40+ Utility Bill Examples
A utility bill is a statement of charges for services like electricity, water, and gas. It includes the watt-hour consumption, representing energy use, and often a fixed cost for service maintenance and infrastructure. The bill details usage rates and total costs for the billing period.
What is a Utility Bill?
A utility bill is a statement provided to customers detailing the charges for essential services such as electricity, water, and gas. Similar to a Billing Invoice or Bill Receipt, it outlines the cost based on usage and any fixed fees. Unlike a Straight Bill of Lading or Transport Bill of Lading, which are documents used in shipping to detail cargo and logistics, a utility bill focuses on the consumption of utilities over a specified period and the corresponding charges.
Examples of Utility Bill
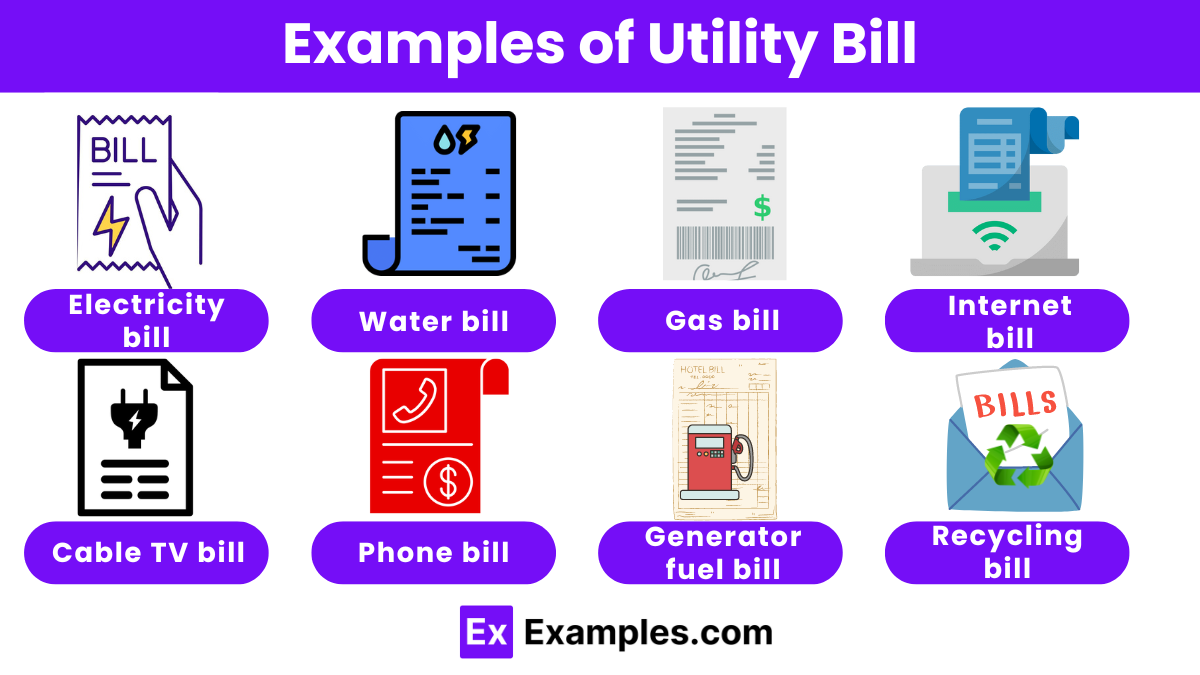
- Electricity bill: The electricity bill increased due to more air conditioner use.
- Water bill: This month’s water bill was lower after fixing the leaky faucet.
- Gas bill: The gas bill reflects the cost of heating during the winter months.
- Internet bill: The internet bill includes charges for high-speed service.
- Cable TV bill: The cable TV bill had an additional charge for premium channels.
- Sewer bill: The sewer bill is included in our monthly water bill.
- Trash collection bill: The trash collection bill covers weekly waste pickup services.
- Recycling bill: Our recycling bill includes a small fee for processing recyclable materials.
- Phone bill: The phone bill details our long-distance call charges.
- Heating oil bill: The heating oil bill was higher this month due to the cold weather.
- Propane bill: Our propane bill reflects the cost of refilling the tank for the grill.
- Home security bill: The home security bill includes monthly monitoring fees.
- HOA dues: The HOA dues cover community utilities like street lighting and irrigation.
- Solar panel bill: The solar panel bill shows savings on our regular electricity bill.
- Stormwater bill: The stormwater bill is a separate charge for managing runoff.
- Electric vehicle charging bill: The electric vehicle charging bill is for using public charging stations.
- Water softener bill: The water softener bill includes rental fees for the equipment.
- Pest control bill: The pest control bill covers monthly maintenance and treatments.
- Lawn irrigation bill: The lawn irrigation bill is part of our overall water usage.
- Firewood bill: The firewood bill is for the delivery and stacking of firewood.
- Generator fuel bill: The generator fuel bill shows the cost of keeping our backup generator ready.
- Snow removal bill: The snow removal bill is for plowing our driveway during heavy snowfalls.
- Pool maintenance bill: The pool maintenance bill includes cleaning and chemical treatments.
- Septic tank service bill: The septic tank service bill covers pumping and inspection services.
- Electric heating bill: The electric heating bill was higher during the cold months.
- Cooling bill: The cooling bill spikes in the summer due to air conditioning use.
- Electric fence bill: The electric fence bill includes installation and energy costs.
- Smart home service bill: The smart home service bill covers the monthly subscription for connected devices.
- Rainwater harvesting system bill: The rainwater harvesting system bill shows maintenance fees.
- Geothermal heating bill: The geothermal heating bill reflects the cost of using natural underground heat.
Examples of Utility Bill in Business
- Office electricity bill: The office electricity bill increased due to extended working hours and additional equipment.
- Commercial water bill: The commercial water bill reflects the water usage for the company’s restrooms and kitchen areas.
- Industrial gas bill: The industrial gas bill covers the fuel needed for manufacturing processes.
- Data center cooling bill: The data center cooling bill is significant due to the need to keep servers at optimal temperatures.
- Warehouse lighting bill: The warehouse lighting bill accounts for the extensive lighting required for operations.
- Factory steam bill: The factory steam bill includes costs for generating steam used in production.
- Retail store HVAC bill: The retail store HVAC bill increased due to seasonal temperature changes.
- Corporate internet bill: The corporate internet bill reflects charges for high-speed business internet services.
- Office building maintenance bill: The office building maintenance bill includes costs for essential utilities like heating, cooling, and plumbing.
- Commercial waste disposal bill: The commercial waste disposal bill covers regular pickup and disposal of business waste.
Reading and interpreting Utility Bills
1. Account Information
- Account Number: Unique identifier for your utility account.
- Billing Period: Dates covered by the current bill.
- Customer Information: Name and address of the account holder.
2. Summary of Charges
- Previous Balance: Amount carried over from the last bill.
- Payments Received: Payments made during the billing period.
- Current Charges: New charges incurred during the billing period.
- Total Amount Due: Total amount to be paid by the due date.
3. Usage Details
- Meter Readings: Starting and ending readings for the billing period.
- Consumption: Amount of utility used, often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) for electricity or gallons for water.
- Usage Graph: Visual representation of usage over time.
4. Charge Breakdown
- Fixed Cost: Flat fee for access to the utility service.
- Variable Charges: Costs based on the amount of utility used.
- Taxes and Fees: Additional government or service charges.
5. Payment Options
- Payment Methods: Ways to pay the bill (online, mail, in-person).
- Due Date: Deadline for payment to avoid late fees.
- Late Fees: Penalties for late payment.
Steps to Budgeting for Utility Expenses
1. Track Your Utility Bills
- Gather past utility bills for at least the past year.
- Record monthly costs for each utility service.
- Note seasonal variations (e.g., higher electricity bills in summer due to air conditioning).
2. Calculate Average Monthly Expenses
- Add up the total cost for each utility over the past year.
- Divide by 12 to find the average monthly cost for each utility.
3. Identify Patterns and Trends
- Look for patterns such as increased heating costs in winter or higher water usage in summer.
- Identify any spikes that may indicate inefficiencies or issues (e.g., water leaks).
4. Set a Monthly Utility Budget
- Based on the average monthly expenses and identified patterns, set a realistic budget for each utility.
- Allocate a bit more for months when higher usage is expected (e.g., budgeting more for heating in winter).
5. Implement Cost-Saving Measures
- Electricity: Use energy-efficient appliances, switch to LED bulbs, and unplug devices when not in use.
- Water: Fix leaks, install low-flow fixtures, and reduce water usage (e.g., shorter showers).
- Gas: Improve home insulation, maintain heating systems, and lower thermostat settings.
- Internet/Phone: Review plans for better deals, eliminate unnecessary services, and bundle services when possible.
- Trash: Recycle more to reduce waste disposal costs.
6. Monitor and Adjust Your Budget
- Regularly compare actual utility expenses to your budget.
- Adjust the budget as needed based on actual usage and any changes in rates or services.
Utility Bill for Bank Account
- Your Name: The bill should be addressed to you.
- Your Address: The address on the bill should match the address you provide to the bank.
- Billing Date: The bill should be recent, typically within the last three months.
- Utility Company Details: Name and contact information of the utility company.
- Account Number: Your unique account number with the utility company.
- Billing Summary: A summary of charges for the billing period.
Steps to Check Utility Bill
- Gather Your Bills: Collect recent utility bills (electricity, water, gas, etc.) for review.
- Verify Account Information: Ensure your name, address, and account number are correct.
- Check the Billing Period: Confirm that the billing period matches the expected dates.
- Review Usage Details: Compare the usage (kWh, gallons, etc.) with previous months to spot any irregularities.
- Examine Charge Breakdown: Review fixed costs, variable charges, taxes, and any additional fees.
- Look for Errors: Check for any discrepancies or unusual charges.
- Compare Rates: Ensure the rates match what your provider advertised.
- Confirm Payments: Verify that previous payments were correctly applied and reflected.
- Review Meter Readings: Check that the start and end meter readings are accurate.
- Contact Customer Service: If you find any errors, contact your utility provider’s customer service for clarification or dispute.
Types of Utility Bills
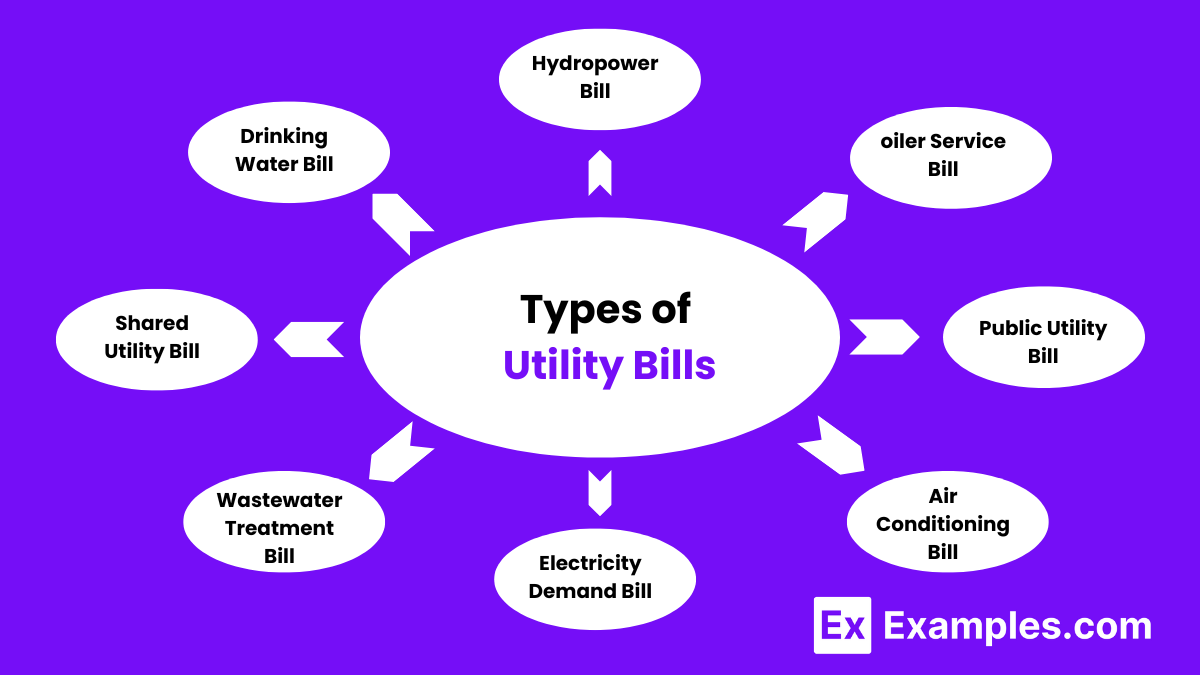
- Drinking Water Bill: Charges for potable water supply used for drinking, cooking, and bathing.
- Stormwater Management Bill: Fees for managing and treating stormwater runoff from properties.
- Street Lighting Bill: Charges for maintaining and operating streetlights in your area.
- Community Water Bill: Charges for water used in community spaces like parks and shared gardens.
- Hydropower Bill: Charges for electricity generated from hydroelectric power plants.
- Bottled Gas Bill: Costs for bottled gas (propane) used for cooking or heating in areas without natural gas lines.
- Boiler Service Bill: Fees for the maintenance and operation of boilers in buildings or industrial settings.
- Ventilation Bill: Charges for systems providing ventilation and air quality control in buildings.
- Cooling Tower Bill: Costs for the operation and maintenance of cooling towers in industrial and commercial buildings.
- Telecommunications Bill: Charges for bundled services, including internet, phone, and cable TV in a single bill.
- Public Utility Bill: Consolidated charges for various public utilities provided by local government or utility companies.
- Air Conditioning Bill: Costs specifically for central air conditioning services in large buildings.
- Home Heating Oil Bill: Charges for heating oil used in home heating systems, typically in rural areas.
- Solar Panel Maintenance Bill: Fees for the upkeep and repair of residential or commercial solar panel systems.
- Electricity Demand Bill: Charges based on peak electricity demand during specific periods, common in industrial settings.
- Wastewater Treatment Bill: Costs for treating and disposing of wastewater from homes or businesses.
- Emergency Generator Bill: Fees for maintaining and operating emergency backup generators.
- Shared Utility Bill: Consolidated charges for utilities shared among multiple tenants in a building or complex.
- Electrical Inspection Bill: Fees for regular inspections and certifications of electrical systems in buildings.
- Green Energy Bill: Additional costs for opting into renewable energy programs offered by utility companies.
List of Utility Bills
- Electricity Bill: Charges for electric power usage.
- Water Bill: Charges for water consumption.
- Natural Gas Bill: Charges for natural gas used for heating and cooking.
- Internet Bill: Charges for internet services.
- Telephone Bill: Charges for landline or mobile phone services.
- Cable TV/Satellite Bill: Charges for television services.
- Trash Collection Bill: Charges for garbage pickup and disposal.
- Sewer Bill: Charges for wastewater treatment and sewage services.
How to get a Utility Bill
1. Check Your Mail
- Paper Bills: Most utility companies send paper bills by mail each month. Look for your most recent utility bill in your mailbox.
2. Access Online Accounts
- Utility Company Website: Most utility companies provide online portals where you can view and download your bills.
- Log In: Use your account number and password to log in to the utility company’s website.
- Find Billing Section: Navigate to the billing or account statements section.
- Download or Print: Download a PDF copy of your bill or print it directly from the website.
3. Contact Customer Service
- Phone: Call the customer service number provided by your utility company and request a copy of your bill.
- Email: Send an email request to the utility company’s customer service department.
- In-Person: Visit the utility company’s office and request a printed copy of your bill.
4. Check Your Email
- E-Bills: If you have opted for paperless billing, check your email inbox for your latest utility bill.
- Search: Use keywords like “utility bill” or the name of the utility company in your email search bar.
5. Use Mobile Apps
- Utility Company Apps: Many utility companies have mobile apps that allow you to access and download your bills.
- Log In: Use your account credentials to access the app.
- View/Download Bills: Navigate to the billing section to view or download your bill.
Why a Phone Bill is Considered a Utility Bill
- Essential Service: Just like electricity and water, phone services are essential for daily communication, especially in emergencies.
- Regular Billing: Phone services are typically billed monthly, similar to other utilities.
- Proof of Address: Phone bills are often used as proof of address for various official purposes, like opening a bank account or verifying residency.
- Usage Charges: Like other utility bills, phone bills detail charges based on usage (calls, texts, data) and fixed costs (line rental, service fees).
Tips for Using Utility Bills
- Organize: Keep all utility bills in a dedicated folder.
- Verify: Check each bill for accuracy before paying.
- Budget: Use bills to track and plan monthly expenses.
- Proof of Address: Use recent bills as proof of residence when needed.
- Set Reminders: Schedule reminders for payment due dates.
- Compare Rates: Use bills to compare utility rates and switch providers if needed.
- Conserve: Analyze usage to identify and reduce high consumption areas.
How often are utility bills issued?
A utility bill is a statement of charges for essential services like electricity, water, gas, and internet.
How often are utility bills issued?
Utility bills are typically issued monthly.
What information is on a utility bill?
A utility bill includes account details, billing period, usage, charges, and payment options.
Can I receive utility bills electronically?
Yes, many utility companies offer paperless billing via email or their online portals.
How can I pay my utility bill?
Utility bills can be paid online, by mail, in person, or through automatic payments.
What if I can’t pay my utility bill on time?
Contact your utility company to discuss payment extensions or installment plans.
Why is my utility bill higher than usual?
Higher usage, rate increases, or billing errors can cause a higher bill.
How are utility charges calculated?
Charges are based on usage, measured in units like kWh or gallons, and fixed fees.
Can I dispute a utility bill?
Yes, contact your utility provider’s customer service to discuss discrepancies.
What should I do if I move?
Notify your utility providers of your move to transfer or terminate services.