Abbreviation Rules – Definition, Rules, Lists, Differences, Examples
Abbreviation Rules refer to the standardized guidelines for shortening words or phrases in writing. These rules ensure clarity and consistency across documents. Key principles include using common abbreviations that are widely recognized, such as “Dr.” for Doctor or “Inc.” for Incorporated. When abbreviating, it’s important to maintain the initial letters of the word, use periods to denote missing letters, and avoid creating ambiguity. Abbreviations should be introduced with their full form followed by the abbreviation in parentheses the first time they appear in a text, ensuring readability and understanding for all readers.
What is Abbreviation?
An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase, typically consisting of letters or a combination of letters and symbols. Abbreviations are commonly used to make writing or speaking more efficient, especially when conveying repetitive or lengthy terms. They are often created by taking the initial letters of words in a phrase or by truncating the phrase in some way. Examples of abbreviations include “Mr.” for “Mister,” “etc.” for “et cetera,” and “USA” for “United States of America.”
What are the Abbreviation Rules?
Abbreviation rules serve as guidelines for creating and using shortened forms of words or phrases effectively in written and spoken communication. These rules ensure clarity, consistency, and understanding among readers or listeners. One key rule is to use periods (full stops) after each letter in an abbreviation unless the abbreviation is a symbol, acronym, or initialism. For example, “etc.” stands for “et cetera,” and “USA” represents “United States of America.” Additionally, it’s important to use standard abbreviations recognized by the intended audience to avoid confusion or misinterpretation.
Another crucial rule is to maintain consistency when using abbreviations throughout a text or conversation. Once an abbreviation is introduced, it should be used consistently thereafter to avoid ambiguity. Furthermore, avoid overusing abbreviations, especially in formal writing, as excessive abbreviation can hinder readability and detract from the clarity of the message. By adhering to these abbreviation rules, writers and speakers can effectively convey information while maintaining clarity and coherence in their communication.
Rules of Abbreviation
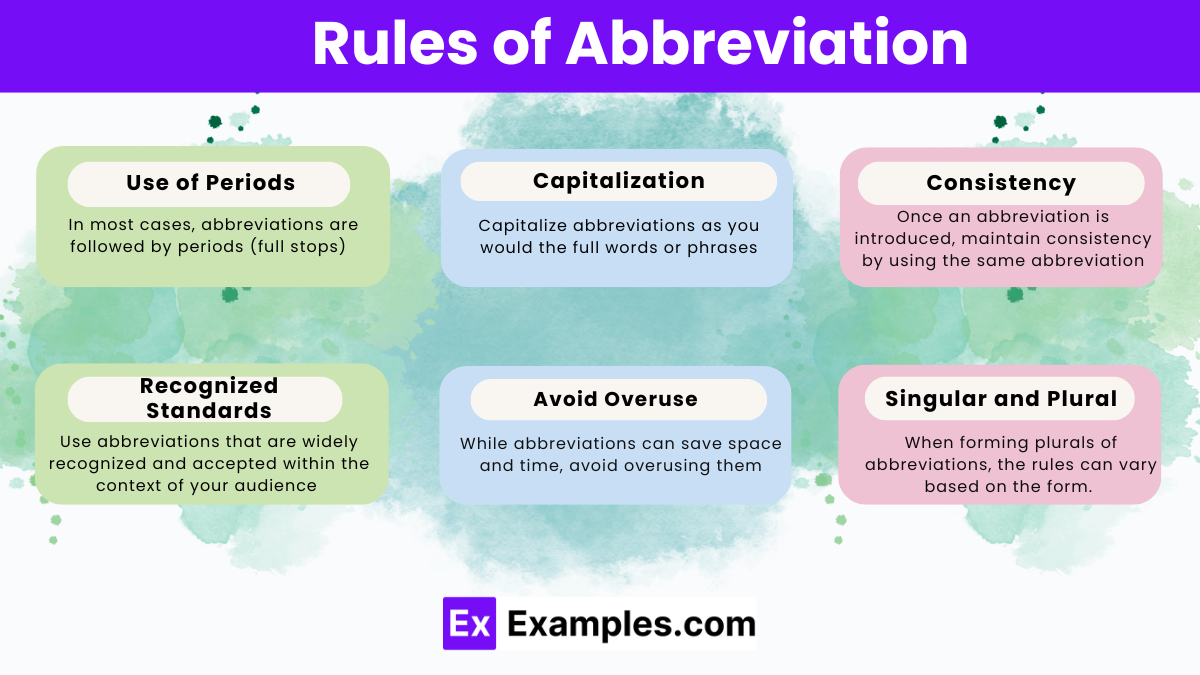
The rules of abbreviation help ensure clarity and consistency in written and spoken communication. Here are some key rules:
Use of Periods:
In most cases, abbreviations are followed by periods (full stops) to indicate shortened forms of words or phrases. For example, “Dr.” for “Doctor,” “Mr.” for “Mister,” and “etc.” for “et cetera.”
Capitalization:
Capitalize abbreviations as you would the full words or phrases they represent. For instance, “USA” for “United States of America” and “NASA” for “National Aeronautics and Space Administration.”
Consistency:
Once an abbreviation is introduced, maintain consistency by using the same abbreviation throughout the text or conversation. This helps avoid confusion and ensures clarity for the reader or listener.
Recognized Standards:
Use abbreviations that are widely recognized and accepted within the context of your audience or field. Avoid using obscure or unfamiliar abbreviations that may cause confusion.
Avoid Overuse:
While abbreviations can save space and time, avoid overusing them, especially in formal writing. Too many abbreviations can make the text difficult to read and understand.
Singular and Plural
When forming plurals of abbreviations, the rules can vary based on the form and usage of the abbreviation itself. Typically, if an abbreviation does not end in a lowercase letter, simply add an “s” without an apostrophe to create the plural form, such as “CDs” for multiple CDs and “PhDs” for multiple doctorates. Example: Add an “s” for plurals if the abbreviation doesn’t involve the last letter, like “p.s.” becomes “p.p.” for postscripts.
list of Abbreviations for Students
Abbreviations are shortened forms of words or phrases that help save space and time, especially in writing. For students, being familiar with common abbreviations is essential as they frequently encounter these in textbooks, exam papers, and during lectures. Below is a list of widely used abbreviations that every student should know:
Educational and Institutional Abbreviations
- Univ. – University
- Dept. – Department
- Lib. – Library
- Adm. – Administration
- B.A. – Bachelor of Arts
- B.Sc. – Bachelor of Science
- Ph.D. – Doctor of Philosophy
- M.A. – Master of Arts
- M.Sc. – Master of Science
General Academic Abbreviations
- e.g. – exempli gratia (for example)
- etc. – et cetera (and so forth)
- i.e. – id est (that is)
- vs. – versus (against)
- N.B. – Nota Bene (note well)
- cf. – confer (compare)
- esp. – especially
- ch. – Chapter
- pg. – Page
Subject-Specific Abbreviations
- Math. – Mathematics
- Geo. – Geography
- Hist. – History
- Bio. – Biology
- Chem. – Chemistry
- Phys. – Physics
- Eng. – English
- Lit. – Literature
- Gov. – Government
Technological Abbreviations
- Comp. Sci. – Computer Science
- AI – Artificial Intelligence
- VR – Virtual Reality
- IT – Information Technology
Miscellaneous
- ASAP – As Soon As Possible
- FYI – For Your Information
- RSVP – Répondez S’il Vous Plaît (Please reply)
- DIY – Do It Yourself
Abbreviations and Acronyms
Abbreviations and acronyms are both used to shorten phrases or groups of words, but they are used differently. An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase that is usually followed by a period (e.g., Dr. for Doctor). An acronym is a type of abbreviation formed from the initial letters of a series of words, and it is typically pronounced as a single word (e.g., NASA).
Here’s a table to illustrate the difference between abbreviations and acronyms with examples:
| Type | Full Form | Shortened Form | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | Doctor | Dr. | Dr. Smith will see you now. |
| Abbreviation | Avenue | Ave. | Turn left on Park Ave. |
| Abbreviation | Department | Dept. | Please report to the HR Dept. |
| Abbreviation | Page | p. | See p. 99 of your textbook. |
| Acronym | National Aeronautics and Space Administration | NASA | NASA conducts advanced aerospace research. |
| Acronym | Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation | LASER | He used a laser pointer during the presentation. |
| Acronym | Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus | SCUBA | They went SCUBA diving in the coral reef. |
| Acronym | Radio Detection and Ranging | RADAR | The ship was detected by radar. |
Abbreviations in English Grammar with Examples
Abbreviations are an integral part of English grammar, offering a convenient way of shortening long titles, names, or phrases. These shortened forms are widely used in written and spoken English and are essential for efficient communication. Below, I will explain different types of abbreviations used in English grammar and provide examples to illustrate their usage.
Common Types of Abbreviations
- Titles and Professions
- Dr. (Doctor)
- Example: Dr. Harris will be speaking at the conference.
- Mr. (Mister), Mrs. (Mistress), Ms. (Miss/Mistress)
- Example: Mr. Smith and Ms. Johnson are getting married next month.
- Prof. (Professor)
- Example: Prof. Robertson teaches Medieval History.
- Geographical Names
- St. (Street), Ave. (Avenue), Blvd. (Boulevard)
- Example: My office is on Washington Blvd.
- U.K. (United Kingdom), U.S. (United States)
- Example: She moved from the U.K. to the U.S. last year.
- Organizational Titles
- UN (United Nations), NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
- Example: The UN passed a new resolution.
- FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation), CIA (Central Intelligence Agency)
- Example: The CIA and FBI often collaborate on national security cases.
- Time References
- Mon. (Monday), Tue. (Tuesday), Dec. (December)
- Example: The meeting is scheduled for Tue., December 15th.
- hrs (hours), min (minutes), sec (seconds)
- Example: The test lasts 2 hrs and 30 min.
- Educational Degrees
- B.A. (Bachelor of Arts), M.Sc. (Master of Science)
- Example: He earned his B.A. in English Literature.
- Ph.D. (Doctor of Philosophy)
- Example: She received her Ph.D. in Chemistry from Harvard.
- Legal and Miscellaneous
- e.g. (for example), etc. (and so forth), vs. (versus)
- Example: You need to bring writing tools, e.g., pens, pencils, and markers.
- i.e. (that is), viz. (namely)
- Example: He prefers traditional desserts, i.e., apple pie and custard.
Benefits of Using Abbreviations
- Efficiency and Space Saving: Abbreviations help in writing concisely and saving space, which is especially useful in academic writing, note-taking, and formal documentation.
- Standardization: Many abbreviations are standardized, making them universally recognized and understood, which facilitates clear communication across different regions and fields.
Are there rules for punctuation in abbreviations?
Yes, some abbreviations require periods after each letter, particularly in U.S. English, like “U.S.” for United States.
Can any word be abbreviated?
Not all words should be abbreviated; generally, common phrases, technical terms, and organizations are abbreviated for convenience.
How do I know if an abbreviation is standard?
Standard abbreviations are widely recognized and often found in dictionaries or professional documents related to specific fields.
Should abbreviations be explained?
The first time an abbreviation is used in a text, it should be fully spelled out with the abbreviation in parentheses.
Are abbreviations used differently in formal and informal writing?
Yes, formal writing typically uses fewer abbreviations, focusing on clarity, while informal writing may use them more liberally.