which project paths to take. Business goal setting is mandatory for all kinds of plans, anyway.
2. Discover the Determiners
All actions are influenced by certain factors. The same thing goes with staffing plans. So, you have to know all of them, whether by internal or external validity. Once these determiners are discovered, you will have better control of your talent supply.
3. Study Unoccupied Positions’ Function
Don’t forget to conduct a project case study for your staffing plan. Involved in it is the examination of your company’s unoccupied positions’ functions. By knowing the roles and responsibilities of these posts, you can create your decision criteria for your recruitment.
4. Predict Necessities
With all the necessary data at hand, you can easily make your way to your prediction research, particularly about the necessities of your plan. Going through such research is one way to have an approximate of the needed budget.
5. Conduct a Gap Analysis
In this step, you identify the needed efforts to reach your desired outcome. Gap analysis is important to keep track of your every activity or performance.
6. Suit Solutions
Based on all the information you have gathered, set the solutions that you see fit for your staffing problems. For a favorable result, you might want to consider researching about staffing strategies.
FAQs
What are the different strategic staffing types?
Eric Dontigney of AZCentral identifies the different strategic staffing approaches as academy staffing, club staffing, fortress staffing, and baseball team staffing. Academy staffing refers to the provision of in-house training to fresh graduates and established employees. Club staffing, on the other hand, concerns the onboarding of professionals who have quite a general knowledge rather than specific ones. As for fortress staffing, it covers the pickiest type of recruitment, where only those with outstanding and business-relevant sets of skills will be employed. Such an approach is often used by companies that are on the brink of insolvency. The last approach, baseball team staffing, discusses the constant recruitment for high-performing professionals to fill positions at any level.
What are the major benefits of strategic staffing?
Strategic staffing not only anticipates future staffing problems but also systematically deals with recruitment-related human resource complications. Not to mention, it enables a company to make the best use of every staff.
What is the difference between staffing and recruitment?
Staffing and recruitment differ in many aspects, including its scope, duration, and levels. Staffing’s scope is wide, while recruitment is the complete opposite. Staffing is done for long-term goals while recruitment settles for short-term goals. Lastly, staffing is available for all levels of employment. Recruitment, on the other hand, is only for starters.
A company’s staff hold total control in all of its aspects. This is why the angle on staffing must not be taken for granted. Planning on such an area must be carefully set, and failure to do so means a large loss in company assets. Plus, a staffing plan provides a course to your actions, specifically towards success.