7+ Nursing Jargon Examples
After a nurse’s shift in the hospital, they need to endorse the patients they have tended to the person covering the next shift. This makes sure that the next person has an organized information about the patients in order to properly care for them in his/her shift. This also ensures that the medication that will be given are the same as or has no complications to what has been given earlier. Through this process and the other procedures nurses have to complete, they use terms or language that will not be comprehensible or at least will be hard to understand to the patients.
These terms or certain language that they use are called nursing jargon. During endorsement nurses discuss their patients in an orderly sequence and this progression of facts, the exchange of jargon repeatedly takes place at specific time intervals. The jargon helps nurses impose order on an easily disordered events in patient wards. Since the amount of information to be shared increases when the patient’s medical condition is high and are recently admitted, they need to make sure that everyone stays on the loop and can easily remember the facts for each patient. This is why jargon is important for nurses.
Aside from that, nurses get to express their worries, complaints, warn about possible errors, acknowledge errors, and set standards of nursing care to each other without having to worry about being overheard. This is also their chance to tell their nursing “war stories” in order to gently guide the inexperienced new nurses on the ward. The use of jargon is basically just a way for the nurses to socialize during sharing the end-of-shift report as well as to show their commitment for continuous coverage and responsibility for all the patients.

What Is Jargon?
Some people, even in ordinary occasion, have a certain language that they can only understand. When you hear them you wonder what they are talking about because almost everything that they said does not make any sense to you. The use of this special language is more common among professionals in various fields or industry. As mentioned earlier, nurses have this special language that they often use when they share information among each other. Contrary to popular belief, although it can be used to share medical information, it can also be used to vent out frustration about patients and others.
This language or term is called a jargon. You may have heard of the term, but do you know what it means? Jargon is the term used to describe specialized or technical language that is only understood by those who are members of a group or who perform a specific trade. These jargon are not only limited to nurses or professionals in the medical field, even teachers, mechanics, engineers, lawyers, and so on have words that are considered as jargon since they use it among themselves frequently.
Although everyone is dissuaded to use jargon when writing or speaking for professional purpose especially when faced up with someone outside one’s field, writers use this as leverage in order to appeal to a specific group or to embed a hidden meaning behind what they have written. Jargon can be very useful for exclusive understanding; however, it can also be a cause for confusion. Therefore, jargon should be used with caution in order to avoid confusing people especially when they are not in the same working filed or industry as you. Here are some examples of commonly heard jargon:
- Medical jargon – I need a script in order to pick up the medicine. (Equivalent for prescription.)
- Medical jargon – I need a nurse to room 12 stat. (Equivalent for in a hurry)
- Legal jargon – Your objection is overruled.
- Educational jargon – We need to take data points to determine if there has been a response to the intervention.
- Police jargon – The suspect is headed west on Route 10. All available units, respond.
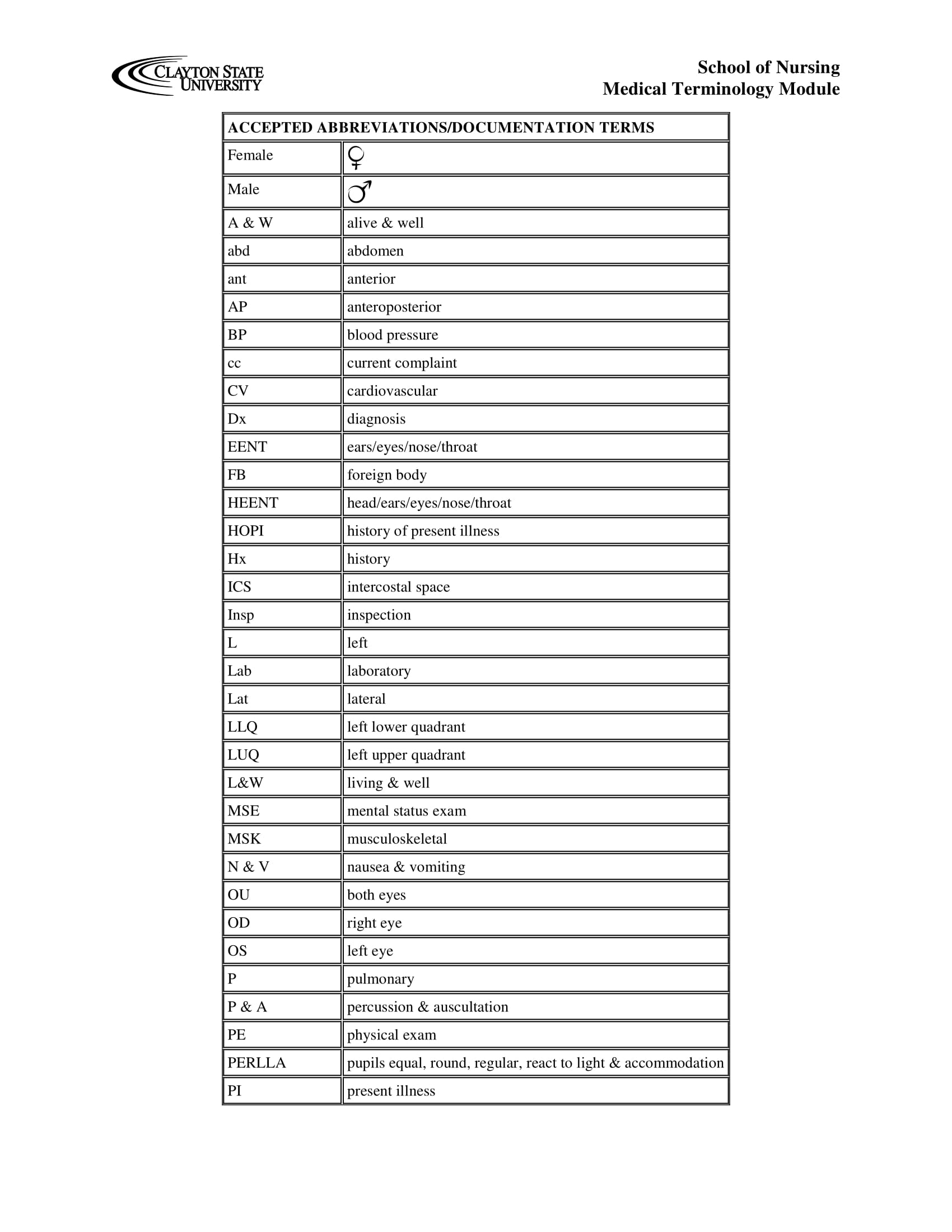
Nursing Documentation Jargon Example
Nursing Abbreviations Example
Usage of Nursing Jargon Analysis Example
Why Nurses Use Nursing Jargon
As mentioned earlier, nurses use nursing to discuss pertinent information about their patient with efficiency and accuracy. They have to make sure their co-nurses are on the loop with what is happening with each patient. They need to share the medical conditions of the patient, his/her numbers (i.e. blood pressure, blood sugar, BMI, heart rate, etc.), the medications the patient has taken, his/her attending physician, his/her diet, and so on. With this amount of information, there is always a need to make things shorter but still maintain its accuracy. Nurses have a lot to cover and attend to, and every second they save off their time is precious.
With that in mind, nurses use nursing jargon to share these information before they leave after their shift and even during when they are attending a patient. Efficiency and accuracy is the key for nurses in order to take care of their patient. When there is an urgent need for assistance or procedure a patient has to go through, nurses use the jargon to instruct fellow workers in order to save time. In addition, it will also help them establish an understanding with fellow nurses.
Aside from all of that, when you are sharing these sensitive information out in the open, there is a tendency for the patient and other people in the ward to overhear. When other people overhear these information and facts they may misinterpret it and may cause miscommunication and confusion. Nurses use jargon so that the patient, other patients, and their visitors cannot easily understand or translate what the nurses are talking about. Unnecessary confusion and panic in the wards can be avoided through using jargon that only nurses can understand.
Standard Nursing Terminologies Analysis Example
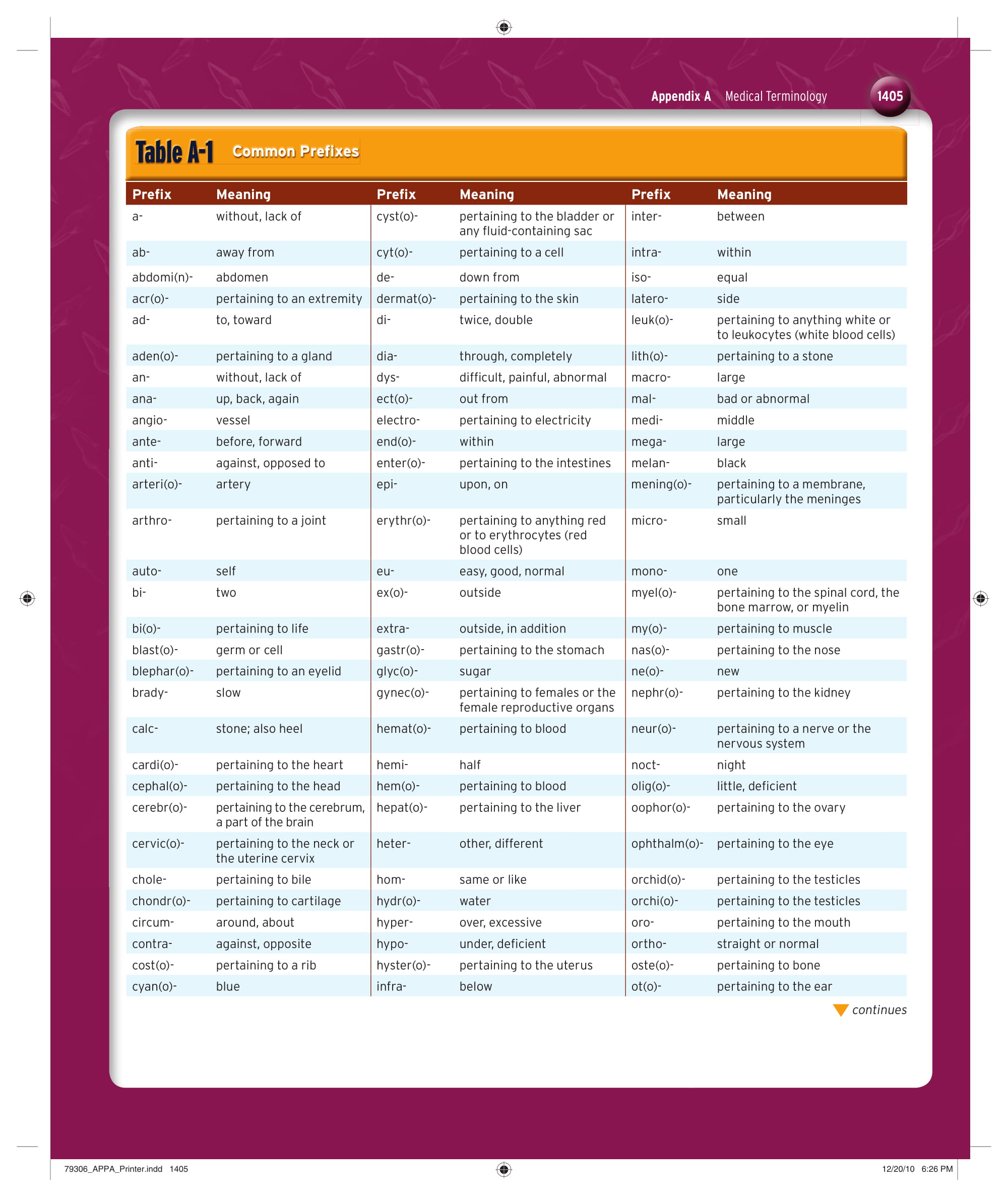
Medical/Nursing Terminology Example
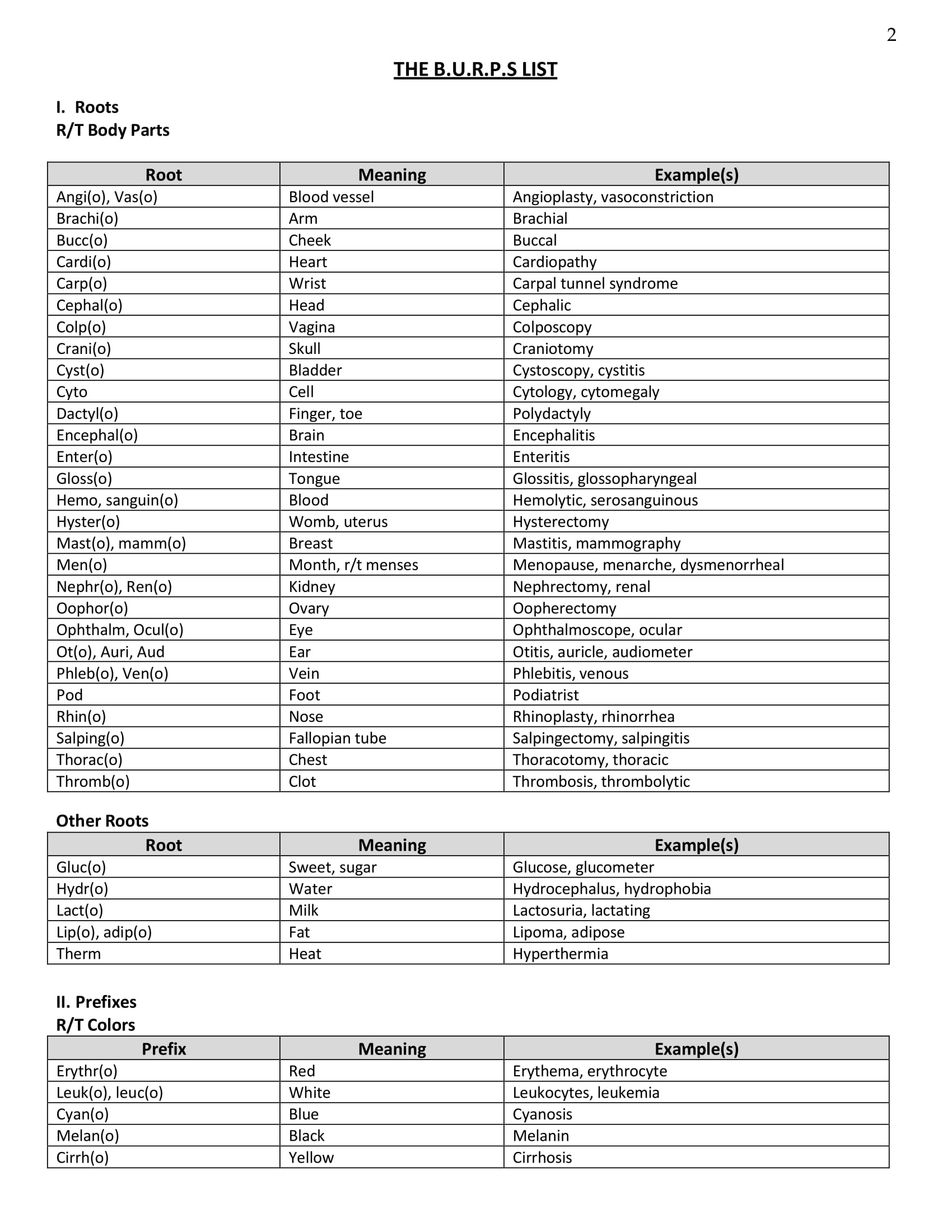
Nursing Jargon List Example
List of Nursing Jargon
You may now understand why nurses use jargon during their shift and even after, but do you have any idea what these common jargon that they use are? In order to give you an idea of what nurses use as nursing jargon, here is a list of compilation of nursing jargon along with their meaning:
1. Princess/Prince/Diva
This pertains to a patient/s who frequently and necessarily rings the bell for minor things and seems to never be satisfied.
2. Celestial Discharge
Sadly, it is not as pretty as it sounds. When a patient is celestially discharged, it means that the patient has died.
3. Code brown
Yes, that is what that means. Large poop. Call backup.
4. Frequent flyer
Usually, this phrase is used along with the second jargon. Refers to patients that come into the ER a lot.
5. Sundowner/sundowning
Usually used for patients with dementia who start going crazy when the sun goes down.
6. Vampire
Contrary to what comes first to mind, a hospital vampire is a phlebotomist or people who are trained to draw blood from patients in order to diagnose illnesses.
7. Trainwreck
This refers to a patient who is not doing quite well and is facing multiple acute problems at one time. For example:
81 y/o confused female, non-ambulatory, incontinent, 2pt nonviolent restraints. Dx: CHF exac, COPD, Afib, 4L NC
Vitals: BP 190/100, HR 100, RR 24, O2 92%, Temp 99.2,
Labs: hgb 6.2 WBC 12 trop 0.12
8. Happy juice
IV pain medication.
9. DT-ing
Referring to DT (Delirium Tremens) protocol.
10. Fluid overload
Hypervolemia or there is too much fluid in the blood, usually in congestive heart failure (CHF) patients.
11. PITA
An apt acronym for a patient who is a “pain in the ass.”
12. About to kick the bucket
Patient is not doing well, about to die.
13. Nurslings
This is a sweet endearment referring to student nurses.
14. Vitamin H
Just for laughs: Vitamin Haldol.
15. Vitamin P
There is no known fact how it came to be, but this is a clever name for Lasix.
16. Milk of amnesia
If someone is getting milk of amnesia it means someone is getting Propofol, a short-acting drug that causes decreased level of consciousness and lack of memory for events.
17. Walkie talkie
This is what every nurses dream of: A patient that can walk and talk, suitable for self-care, and is low maintenance.
18. Drug seeker
This is a term used to refer for patients who are addicted to narcotics or other controlled substances. These patients usually come to the ER and are always needing “a fix” for whatever reason.
19. Breathing treatment
This pertains to smoking a cigarette or a smoke break.
20. Penile intubation
Placing a Foley catheter in a male patient.
21. Rotater
Refers to a patient who is complex or high maintenance that they are rotated to another nurse each day.
22. Jack in the Box
Refers to a patient who can’t stand or walk yet insists on trying.
23. Yellow Submarine
An obese patient with jaundice, usually suffers from liver cirrhosis and needs complex medical attention.
24. Fits
A short medical term for sudden seizure attack.
25. BONITA
This can be translated to a “Big Old Needle In The Ass” that ER nurses use in giving intramuscular injections in the patient’s buttocks.
26. Chocolate Hostage
Refers to a patient who has constipation or having difficulty in passing stools.
27. Crispies
This refers to a patient tanning booth victim.
28. 45C
This term pertains to a “thick” patient or has questionably low IQ.
29. Slashers and Cutters
This term is used to refer to surgeons.
30. Snorkel
Is used to refer to an endotracheal breathing tube because of their resemblance.
Medical Words for Nurses Example
Basic Medical Terms Guide for Nurses Example
Abbreviations Used in Nursing
In order for you to understand even more the language nurses speak and the terminologies that they use, here are some of the abbreviations that nurses most commonly use:
- Abd – Abdomen
- A&D – Admission and discharge
- ADL – Activities of daily living
- Amb – Ambulatory, able to walk
- Amt – Amount
- AP – Appendectomy
- Cath – Catheter
- CBC – Complete blood count
- CCU – Cardiac care unit/ coronary care unit
- CBR – Complete bed rest
- C/O – Complaint of
- CVA – Cerebrovascular accident or stroke
- CPR – Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- DC or d/c – Discontinue
- DX – Diagnosis
- ECG – Electrocardiogram
- EEG – Electroencephalogram
- FBS – Fasting blood sugar
- FF – Forced feeding or forced fluids
- Fx – Fracture
- GI – Gastrointestinal
- Gtt – Glucose tolerance test
- Gyn – Gynecology
- HOB – Head of bed
- ICU – Intensive care unit
- I&O – Intake and output
- Isol – Isolation
- IV – Intravenous
- Noct – At night
- NPO – Nothing by mouth
- PAR – Postanesthesia room
- PO – By mouth
- Post op spec – After surgery urine specimen
- PT – Patient, pint
- ROM – Range of motion
- SOB – Shortness of breath
- Stat – At once, immediately
- TPR – Temperature, pulse, respiration
- U/A – Urinalysis
- VS – Vital signs
- W/C – Wheel chair
Conclusion
Although not really that necessary, using jargon can ease the burden of having to communicate with coworkers in such a hectic environment. Nurses use jargon in order to establish that understanding that they already have with fellow nurses. Aside from that, it is one of there ways of socializing and beating the stress brought about by the environment. Furthermore, it helps them relay important information and facts about the patient, the patient’s overall condition, and what should be done to help the patient.
Although some may think that using a language that exclusively belongs to a certain groups is taboo, it can still help establish a clear communication if there is mutual understanding to what is being said. Therefore, nurses using jargon can greatly help them communicate better and faster should the situation need it. It also helps them avoid sharing sensitive information so freely since people who do not belong in the same field cannot easily decode the message being shared.
Jargon, as taboo as they may seem, can still help nurses communicate clearly and efficiently. Thus, it is still a big help for the nurses to get the job done when working the wards.